La pérdida de peso en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC) grave indica mal pronóstico. El objetivo de este estudio es analizar la efectividad del acetato de megestrol (AM) como estimulante del apetito en estos pacientes.
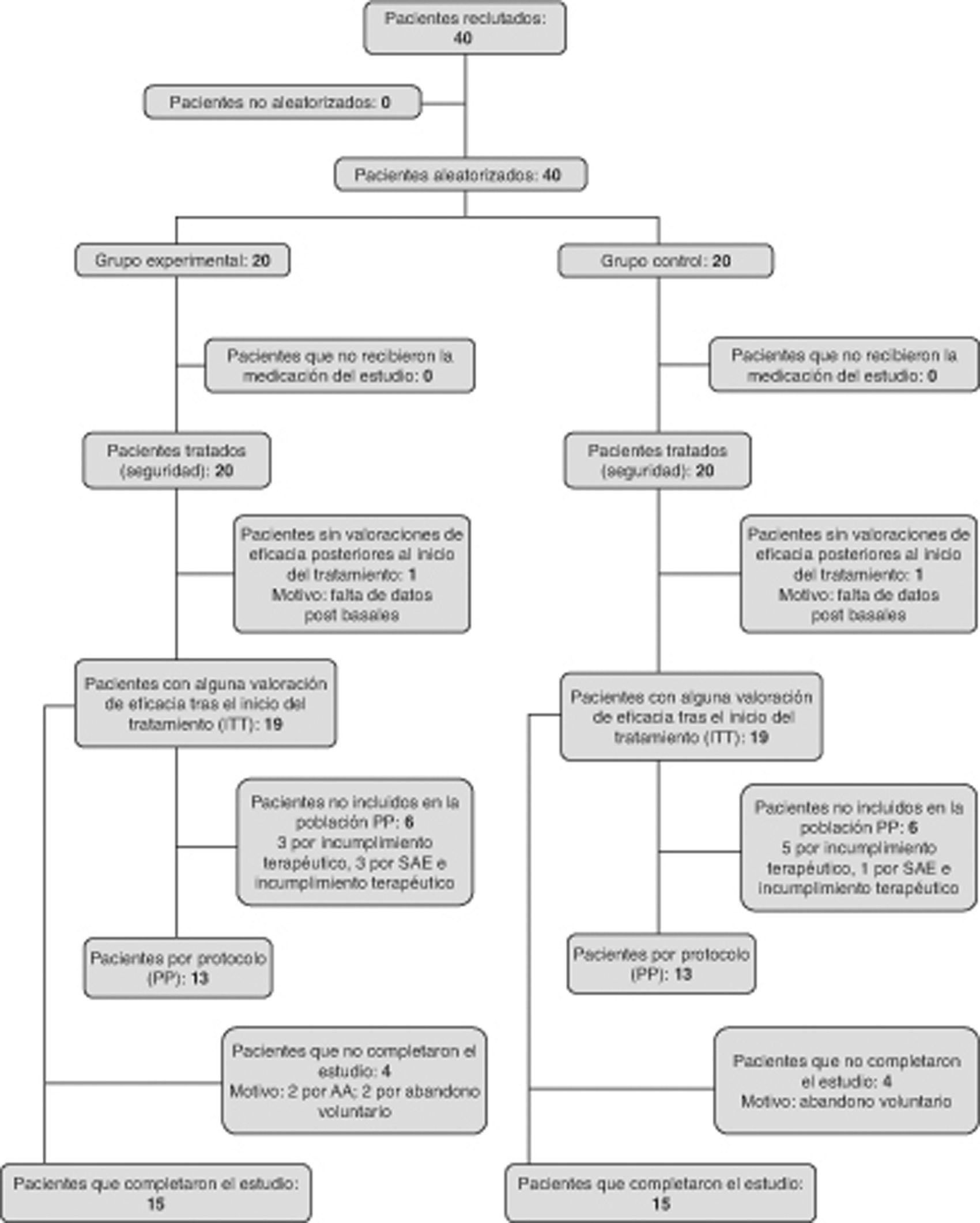
Pacientes y métodoEnsayo clínico aleatorizado, doble ciego y controlado con placebo para estudiar el efecto de 320mg/d de AM durante 8 semanas sobre parámetros nutricionales, funcionales, analíticos y de calidad de vida en 38 pacientes con EPOC grave e índice de masa corporal (IMC) < 21kg/m2, o entre 21-25kg/m2 con pérdida involuntaria del 5% del peso en los últimos 3 meses.
