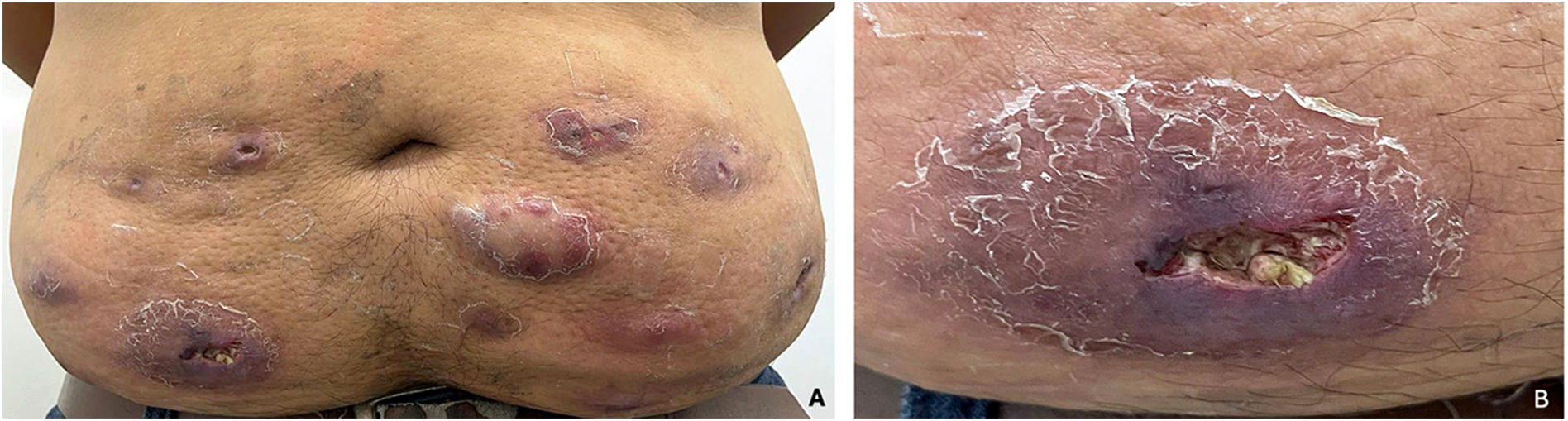
A 24-year-old man presented to our clinic due to multiple abscessed ulcerated lesions located in the abdominal area after mesotherapy treatment 2 months ago. The patient received 40 injections of unidentified substance, to diminish his adipose tissue. He started with erythematous lesions in each puncture site 48–72 h after injections, developing nodular and abscessed ulcerated lesions after 1 week. Physical examination revealed numerous nodules, fistulae, and abscessed ulcers on the skin of the abdomen (Fig. 1A, B), 40 lesions were quantified (video). Laboratory analysis showed a positive smear for Acid Fast Baccilli. A biopsy was performed and confirmed a granulomatous infiltration, and the PCR and culture from the fresh sample were positive for Mycobacterium abscessus. Immunosuppression studies were negative. The diagnosis was M. abscessus infection after mesotherapy injections. He received amikacin and imipenem for 3 months and oral clarithromycin for 7 months.
The following are the supplementary data related to this article.
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcpsp.2024.100452.
Ethical considerationPatient written informed consent was obtained.
Ethical committeeComité de Investigación de la UDEM.
Registry number: 07042024-DER-CI.
Declarations of competing interestNone.
There was no funding or financial support in the creation of this clinical image.