This research was aimed to observe the hard and soft tissue lesion in the oral cavity assessed with the periapical and panoramic radiographic examination in Dental Hospital of Hasanuddin University.
MethodsIt was an observational descriptive study with cross-sectional design through periapical and panoramic data from April–May 2017. The results were presented in the distribution table and graphic.
ResultsTo diagnose almost various oral cavity lesions, the dentist need to receipt a radiographic examination both intraoral and extraoral radiography. The most common hard tissue lesions that detected through periapical radiographic were caries 37.1%, pulp lesion 34.6% and periodontal lesion 17.9%. In panoramic radiographic data, the highest prevalence of tissue lesion was periodontal lesion and periapical abnormality 33.7% with the number of women was higher than men in the 12–25 year age group.
ConclusionThe prevalence of hard and soft tissue lesion in the oral cavity was high.
Oral cavity lesion is a type of lesion that ranks first from the list of ten major lesions most often complained of Indonesian society. This happens because the perception and behavior of Indonesian people on dental and oral health is still relatively poor.1
Oral cavity lesion can cause damage to the soft tissues (e.g. various lesions of the oral mucosa) as well as damage to the hard tissues of the oral cavity such as caries, periodontal lesion, periapical disorders, to cysts and oral cavity tumors. Oral cavity lesion that common in the community is caries and periodontitis.
Based on the results of 2007 RISKESDAS, the prevalence of people with dental and oral problems is 23.4%, the national prevalence of active caries is 43.4%, and the prevalence of caries experience is 67.2%.2 In addition to caries that can trigger a variety of damage in the oral cavity, the periodontal lesion is also a second problem that is often complained about by society. Periodontal lesion affects humans almost all over the world and reaches 50% of the adult population.3
The development of caries and the periodontal lesion is not confined to the dental region because the inflammatory process will continue into the pulp chamber resulting in pulpal lesion and periapical abnormalities if it's not undergoing any dental treatment.4,5
To diagnose almost various oral cavity lesions, the dentist needs to receipt a radiographic examination both intraoral and extraoral radiography.6 Early detection of oral cavity lesions through radiography examination becomes important because it may help the dentist to determine the diagnose of a lesion.7,8
Material and methodsThis research was a descriptive observational with cross sectional design and conducted at Dental Hospital of Hasanuddin University on April–May 2017. The samples were all periapical and panoramic radiography data. The inclusion criteria in this study were periapical and panoramic radiographic photo data with hard and soft tissue lesion.
ResultsThis research was obtained ethical clearance with register number UH17040269 on May 8, 2017. The research results were shown in the table as follows.
Table 1 showed the most common hard and soft tissue lesion found through examination of periapical radiographic of the oral cavity were caries 372 (37.1%), pulp lesion 347 (34.6%), and periodontal lesion 179 (17.9%).
Table 2 showed that through periapical radiographic photo data assessed by gender, the prevalence of hard and soft tissue lesion of the oral cavity more commonly found in female.
Hard and soft tissue lesion assessed by periapical radiography based on gender.
| Lesion | Gender | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | |||
| n | % | n | % | |
| Caries | 188 | 37.2 | 184 | 37.1 |
| Pulp lesion | 178 | 35.2 | 169 | 34.1 |
| Periapical lesion | 46 | 9.1 | 46 | 9.3 |
| Periodontal lesion | 7 | 1.4 | 5 | 1 |
| Radiolucent and radiopaque lesion on the jaw | 87 | 17.2 | 92 | 18.5 |
| Total | 506 | 100 | 496 | 100 |
Based on Table 3 the most commonly of hard and soft tissue lesions of the oral cavity was in the age group of 12–25 years.
Hard and soft tissue lesion assessed by periapical radiography based on age.
| Lesion | Age (years) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5–11 | 12–25 | 26–45 | 46–65 | >65 | ||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Caries | 40 | 46 | 183 | 35.1 | 106 | 39.8 | 27 | 30.3 | 3 | 42.9 |
| Pulp lesion | 39 | 44.8 | 184 | 35.2 | 86 | 32.3 | 25 | 28.1 | 2 | 28.6 |
| Periapical lesion | 2 | 2.3 | 55 | 10.5 | 24 | 9 | 10 | 11.2 | 0 | 0 |
| Periodontal lesion | 0 | 0 | 7 | 1.3 | 3 | 1.1 | 1 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| Radiolucent and radiopaque lesion on the jaw | 6 | 6.9 | 93 | 17.8 | 47 | 17.7 | 26 | 29.2 | 2 | 28.6 |
| Total | 87 | 100 | 522 | 100 | 266 | 100 | 89 | 100 | 7 | 100 |
Table 4 showed the most common lesion found through examination of panoramic radiographic were periodontal lesion and periapical abnormalities 33.7%.
Table 5 showed that through panoramic radiographic photo data assessed by gender, the prevalence of hard and soft tissue lesion of the oral cavity more commonly found in female and male.
Hard and soft tissue lesion assessed by panoramic radiography based on gender.
| Lesion | Gender | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | |||
| n | % | n | % | |
| Periodontal lesion | 15 | 27.3 | 16 | 43.2 |
| Periapical lesion | 22 | 40 | 9 | 24.3 |
| Oral cavity cyst | 4612 | 21.8 | 7 | 18.9 |
| Oral cavity tumor | 72 | 3.6 | 1 | 2.7 |
| Other lesions on the jaw bone | 874 | 7.3 | 4 | 10.8 |
| Total | 55 | 100 | 496 | 100 |
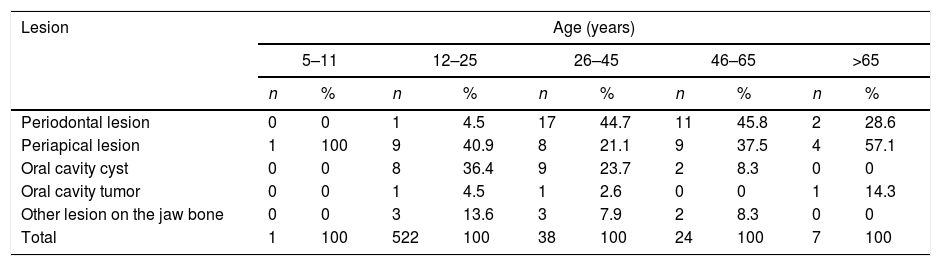
Based on Table 6 the most commonly of hard and soft tissue lesions of the oral cavity was in the age group of 12–25 years.
Hard and soft tissue lesion assessed by panoramic radiography based on age.
| Lesion | Age (years) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5–11 | 12–25 | 26–45 | 46–65 | >65 | ||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Periodontal lesion | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4.5 | 17 | 44.7 | 11 | 45.8 | 2 | 28.6 |
| Periapical lesion | 1 | 100 | 9 | 40.9 | 8 | 21.1 | 9 | 37.5 | 4 | 57.1 |
| Oral cavity cyst | 0 | 0 | 8 | 36.4 | 9 | 23.7 | 2 | 8.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Oral cavity tumor | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4.5 | 1 | 2.6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14.3 |
| Other lesion on the jaw bone | 0 | 0 | 3 | 13.6 | 3 | 7.9 | 2 | 8.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 1 | 100 | 522 | 100 | 38 | 100 | 24 | 100 | 7 | 100 |
There were 408 periapical and 144 panoramic radiographic data that met the criteria. In this study, the various hard and soft tissue lesion of the oral cavity identified referred to a diagnosis commonly found in dentistry practice. Table 1 showed the most commonly hard and soft tissue lesion found through examination of periapical radiographic of the oral cavity were caries 37.1%, pulp lesion 34.6%, and periodontal lesion 17.9%. The results of this study indicate that caries, pulp lesion, and periodontal lesion had a higher prevalence than other types of lesions. The high prevalence of these three lesions was due to lack of knowledge and awareness of oral and dental health.
Periapical and panoramic radiographic photo data assessed by gender, the prevalence of hard and soft tissue lesion of the oral cavity more commonly found in female. The results of this study were in accordance with the study of Nindya Larasati, et al. (2014) on the prevalence of pulp lesion caused by caries at RSKGM-FKG UI in 2009–2013, the number of female patients as many as 3107 (61, 7%) and male patients as many as 1932 (3.3%).9
This was in accordance with the study conducted by Soekidjo (2003) that the number of morbidities was higher in the female. Female were more susceptible to oral lesions, such as caries due to the eruption of teeth in female early, high estrogen hormone levels, lower salivary flow rate, and more time to consume snacks between meals.10,11
Based on Table 3 the most commonly of hard and soft tissue lesions of the oral cavity was in the age group of 12–25 years.
Based on Table 4 on the most commonly lesion found through examination of panoramic radiographic were periodontal lesion and periapical abnormalities 33.7%, Then the cyst of the oral cavity amounted to 20.7%, other lesions of the jawbone such as cemento-osseous dysplasia, fibrous dysplasia, osteosclerosis idiopathic, and condensing osteitis amounted to 8.7%, and the last was the oral cavity tumors which amounted to 3.3%. Based on Table 6 on the prevalence of hard-tissue lesions of the oral cavity most commonly found through examination of panoramic radiographic photo data shows the varying distribution of different age groups.
ConclusionThe hard and soft tissue lesions of the oral cavity most commonly found through periapical radiographic data were caries, pulp lesion, periodontal lesion. In panoramic radiographic data, the highest prevalence was found in the periodontal lesion and periapical disorders, respectively, with more women than men in the 12–25 year age group. The high prevalence was due to the lack of knowledge and public awareness of oral health maintenance.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the International Conference on Women and Societal Perspective on Quality of Life (WOSQUAL-2019). Full-text and the content of it is under responsibility of authors of the article.