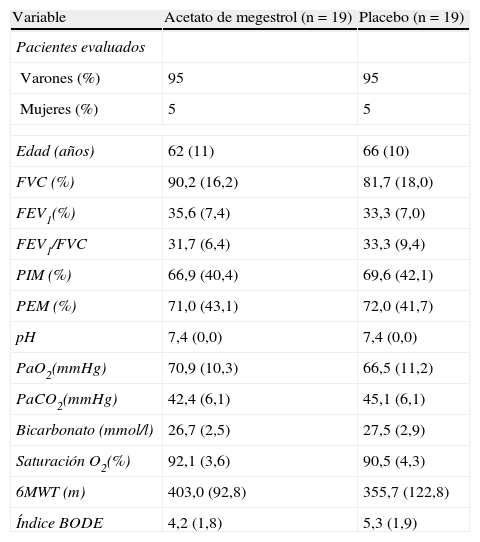
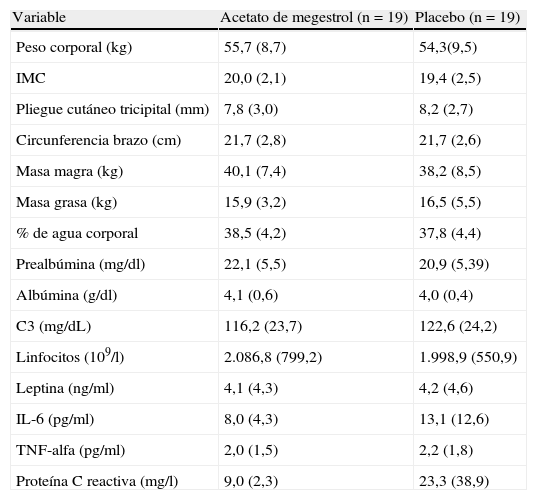
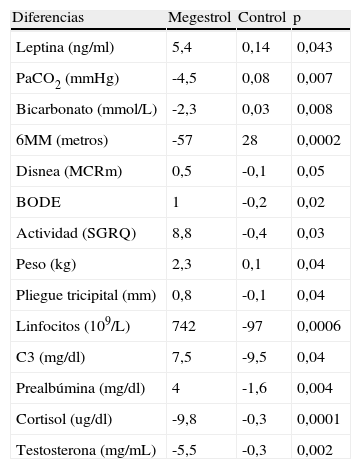
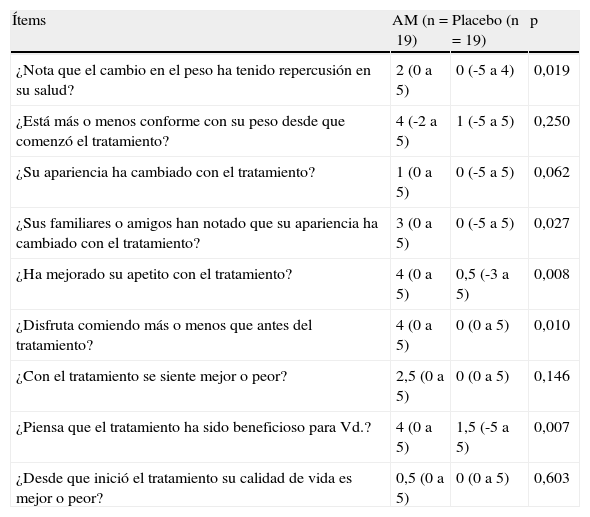
ResultadosA las 8 semanas, el peso aumentó en el grupo AM (2,3kg) respecto al control (0,1kg) (p < 0,04). Mejoraron con AM de forma significativa el grosor del pliegue tricipital (p < 0,04), los valores de prealbúmina (p<0,004), linfocitos (p<0,0006), fracción 3 del complemento (C3) (p<0,04), presión parcial de dióxido de carbono (PCO2) (p<0,007) y bicarbonato (p<0,008). No mejoraron las escalas MCR y SGRQ, la distancia recorrida en 6 minutos (6MWT) ni el índice BODE. La interleucina 6 (IL-6) y el factor de necrosis tumoral alfa (TNF-alfa) tampoco se modificaron en el grupo AM, pero aumentó la leptina (p<0,043). El AM mejoró la sensación de bienestar (p<0,02) y el apetito (p<0,008) frente al control. El índice de acontecimientos adversos fue similar en ambos grupos.
ConclusionesEl AM incrementa de forma segura el peso y el apetito en pacientes con EPOC grave y pérdida de peso. Mejora los parámetros gasométricos, nutricionales y la sensación de bienestar, pero no la función muscular respiratoria o la tolerancia al ejercicio.
Weight loss in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a prognostic bad factor. The objective of this study is to analyze the effectively of megestrol acetate (MA) to increase appetite of these patients.
Patients and methodsRandomized double blind placebo controlled trial to study the effect of 160mg/bid of MA, for 8weeks, on nutritional, functional, analytical and quality of life parameters, in 38 patients with severe COPD and body mass index (BMI) < 21kg/m2, or between 21-25 with involuntary weight loss of 5% in the last 3 months.
ResultsAt 8weeks, in the MA group the body weight increased (2.3kg) with respect to the control group (0.1kg) (p<0.04). MA improved significantly the triceps skin-fold thickness (p < 0.04), prealbumin (p<0.004), lymphocytes (p<0.0006), C3 (p<0.04), PCO2 (p<0.007) and bicarbonate levels (p<0.008). MA did not increase the MRC and SGRQ scales, the distance of 6MWT nor BODE index. The IL-6 and TNF alpha levels were not modified in the MA group, but leptin did increase (p<0.043). MA improved the sense of wellbeing (p<0.02) and the appetite (p<0.008), compared to the control group. Adverse effects were similar in both groups.
ConclusionsMA safely increases the body weight and the appetite in severe COPD patients with weight loss. MA improves blood gases and nutritional parameters and the sense of wellbeing, but it does not improve the respiratory muscular function or exercise tolerance.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora