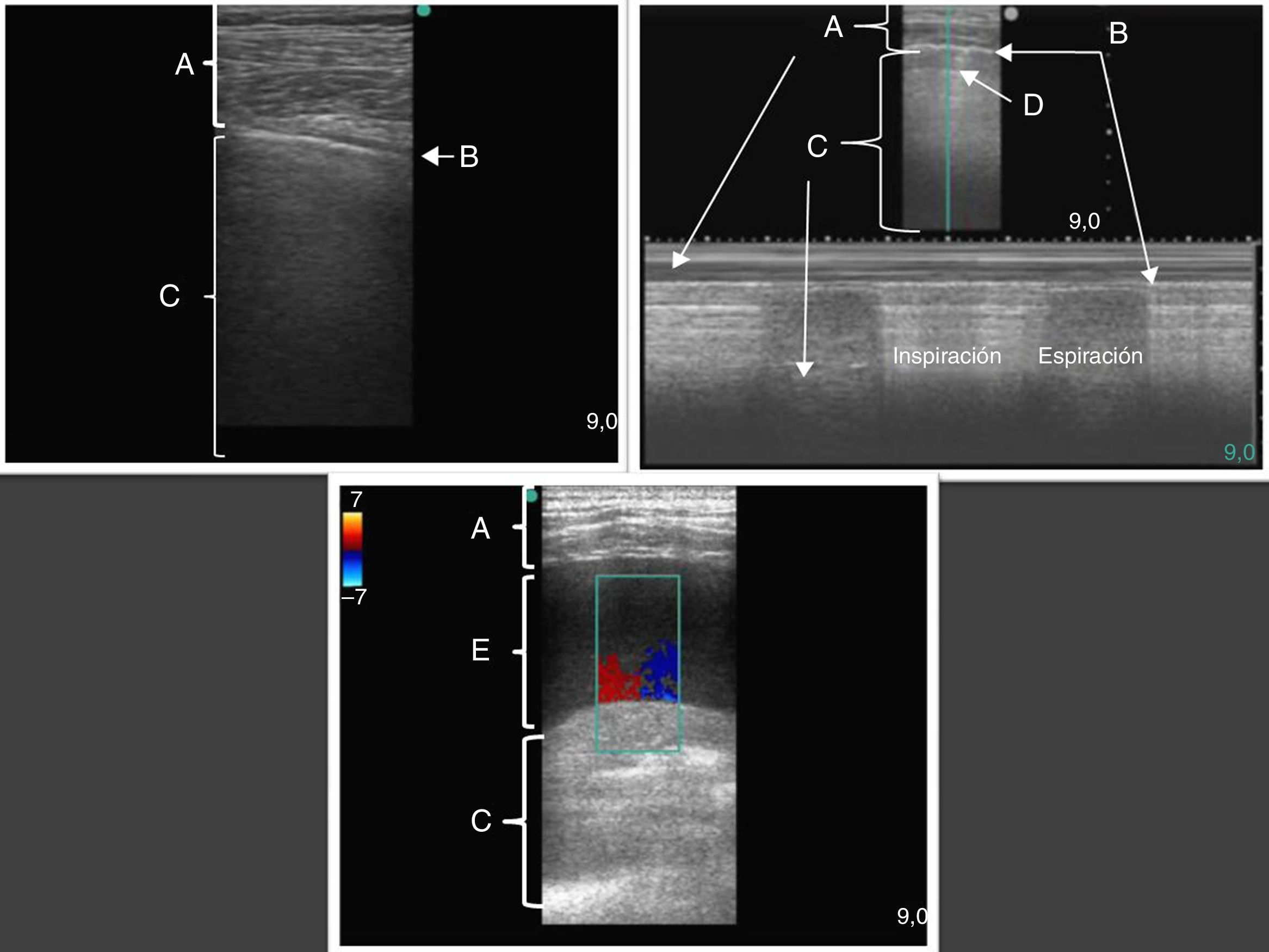
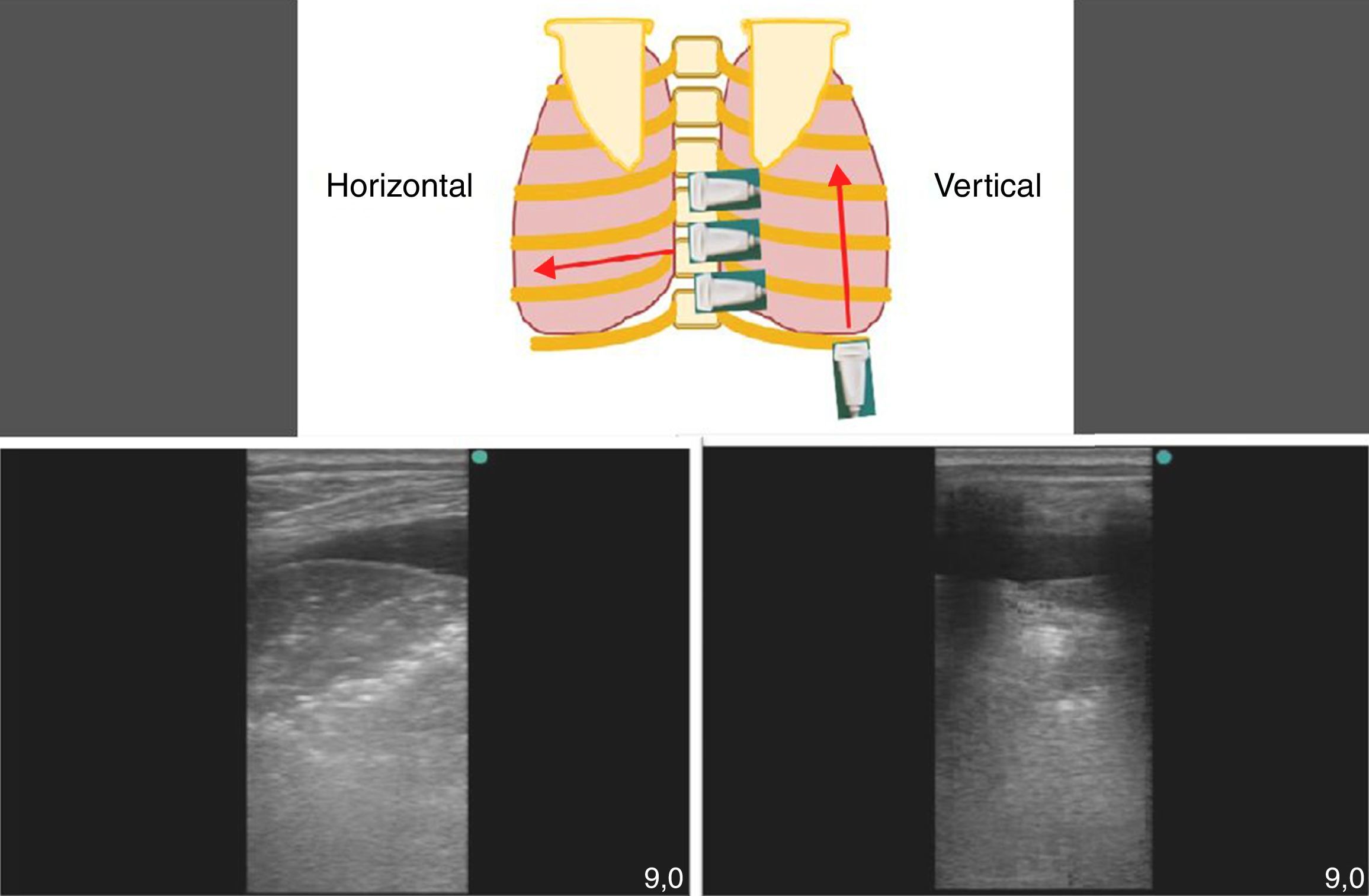
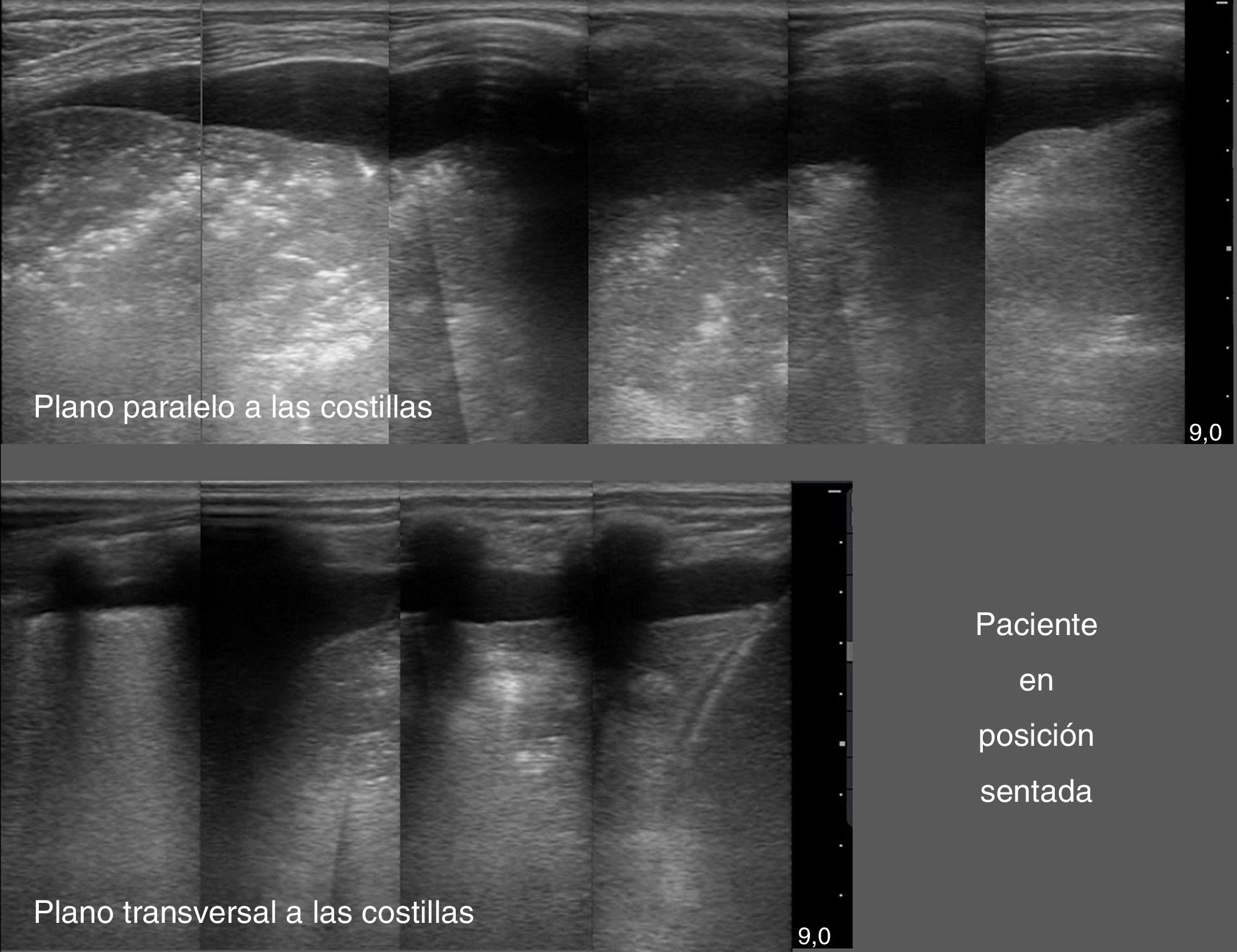
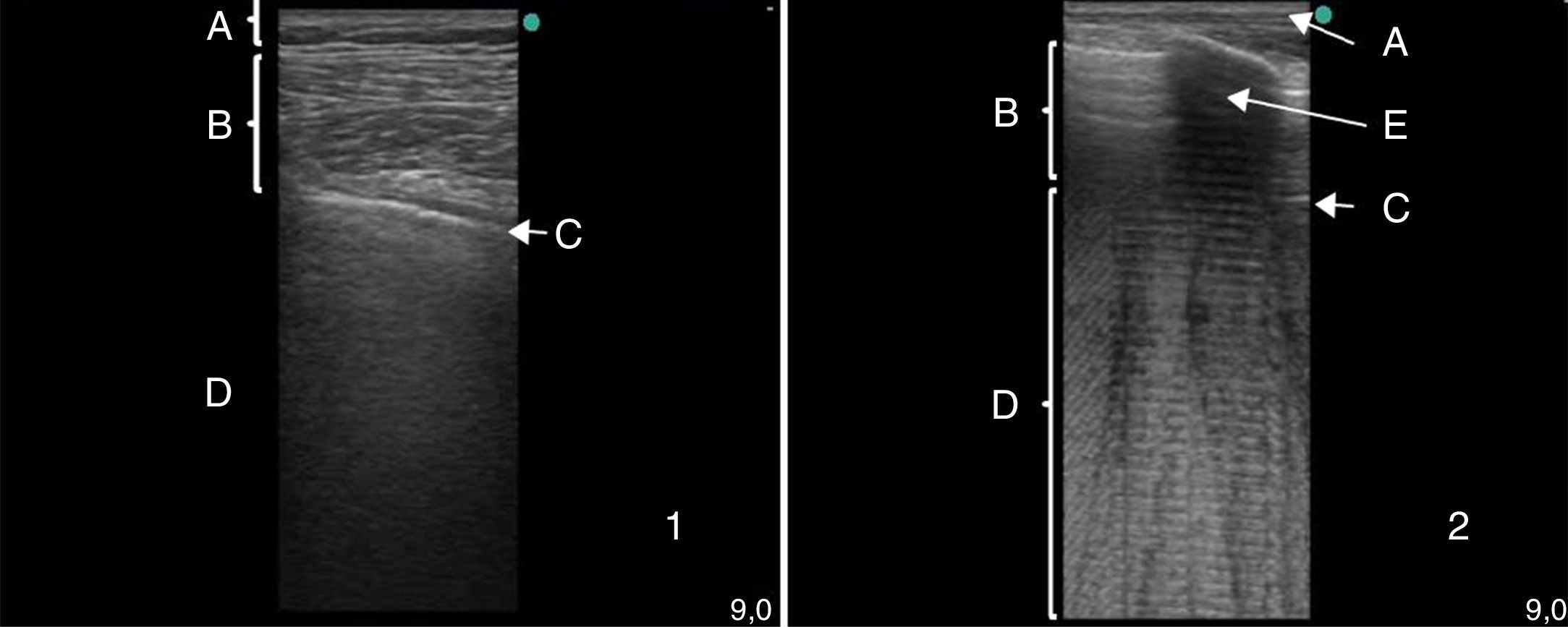
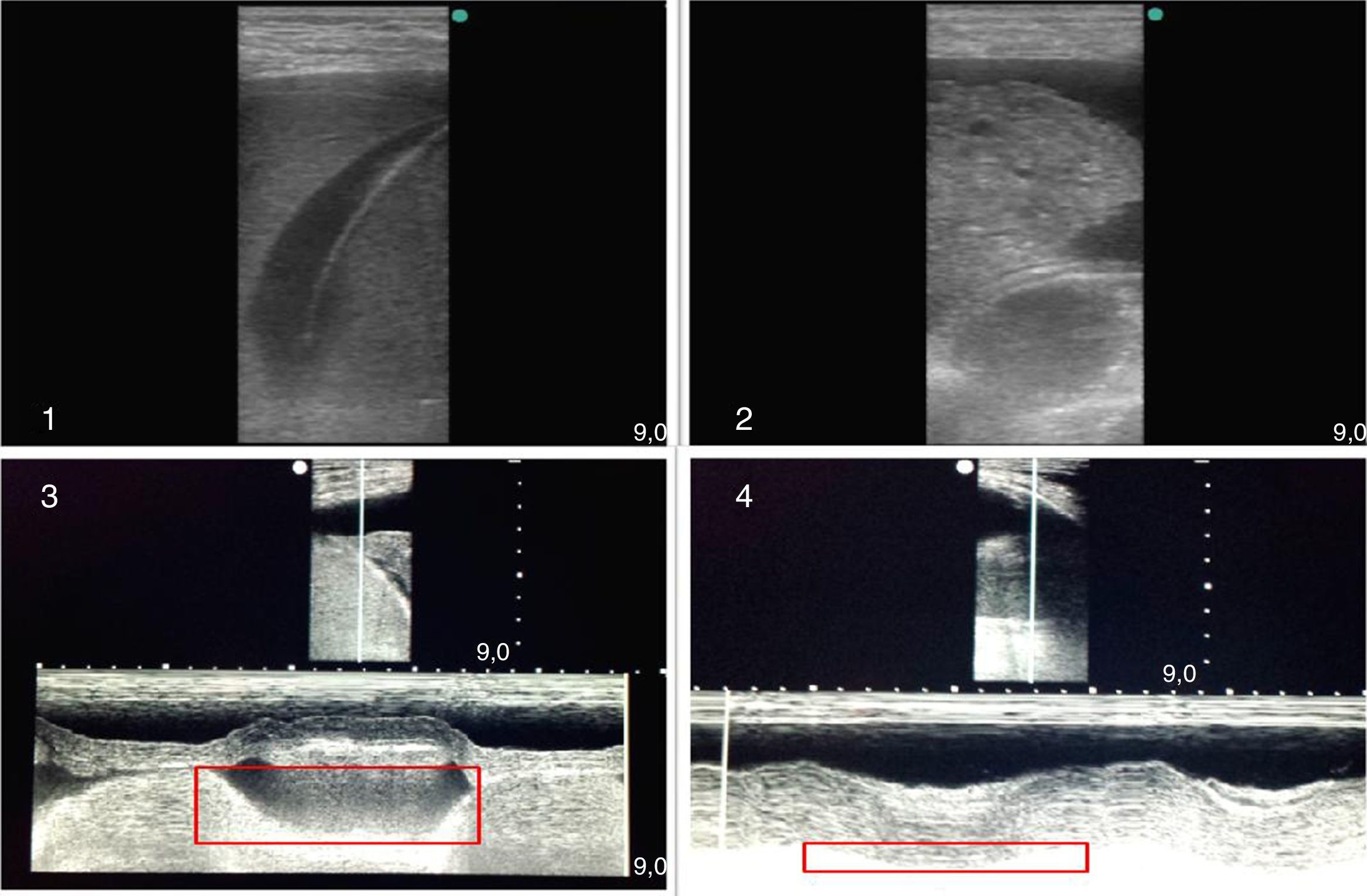
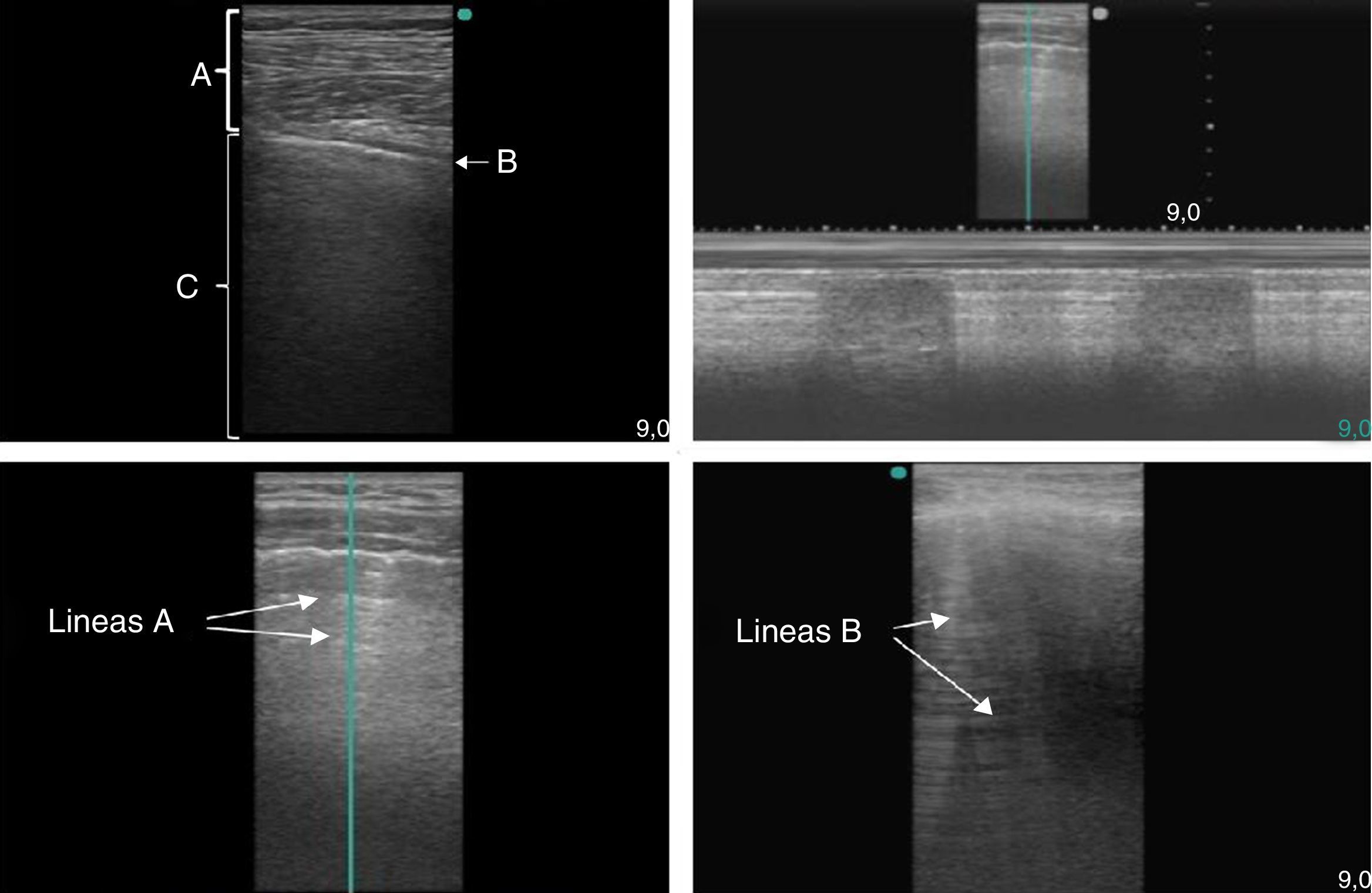
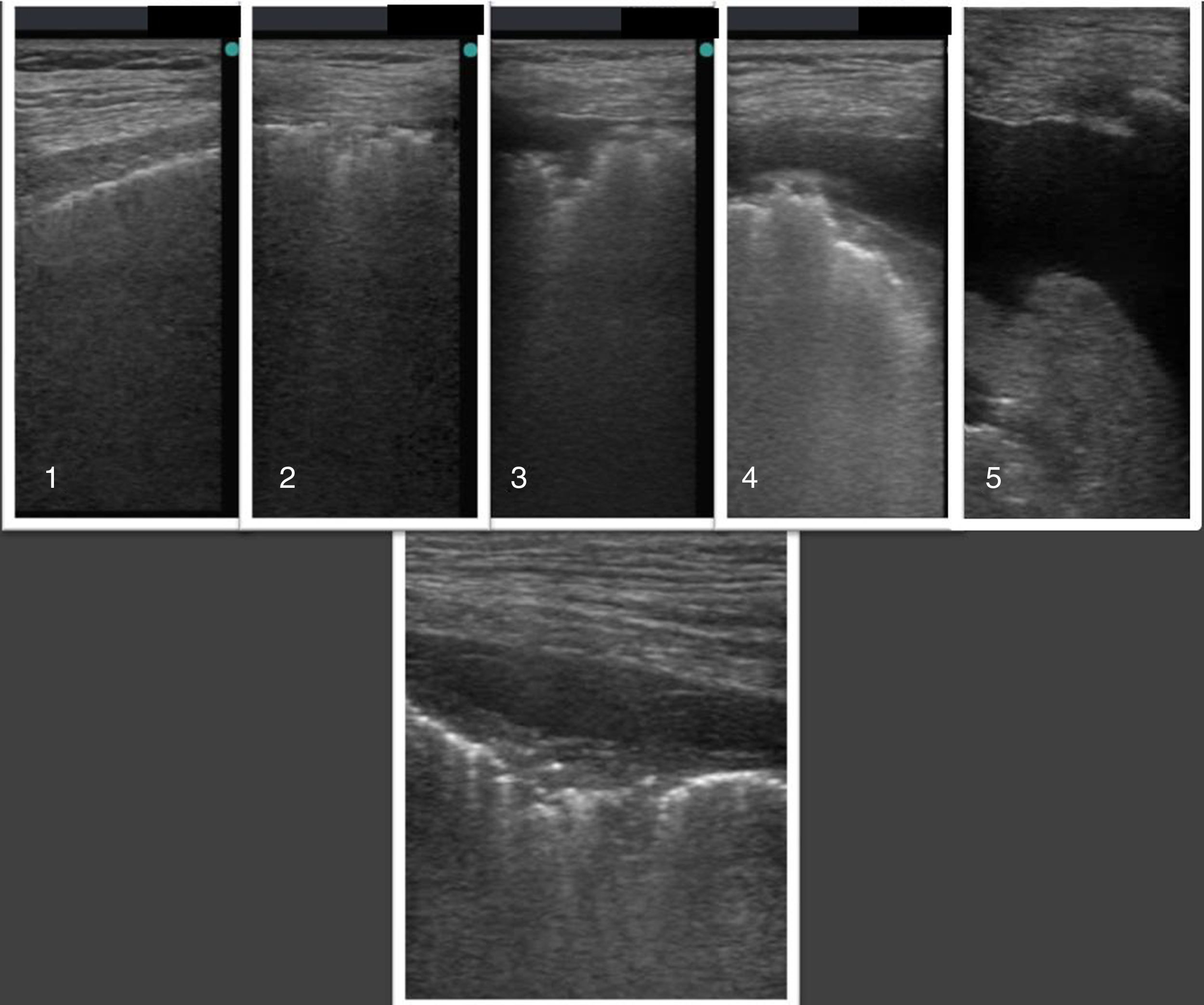
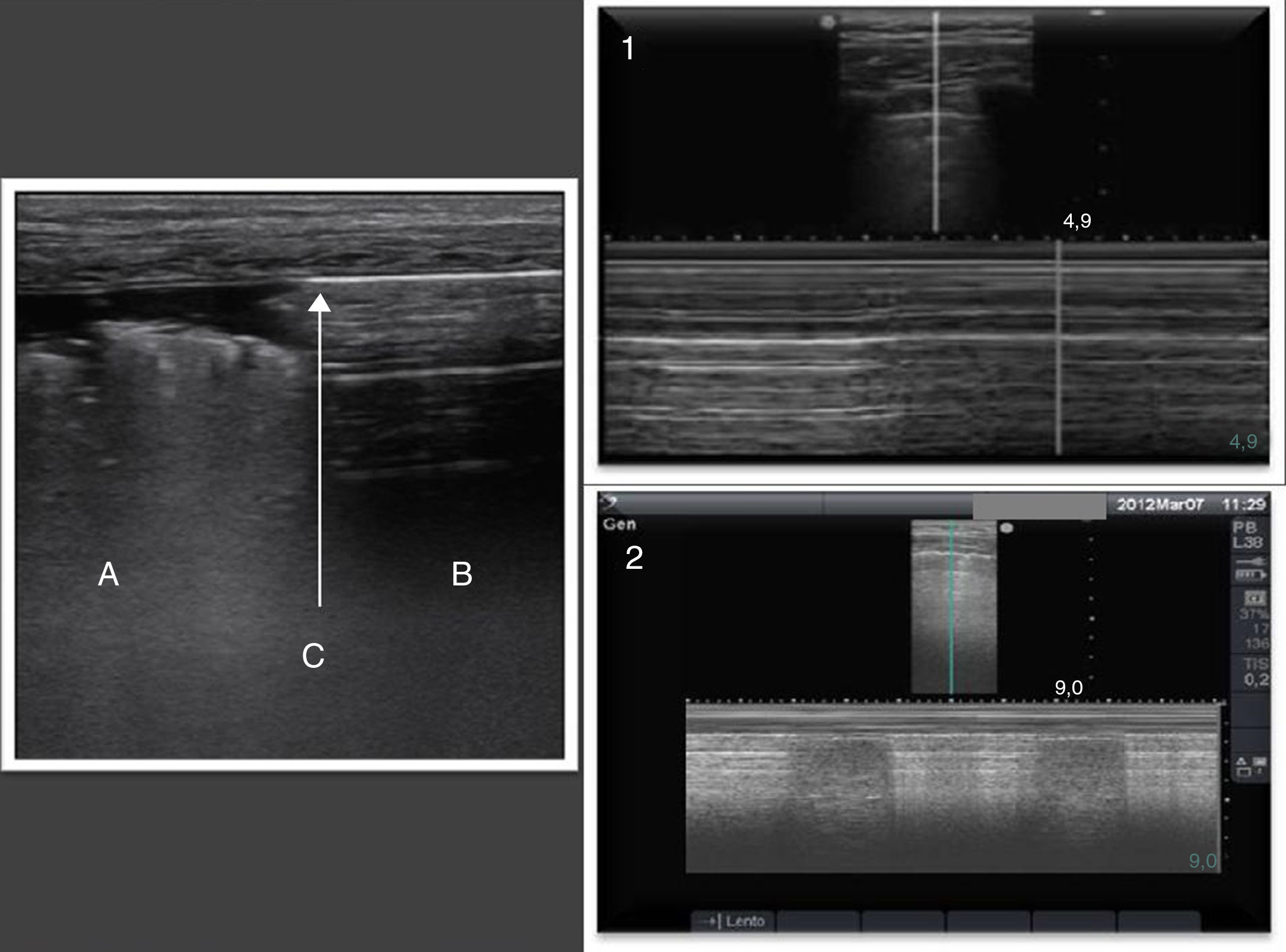
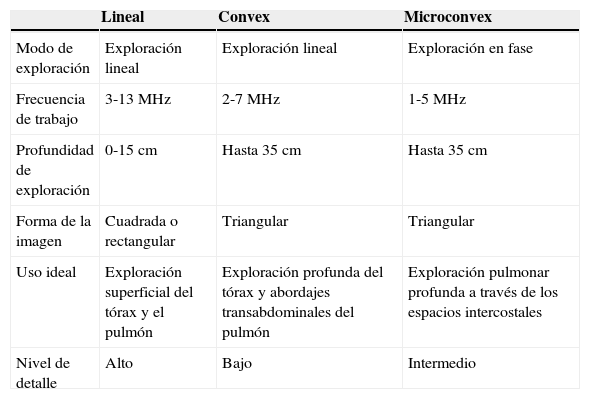
La ecografía pulmonar ha aparecido en el arsenal diagnóstico de las unidades de reanimación con un potencial enorme gracias a sus múltiples ventajas: capacidad para diagnosticar con más precisión que la radiología convencional, precocidad a la hora del diagnóstico, comodidad derivada de poderse hacer a pie de cama, posibilidad de hacerla uno mismo, ausencia de radiación ionizante y por su carácter dinámico, que permite transformar en procesos fisiológicos lo que hasta ahora eran imágenes estáticas. Sin embargo, la ecografía pulmonar tiene también sus limitaciones y presenta una curva de aprendizaje.
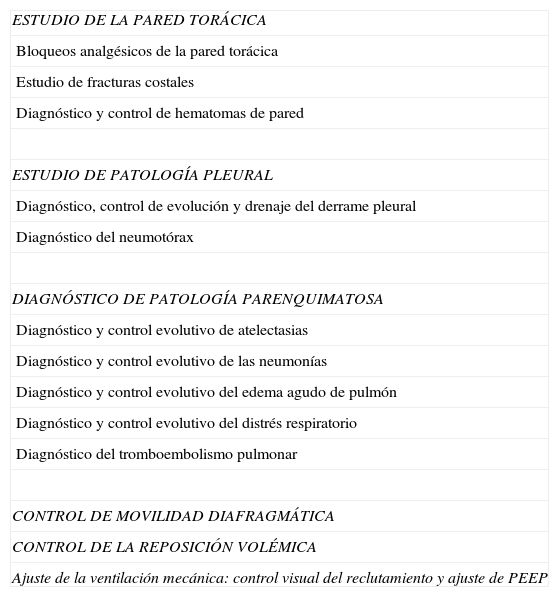
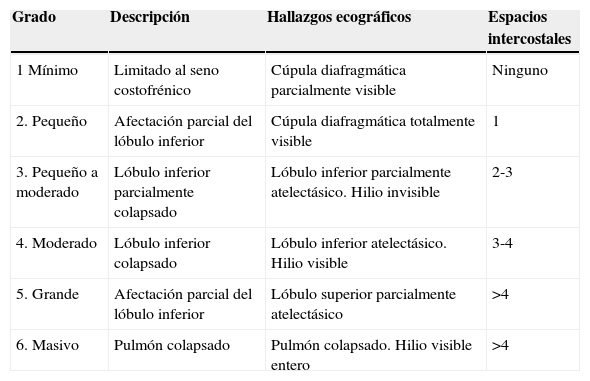
El objetivo de esta revisión es ofrecer una información suficiente que ayude al especialista que se inicia en este terreno a abordar la técnica con buenas posibilidades de éxito. Para ello se ha estructurado el conjunto de la revisión en dos partes. En la primera, se describe la ecografía normal de pared torácica, pleura, diafragma y parénquima pulmonar así como la patología más importante de la pared torácica (fracturas costales y hematomas), la pleura (derrame pleural y sus diferentes tipos, y neumotórax) y el diafragma (hipoquinesia y parálisis). En la segunda parte, se abordará la patología parenquimatosa, incluyendo atelectasias, neumonía y absceso, edema pulmonar, distrés respiratorio y tromboembolismo pulmonar.
Lung ultrasound has become part of the diagnostic armamentarium in Resuscitation and Recovery Units with an enormous potential due to its many advantages: capacity to diagnose more precisely than conventional radiology, earlier diagnosis, convenience due to being able to performed at the bedside, possibility of being performed by one person, absence of ionising radiation, and, due to its dynamic character, is capable of transforming into physiological processes that were once static images. However, lung ultrasound also has its limitations and has a learning curve.
The aim of this review is to provide sufficient information that may help the specialist starting in this field to approach the technique with good possibilities of success. To do this, the review is structured into two parts. In the first, the normal ultrasound of the chest wall is presented, as well as the pleura, diaphragm, and lung parenchyma, and the most important pathologies of the chest wall (rib fractures and hematomas), the pleura (pleural effusion and its different types, and pneumothorax), and the diaphragm (hypokinesia and paralysis). In the second part, parenchymal diseases will be approached and will include, atelectasis, pneumonia and abscess, lung oedema, respiratory distress, and pulmonary thromboembolism.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora