Carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria by production of carbapenemases is one of the most challenging issues regarding healthcare worldwide. We review the epidemiology and prevalence of carbapenemases in carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Latin American countries. High resistance rates to antimicrobial agents, particularly to carbapenems, are observed in this region. OXA-23 is the most widely disseminated class D-carbapenemase; it is present in all the countries of the region and is frequently associated to endemic clones CC113/CC79, CC104/CC15, CC110/ST25 and CC109/CC1. The emergence of OXA-72 and NDM-1 represents a novel finding which is observed simultaneously and without clonal relatedness in different countries, some of which are distant from one another, whereas OXA-143 is only present in Brazil. Further collaborative intraregional studies would provide a better understanding of these issues in most of the countries and thus, policies to control the spread of these isolates could be implemented.
En bacilos gram negativos, la resistencia a carbapenemes por producción de carbapenemasas es uno de los mayores problemas en la atención de la salud a nivel mundial. Reseñamos en este artículo la epidemiologia y la prevalencia de las carbapenemasas descritas en aislamientos de Acinetobacter baumannii recuperados en América Latina. En esta región se ha observado un alto porcentaje de resistencia a los antimicrobianos, particularmente a los carbapenemes. La carbapenemasa más frecuentemente descrita es OXA-23, que ha sido recuperada en todos los países de la región y fue asociada a los clones endémicos CC113/CC79, CC104/CC15, CC110/ST25 y CC109/CC1. La emergencia de OXA-72 y NDM-1 representa un nuevo hallazgo en varios países, algunos de los cuales se encuentran muy distantes entre sí. Por el momento, OXA-143 solo se recuperó de aislamientos obtenidos en Brasil. Serían necesarios estudios colaborativos dentro de la región para lograr una mejor comprensión de la resistencia a carbapenemes en Acinetobacter baumannii, a fin de poder instaurar medidas de control que eviten una mayor diseminación de esta bacteria.
The genus Acinetobacter, as currently defined, comprises gram-negative, strictly aerobic, nonfermenting, nonfastidious, nonmotile, catalase-positive, oxidase-negative bacteria with a DNA G+C content of 39–47%24.
Implementation of molecular techniques and mass spectrometry such as matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time and flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) in clinical microbiology laboratories has greatly improved the identification of Acinetobacter species. Acinetobacter baumannii is the most important in the clinical context. This is the genospecies which is most frequently associated with hospital outbreaks24. The ability to survive on inanimate surfaces and resistance to disinfectants or antimicrobials are crucial to this behavior24.
Carbapenems are currently the antibiotics of choice against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter infections. However, carbapenem-resistance (CR) is increasingly being reported, leaving few therapeutic options available24,37,38.
The aim of this review is to analyze the prevalence and molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii (CR-Ab) isolates in Latin American countries.
Literature associated with CR-Ab in Latin America (LA) was included. The articles in English and Spanish language were accessed through PubMed and Scientific Electronic Library Online (SciELO). Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) documents were also consulted19–23. It is important to mention that a heterogeneous distribution of molecular epidemiology studies performed in the region was noticed; although 60% of the countries in LA have presented data, more than 50% of these correspond to Brazil and Argentina.
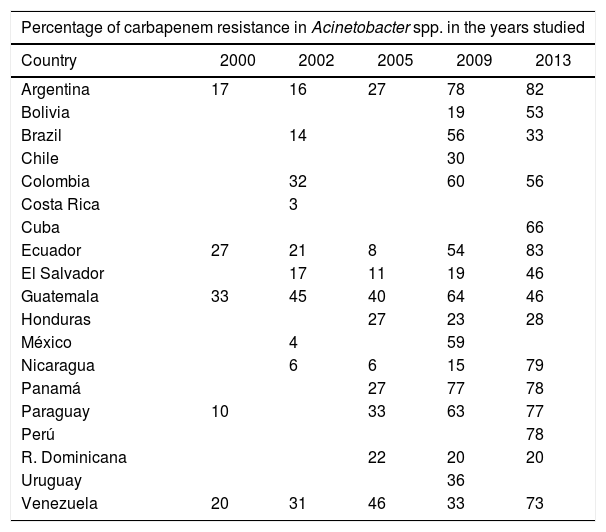
Prevalence of carbapenem-resistant A. baumanniiRates of carbapenem resistance in LA appear to be among the highest in the world. A wide range of resistance has been reported among the different countries (1–90%), the lowest values belong to Central America and the highest ones to some studies in Argentina and Brazil12. In addition, reports of the Latin American Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (ReLAVRA-PAHO) showed a progressive increase in the percentages of resistance reported during the period 2000–201319–23 (Table 1). Even though statistics do not show discrimination among genospecies, some studies conducted in the area evidence a participation of A. baumannii in nosocomial infections higher than 90%27. Therefore, it could be affirmed that resistance rates would not vary significantly if only A. baumannii isolates had been considered in the analysis27.
Evolution of carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter spp. isolates recovered in several Latin American countries. Annual reports by ReLAVRA-PAHO
| Percentage of carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter spp. in the years studied | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | 2000 | 2002 | 2005 | 2009 | 2013 |
| Argentina | 17 | 16 | 27 | 78 | 82 |
| Bolivia | 19 | 53 | |||
| Brazil | 14 | 56 | 33 | ||
| Chile | 30 | ||||
| Colombia | 32 | 60 | 56 | ||
| Costa Rica | 3 | ||||
| Cuba | 66 | ||||
| Ecuador | 27 | 21 | 8 | 54 | 83 |
| El Salvador | 17 | 11 | 19 | 46 | |
| Guatemala | 33 | 45 | 40 | 64 | 46 |
| Honduras | 27 | 23 | 28 | ||
| México | 4 | 59 | |||
| Nicaragua | 6 | 6 | 15 | 79 | |
| Panamá | 27 | 77 | 78 | ||
| Paraguay | 10 | 33 | 63 | 77 | |
| Perú | 78 | ||||
| R. Dominicana | 22 | 20 | 20 | ||
| Uruguay | 36 | ||||
| Venezuela | 20 | 31 | 46 | 33 | 73 |
Acquired carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter spp. is often associated with acquired carbapenemase production. The most frequent ones are carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D β-lactamases (CHDLs) and secondly, metalloenzymes (MBL) such as VIM, IMP and NDM37,38.
OXA-type carbapenemasesCurrently, there are six subclasses of CHDLs associated with A. baumannii: intrinsic chromosomal OXA-51-like enzymes and acquired OXA-23-like, OXA-24-like, OXA-58-like, OXA-143-like and OXA-235-like. CHDLs exhibit weak carbapenem hydrolysis; however, they can confer resistance mediated by the combination of natural low permeability and ISAba elements located upstream of the gene. The blaOXA-51-like gene codes for the intrinsic carbapenemase found in A. baumannii although clinically significant resistance to carbapenems mediated by blaOXA-51-like has only been observed in isolates with the insertion sequence ISAba1 located immediately upstream of the gene. However, plasmids harboring ISAba1 – blaOXA-51-like have been detected in A. baumannii, Acinetobacter nosocomialis and Acinetobacter pittii, as well. This affects the accuracy of using blaOXA-51-like detection as a tool for differentiating A. baumannii from other Acinetobacter species.
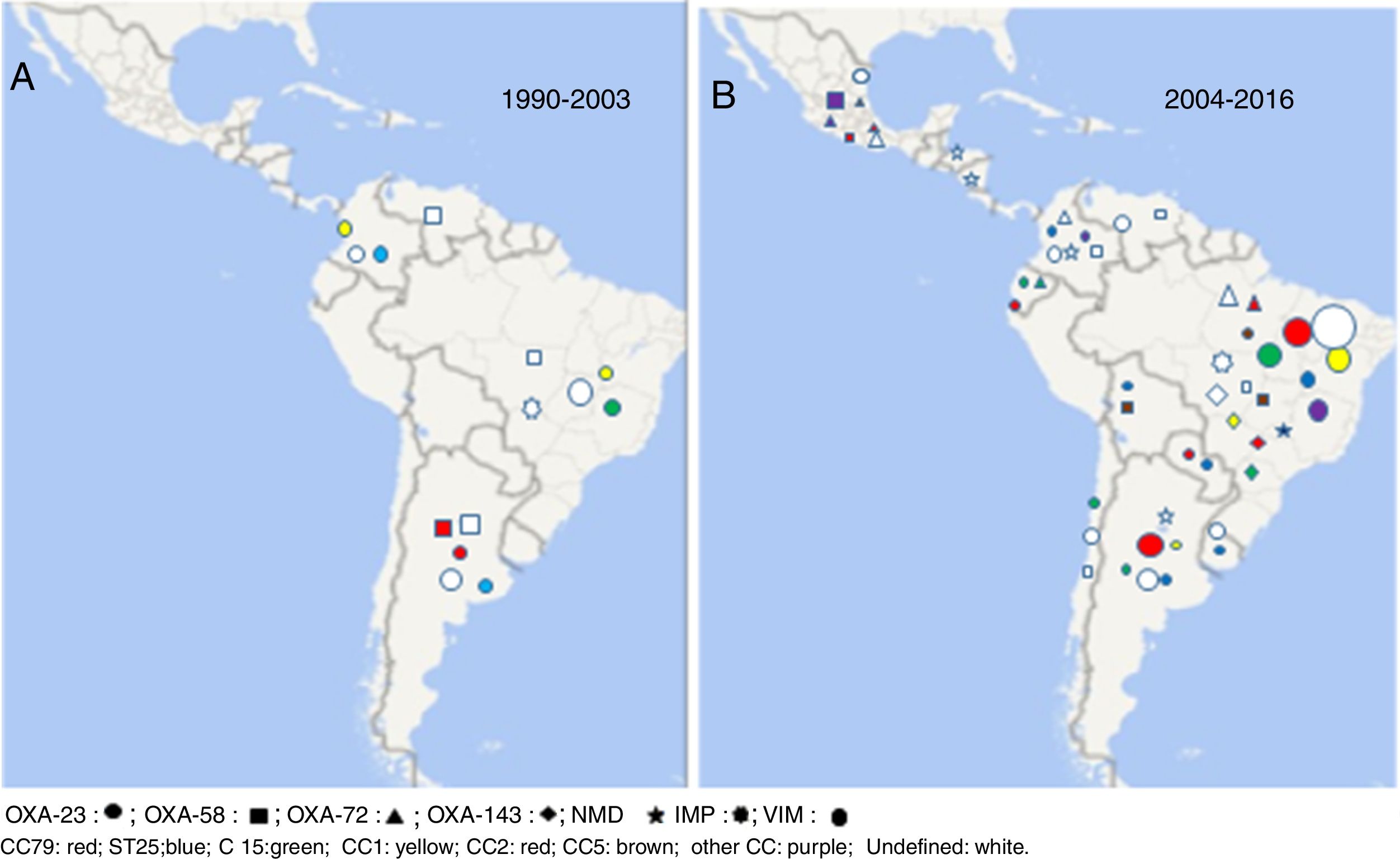
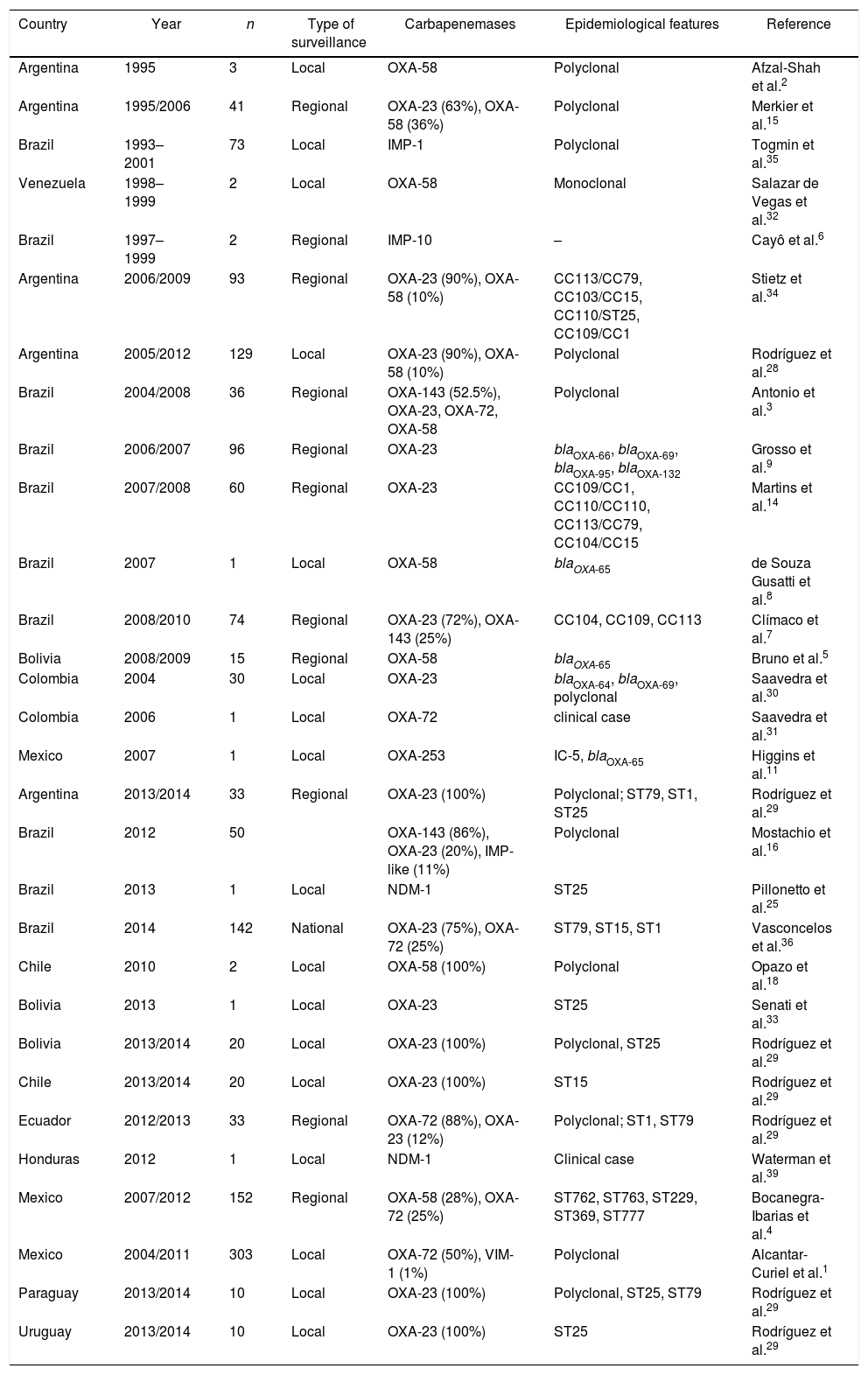
The first reported OXA-type enzyme was a plasmid-encoded β-lactamase described in 1985 that was initially named ARI-1 and later OXA-2324,37. The blaOXA-23 gene can be located either on the chromosome or on plasmids37. This carbapenemase was the first described in LA in addition to being the most frequently reported and geographically most disseminated in LA. Its presence has been reported in all the Latin American countries where molecular epidemiology studies have been published (Table 2 and Fig. 1).
Reports of epidemiological and microbiological features of carbapenemase-producing A. baumannii in Latin America
| Country | Year | n | Type of surveillance | Carbapenemases | Epidemiological features | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argentina | 1995 | 3 | Local | OXA-58 | Polyclonal | Afzal-Shah et al.2 |
| Argentina | 1995/2006 | 41 | Regional | OXA-23 (63%), OXA-58 (36%) | Polyclonal | Merkier et al.15 |
| Brazil | 1993–2001 | 73 | Local | IMP-1 | Polyclonal | Togmin et al.35 |
| Venezuela | 1998–1999 | 2 | Local | OXA-58 | Monoclonal | Salazar de Vegas et al.32 |
| Brazil | 1997–1999 | 2 | Regional | IMP-10 | – | Cayô et al.6 |
| Argentina | 2006/2009 | 93 | Regional | OXA-23 (90%), OXA-58 (10%) | CC113/CC79, CC103/CC15, CC110/ST25, CC109/CC1 | Stietz et al.34 |
| Argentina | 2005/2012 | 129 | Local | OXA-23 (90%), OXA-58 (10%) | Polyclonal | Rodríguez et al.28 |
| Brazil | 2004/2008 | 36 | Regional | OXA-143 (52.5%), OXA-23, OXA-72, OXA-58 | Polyclonal | Antonio et al.3 |
| Brazil | 2006/2007 | 96 | Regional | OXA-23 | blaOXA-66, blaOXA-69, blaOXA-95, blaOXA-132 | Grosso et al.9 |
| Brazil | 2007/2008 | 60 | Regional | OXA-23 | CC109/CC1, CC110/CC110, CC113/CC79, CC104/CC15 | Martins et al.14 |
| Brazil | 2007 | 1 | Local | OXA-58 | blaOXA-65 | de Souza Gusatti et al.8 |
| Brazil | 2008/2010 | 74 | Regional | OXA-23 (72%), OXA-143 (25%) | CC104, CC109, CC113 | Clímaco et al.7 |
| Bolivia | 2008/2009 | 15 | Regional | OXA-58 | blaOXA-65 | Bruno et al.5 |
| Colombia | 2004 | 30 | Local | OXA-23 | blaOXA-64, blaOXA-69, polyclonal | Saavedra et al.30 |
| Colombia | 2006 | 1 | Local | OXA-72 | clinical case | Saavedra et al.31 |
| Mexico | 2007 | 1 | Local | OXA-253 | IC-5, blaOXA-65 | Higgins et al.11 |
| Argentina | 2013/2014 | 33 | Regional | OXA-23 (100%) | Polyclonal; ST79, ST1, ST25 | Rodríguez et al.29 |
| Brazil | 2012 | 50 | OXA-143 (86%), OXA-23 (20%), IMP-like (11%) | Polyclonal | Mostachio et al.16 | |
| Brazil | 2013 | 1 | Local | NDM-1 | ST25 | Pillonetto et al.25 |
| Brazil | 2014 | 142 | National | OXA-23 (75%), OXA-72 (25%) | ST79, ST15, ST1 | Vasconcelos et al.36 |
| Chile | 2010 | 2 | Local | OXA-58 (100%) | Polyclonal | Opazo et al.18 |
| Bolivia | 2013 | 1 | Local | OXA-23 | ST25 | Senati et al.33 |
| Bolivia | 2013/2014 | 20 | Local | OXA-23 (100%) | Polyclonal, ST25 | Rodríguez et al.29 |
| Chile | 2013/2014 | 20 | Local | OXA-23 (100%) | ST15 | Rodríguez et al.29 |
| Ecuador | 2012/2013 | 33 | Regional | OXA-72 (88%), OXA-23 (12%) | Polyclonal; ST1, ST79 | Rodríguez et al.29 |
| Honduras | 2012 | 1 | Local | NDM-1 | Clinical case | Waterman et al.39 |
| Mexico | 2007/2012 | 152 | Regional | OXA-58 (28%), OXA-72 (25%) | ST762, ST763, ST229, ST369, ST777 | Bocanegra-Ibarias et al.4 |
| Mexico | 2004/2011 | 303 | Local | OXA-72 (50%), VIM-1 (1%) | Polyclonal | Alcantar-Curiel et al.1 |
| Paraguay | 2013/2014 | 10 | Local | OXA-23 (100%) | Polyclonal, ST25, ST79 | Rodríguez et al.29 |
| Uruguay | 2013/2014 | 10 | Local | OXA-23 (100%) | ST25 | Rodríguez et al.29 |
The worldwide dissemination of blaOXA-23 would be related to International clones I or II. In South America (SA) this carbapenemase has been commonly associated with CC113/CC79; however, it has also been detected in clones recovered in a lower proportion (CC104/CC15, CC110/ST25, CC109/CC1) and in many sporadic isolates3,6,9,14–17,28–30,34,36. Some OXA-23 allelic variants, such as OXA-239, have been described, which showed a major presence in studies conducted in the south of Mexico in the year 20141.
As it can be observed in Figure 1, OXA-23 predominates in all the countries of the region, it is the most frequently detected carbapenemase in the CR-Ab population, except for some studies carried out in the south of Mexico1,4.
In the mid-1990s, blaOXA-58 was reported in Argentina and Venezuela2,32. Ten years later, outbreaks by CR-Ab have shown the presence of OXA-58 as the main carbapenem-resistance mechanism in Bolivia and Chile5,18. Coincidentally to what has been detected in other regions in recent years, a total displacement of blaOXA-58 by blaOXA-23 was observed in LA. In Argentina, the presence of OXA-58 in the resistant population has gradually declined from 36% in 1995 to 0% in studies conducted after the year 201428. It is also noteworthy to mention the low presence of this carbapenemase in Brazil, where the first isolate harboring OXA-58 was recovered in the year 2007, and so far, has only been detected sporadically8,36. In Brazil and Bolivia blaOXA-58-producing isolates belonged to CC113/CC79, reaffirming its important presence in the CR-Ab population of LA, whereas in Argentina some strains were found to be associated to CC109/CC15,8,28.
The fact that both carbapenemases have been described in the same STs suggests that the prevalence of one enzyme over another does not only depend exclusively on the clone, but also on the ability to acquire resistance through horizontal gene transfer and the impact on the MIC value of the antimicrobial agents affected, among other factors5,9,14,29,30,34,36.
Earlier, Opazo et al.18 reported the presence of CR-Ab isolates belonging to the 24/40 group in LA, however, unfortunately, they were not sequenced. This carbapenemase, often plasmid-mediated, has been reported to cause hospital outbreaks in many Intensive Care Units (ICUs) worldwide37. In LA sporadic isolates were described in Brazil and Colombia in the middle of the last decade3,31. Since 2010 the first outbreaks have been detected in Guayaquil, Ecuador (2012) and in Brazil (2014). These isolates belonged to ST15 and CC113/CC79 in Ecuador and Brazil, respectively17,36. In Mexico, on the other hand, OXA-72 seems to be the most important contributor to carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii in several studies conducted in different cities in the north and center of the country1,4.
Two new CHDL variants, OXA-143 and OXA-235, have been described in the last 10 years in LA; OXA-143, of plasmid encoding, possesses 40% similarity with OXA-40; there are two variants of this enzyme: OXA-231 and OXA-25311. As the blaOXA-143 gene is undetectable using the current multiplex PCR assay available, Higgins et al. showed a modified multiplex PCR which can help to monitor the spread of this carbapenemase20.
OXA-143 was detected for the first time in 2004 and to date, it has only been isolated in Brazil, its presence in the south of that country reaching about 70%. blaOXA-143 like genes mainly belong to clonal complexes CC104/CC15, CC109/CC1 and CC113/CC793,7,10,16.
On the other hand, OXA-235 hydrolyzes penicillins and carbapenems but it does not show activity against extended-spectrum cephalosporins. Only one strain was isolated in Mexico in 201611.
Metallo-β-lactamase carbapenemasesMetallo-β-lactamases are divided into six families; of these, only IMP, VIM, SIM and NDM enzymes have been detected in A. baumannii38. We can differentiate 2 periods regarding the presence of MBLs in LA. The first period started in the mid-1990s, with the detection of IMP-1 in Brazil35. Even though more than 15 years have passed and that more allelic variants have been detected (IMP-10), these isolates have been restricted to a few hospitals located in e Sao Pablo State6. Apart from Brazil, sporadic isolates harboring blaIMP, blavIM-1 and blaVIM-4 have been described in Mexico1,4. The second period started with the detection of the blaNDM-1 gene almost simultaneously in Honduras (2012) and Brazil (2013) in A. baumannii isolates belonging to ST2525,39. Later in the following years, its presence was communicated in Argentina, Colombia, Nicaragua and Paraguay21–23. Moreover, this enzyme was also detected in other genospecies different from A. baumannii as well as in Enterobacteriaceae.
Other carbapenemasesCarbapenemases different from CHDLs and MBLs are rare in A. baumannii24. However, it is noteworthy to mention the importance of the presence of KPC in A. baumannii isolates recovered in Puerto Rico13-26. The possibility of transmission of multidrug-resistant A. baumannii by tourism and/or human migration is a widely described phenomenon in A. baumannii. Therefore, the important interrelationship between the Caribbean country and SA would imply the need to implement measures to detect this enzyme in A. baumannii.
In the comparative analysis of the 2 symmetric periods shown in Figure 1, it can be observed that OXA-23 is the carbapenemase/oxacillinase mostly present in both periods (1990–2003 and 2006–2016), whereas OXA-58 was mainly detected in the first period and OXA-72; OXA-143 and NDM in the second one.
Clonal disseminationDifferent tools have been proposed to investigate the epidemiology of A. baumannii outbreaks. Pulsed-field electrophoresis (PFGE) has been considered the gold-standard technique for fine-scale typing of A. baumannii isolates. The presence of multiple clones has been detected in most of the studies conducted in one hospital unit, which evidences endemic features in the CR-Ab population in LA. Conversely, the multilocus sequence typing technique (MLST) has a better ability to group isolates during large-sized epidemiological analyses. blaOXA-51-like sequence-based typing and 3-locus sequence typing represent economic and rapid methodologies which show a discriminatory power similar to MLST. Most recently, MALDI-TOF has shown to behave less effectively to perform A. baumannii clonal discrimination24.
Despite the widely-accepted idea that a few genotypic groups are responsible for a large proportion of A. baumannii infections, particular characteristics of each region have been reported. Contrary to what was reported in Europe and other countries worldwide, in LA, the presence of the international clones II and III represented a minority in the year 20167,8,14,24,29,30,34,36.
Research performed in SA has shown a predominance of CC113/CC79. Stietz et al.34 evidenced its presence in isolates recovered before the year 2000 in a retrospective study. Subsequent studies carried out mainly in Brazil, but also in Argentina and Colombia, confirmed the predominance of CC113/CC79 together with CC103/CC15 and CC109/CC1 in CR-Ab isolates7,8,14,30,34,36. In the year 2014 the first plurinational study performed in LA, which involved 9 hospitals belonging to 6 countries, evidenced that its predominance was also extended to countries such as Chile, Uruguay, Paraguay and Ecuador29. The spread of ST25 was also highlighted in the mentioned study in different LA countries, similarly to what was observed in other regions12,29,30,34.
SummaryThe main findings and recent changes in the molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii clinical isolates in LA were revised in the present study. Among them, we have observed common features with other regions: (1) A. baumanii represents the predominant genospecies; (2) the main presence of A. baumanii in nosocomial infections and the progressive increase in carbapenem resistance rates; (3) the high prevalence of the blaOXA-23 gene; (4) the emergence of OXA-72 and NDM-1, and other features such as the low predominance of international clones I, II and III. Therefore, we believe that being able to obtain our own results and figures will lead to the elaboration of a regional casuistic report, which would guide the implementation of the adequate policies to prevent and/or control the spread of multidrug-resistant A. baumannii isolates.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.