Adalimumab es un anticuerpo monoclonal IgG1 humano que se une al factor de necrosis tumoral-α implicado en la patogenia de la psoriasis. Se realizó un estudio retrospectivo para caracterizar a los pacientes con psoriasis que precisaron tratamiento con adalimumab, y evaluar la efectividad y seguridad de dicho tratamiento en la práctica clínica diaria.
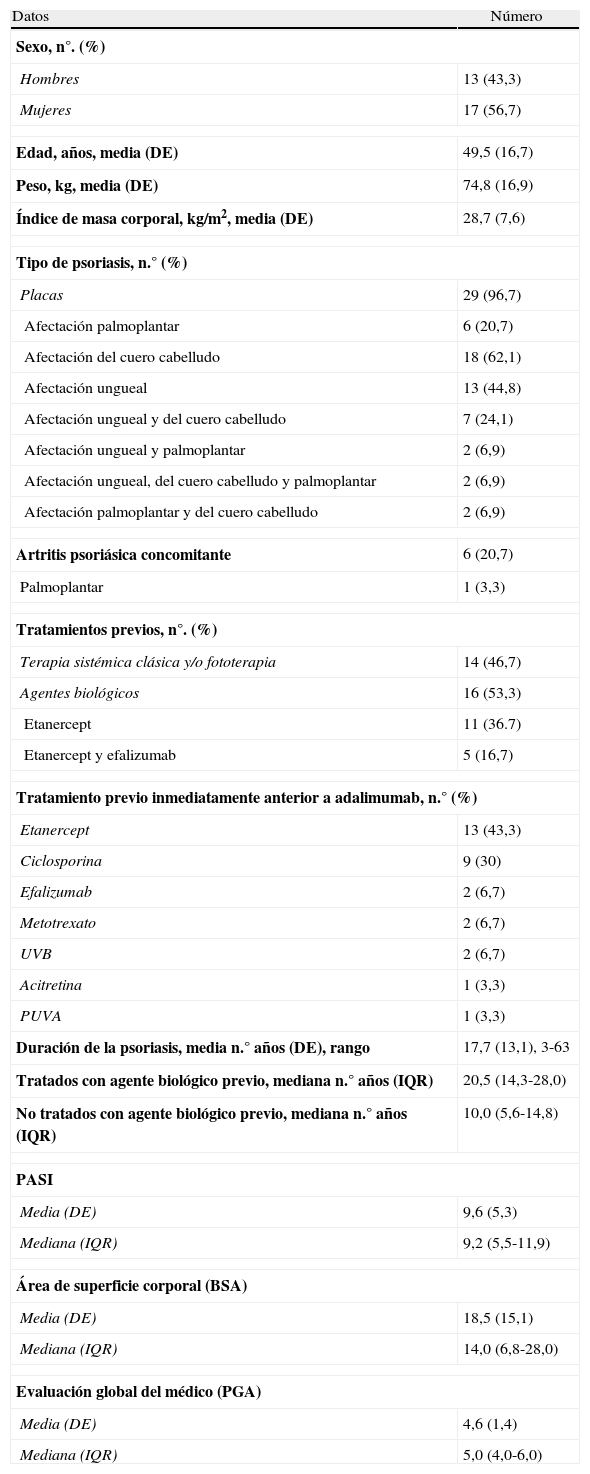
Pacientes y métodosSe revisaron las historias clínicas de 30 pacientes con psoriasis moderada-severa tratados con adalimumab desde enero de 2008 hasta abril de 2011.
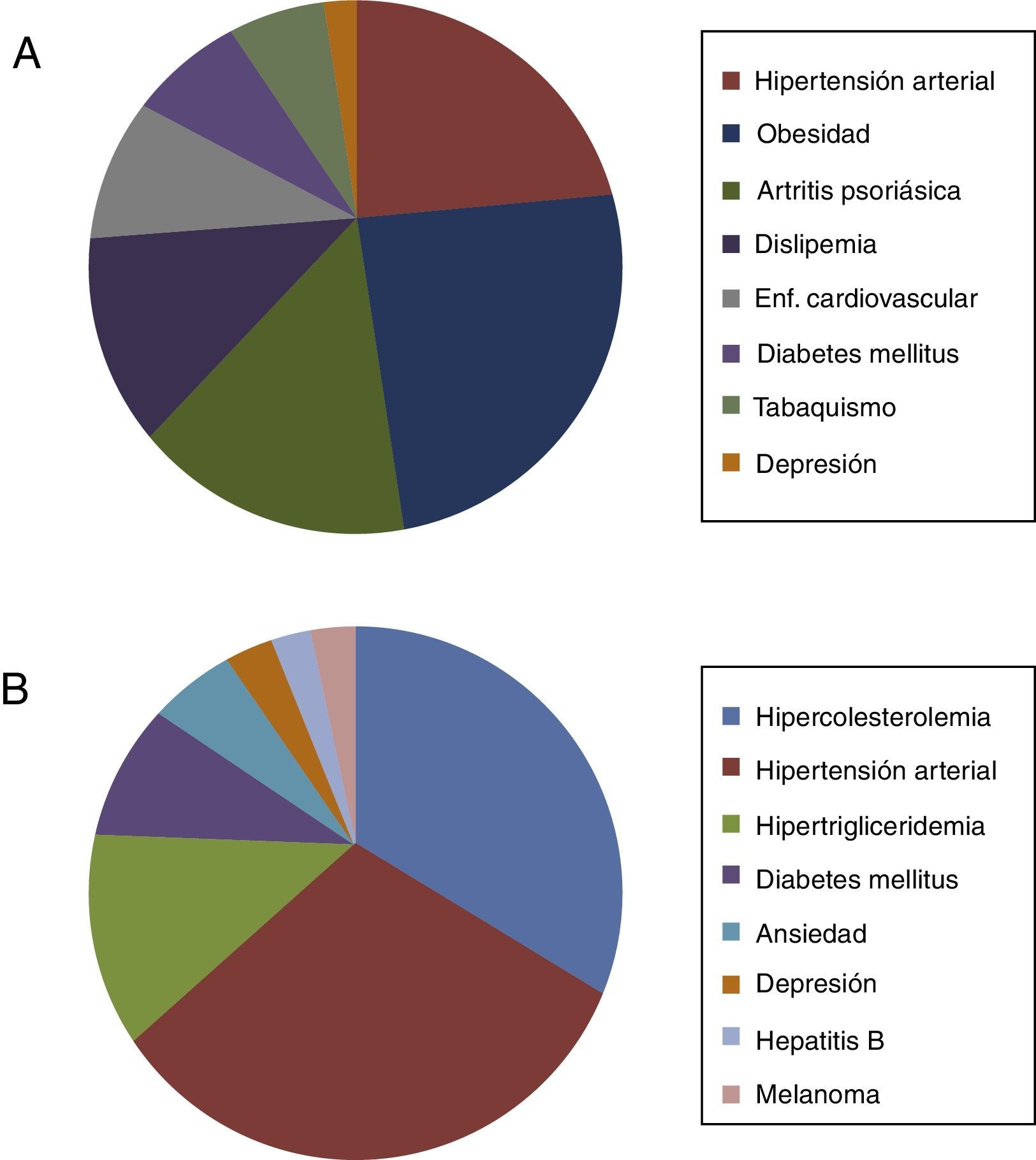
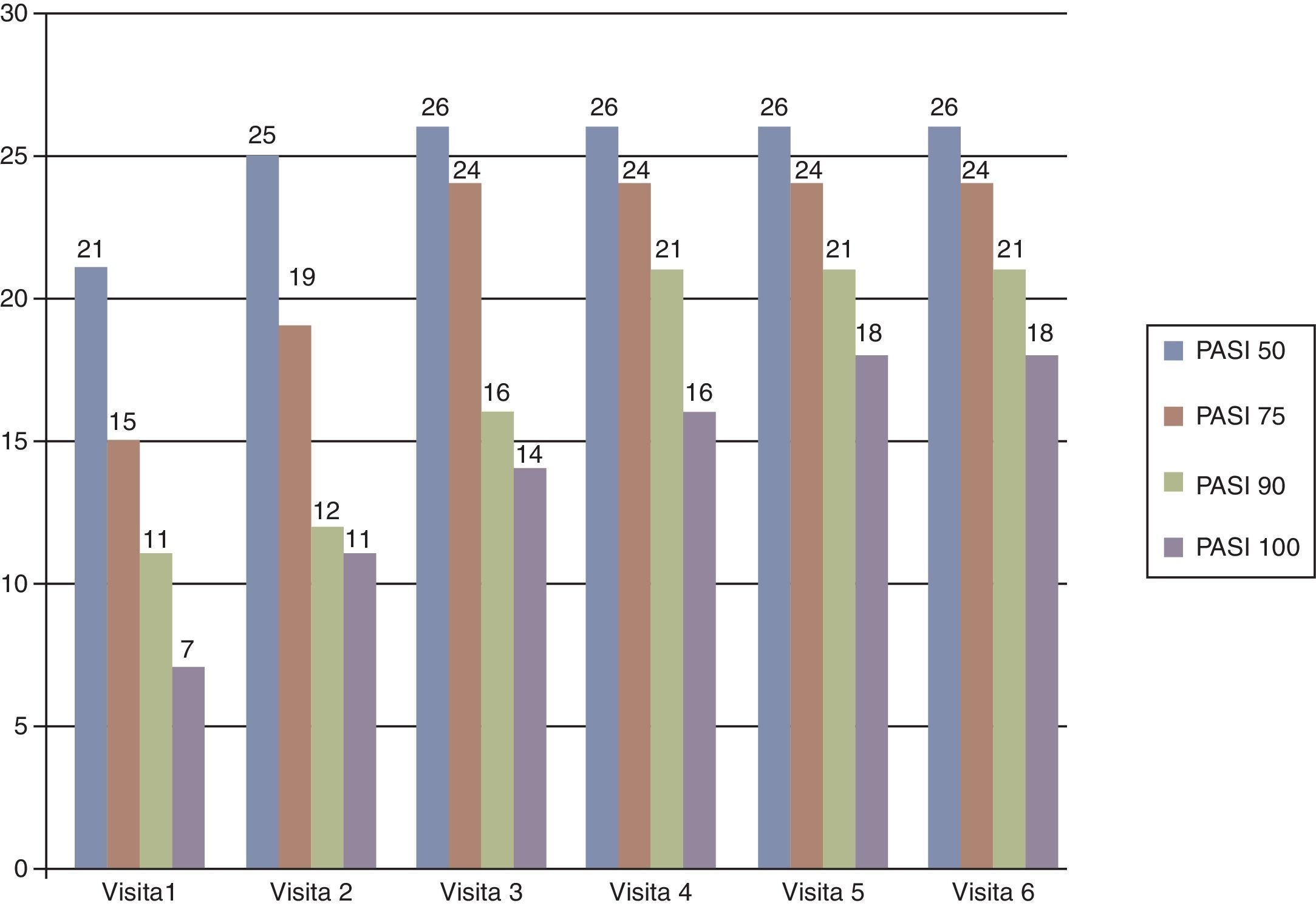
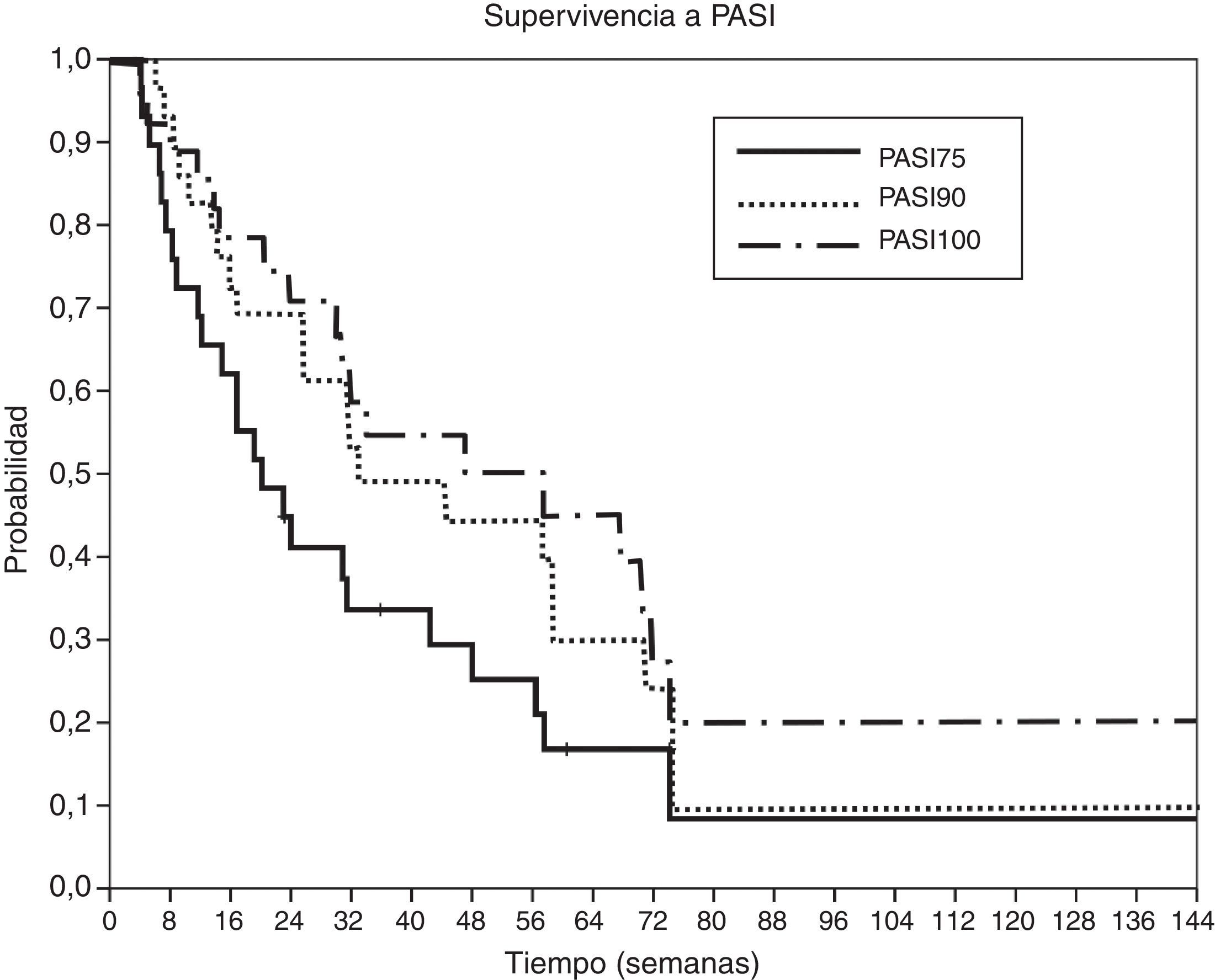
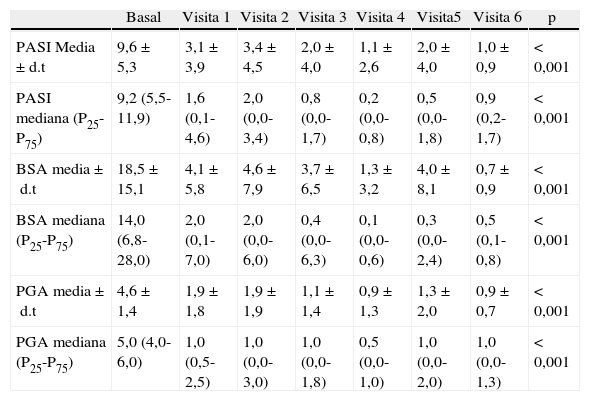
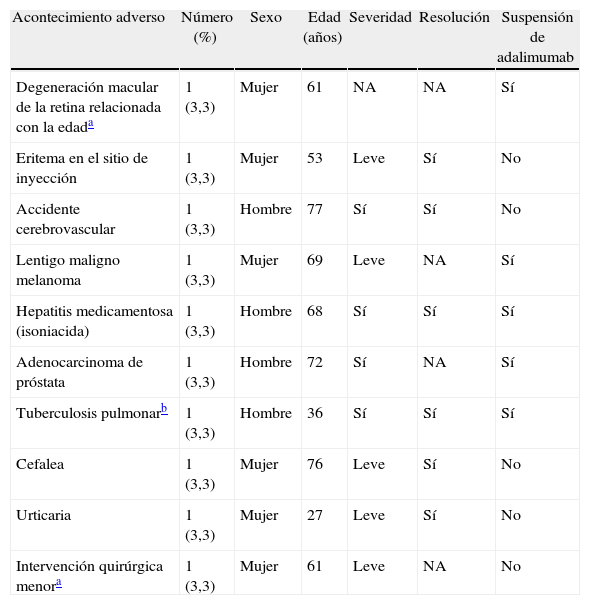
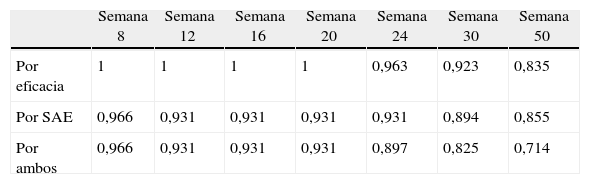
ResultadosTrece hombres y 17 mujeres con psoriasis precisaron tratamiento con adalimumab; 16 de ellos presentaban alguna comorbilidad, siendo las más frecuentes: hipertensión, obesidad, artritis y dislipidemia. Todos los pacientes presentaron mejoría del PASI, BSA y PGA (p<0,001). La mediana de supervivencia a PASI75, PASI90 y PASI100 fue de 20,1, 31,4 y 57,6 semanas, respectivamente. Se demostró algún acontecimiento adverso en 9 pacientes, en 5 de ellos este fue la causa de abandono del tratamiento. Al final del estudio 21 pacientes continúan en tratamiento con adalimumab.
ConclusiónAdalimumab ha demostrado ser un tratamiento muy efectivo y seguro para nuestros pacientes con psoriasis, quienes presentaban las comorbilidades más frecuentemente asociadas a esta enfermedad, y en los que habían fallado otras terapias sistémicas y biológicas previas. El porcentaje de respuesta PASI90 y PASI100 ha sido superior al obtenido en los ensayos clínicos pivotales. Adalimumab presentó un porcentaje de supervivencia del 70% a las 89 semanas de tratamiento.
Adalimumab is a fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody against TNF-α, which is implicated in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. A retrospective study was carried out to characterize patients with psoriasis who required adalimumab therapy, and to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of this treatment in daily clinical practice.
Patients and methodsWe reviewed the clinical histories of 30 patients with moderate to severe psoriasis treated between January 2008 and April 2011.
ResultsA total of 13 men and 17 women with psoriasis required adalimumab therapy. Of these, 16 had at least one comorbidity. The most common comorbidities were hypertension, obesity, arthritis and dyslipidemia. All patients showed improvement from baseline in PASI, BSA and PGA scores (P<.001). The median survival to achieve PASI 75, PASI 90 and PASI 100 were 20.1, 31.4 and 57.6 weeks, respectively. Adverse events were observed in 9 patients, requiring treatment withdrawal in 5. At the end of the study, 21 patients continued adalimumab therapy.
ConclusionAdalimumab proved to be highly effective and safe for the treatment of our patients with psoriasis, who had the most common comorbidities associated with psoriasis, and even in those with prior failure to other systemic and biological therapies. The percentages of PASI 90 and PASI 100 responses were higher than those achieved in pivotal clinical trials. Adalimumab presented a survival rate of 70% at week 89 of treatment.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora