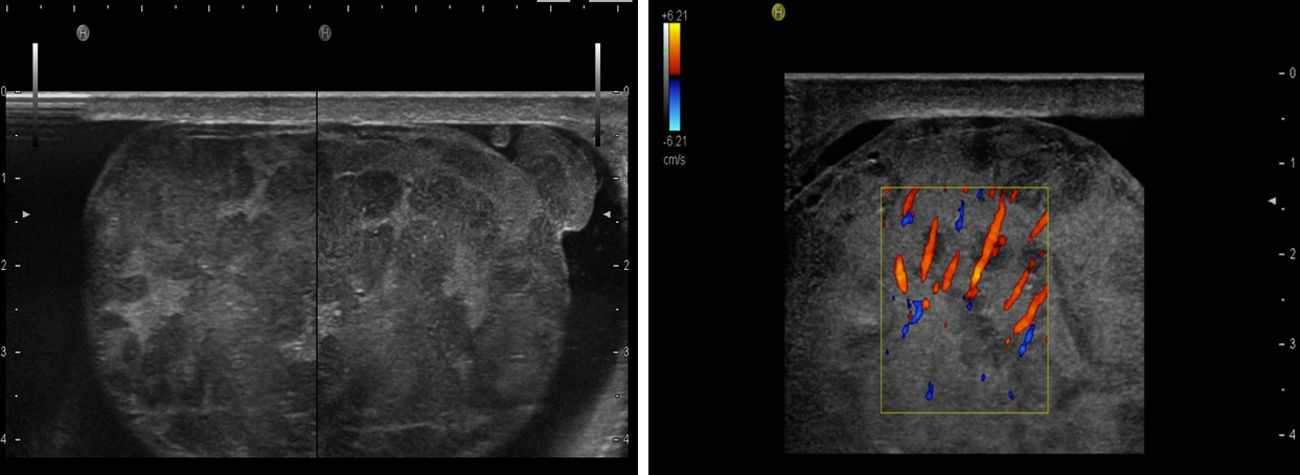
A 62-year-old Ecuadorian male presented with a progressive and painless left testis swelling in the last month without improvement after 2-week course of fluoroquinolones. Physical examination revealed an enlarged non-tender testis. Doppler ultrasound scan (Fig. 1) showed diffuse enlargement of testis and epididymis with ill-defined hypoechoic signal and markedly increased vascularity. Serum alpha fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin, urine culture and urinary PCR to identify mycobacterial DNA were all negative. The patient underwent unilateral radical inguinal orchiectomy.
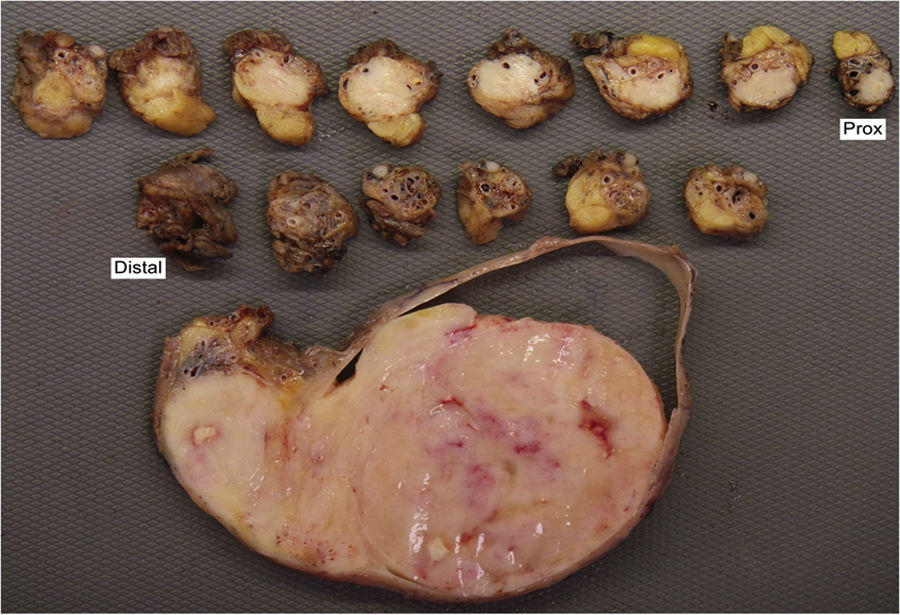
Gross examination (Fig. 2) revealed a 10 cm swollen testicle and a nodule on the spermatic cord. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining showed positivity for CD20 and histopathological analysis confirmed the diagnosis of primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. No evidence of nodal and extranodal disease was found on a staging PET/CT. The patient has been planned for R-CHOP chemotherapy (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone).
Primary testicular lymphoma is a rare and aggressive form of extranodal lymphoma. It represents 1–2% of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is the most common histological subtype. It must be considered in the differential diagnosis of a testicular mass, especially in patients over 60 years old.