The enthesis is one of the target organs in patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA), since inflammation of it, known as enthesitis, can be observed, which in many patients with spondyloarthritis could go unnoticed.
ObjectiveTo find the relationship between the MASEI index (MAdrid Sonographic Enthesitis Index) in entheses and other indices/serological activity markers (such as BASDAI, DAPSA or ASDAS and ESR, CRP) in spondyloarthritis patients.
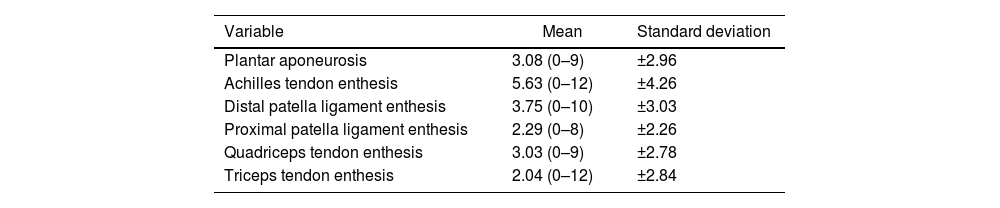
Materials and methodsObservational, descriptive, and cross-sectional study. Data were collected from patients with SpA who underwent musculoskeletal ultrasound using the MASEI index and who were treated in our clinics from May 2021 to September 2021. As appropriate, the variables evaluated were described using frequency and central tendency/dispersion measures. First, we tested the normality of all the variables using a Shapiro–Wilk test. Then we studied the correlation of parametric and non-parametric numerical variables, using Pearson's and Spearman's coefficients. We used the T-Student, Mann–Whitney U, and chi-square tests for the categorical variables.
ResultsWe analyzed 24 patients with SpA (with a mean age of 50.50±10.63 years), 8 women and 16 men. The variables have the following average levels: ASDAS 2.35 (±1.09); BASDAI (for those with axial involvement) 4.54 (±2.93); DAPSA (for psoriatic arthritis) 10.98 (±6.85), and total MASEI 19.88 (±14.77). We found a correlation between the total MASEI and the following variables: ASDAS (Pearson coefficient=.696), BASDAI (Spearman coefficient=.823), and DAPSA (Pearson coefficient=.823).
ConclusionPatients with spondyloarthritis with more significant disease activity measured by ASDAS, BASDAI/DAPSA, and the serological markers of inflammation CRP and ESR present a higher total MASEI than patients who are controlled.
La entesis es uno de los órganos diana en los pacientes con espondiloartritis (EspA), ya que se puede observar una inflamación de esta, conocida como entesitis, que en muchos pacientes con EspA podría pasar desapercibida.
ObjetivoEncontrar la relación entre el índice entesítico MASEI (MAdrid Sonographic Enthesitis Index) y otros índices/marcadores de actividad serológica (como BASDAI, DAPSA, ASDAS, VSG y PCR) en pacientes con EspA.
Materiales y métodosEstudio observacional, descriptivo y transversal. Se recogieron datos de pacientes con EspA a los que se les realizó ecografía musculoesquelética mediante el índice MASEI y que fueron atendidos en nuestras consultas desde mayo del 2021 hasta septiembre del 2021. Las variables evaluadas se describieron mediante medidas de frecuencia y de tendencia central/dispersión, según correspondía. Primero, probamos la normalidad de todas las variables usando la prueba de Shapiro-Wilk. Luego estudiamos la correlación de variables numéricas paramétricas y no paramétricas, para lo cual utilizamos los coeficientes de Pearson y Spearman. Utilizamos las pruebas T-Student, Mann-Whitney U y chi-cuadrado para las variables categóricas.
ResultadosSe analizaron 24 pacientes con EspA (con una edad media de 50,50±10,63 años), 8 mujeres y 16 hombres. Las variables tienen los siguientes niveles promedio: ASDAS 2,35 (±1,09), BASDAI (para aquellos con afectación axial) 4,54 (±2,93), DAPSA (para artritis psoriásica) 10,98 (±6,85) y MASEI total 19,88 (±14,77). Hemos encontrado correlación entre el MASEI total y las siguientes variables: ASDAS (coeficiente de Pearson=0,696), BASDAI (coeficiente de Spearman=0,823) y DAPSA (coeficiente de Pearson=0,823).
ConclusiónLos pacientes con EspA con mayor actividad de la enfermedad medida por ASDAS, BASDAI/DAPSA y los marcadores serológicos de inflamación PCR y VSG presentan un MASEI total mayor que los pacientes controlados.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora