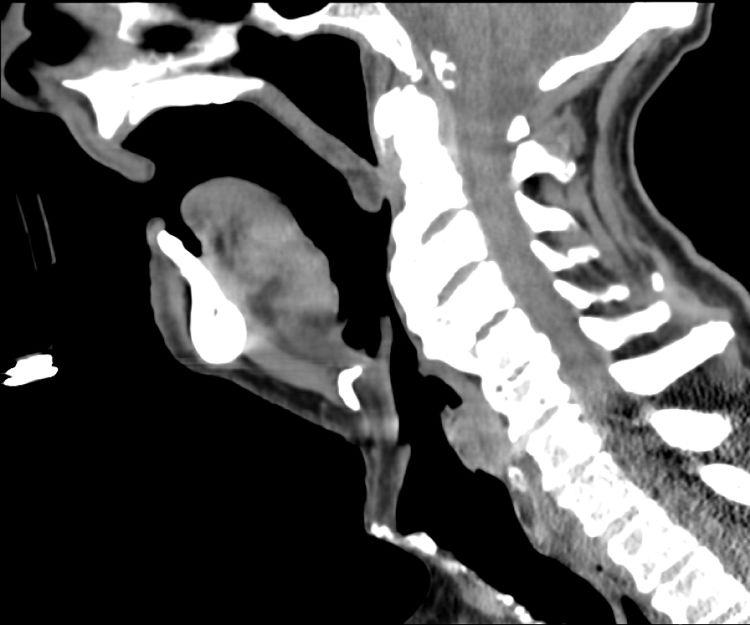
La osificación del ligamento anterior longitudinal vertebral, conocida como enfermedad de Forestier o hiperostosis esquelética idiopática difusa, es una enfermedad que suele cursar de forma asintomática. Se produce sobre todo en la región torácica, seguida por la lumbar y cervical. Cuando existe afectación cervical, en caso de producir clínica, los síntomas más frecuentes son disfagia, disnea o disfonía y, de forma excepcional, obstrucción aguda de la vía aérea. Este proceso patológico supone un reto anestésico en el manejo de la vía aérea de estos pacientes. Por ello presentamos el caso de un paciente de 85 años con obstrucción aguda de vía aérea asociada a enfermedad de Forestier, al que se le realizó intubación mediante fibroscopio bajo anestesia inhalada con sevoflurano manteniendo ventilación espontánea para la posterior realización de traqueotomía por los otorrinolaringólogos.
Ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament of the spine, known as Forestier disease or diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis, is usually an asymptomatic disorder. The area most frequently affected is the thoracic spine, followed by lumbar and cervical regions. In the case of cervical involvement with clinical manifestations, the most common symptoms include dysphagia, dyspnoea, dysphonia, and can exceptionally cause an acute airway obstruction. The airway management of these patients represents a great anaesthetic challenge. The case is reported of an eighty-five-year-old patient who had an acute airway obstruction associated with Forestier disease. A fibre-optic-assisted intubation was accomplished under sevoflurane inhaled anaesthesia, maintaining spontaneous ventilation, with subsequent tracheostomy performed by ENT surgeons.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora