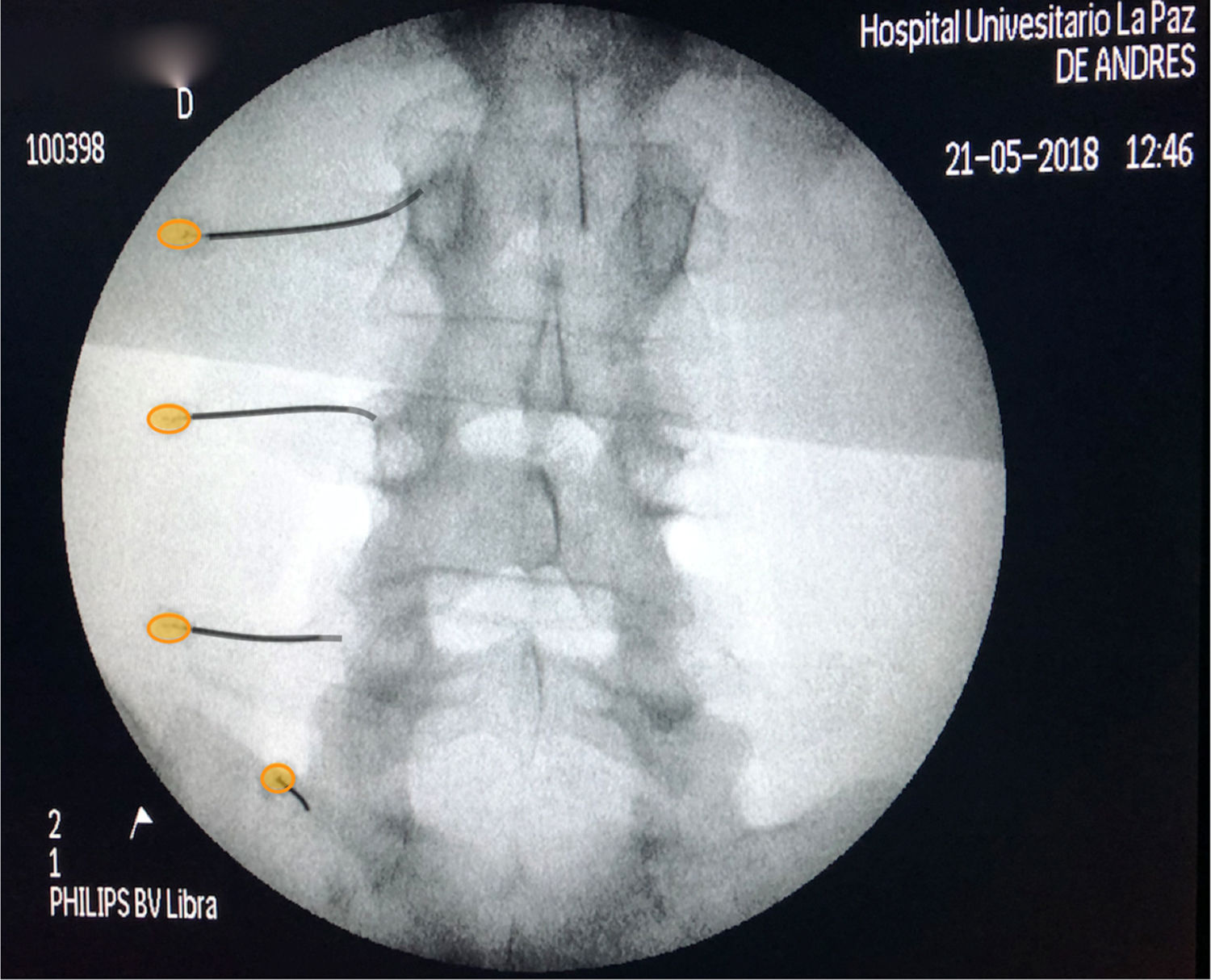
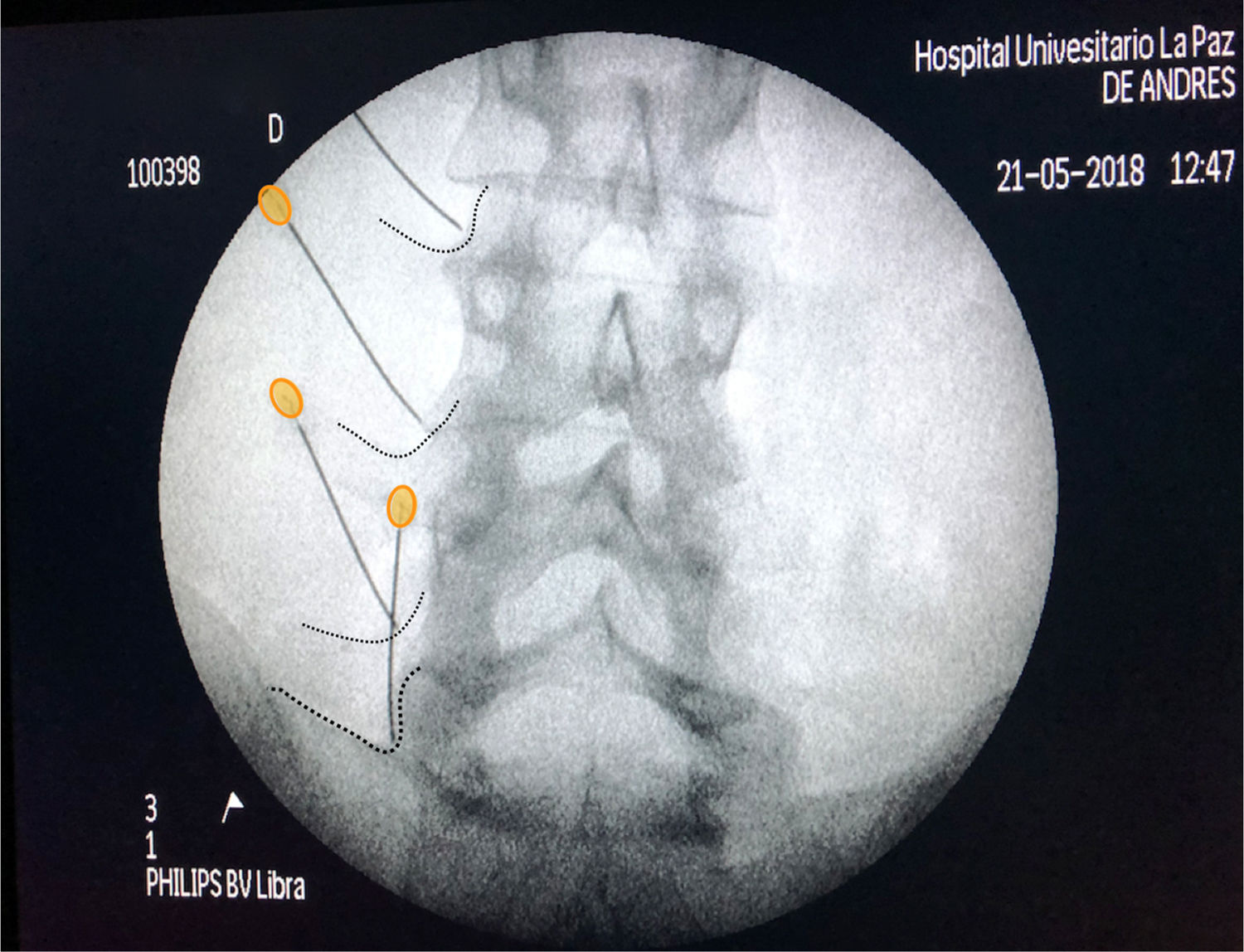
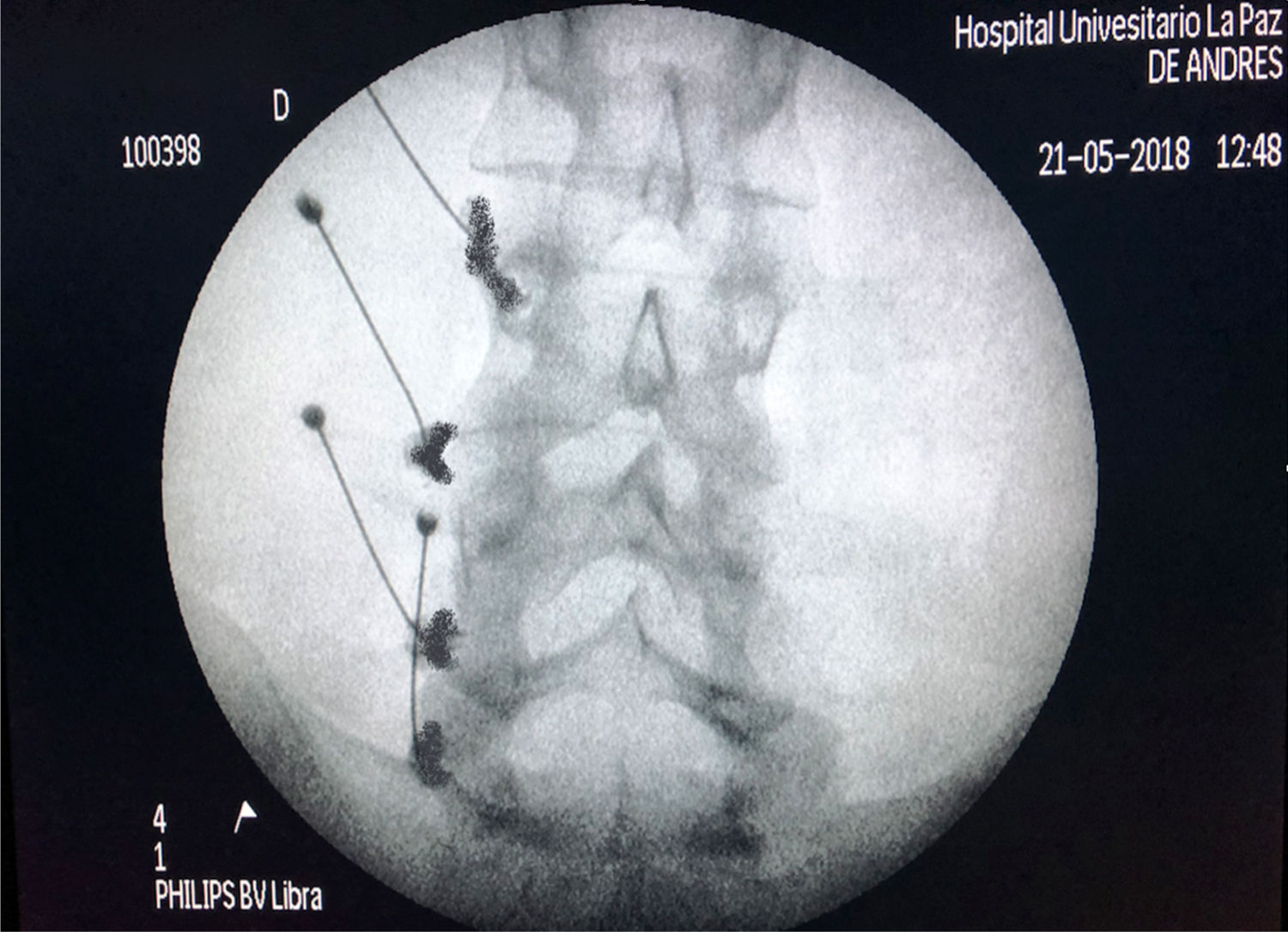
Low back pain is currently one of the main public health problems. Among the multiple causes, pain in the zygapophysial joints, also called facets or posterior vertebral joints, are an important cause, usually secondary to osteoarthritis. The source of low back pain is often difficult to find, making the therapeutic approach to the patient sub-optimal. Diagnostic blocks are a very important tool in establishing an adequate treatment for patients with low back pain, as long as they are performed accurately, with an adequate local anaesthetic volume, with a suitable image and fluoroscopic projection and its result are precisely interpreted. In this article a review is presented on the importance of diagnostic blocks, as well as how they should be performed in order to obtain the maximum information and the greatest therapeutic benefit.
El dolor lumbar o lumbalgia es uno de los principales problemas de salud pública de la sociedad actual. De entre las múltiples causas de la misma las articulaciones zigoapofisarias, también denominadas facetas o articulaciones vertebrales posteriores, son una causa importante, generalmente secundaria a artrosis. El diagnóstico de la causa de la lumbalgia suele ser en muchas ocasiones difícil, haciendo que el enfoque terapéutico del paciente no sea el óptimo. Los bloqueos diagnósticos constituyen una herramienta de suma importancia para establecer un tratamiento adecuado del paciente con lumbalgia, siempre y cuando sean realizados de manera precisa, con un volumen adecuado de anestésico local, con una imagen y proyección fluoroscópica idónea y el resultado sea interpretado de manera exacta. En el siguiente artículo revisaremos la importancia de los bloqueos diagnósticos, así como el modo en que deben ser realizados, para obtener la máxima información de los mismos y el mayor beneficio terapéutico.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora