Carotid aneurysm is a rare pathology with an incidence of 0.3% among aneurysms in general. Many cases remain asymptomatic until ischemic neurological symptoms appear, so their early detection and treatment are important. Their most common location is at the level of the carotid bulb and in the proximal internal carotid,1 and the treatment of choice is open surgery with exclusion of the aneurysm and restoration of circulation through a graft.
We report a patient with an aneurysm of the extracranial internal carotid artery, which was treated by resection and graft interposition.
The patient was a 67-year-old male who was referred to our outpatient service due to the incidental finding of an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), 4.8cm in size, during the course of an ultrasound study for toxic syndrome.
The patient presented the following as history: allergy to penicillin and pyrazolones, arterial hypertension, former smoker, former drinker, COPD, chronic liver disease, chronic anaemia, vertigo syndrome and non-specific memory loss disorder.
A vascular examination found increased left carotid pulse, soft painless abdomen with a pulsating mass and distal pulses present at both ends.
Vascular studies were initiated with full blood tests, abdominal computed tomography angiography (CTA), ankle-brachial indices and Doppler ultrasound of the supra-aortic trunks (SAT).
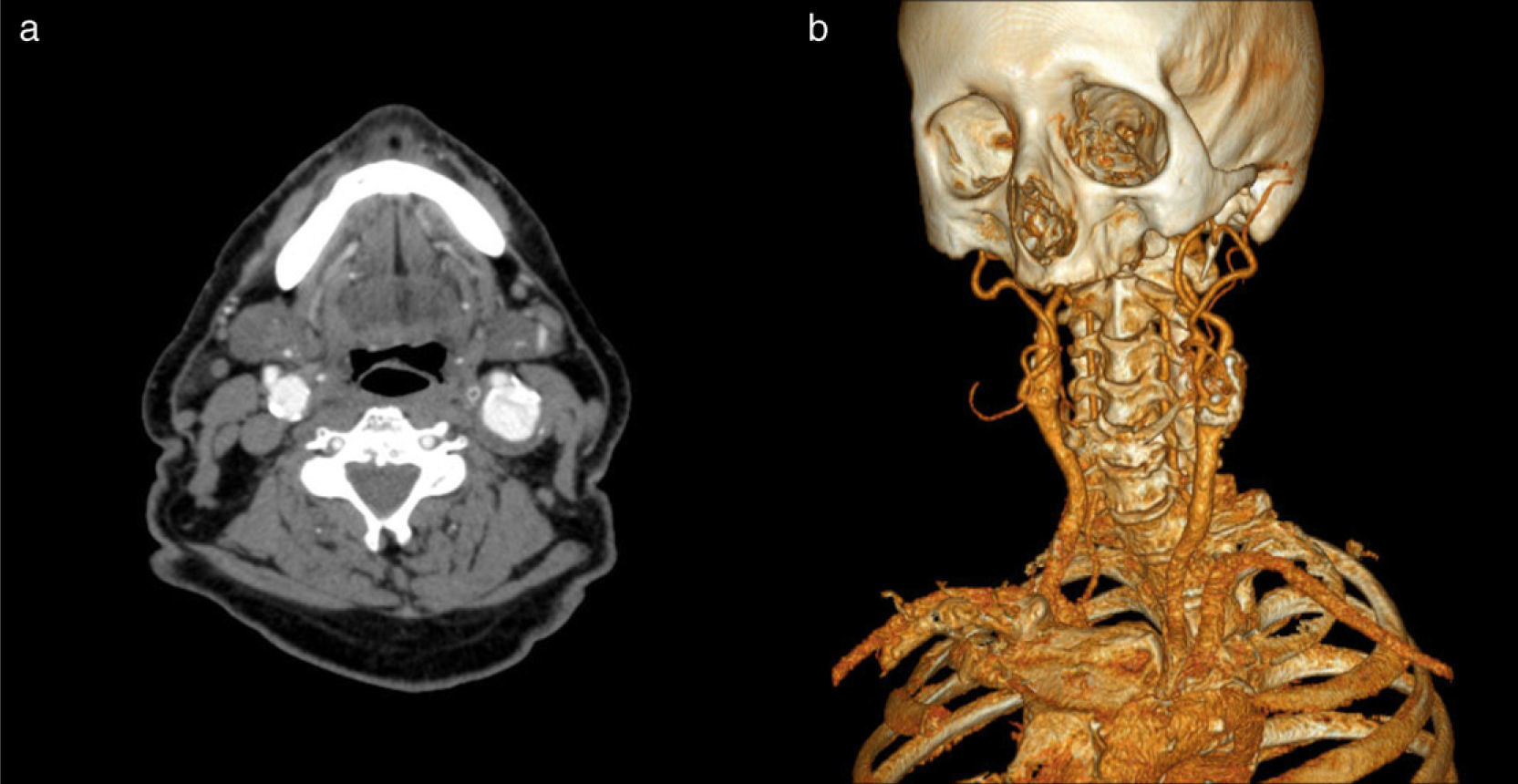
The abdominal CTA confirmed the presence of an infrarenal AAA, of 4.5cm maximum size, with elongation of common iliac arteries. It also revealed the presence of hepatosplenomegaly with ascites and mediastinal and abdominal lymph node formations. The patient presented ankle-brachial indices of 1 on the right side and 0.86 on the left. Finally, the SAT ultrasound found an ectasia in the right distal internal carotid and a true aneurysm of 4cm maximum diameter at the level of the carotid bulb, extending into the left proximal internal carotid, with a mural thrombus in its interior.
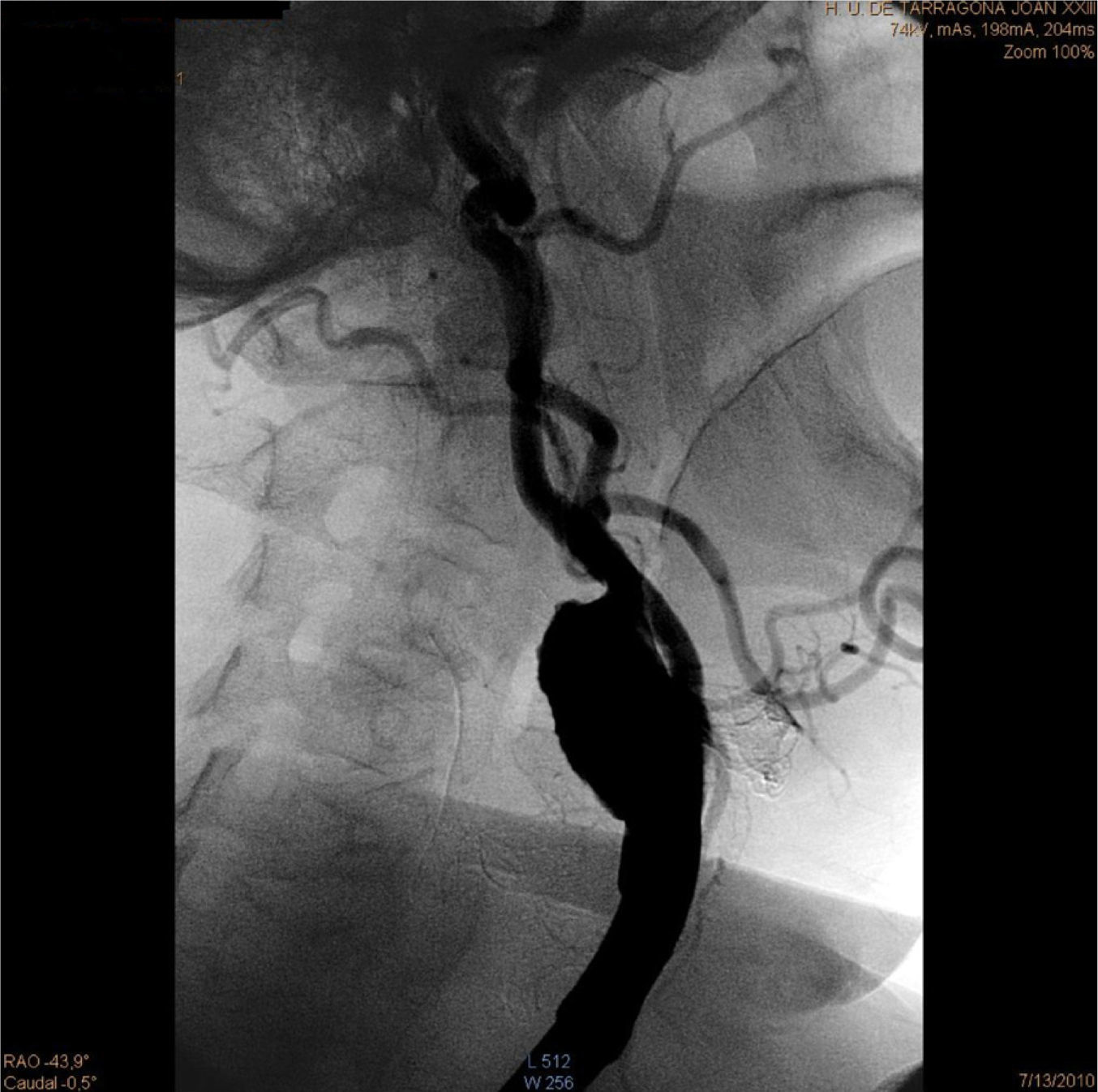
To confirm these findings and plan adequate treatment, we performed CTA and SAT arteriography. The CTA confirmed the existence of a left carotid aneurysm of 3cm maximum diameter, with a thrombus in its interior and right internal carotid artery ectasia (Fig. 1). The arteriography demonstrated the existence of this aneurysm, without showing significant stenosis in the distal exit (Fig. 2). The patient was rapidly intervened. We carried out resection of the carotid aneurysm with replacement of the flow through interposition of a 6-mm Dacron prosthetic graft. The clamping time was 25min without shunt placement. The patient presented a good postoperative evolution without any complications, so he was discharged after 3 days.
Aneurysms of the extracranial internal carotid artery are rare, accounting for only 0.1%–2% of carotid interventions.2 Their aetiology is varied; some of the most common are atheromatous degeneration (in 40% of cases) and trauma.3 Most cases are asymptomatic and are diagnosed incidentally. Up to 40% of carotid aneurysms appear with neurological deficits, most of them as episodes secondary to cerebral transient ischemic attacks (TIA), established cerebrovascular accidents (CVA) or ischemic retinopathy by embolisms.4 Other symptoms may be due to compression of the aneurysm on surrounding structures, such as cranial nerves.5,6 The diagnosis is confirmed by CTA or MRI angiography; the angiography can delineate extension, detect stenosis and help during surgical planning.
With respect to treatment, surgery is indicated in most cases because the risk of vascular events in patients managed conservatively is over 50%.7 Conservative treatment is considered only in cases of very small or asymptomatic aneurysms located in the most distal section, near the base of the skull, due to the high surgical risk involved.
The current technique varies according to the type of aneurysm. In saccular and fusiform aneurysms with local extension and in an anatomically accessible neck, resection of the aneurysm and replacement by vein or prosthetic graft is the preferred technique and that with a better prognosis.
The endovascular option, using a covered stent for the exclusion of the aneurysm, has represented an improvement in the repair of these aneurysms. It is less aggressive and should be considered in cases of extensive aneurysms with a high location and a difficult surgical approach, or in patients with high co-morbidity for surgery, since they present a higher rate of neurological complications than conventional treatment, with a morbidity–mortality of about 7%.8,9
In our case we opted for surgical treatment of the left carotid aneurysm due to its large size and consequent high risk of embolisms. The decision to use open surgery was based on the low surgical risk and the accessible anatomy.
Please cite this article as: Argilés Mattes N, et al. Aneurisma de arteria carótida interna extracraneal. Una patología infrecuente de los troncos supraaórticos. Neurología. 2011;27:53–55.