The real prevalence of bronchiectasis is unknown and difficult to stablish.1 There is limited data on this matter and the published series probably underestimate it. However, the incidence and prevalence of bronchiectasis is increasing.1
The aetiology of bronchiectasis is heterogeneous. The most common causes are idiopathic (38.1%) and post-infectious (21.2%).2 Primary or secondary immunodeficiencies are responsible for 4.2–5.8% of bronchiectasis approximately.3,4
An uncommon and poorly described cause of bronchiectasis is the secondary immunodeficiency due to immunosuppressive drugs after solid organ transplantation (SOT) or bone marrow transplantation (BMT), among others.5 Immunosuppressive regimens after solid organ transplantation typically include glucocorticoids, an antimetabolite (mycophenolate mofetil or azathioprine) and a calcineurin inhibitor (tacrolimus or cyclosporine).6
To this date, very few studies have evaluated the association between SOT and bronchiectasis. Most of them are limited to paediatric population7,8 or adults after renal transplantation,9 mainly focusing mycophenolate as a possible cause.10,11 Similarly, there are only a few case reports regarding the relationship between bronchiectasis and bone marrow transplantation,12 mostly limited to the assessment of bronchiectasis as a manifestation of Graft vs Host Disease.13,14
The objective of this study is to characterize a population with bronchiectasis due to immunosuppression after SOT or BMT.
This retrospective, observational, single-centre study included patients followed at Bronchiectasis Clinic of Bellvitge University Hospital from April 2022 to February 2023. Inclusion criteria were a diagnosis of bronchiectasis after SOT or BMT, including a confirming CT scan. Exclusion criteria were bronchiectasis diagnosed before transplantation, the absence of bronchiectasis in CT scan after transplantation or the absence of a confirming CT scan.
Demographic and clinical data were registered. Data were stratified for statistical analysis by the presence of chronic bronchial infection and by type of transplantation. Patients’ data were collected as part of a larger retrospective study approved by local ethics committee (CEIC-2907).
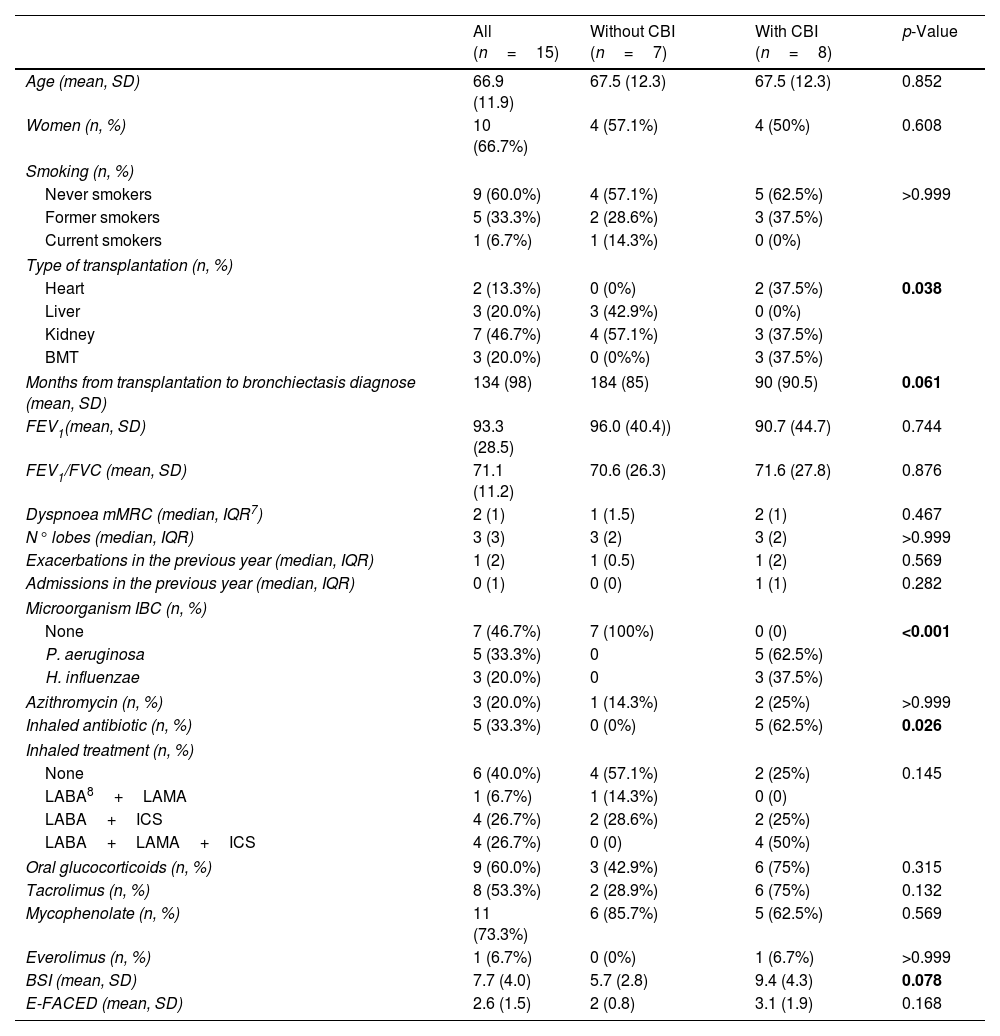
Fifteen patients were included; 66.7% were women. Median age was 67±12 years. Table 1 shows demographic and clinical data. The most common type of transplantation was renal (46.7%) and 3 patients underwent BMT (20%). Mean time from transplantation to bronchiectasis’ diagnosis was 134 months. The most commonly used immunosuppressive drugs were Mycophenolate (73.3%), oral glucocorticoids (60%) and Tacrolimus (53.3%). The majority of patients had chronic bronchial infection (CBI) (53.3%) with Pseudomonas aeruginosa being the most frequently identified microorganism (62.5%). Bronchiectasis severity index (BSI) mean score was 7.7 (moderate severity) and the E-FACED's was 2.6 (moderate severity).
Clinical data of the study patients and comparison by the presence of CBI.
| All (n=15) | Without CBI (n=7) | With CBI (n=8) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean, SD) | 66.9 (11.9) | 67.5 (12.3) | 67.5 (12.3) | 0.852 |
| Women (n, %) | 10 (66.7%) | 4 (57.1%) | 4 (50%) | 0.608 |
| Smoking (n, %) | ||||
| Never smokers | 9 (60.0%) | 4 (57.1%) | 5 (62.5%) | >0.999 |
| Former smokers | 5 (33.3%) | 2 (28.6%) | 3 (37.5%) | |
| Current smokers | 1 (6.7%) | 1 (14.3%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Type of transplantation (n, %) | ||||
| Heart | 2 (13.3%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (37.5%) | 0.038 |
| Liver | 3 (20.0%) | 3 (42.9%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Kidney | 7 (46.7%) | 4 (57.1%) | 3 (37.5%) | |
| BMT | 3 (20.0%) | 0 (0%%) | 3 (37.5%) | |
| Months from transplantation to bronchiectasis diagnose (mean, SD) | 134 (98) | 184 (85) | 90 (90.5) | 0.061 |
| FEV1(mean, SD) | 93.3 (28.5) | 96.0 (40.4)) | 90.7 (44.7) | 0.744 |
| FEV1/FVC (mean, SD) | 71.1 (11.2) | 70.6 (26.3) | 71.6 (27.8) | 0.876 |
| Dyspnoea mMRC (median, IQR7) | 2 (1) | 1 (1.5) | 2 (1) | 0.467 |
| N° lobes (median, IQR) | 3 (3) | 3 (2) | 3 (2) | >0.999 |
| Exacerbations in the previous year (median, IQR) | 1 (2) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (2) | 0.569 |
| Admissions in the previous year (median, IQR) | 0 (1) | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 0.282 |
| Microorganism IBC (n, %) | ||||
| None | 7 (46.7%) | 7 (100%) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| P. aeruginosa | 5 (33.3%) | 0 | 5 (62.5%) | |
| H. influenzae | 3 (20.0%) | 0 | 3 (37.5%) | |
| Azithromycin (n, %) | 3 (20.0%) | 1 (14.3%) | 2 (25%) | >0.999 |
| Inhaled antibiotic (n, %) | 5 (33.3%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (62.5%) | 0.026 |
| Inhaled treatment (n, %) | ||||
| None | 6 (40.0%) | 4 (57.1%) | 2 (25%) | 0.145 |
| LABA8+LAMA | 1 (6.7%) | 1 (14.3%) | 0 (0) | |
| LABA+ICS | 4 (26.7%) | 2 (28.6%) | 2 (25%) | |
| LABA+LAMA+ICS | 4 (26.7%) | 0 (0) | 4 (50%) | |
| Oral glucocorticoids (n, %) | 9 (60.0%) | 3 (42.9%) | 6 (75%) | 0.315 |
| Tacrolimus (n, %) | 8 (53.3%) | 2 (28.9%) | 6 (75%) | 0.132 |
| Mycophenolate (n, %) | 11 (73.3%) | 6 (85.7%) | 5 (62.5%) | 0.569 |
| Everolimus (n, %) | 1 (6.7%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (6.7%) | >0.999 |
| BSI (mean, SD) | 7.7 (4.0) | 5.7 (2.8) | 9.4 (4.3) | 0.078 |
| E-FACED (mean, SD) | 2.6 (1.5) | 2 (0.8) | 3.1 (1.9) | 0.168 |
CBI: chronic bronchial infection; SD: standard deviation; BMI: bone marrow transplantation; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in the 1st second; FVC: forced vital capacity; mMRC: dyspnoea modified scale of the Medical Research Council; IQ: interquartile range; LABA: long-acting beta agonist; LAMA: long-acting antimuscarinic; ICS: inhaled glucocorticoid; BSI: bronchiectasis severity index.
Bold values denote statistical significance at the p <0.05 level.
Patients with CBI were more likely to have undergone heart transplantation or BMT compared to those without CBI. Patients with CBI were diagnosed with bronchiectasis earlier than patients without CBI (90±91 vs 184±85 months; p=0.06). Moreover, patients with CBI had a higher severity of bronchiectasis measured by the BSI (9.4±4.3 vs 5.7±2.8 points; p=0.078).
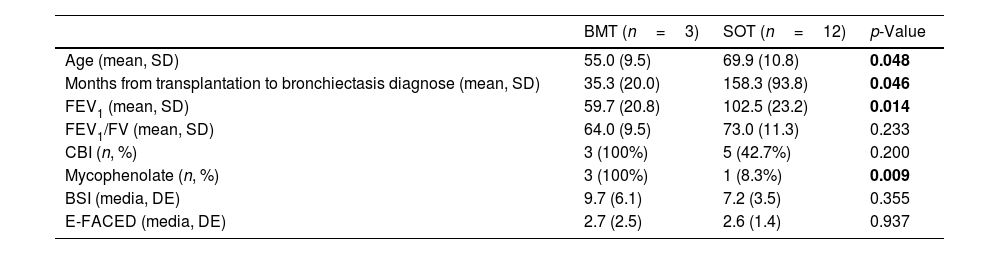
Table 2 shows comparison by type of transplantation. Patients who underwent BMT were younger (55±10 vs 70±11 years; p=0.048) and had worse lung function than those who underwent SOT (FEV1 59.7±20.8% vs 102.5±23.2%; p=0.014). BMT patients were diagnosed with bronchiectasis earlier than those with SOT (35±20 months vs 158±94 months; p=0.046). Also, there was a non-significant tendency for patients who underwent BMT to be more likely to have CBI compared to those who underwent SOT (100% vs 42.7%; p=0.2) and to have more severe bronchiectasis measured by BSI (9.7±6.1 vs 7.2±3.5 points; p=0.355).
Comparison by type of transplantation.
| BMT (n=3) | SOT (n=12) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean, SD) | 55.0 (9.5) | 69.9 (10.8) | 0.048 |
| Months from transplantation to bronchiectasis diagnose (mean, SD) | 35.3 (20.0) | 158.3 (93.8) | 0.046 |
| FEV1 (mean, SD) | 59.7 (20.8) | 102.5 (23.2) | 0.014 |
| FEV1/FV (mean, SD) | 64.0 (9.5) | 73.0 (11.3) | 0.233 |
| CBI (n, %) | 3 (100%) | 5 (42.7%) | 0.200 |
| Mycophenolate (n, %) | 3 (100%) | 1 (8.3%) | 0.009 |
| BSI (media, DE) | 9.7 (6.1) | 7.2 (3.5) | 0.355 |
| E-FACED (media, DE) | 2.7 (2.5) | 2.6 (1.4) | 0.937 |
BMT: bone marrow transplantation; SOT: solid organ transplantation; SD: standard deviation; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in the 1st second; FVC: forced vital capacity; CBI: chronic bronchial infection; BSI: bronchiectasis severity index.
Bold values denote statistical significance at the p <0.05 level.
This study highlights that secondary immunosuppression after SOT and BMT is a serious and poorly studied cause of bronchiectasis, showing high severity scores and CBI rates, especially in those with BMT. There is limited data on this regard, so the true impact of immunosuppression in bronchiectasis is not completely understood. The largest series to date was published in 2015 by Dury et al.,9 which included 46 patients who had undergone renal transplantation in 14 French centres. There was no data regarding the severity of bronchiectasis neither about non-renal transplantation in these series to compare with our sample.
Compared to observations from European and Spanish bronchiectasis registries,2–4 our sample had a similar median age, gender distribution, smoking history and prevalence of airway obstruction. The severity of bronchiectasis was higher in our sample compared to the European registries and similar to the Spanish registry RIBRON. The prevalence of CBI was higher compared to these registries, with P. aeruginosa being the most frequently identified microorganism in both.
Furthermore, most studies and clinical trials tend to exclude patients who have undergone SOT or BMT. Therefore, management strategies are extrapolated from general bronchiectasis recommendations, which may not be adequate for all immunocompromised patients. In addition, we observed a significant diagnostic delay on these patients, thus effective bronchiectasis treatments such as physiotherapy and chronic antibiotics may be started later. In this regard, we speculate that a thoracic CT scan and a prompt referral to respiratory specialists in all patients with compatible clinical syndrome and/or recurrent lung infections after SOT or BMT would probably improve patient outcomes.
Finally, patients who undergo BMT are younger and have a more serious disease than those who undergo SOT. Consequently, bronchiectasis in these patients should be suspected, studied and, if necessary, referred promptly to the respiratory specialist for proper examination, treatment and follow-up.
Our study has several limitations related to the small sample size and retrospective nature. However, to this date, this is the first study specifically assessing the severity and clinical characteristics of post-transplant bronchiectasis, both SOT and BMT. Our results are robust and highlight the importance of considering this condition in post-transplant patients to prevent diagnostic delays and inadequate treatment.
Bronchiectasis due to transplant-related immunosuppression is an uncommon but serious disease. There are very limited data available regarding the characteristics and proper management of these patients, which may contribute to diagnosis and treatment delay. Further research and larger studies are needed to better characterize these patients and to develop effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
FundingNo external financing has been needed for this study.
Authors’ contributionsDavid Rodríguez-Plaza and Guillermo Suárez-Cuartín wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Conflicts of interestDavid Rodríguez-Plaza, Ane Martínez de las Fuentes, Javier Burgos, Núria Sabé and Salud Santos declare no conflicts of interest.
Guillermo Suárez-Cuartín has received grants from Grifols, travel grants from Teva and Pari and participated in advisory boards for Insmed.