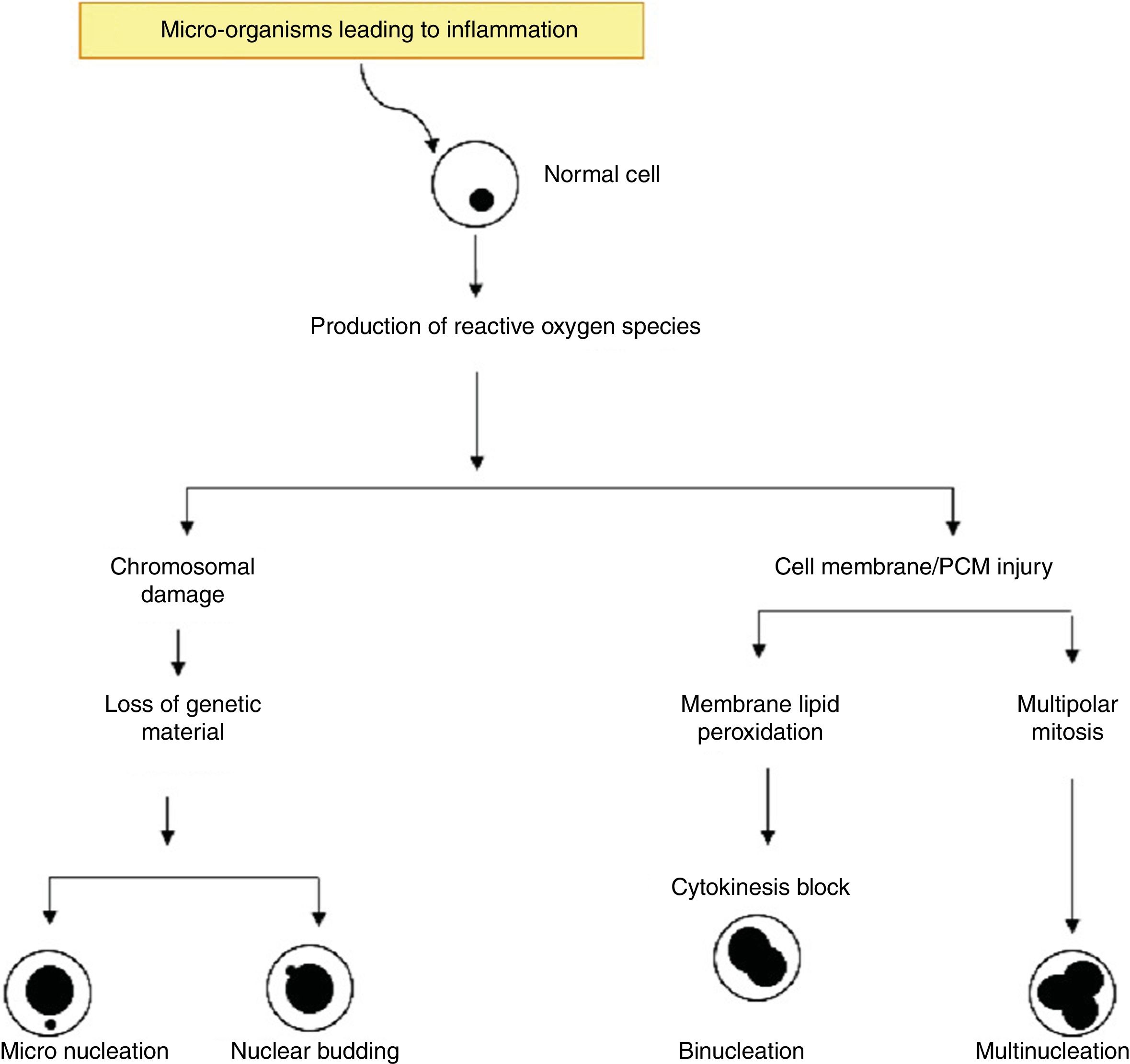
The objective of this study was to observe the evolution of genotoxicity (micronucleation, binucleation and multinucleation) from normal to periodontally compromised gingival epithelium (gingivitis and periodontitis) and to compare the severity of damage.
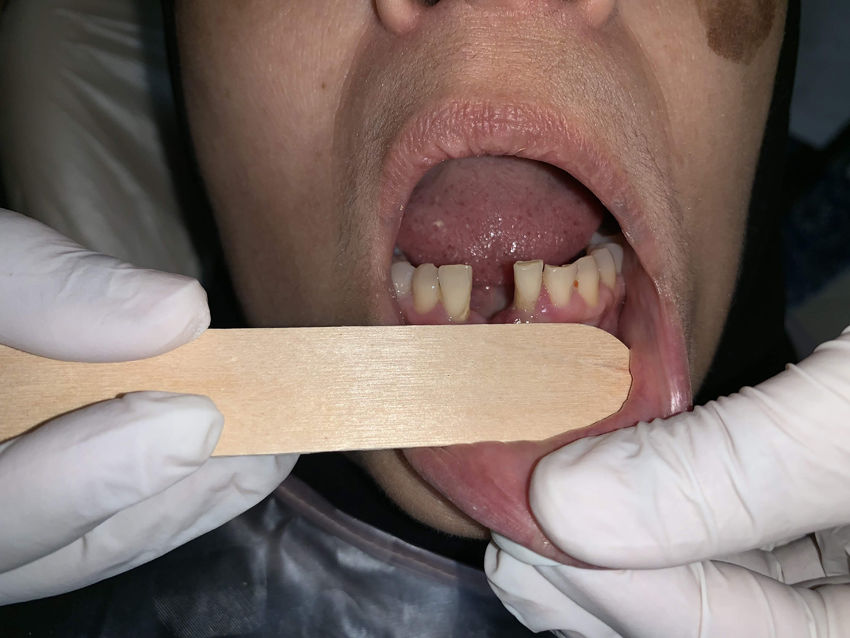
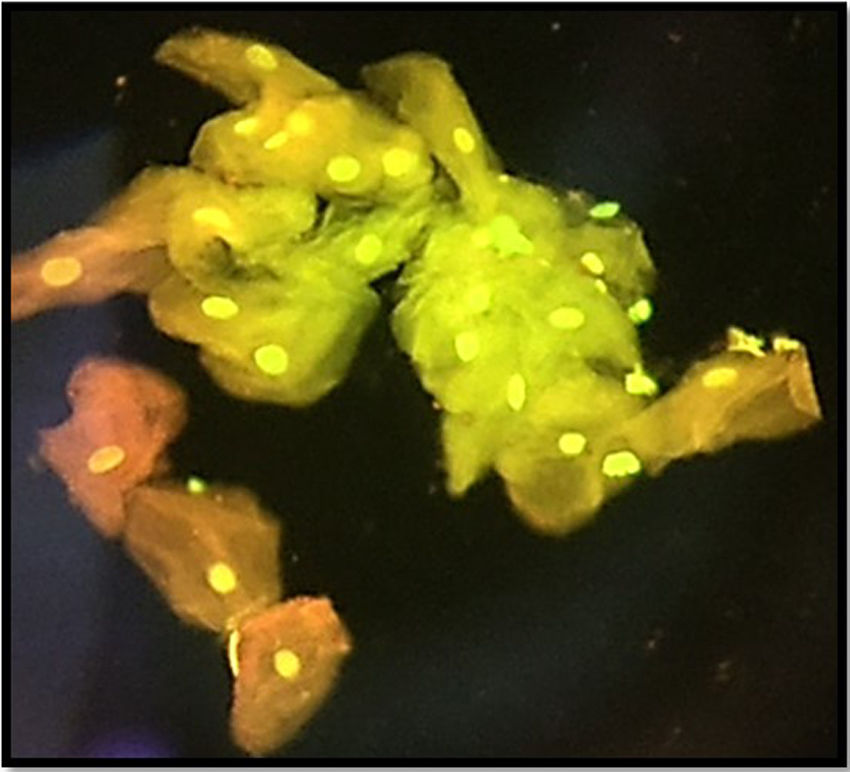
Methods and material45 participants formed 3 different categories; a control group of 15 healthy subjects, 15 subjects with gingivitis and 15 with chronic periodontitis. Smears were collected from all the gingiva and stained with acridine orange stain. A total of 500 cells were evaluated under fluorescent microscopy for nuclear abnormalities such as micronuclei, binucleation and multinucleation. The statistical analysis used was one way ANOVA and posthoc Tukey test.
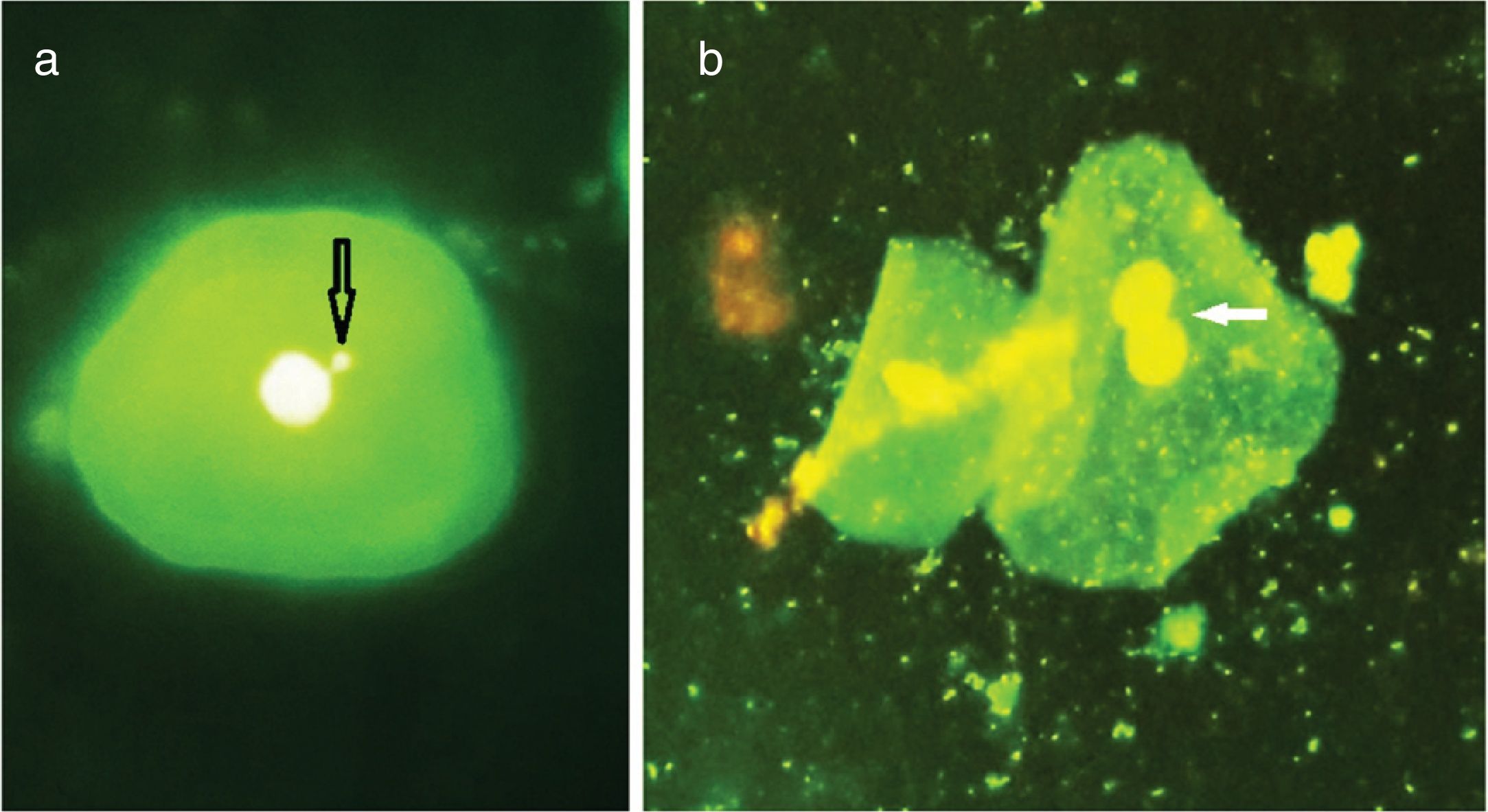
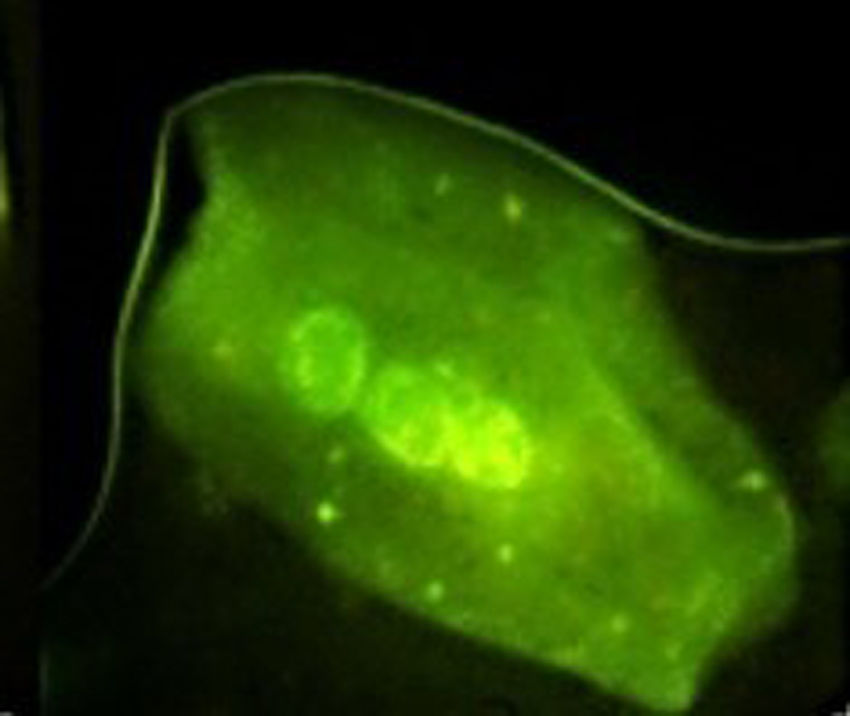
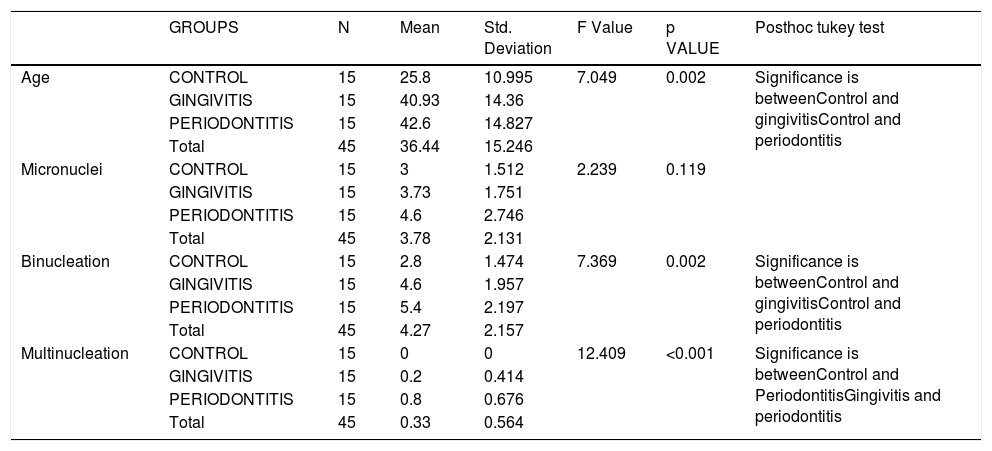
Results and conclusionA statistically significant difference was observed when the age of the 3 groups were compared (p=0.002); the control group were younger than those with chronic periodontitis or gingivitis. With respect to genotoxic changes, the differences for binucleation (p=0.002) and multinucleation (p<0.001) were statistically significant thus suggesting advanced damage in the nucleus. Such changes in genotoxicity could be of help to a clinician in determining prognosis.
El objetivo de este estudio fue observar las tendencias en cuanto a genotoxicidad (micronucleación, binucleación y multinucleación) a partir de epitelio gingival de normal a periodoncialmente-comprometido (gingivitis y periodontitis), y comparar la gravedad del daño entre ambas situaciones.
Métodos y materialSeleccionamos a cuarenta y cinco sujetos, que agrupamos en 3 categorías (15 sujetos sanos, 15 con gingivitis y 15 con periodontitis crónica). Se recogieron frotis del tejido gingival de dichos sujetos, que se tiñeron con acridina naranja. Evaluamos un total de 500 células bajo el microscopio fluorescente en busca de anomalías nucleares de tipo micronúcleos, binucleación y multinucleación. El análisis estadístico utilizado fue ANOVA unidireccional y Tukey posthoc.
Resultados y conclusiónObservamos una diferencia estadísticamente significativa al comparar los 3 grupos de edad (p=0,002), donde el grupo control (sujetos sanos) pertenecía a un rango de edad inferior a los sujetos con periodontitis o gingivitis crónicas. Con respecto a los cambios genotóxicos, las diferencias para binucleación (p=0,002) y multinucleación (p<0,001) fueron estadísticamente significativas, lo cual sugiere un daño avanzado en el núcleo. Las tendencias en cuanto a genotoxicidad podrían ayudar a los clínicos a determinar el pronóstico de la enfermedad.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora