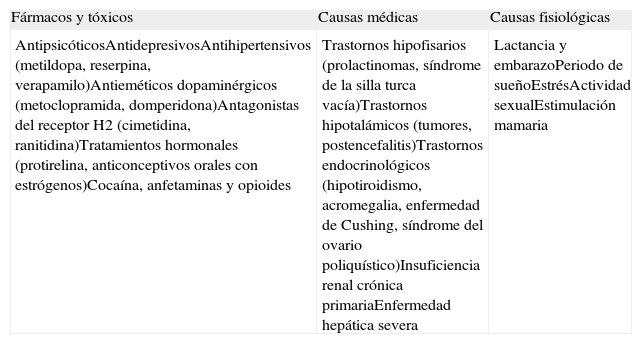
La hiperprolactinemia (HPRL) ha sido considerada hasta hace poco un efecto secundario inevitable e inherente al tratamiento antipsicótico y probablemente por ello sus efectos clínicos sean poco evaluados en la práctica clínica habitual. En esta revisión se evaluará el diferente potencial elevador de prolactina de los fármacos antipsicóticos (AP) y aquellas situaciones clínicas e individuales en las que hay que tener especiales precauciones a la hora de utilizar AP con potencial elevador de prolactina. Las consecuencias clínicas más comunes y conocidas de la HPRL por uso de AP son los síntomas sexuales y reproductivos, con diferentes características según género, pero recientemente se ha presentado mayor evidencia de una afectación también en la densidad mineral ósea, carcinogénesis y sistema cardiovascular. Aunque estos efectos precisan actualmente de mayor evidencia, se han de tener en cuenta a la hora de prescribir fármacos AP especialmente en pacientes susceptibles a desarrollarlos. Se considera de especial interés prevenir y minimizar los efectos de la HPRL por uso de AP así como, una vez instaurada, valorar su gravedad y afectación clínica y poderla manejar, y en su caso tratar, considerando la actuación de otras disciplinas.
Hyperprolactinemia (HPRL) has until recently been considered an unavoidable side effect inherent to antipsychotic treatment, and has probably been the reason why its clinical effects are underestimated in daily clinical practice. In this review we evaluate the different prolactin raising potential of the antipsychotic (AP) drugs, as well as the clinical and individual situations where special precautions must be taken when using these medications. The most common and better known clinical consequences of HPRL-induced by APs are sexual and reproductive symptoms, with different characteristics depending on gender, but recently more evidence has also been provided on an involvement in bone mineral density, carcinogenesis and the cardiovascular system. Though these effects still require more evidence, they are important to be taken into account when prescribing APs drugs in susceptible patients. It is essential to prevent and minimize the effect of HPRL-induced by APs and, once established, to consider its severity and clinical effects, and to provide a proper management, treatment and the involvement of other disciplines.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora