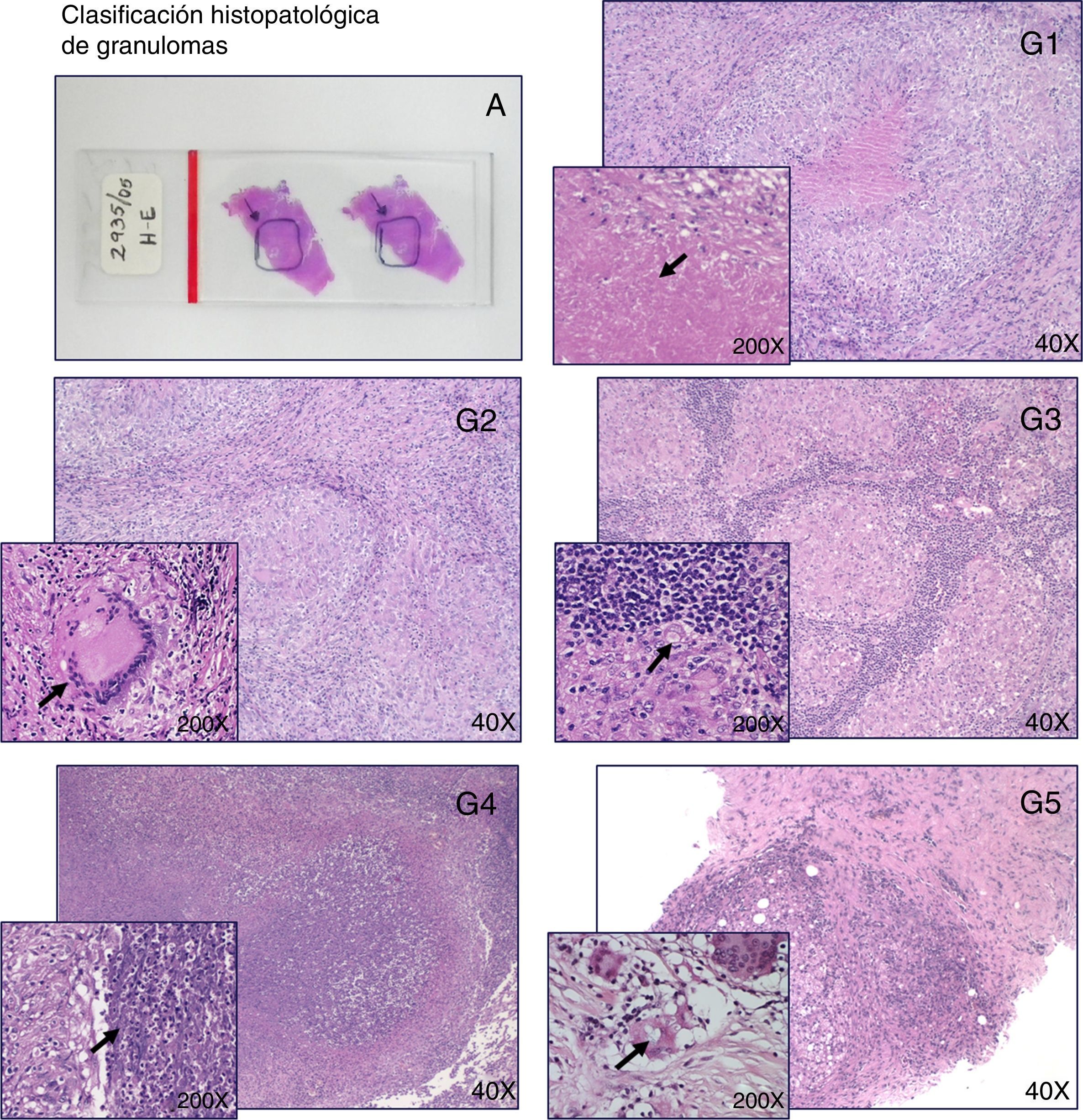
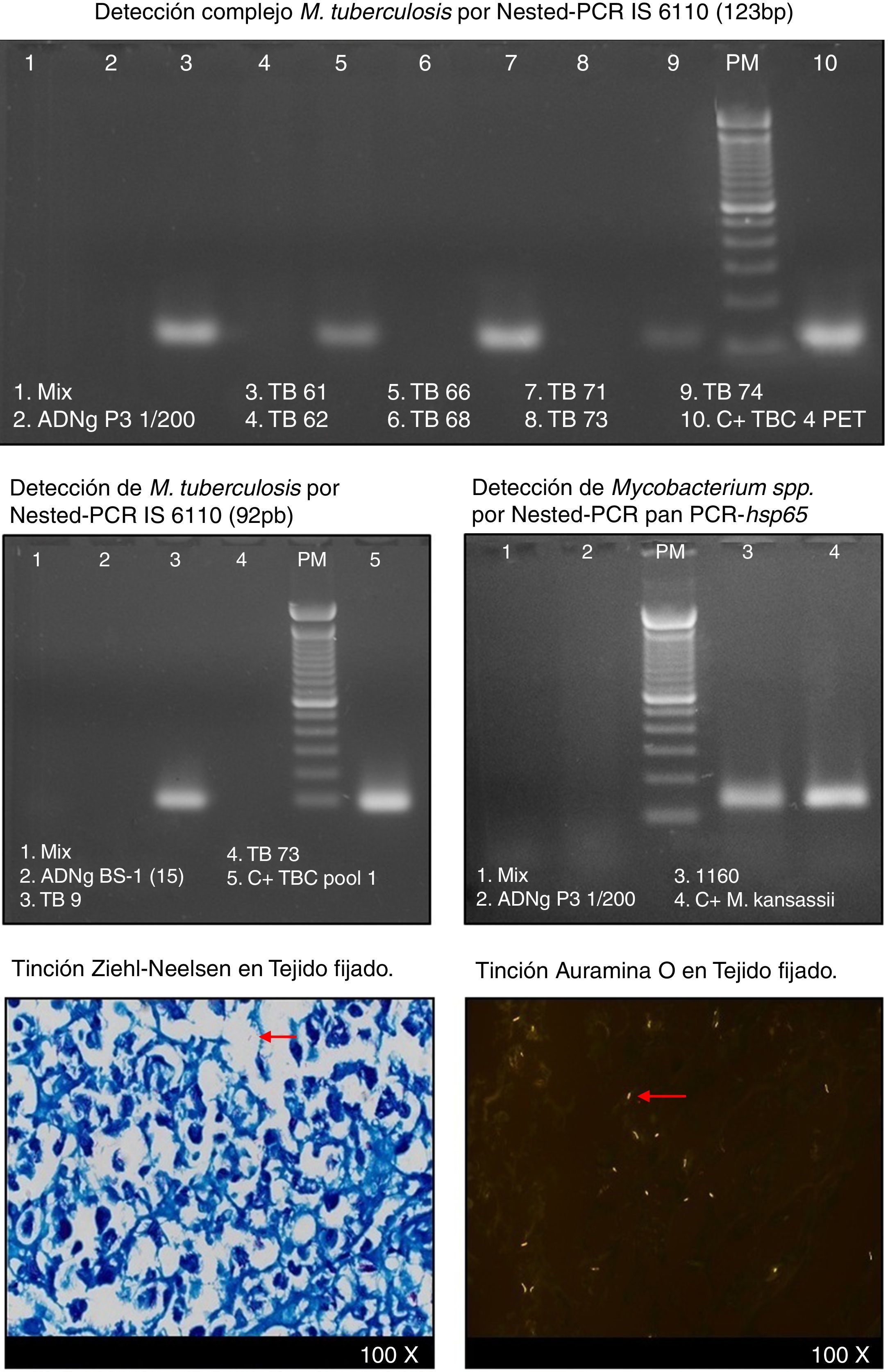
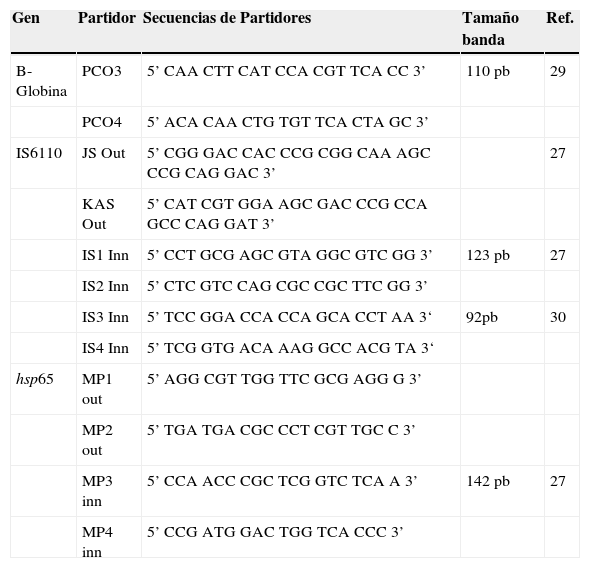
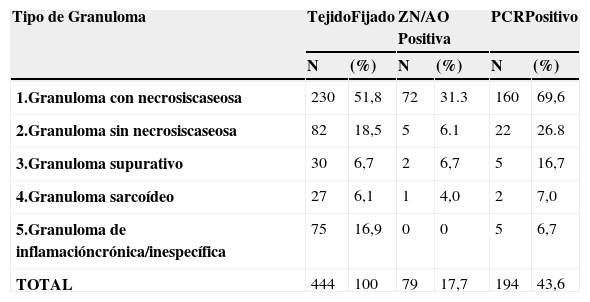
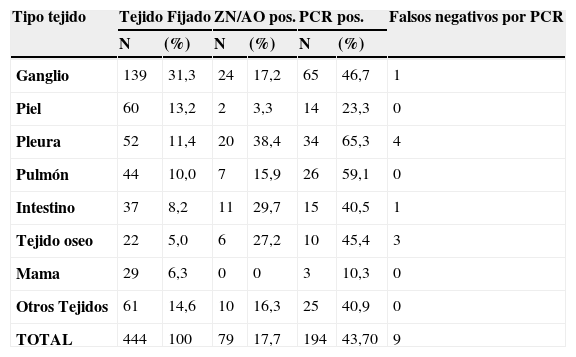
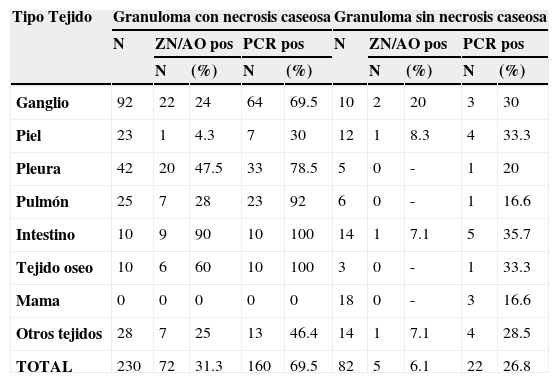
El diagnóstico diferencial de tuberculosis en tejidos fijados en formalina e incluidos en parafina es necesario porque la morfología de la lesión tuberculosa es variada, hay diversos granulomas clasificados en necrobióticos, tuberculoideos, supurativos, sarcoideo, a cuerpo extraño/crónico inespecífico. Las lesiones granulomatosas ocurren en tuberculosis y también en otras infecciones (hongos, parásitos, brucelosis, lepra) en condiciones tóxicas, alérgicas, autoinmunes, tumores y otras. El diagnóstico histológico no es confirmatorio de tuberculosis y en ausencia de una baciloscopia positiva, se hace necesaria la confirmación molecular para el diagnóstico diferencial. Evaluamos la eficacia de la técnica de PCR para la detección de tuberculosis en tejidos fijados y comparamos esos resultados con la histología del granuloma y la baciloscopia. Analizamos 444 biopsias de diferentes tejidos (ganglios, piel, pleura, pulmón, intestino, tejido óseo, mama y otros) de 5 tipos de granulomas: G1.tuberculoideo con necrosis caseosa; G2.tuberculoideo sin necrosis caseosa; G3. supurativo; G4. sarcoideo l; G5. a cuerpo extraño/inespecífico. Utilizamos dos PCR-IS6110 nested para detección del complejo Mycobacterium tuberculosis y un pan PCR-hsp65 nested para detección de Mycobacterium spp. Los resultados obtenidos muestran que la detección de tuberculosis mediante PCR fue significativamente superior que mediante baciloscopia. G1: PCR 69,6%, baciloscopia 31,3%; G2: PCR 26,8%, baciloscopia 6,1%; G3: PCR 16,7%, baciloscopia 6,7%; G4: PCR 7%, baciloscopia 4%; G5: PCR 6,7%, baciloscopia 0%. Concluimos que el diagnóstico molecular de tuberculosis mediante un PCR robusto adaptado a tejidos fijados es eficaz, rápido, sensible y contribuye a la precisión del diagnóstico diferencial en diferentes tipos de granulomas.
The differential diagnosis of tuberculosis in fixed paraffin embedded-tissues is necessary due to both the diverse morphology of tuberculous lesions and the varying histological types of granulomas (necrobiotic, tuberculoid, suppurative, sarcoidal and foreign body/inespecific). Granulomatous lesions occur in tuberculosis, in other infections (fungal, parasitic, brucelosis, lepra), in toxic, allergic and autoimmune, tumours and in conditions of unknown etiology. Diagnosis of tuberculosis cannot be confirmed by histopathology alone and in absence of a positive acid-fast bacilli (AFB) stain, molecular confirmation of tuberculosis is necessary for a correct differential diagnosis. The aim of our study was to assess PCR efficacy for mycobacterial infection detection in fixed tissues and to correlate those findings with granuloma histology and with AFB staining. We analyzed 444 biopsies from various tissues (lymph nodes, skin, pleura, lung, intestine, bone tissue, breast and others) with 5 granuloma types: G1: with caseous necrosis; G2: without caseous necrosis; G3: suppurative; G4: sarcoidal; G5: chronic/nonspecific. For molecular detection, we used nested PCR-IS6110 for Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and a nested pan PCR-hsp65 for Mycobacterium sp.. The results obtained demonstrated that PCR was significantly better than AFB stain for tuberculosis detection. G1: PCR 69.6%, AFB staining 31.3%. G2: PCR 26.8%, AFB staining 6.1%; G3: PCR 16.7%, AFB staining 6.7%; G4: PCR 7%, AFB staining 4%. G5: PCR 6.7%, AFB staining 0%. We conclude that molecular diagnosis of tuberculosis using robust PCR-based testing adapted to fixed tissues is a fast, efficient and sensitive method that increases the accuracy of the differential diagnosis of granulomatous lesions.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora