Although the increasing prevalence of hypospadias has been reported in many countries, there is a lack of bibliometric studies that make a holistic assessment of the publications about this issue. This study aims to make a holistic evaluation, latest developments, and trend topics about hypospadias publications between 1980 and 2018 through bibliometric analysis.
MethodsAll the publications about hypospadias published in the Web of Science index between 1980 and 2018 were downloaded and analyzed using bibliometric methods. The Spearman's correlation coefficient was utilized to analyze the correlations between economic productivity and performance of the countries on hypospadias. Linear regression analysis was performed to estimate the number of publications for the following years.
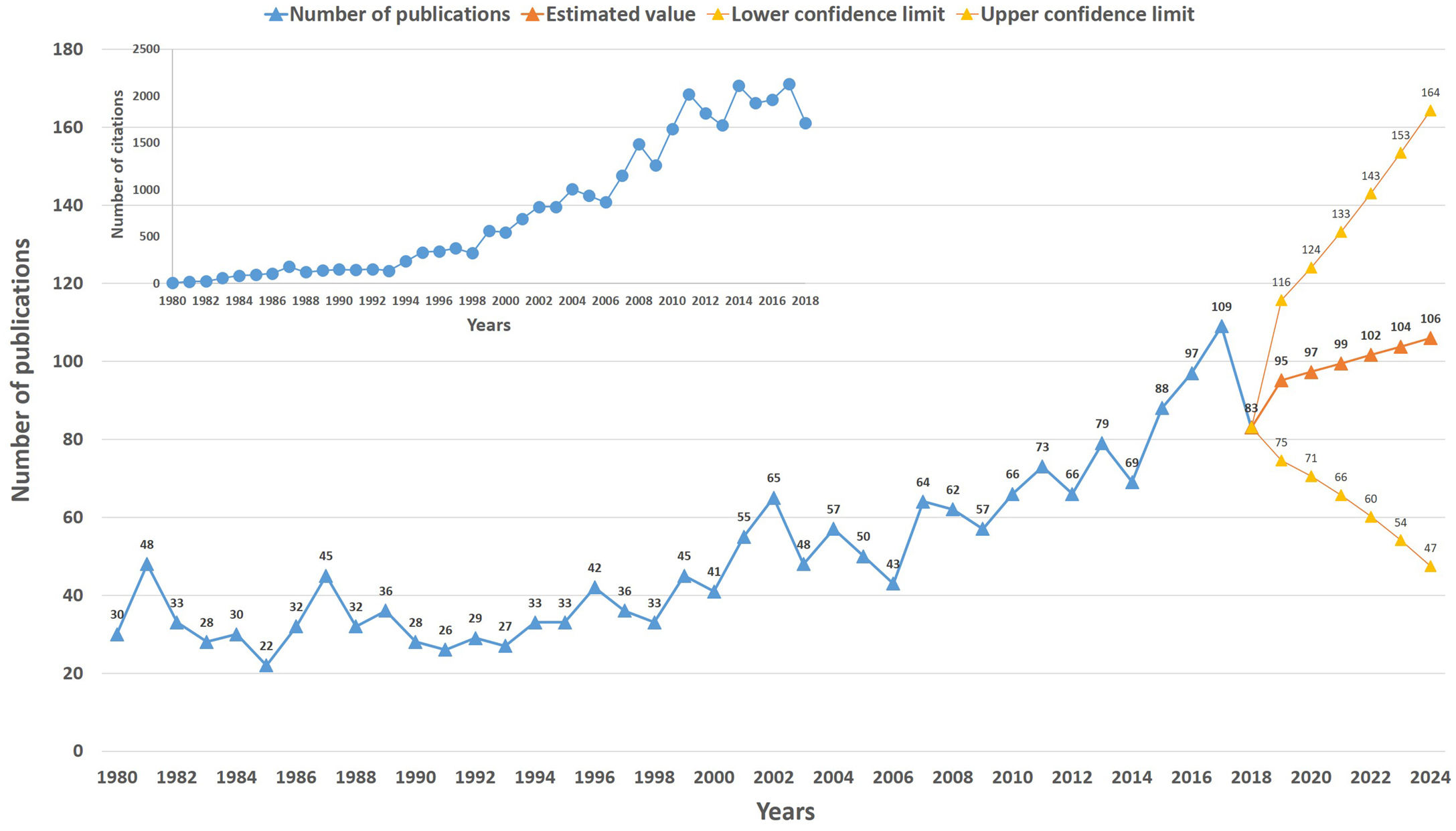
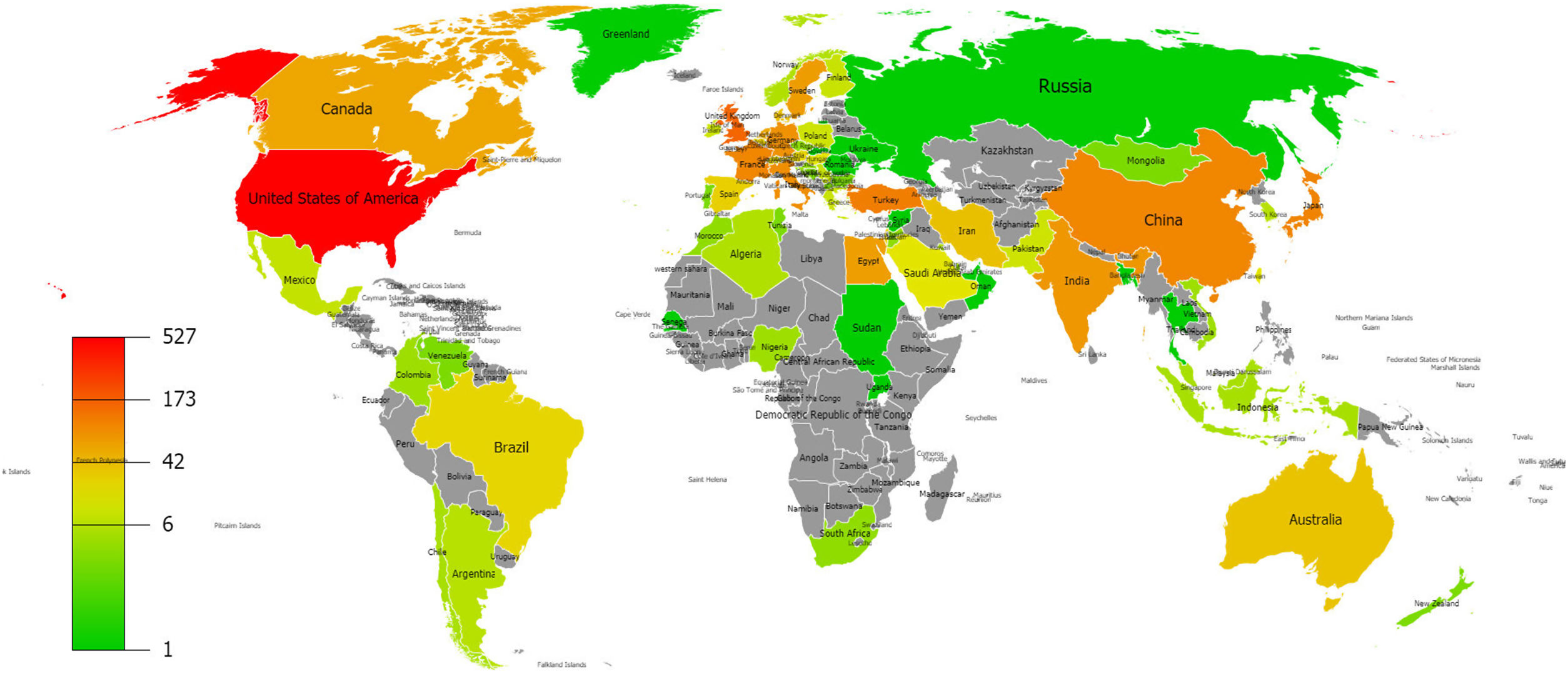
ResultsBibliometric analyses were performed with 1940 articles. With 527 (27.2%) publications, the USA was the country that made the most contribution to the literature. The top active 3 journals were the Journal of Urology, Journal of Pediatric Urology, and Urology. A high correlation was detected between hypospadias publication productivity and GDP (r=0.791, p<0.001). The regression analysis results showed that the expected number of articles to be produced was 95 (75–116) for 2019 and 106 (47–164) for 2024.
ConclusionsThis study provides a holistic evaluation of the articles about hypospadias, which is an anomaly that should be repaired and treated with surgery due to its potential problems for the children at kindergarten and school age. Increasing the collaboration between especially developing countries and research in different countries with samples from different communities through multidisciplinary studies are recommended.
Aunque en muchos países se ha reportado el incremento de la prevalencia del hipospadias, existe una falta de estudios bibliométricos que realicen una evaluación holística de las publicaciones sobre esta cuestión. El objetivo de este estudio es realizar una evaluación holística, los últimos desarrollos y las tendencias acerca de las publicaciones sobre el hipospadias entre 1980 y 2018, mediante análisis bibliométricos.
MétodosSe descargaron y analizaron todas las publicaciones sobre hipospadias publicadas en el índice de Web of Science de 1980 a 2018, utilizando métodos bibliométricos. Se utilizó el coeficiente de correlación de Spearman para analizar las correlaciones entre productividad económica y desempeño de todos los países, con relación al hipospadias. Se realizó un análisis de regresión lineal para calcular el número de publicaciones para los años siguientes.
ResultadosSe realizaron análisis bibliométricos con 1.920 artículos. Con 527 publicaciones (27,2%), EE. UU. fue el país que más contribuciones realizó a la literatura. Las 3 publicaciones más activas fueron Journal of Urology, Journal of Pediatric Urology, y Urology. Se detectó una elevada correlación entre la productividad de las publicaciones sobre hipospadias y el PIB (r=0,791; p<0,001). Los resultados del análisis de regresión reflejaron que el número esperado de artículos a elaborar era de 95 (75-116) para 2019, y de 106 (47-164) para 2024.
ConclusionesEste estudio aporta una evaluación holística de los artículos relativos al hipospadias, que es una anomalía que debe repararse y tratarse con cirugía, debido a sus problemas potenciales para niños en guarderías y edad escolar. Se recomienda incrementar la colaboración, especialmente entre los países en desarrollo y la investigación en los diferentes países, con muestras procedentes de las diferentes comunidades, a través de estudios multidisciplinares.
Hypospadias, which is considered to be a mild 46,XY sex development disorder, is the most common congenital anomaly. It is seen in every 250 males at birth .1 The ventral side of the penis demonstrates a urethral opening. In addition, the ventral tissues have hypoplasia in various degrees, penile curvature, and excessive prepuce. Genetic and environmental factors are reported to be closely associated with the etiology of hypospadias .2 Socioeconomic resources are required for the surgical repair of hypospadias and for management of the long-term consequences of the condition. For this reason, it is important to know the exact prevalence of hypospadias. Given the potential effects of the environmental factors, there has been a major debate about the epidemiology of the condition and whether there is an increase in its prevalence .3 The severity of Hypospadias could occur in varying degrees ranging from glanular (coronal, distal penile, and midshaft) and proximal (penile, proximal penile, and perineal). 4 A functional and cosmetically normal penis is the main goal of the surgical repair of hypospadias .5 The literature involves several different repair techniques; however, assessment of the surgical outcomes has been performed in only a few systems. Normal urination and reproduction can be possible for most men through a successful treatment .6
Infants younger than 6 months have a higher anesthesia risk. After the 18th month, children still experience surgery-related problems (awareness of recognizing organs and related problems, and the problems to be experienced during toilet training are the most important ones). It is recommended to make necessary interventions before the child recognizes his sexual identity and faces this reality. Therefore, these surgical procedures are recommended to be completed before toilet training, and generally, the preferred surgery time is between 6 months and 1 year. In addition, the treatment of hypospadias might require a gradual procedure that might include surgeries to be performed in a few sessions. Considering that any complications to occur might need to be recovered with a separate operation, it is important to plan all the operations in a way to be finished in the pre-school period, which helps to prevent any negative effects on the education process .1–6
Bibliometrics is the statistical analysis of written publications such as books or articles .7 Bibliometric methods are frequently used in information science including libraries and scientometrics. Given the increasing number of publications particularly in recent years, quantitative analysis of the massive academic literature could be possible through bibliometric methods .8 Citation analysis, citation graph, is a widely used bibliometric method based on forming the representative graph of the citations between a web or documents. Various study fields utilize bibliometric methods in order to identify the effects of fields, effects of a series of researchers, effect of a specific study or define effective articles in a specific research field .9–11
Hypospadias has negative effects on children's quality of life. Children with hypospadias could experience psychological problems because they cannot comfortably stand to urinate. If this problem is not solved in time, it may also cause some other problems during sexual intercourse in the future. The prevalence of hypospadias is reported to have increased in many countries .12–16 Although hypospadias is an important issue, there are still no bibliometric studies that make a holistic analysis of the publications on this issue. This study aims to make a holistic evaluation, latest developments, and trend topics about hypospadias publications between 1980 and 2018 through bibliometric analysis. In this study, we also investigated the relationship between hypospadias publication productivity and some economic indicators of countries.
Material and methodsAll the publications about hypospadias published in the WoS (Web of Science Core Collection database maintained by Clarivate Analytics) index between 1980 and 2018 were downloaded and analyzed using bibliometric methods. “hypospadi*” (hypospadias, hypospadiac, hypospadiology; (Title: “hypospadi*”) keyword was used for search, and only the documents that had the keyword in the title were found. Bibliometric network visualization was performed using the VOSviewer (Version 1.6.10) package programming.
Statistical analysis was conducted with SPSS (Version 22.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA, License: Hitit University). Distributions of the data were evaluated with Shapiro–Wilk tests. The Spearman's correlation coefficient was utilized to analyze the correlations between economic productivity and performance of the countries on the topic of hypospadias. Linear regression analysis was performed in order to estimate the number of publications for the following years.
ResultsTotally, 3173 publications were found in WoS. Of all these publications, 1940 (61.14%) were articles, 457 (14.40%) were meeting abstracts, 388 (12.23%) were editorial material, 218 (6.87%) were letter, 126 (3.97%) were proceedings paper, 92 (2.90%) were review, and 65 (2.05%) were others (note, correction, reprint, discussion, news item). Bibliometric analyses in this study were performed with 1940 articles. The other publication types were not analyzed. Of all the articles, 1769 (91.2%) were English, 83 were French, 69 were German, and 19 were written in other languages (Spanish, Hungarian, Italian, Portuguese, Serbian, Romanian, Russian, Turkish). H-index of the 1940 articles was 70, average citation per item was 15.75, and the Sum of Times Cited was 30.564 (without self-citations 16.759).
Research areasThe articles were written mostly in the Urology Nephrology (1047; 53.97%) research field, which was followed by Pediatrics (420; 21.65%), Surgery (321; 16.55%), Genetics Heredity (81; 4.18%), and Medicine General Internal (71, 3.66%) respectively.
Development of publications and citationsFig. 1 demonstrates the distribution of the publications and citations according to years. Fig. 1 shows the estimations obtained from regression analysis at a 95% confidence interval for the years 2019 and 2024. The analysis results showed that the expected number of articles to be produced was 95 (75–116) for 2019 and 106 (47–164) for 2024. Fig. 1 also demonstrates the citation analysis.
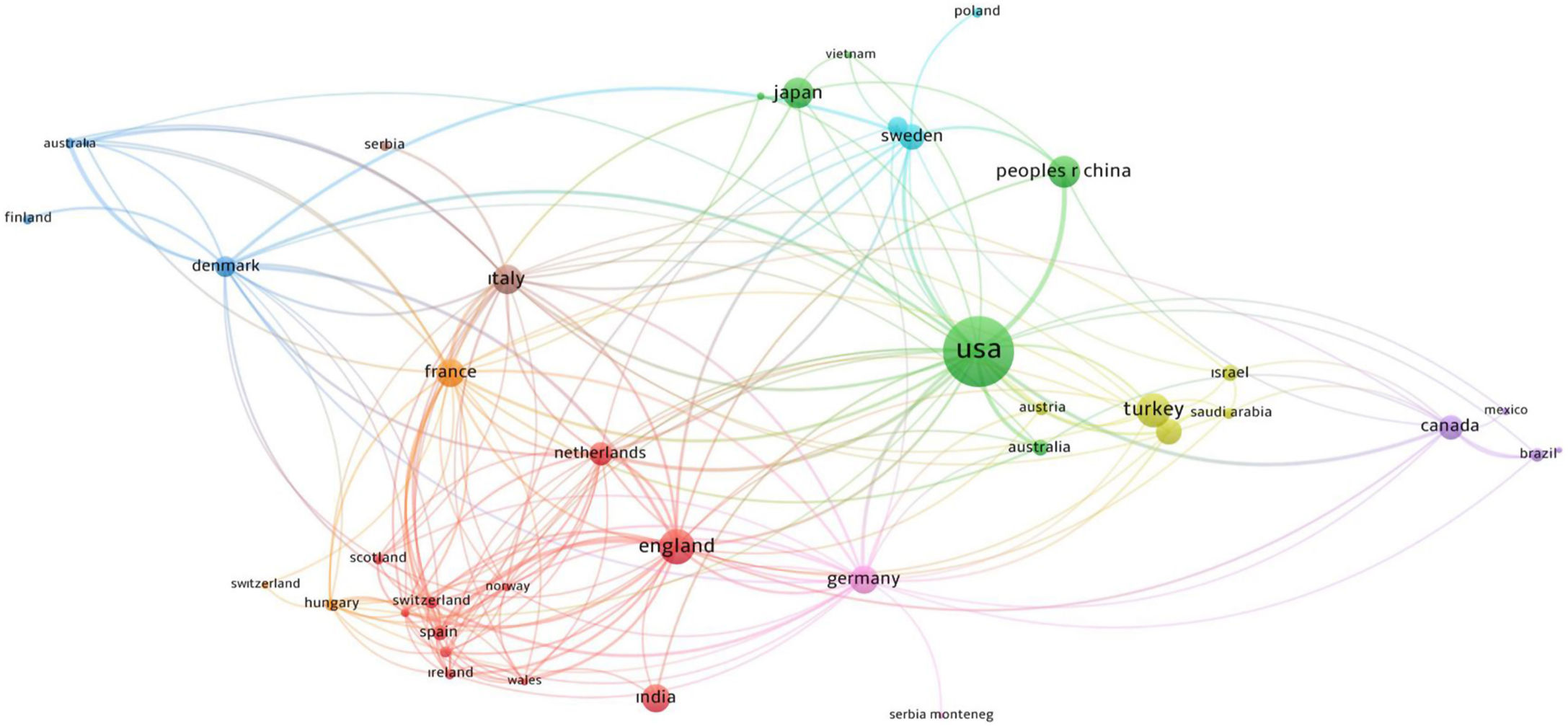
Active countriesThere were a total number of 84 countries that produced publications about hypospadias. Publication productivity of the world countries is demonstrated in Fig. 2. With 527 (27.2%) publications, the USA was the country that made the most contribution to the literature. The USA was followed by England (137), Turkey (116), Japan (106), France (104), China (104), Italy (90), Germany (86), India (79), Sweden (73), Egypt (71), Canada (61), Netherlands (59), Denmark (41), Iran (38), Australia (36), Israel (30), Belgium (29), Spain (28), Austria (26), and Brazil (25). The network visualization map of the international collaboration of the 41 countries is given in Fig. 3.
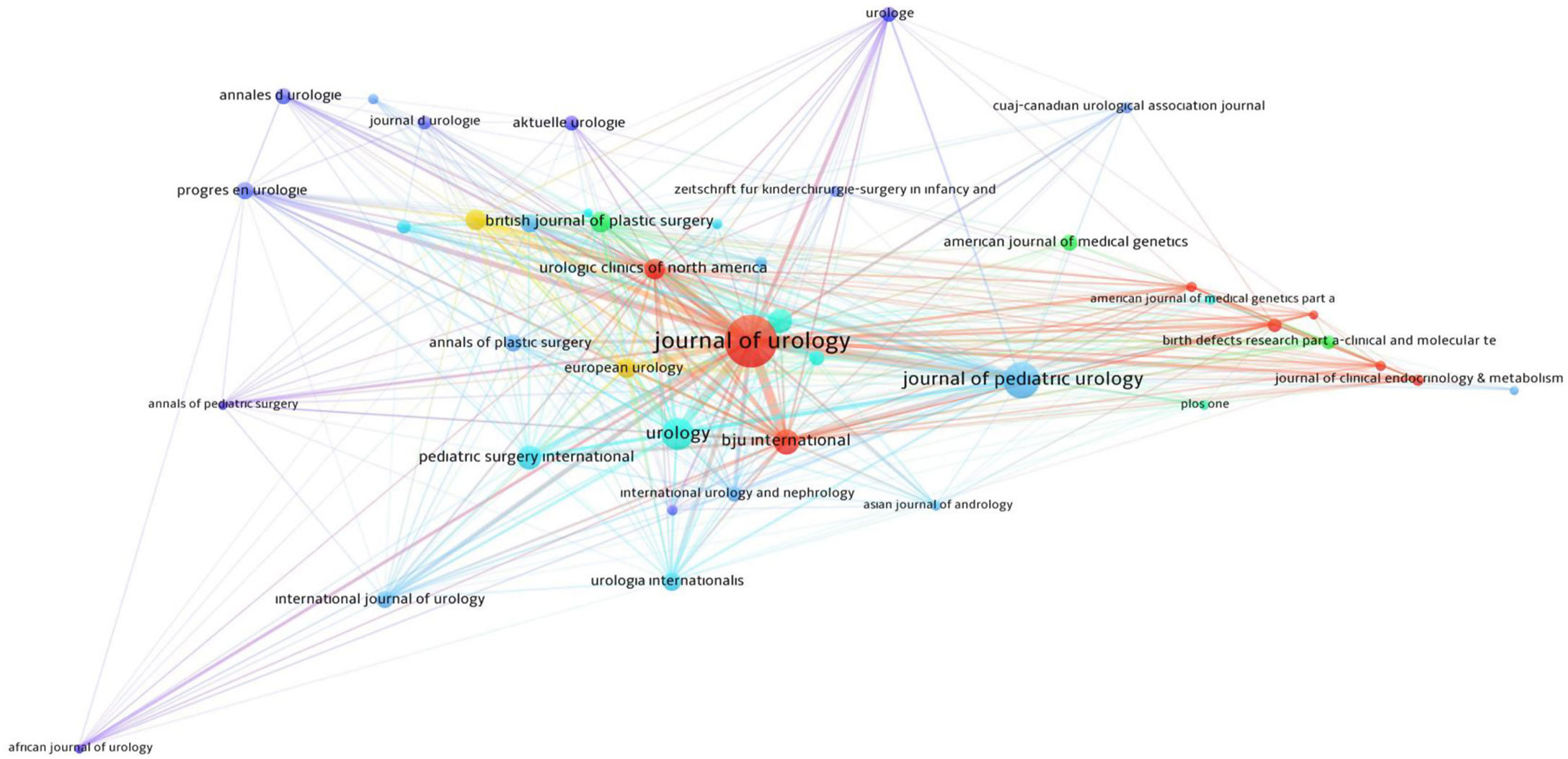
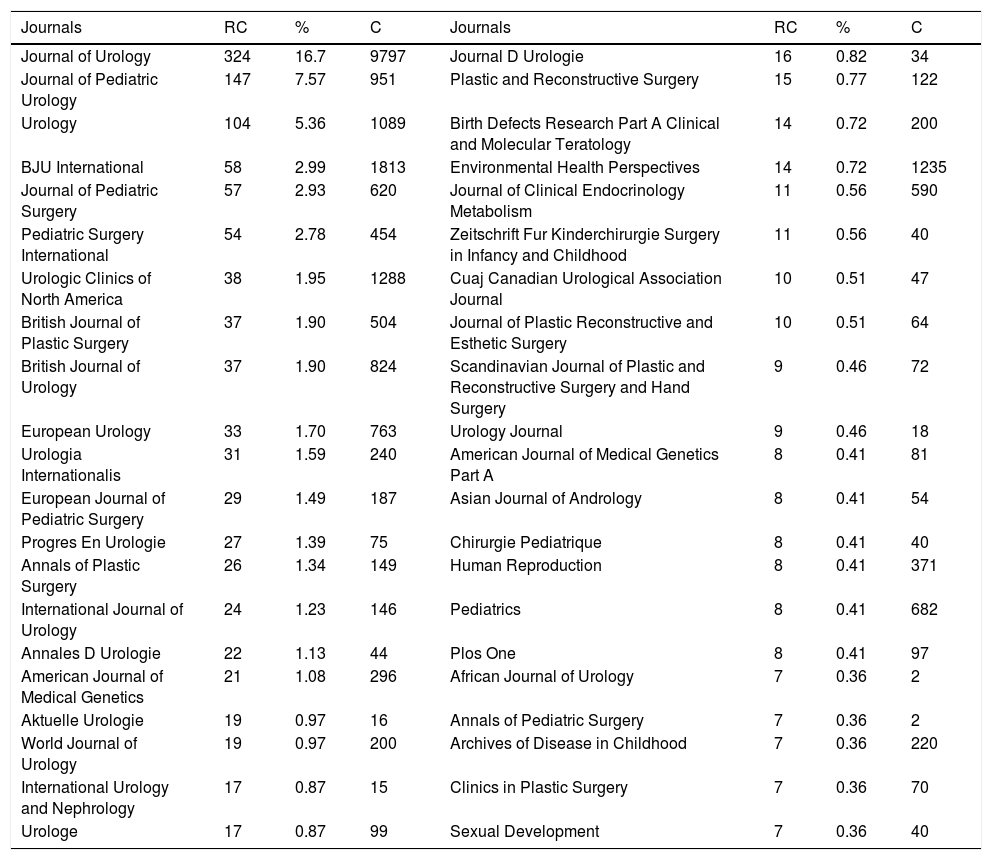
There were 373 journals where the 1940 articles were published. Table 1 lists the 42 journals that published at least 7 articles, and the citation analysis of the 42 articles is given in Fig. 4. While bigger circles indicate higher number of publications, the colors indicate the average number of citations.
Active journals on hypospadias.
| Journals | RC | % | C | Journals | RC | % | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Journal of Urology | 324 | 16.7 | 9797 | Journal D Urologie | 16 | 0.82 | 34 |
| Journal of Pediatric Urology | 147 | 7.57 | 951 | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | 15 | 0.77 | 122 |
| Urology | 104 | 5.36 | 1089 | Birth Defects Research Part A Clinical and Molecular Teratology | 14 | 0.72 | 200 |
| BJU International | 58 | 2.99 | 1813 | Environmental Health Perspectives | 14 | 0.72 | 1235 |
| Journal of Pediatric Surgery | 57 | 2.93 | 620 | Journal of Clinical Endocrinology Metabolism | 11 | 0.56 | 590 |
| Pediatric Surgery International | 54 | 2.78 | 454 | Zeitschrift Fur Kinderchirurgie Surgery in Infancy and Childhood | 11 | 0.56 | 40 |
| Urologic Clinics of North America | 38 | 1.95 | 1288 | Cuaj Canadian Urological Association Journal | 10 | 0.51 | 47 |
| British Journal of Plastic Surgery | 37 | 1.90 | 504 | Journal of Plastic Reconstructive and Esthetic Surgery | 10 | 0.51 | 64 |
| British Journal of Urology | 37 | 1.90 | 824 | Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Hand Surgery | 9 | 0.46 | 72 |
| European Urology | 33 | 1.70 | 763 | Urology Journal | 9 | 0.46 | 18 |
| Urologia Internationalis | 31 | 1.59 | 240 | American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A | 8 | 0.41 | 81 |
| European Journal of Pediatric Surgery | 29 | 1.49 | 187 | Asian Journal of Andrology | 8 | 0.41 | 54 |
| Progres En Urologie | 27 | 1.39 | 75 | Chirurgie Pediatrique | 8 | 0.41 | 40 |
| Annals of Plastic Surgery | 26 | 1.34 | 149 | Human Reproduction | 8 | 0.41 | 371 |
| International Journal of Urology | 24 | 1.23 | 146 | Pediatrics | 8 | 0.41 | 682 |
| Annales D Urologie | 22 | 1.13 | 44 | Plos One | 8 | 0.41 | 97 |
| American Journal of Medical Genetics | 21 | 1.08 | 296 | African Journal of Urology | 7 | 0.36 | 2 |
| Aktuelle Urologie | 19 | 0.97 | 16 | Annals of Pediatric Surgery | 7 | 0.36 | 2 |
| World Journal of Urology | 19 | 0.97 | 200 | Archives of Disease in Childhood | 7 | 0.36 | 220 |
| International Urology and Nephrology | 17 | 0.87 | 15 | Clinics in Plastic Surgery | 7 | 0.36 | 70 |
| Urologe | 17 | 0.87 | 99 | Sexual Development | 7 | 0.36 | 40 |
RC: Record Count; C: Number of Citation.
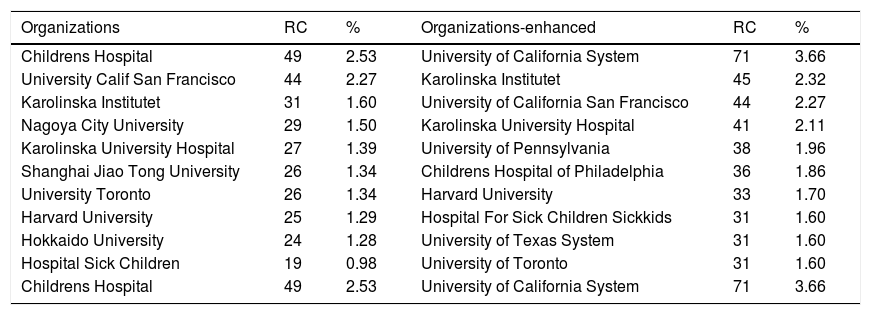
Organizations and Organizations-Enhanced that produced the highest number of publications about hypospadias are presented in Table 2.
Active organization and organizations-enhanced on hypospadias.
| Organizations | RC | % | Organizations-enhanced | RC | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Childrens Hospital | 49 | 2.53 | University of California System | 71 | 3.66 |
| University Calif San Francisco | 44 | 2.27 | Karolinska Institutet | 45 | 2.32 |
| Karolinska Institutet | 31 | 1.60 | University of California San Francisco | 44 | 2.27 |
| Nagoya City University | 29 | 1.50 | Karolinska University Hospital | 41 | 2.11 |
| Karolinska University Hospital | 27 | 1.39 | University of Pennsylvania | 38 | 1.96 |
| Shanghai Jiao Tong University | 26 | 1.34 | Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia | 36 | 1.86 |
| University Toronto | 26 | 1.34 | Harvard University | 33 | 1.70 |
| Harvard University | 25 | 1.29 | Hospital For Sick Children Sickkids | 31 | 1.60 |
| Hokkaido University | 24 | 1.28 | University of Texas System | 31 | 1.60 |
| Hospital Sick Children | 19 | 0.98 | University of Toronto | 31 | 1.60 |
| Childrens Hospital | 49 | 2.53 | University of California System | 71 | 3.66 |
RC: Record Count.
The top 10 authors who made the highest contribution to the literature about hypospadias were Nordenskjold A (n=34), Hayashi Y (30), Baskin LS (29), Kohri K (28), Kojima Y (28), Mizuno K (23), Duckett JW (22), Nonomura K (21), Snodgrass W (20), and Carmichael SL (19).
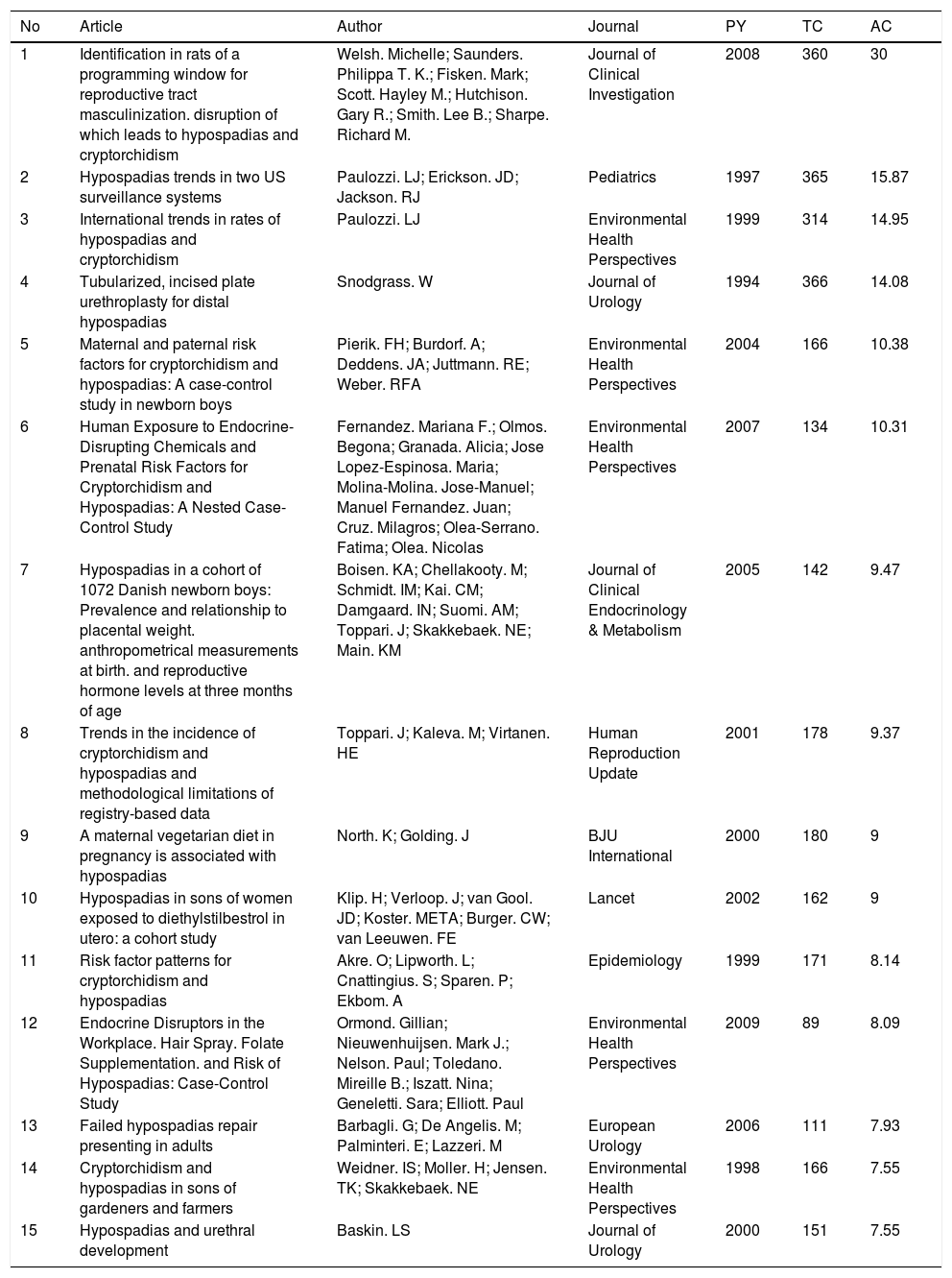
The most cited manuscriptsTable 3 displays 15 average top-cited articles according to years.
The 15 most cited manuscripts on hypospadias.
| No | Article | Author | Journal | PY | TC | AC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identification in rats of a programming window for reproductive tract masculinization. disruption of which leads to hypospadias and cryptorchidism | Welsh. Michelle; Saunders. Philippa T. K.; Fisken. Mark; Scott. Hayley M.; Hutchison. Gary R.; Smith. Lee B.; Sharpe. Richard M. | Journal of Clinical Investigation | 2008 | 360 | 30 |
| 2 | Hypospadias trends in two US surveillance systems | Paulozzi. LJ; Erickson. JD; Jackson. RJ | Pediatrics | 1997 | 365 | 15.87 |
| 3 | International trends in rates of hypospadias and cryptorchidism | Paulozzi. LJ | Environmental Health Perspectives | 1999 | 314 | 14.95 |
| 4 | Tubularized, incised plate urethroplasty for distal hypospadias | Snodgrass. W | Journal of Urology | 1994 | 366 | 14.08 |
| 5 | Maternal and paternal risk factors for cryptorchidism and hypospadias: A case-control study in newborn boys | Pierik. FH; Burdorf. A; Deddens. JA; Juttmann. RE; Weber. RFA | Environmental Health Perspectives | 2004 | 166 | 10.38 |
| 6 | Human Exposure to Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Prenatal Risk Factors for Cryptorchidism and Hypospadias: A Nested Case-Control Study | Fernandez. Mariana F.; Olmos. Begona; Granada. Alicia; Jose Lopez-Espinosa. Maria; Molina-Molina. Jose-Manuel; Manuel Fernandez. Juan; Cruz. Milagros; Olea-Serrano. Fatima; Olea. Nicolas | Environmental Health Perspectives | 2007 | 134 | 10.31 |
| 7 | Hypospadias in a cohort of 1072 Danish newborn boys: Prevalence and relationship to placental weight. anthropometrical measurements at birth. and reproductive hormone levels at three months of age | Boisen. KA; Chellakooty. M; Schmidt. IM; Kai. CM; Damgaard. IN; Suomi. AM; Toppari. J; Skakkebaek. NE; Main. KM | Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism | 2005 | 142 | 9.47 |
| 8 | Trends in the incidence of cryptorchidism and hypospadias and methodological limitations of registry-based data | Toppari. J; Kaleva. M; Virtanen. HE | Human Reproduction Update | 2001 | 178 | 9.37 |
| 9 | A maternal vegetarian diet in pregnancy is associated with hypospadias | North. K; Golding. J | BJU International | 2000 | 180 | 9 |
| 10 | Hypospadias in sons of women exposed to diethylstilbestrol in utero: a cohort study | Klip. H; Verloop. J; van Gool. JD; Koster. META; Burger. CW; van Leeuwen. FE | Lancet | 2002 | 162 | 9 |
| 11 | Risk factor patterns for cryptorchidism and hypospadias | Akre. O; Lipworth. L; Cnattingius. S; Sparen. P; Ekbom. A | Epidemiology | 1999 | 171 | 8.14 |
| 12 | Endocrine Disruptors in the Workplace. Hair Spray. Folate Supplementation. and Risk of Hypospadias: Case-Control Study | Ormond. Gillian; Nieuwenhuijsen. Mark J.; Nelson. Paul; Toledano. Mireille B.; Iszatt. Nina; Geneletti. Sara; Elliott. Paul | Environmental Health Perspectives | 2009 | 89 | 8.09 |
| 13 | Failed hypospadias repair presenting in adults | Barbagli. G; De Angelis. M; Palminteri. E; Lazzeri. M | European Urology | 2006 | 111 | 7.93 |
| 14 | Cryptorchidism and hypospadias in sons of gardeners and farmers | Weidner. IS; Moller. H; Jensen. TK; Skakkebaek. NE | Environmental Health Perspectives | 1998 | 166 | 7.55 |
| 15 | Hypospadias and urethral development | Baskin. LS | Journal of Urology | 2000 | 151 | 7.55 |
PY: Publication Year. TC: Total Citation. AC: Average Citations per Year.
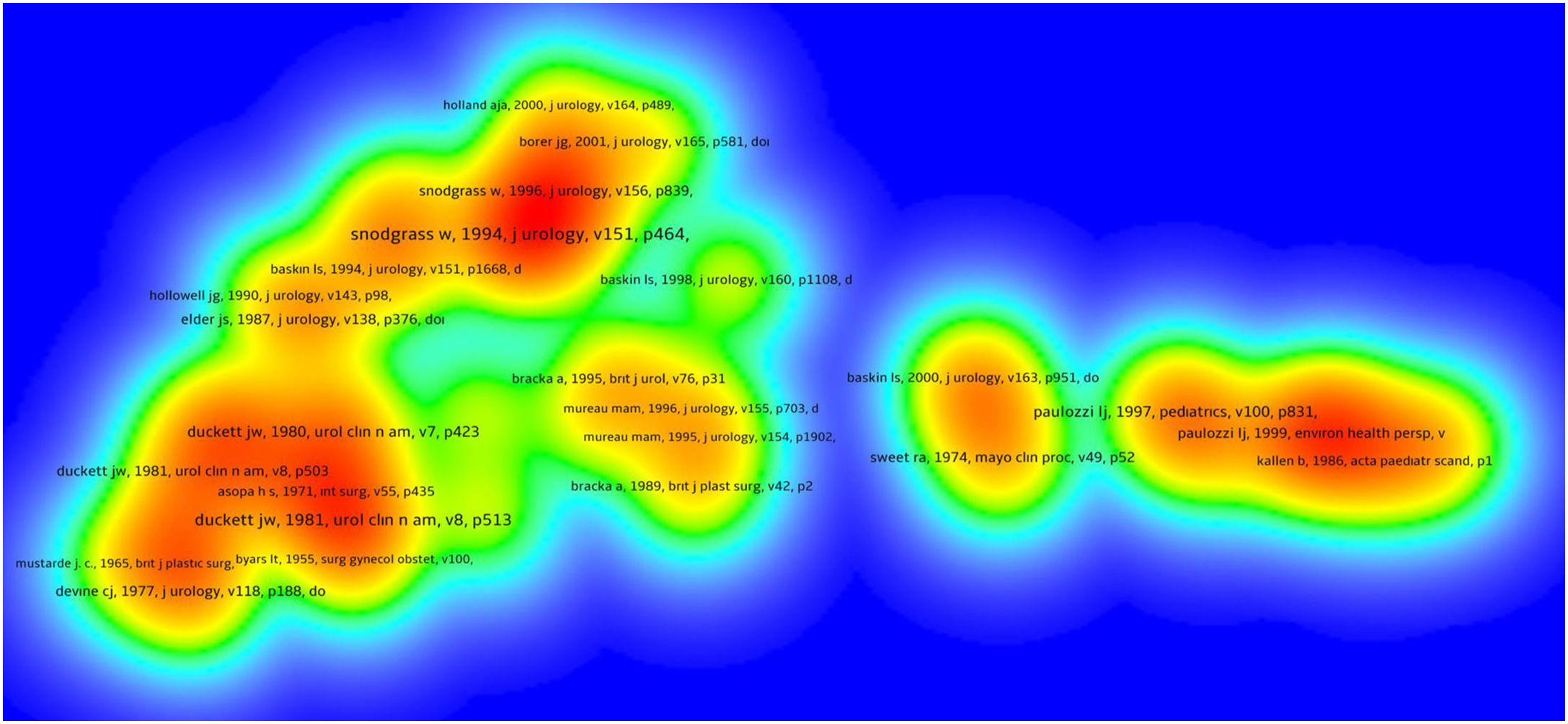
References of the articles received 14,352 citations. Fig. 5 demonstrates the network map of the 43 documents that received at least 50 citations. There were citations to the studies of Snodgrass W (1994), Duckett JW (1981), Duckett JW (1980) and Paulozzi LJ (1997) mostly in the references .13,17–19
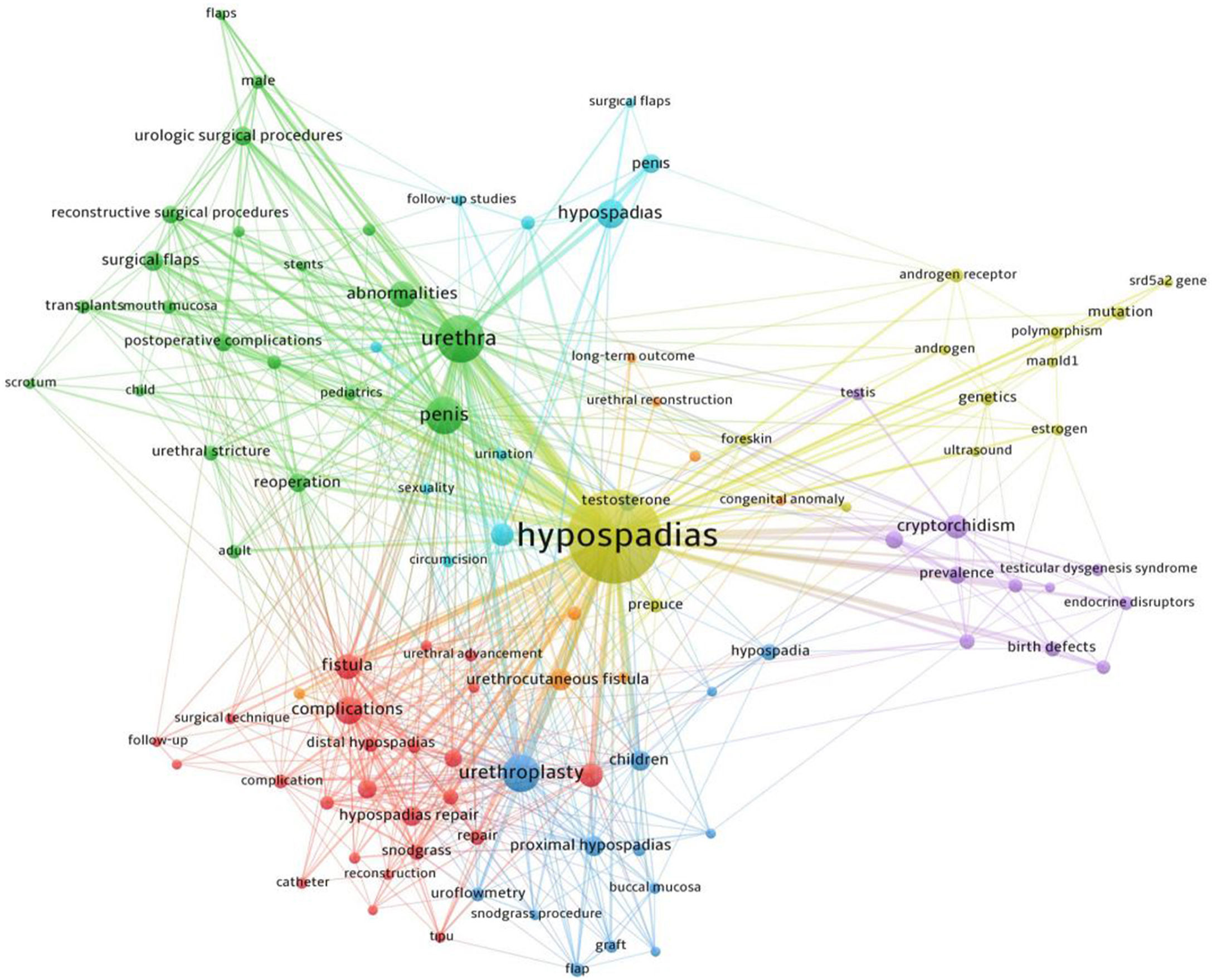
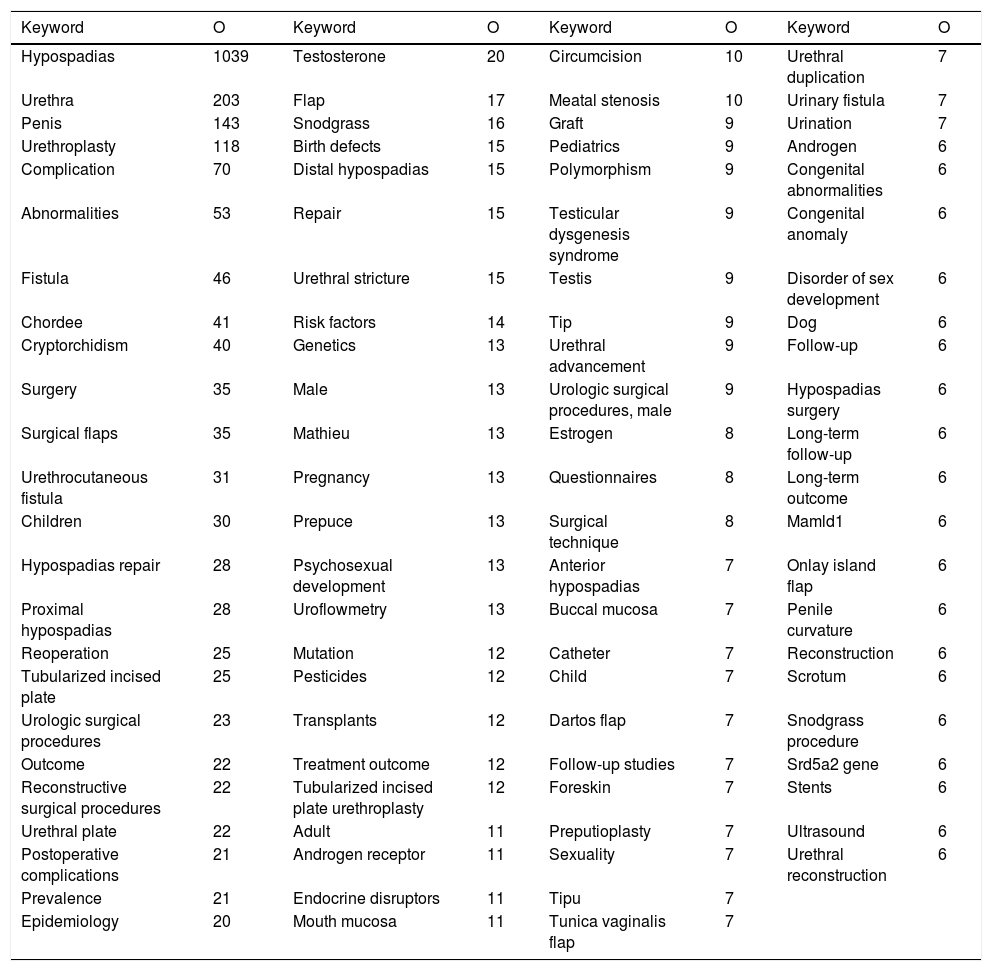
Trend topicsThere were totally 2009 keywords used in all the articles. Table 4 demonstrates the 94 keywords that were used at least 6 times. Fig. 6 shows the cluster network visualization map between the keywords.
The first 63 trend keywords on hypospadias.
| Keyword | O | Keyword | O | Keyword | O | Keyword | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypospadias | 1039 | Testosterone | 20 | Circumcision | 10 | Urethral duplication | 7 |
| Urethra | 203 | Flap | 17 | Meatal stenosis | 10 | Urinary fistula | 7 |
| Penis | 143 | Snodgrass | 16 | Graft | 9 | Urination | 7 |
| Urethroplasty | 118 | Birth defects | 15 | Pediatrics | 9 | Androgen | 6 |
| Complication | 70 | Distal hypospadias | 15 | Polymorphism | 9 | Congenital abnormalities | 6 |
| Abnormalities | 53 | Repair | 15 | Testicular dysgenesis syndrome | 9 | Congenital anomaly | 6 |
| Fistula | 46 | Urethral stricture | 15 | Testis | 9 | Disorder of sex development | 6 |
| Chordee | 41 | Risk factors | 14 | Tip | 9 | Dog | 6 |
| Cryptorchidism | 40 | Genetics | 13 | Urethral advancement | 9 | Follow-up | 6 |
| Surgery | 35 | Male | 13 | Urologic surgical procedures, male | 9 | Hypospadias surgery | 6 |
| Surgical flaps | 35 | Mathieu | 13 | Estrogen | 8 | Long-term follow-up | 6 |
| Urethrocutaneous fistula | 31 | Pregnancy | 13 | Questionnaires | 8 | Long-term outcome | 6 |
| Children | 30 | Prepuce | 13 | Surgical technique | 8 | Mamld1 | 6 |
| Hypospadias repair | 28 | Psychosexual development | 13 | Anterior hypospadias | 7 | Onlay island flap | 6 |
| Proximal hypospadias | 28 | Uroflowmetry | 13 | Buccal mucosa | 7 | Penile curvature | 6 |
| Reoperation | 25 | Mutation | 12 | Catheter | 7 | Reconstruction | 6 |
| Tubularized incised plate | 25 | Pesticides | 12 | Child | 7 | Scrotum | 6 |
| Urologic surgical procedures | 23 | Transplants | 12 | Dartos flap | 7 | Snodgrass procedure | 6 |
| Outcome | 22 | Treatment outcome | 12 | Follow-up studies | 7 | Srd5a2 gene | 6 |
| Reconstructive surgical procedures | 22 | Tubularized incised plate urethroplasty | 12 | Foreskin | 7 | Stents | 6 |
| Urethral plate | 22 | Adult | 11 | Preputioplasty | 7 | Ultrasound | 6 |
| Postoperative complications | 21 | Androgen receptor | 11 | Sexuality | 7 | Urethral reconstruction | 6 |
| Prevalence | 21 | Endocrine disruptors | 11 | Tipu | 7 | ||
| Epidemiology | 20 | Mouth mucosa | 11 | Tunica vaginalis flap | 7 |
O: Number of occurrences.
A high correlation was detected between hypospadias publication productivity and GDP and GDP PPP (r=0.791, p<0.001; r=0.683, p<0.001).
DiscussionAn analysis of the publications showed that around 40 publications per year were produced between 1980 and 2000, and with a little increase, this number was around 60 publications per year from 2001 to 2009. There seems to be an increase trend in 2010, and the number of articles reached 109 in 2017. According to the estimations about publications in the future obtained with regression analysis, the increase in the number of publications will continue. As for the number of citations, 1998 was the critical year as there was an increase after this year.
It was found that the publication productivity of the countries showed the developed countries with economic power at the top. This hypothesis was confirmed with the highly positive correlation found between GDP and publication productivity. However, although the contribution of the developed countries was more notable, Turkey was the third country, and similarly, China, India, Egypt, and Iran were among the top 15 most productive countries, which indicates that the contribution of the developed or developing countries to literate cannot be underestimated. Collaboration between the countries indicated that collaborations were generally based on geographical location.
An analysis of the journals showed that the top active 6 journals were the Journal of Urology, Journal of Pediatric Urology, Urology, BJU International, Journal of Pediatric Surgery, and Pediatric Surgery International. An analysis based on the number of citations revealed that the top-cited journals were the Journal of Urology, BJU International, Urologic Clinics of North America, Environmental Health Perspectives, Urology, and Journal of Pediatric Urology. Researchers investigating this topic are recommended to follow these journals about hypospadias.
The article written by Snodgrass. W. in 1994 and published in the Journal of Urology with the title of “Tubularized, incised plate urethroplasty for distal hypospadias” was the top-cited article according to the total number of citations .17 The study reported a technique for the correction of distal with minimal chordee through the tubularization of the urethral plate. The second top-cited publication was the article entitled “Hypospadias trends in two US surveillance systems” written by Paulozzi, et al. in 1997; the article was published in the Journal of Pediatrics and reported the prevalence of hypospadias .13 According to the average number of citations per year, the study conducted by Welsh et al. in the Journal of Clinical Investigation in 2008 with the title of “Identification in rats of a programming window for reproductive tract masculinization. disruption of which leads to hypospadias and cryptorchidism” was notable .20 The study conducted with rats reported that the lack of androgen induced hypospadias and undescended testes.
Another publication that was notable according to the average number of citations was Paulozzi's article published in the Journal of Environmental Health Perspectives in 1999 with the title of “International trends in rates of hypospadias and cryptorchidism” .21 This prevalence study investigated the changes in the rates of hypospadias according to years and discussed the factors that might have effects on the increase in prevalence. The articles that were highly cited and noticed were generally the studies that investigated the etiology of hypospadias (the cause of the condition). These studies reported that the etiology of hypospadias is believed to be unknown and multifactorial (environmental, genetic). The factors that were considered to increase the risk of hypospadias were reported family inheritance, early age of pregnancy, birth before 33rd gestational week, father's smoking, use of estrogen-progesterone during pregnancy, phytate-containing food, exposure to chemicals such as polychlorinated biphenyls, diethylstilbestrol klorofenottan and some other pesticides, vegetarian diet during pregnancy, and an episode of influenza in the first trimester of pregnancy.
An analysis of the keywords showed that the top-cited keywords were cryptorchidism, pregnancy, endocrine disruptors, pesticides, and estrogen. The trend keywords published in recent years were mainly androgen, mutation, mamld1, srd5a2 gene, proximal hypospadias, urethrocutaneous fistula, congenital anomaly, and postoperative complication. An analysis of the trend keywords showed that recent studies focused mainly on androgen, congenital anomaly, mutation, mamld1, srd5a2 topics, and their relationship with hypospadias. In previous years, factors such as proximal hypospadias, urethrocutaneous fistula, postoperative complication, birth defects, endocrine disruptors were investigated. Cluster analysis indicated words such as urethra, cryptorchidism, urethroplasty, complications, and fistula. The most notable keywords in the articles were complication, fistula, and chordee.
One limitation of the present study is that the publications before 1980 could not be accessed since the first publication in the Web of Science database is in 1980. In addition, since the WoS database is known to be the most reliable database in publications and citations, the analyses did not include PubMed and Scopus .22–24 WoS database indexes only the journals with a high impact factor.
ConclusionThis study provides a holistic evaluation of the articles about hypospadias, which is an anomaly that should be repaired and treated with surgery due to its potential problems for the children at kindergarten and school age. It is thus believed to provide important information to primarily pediatric surgeons and researchers and health sciences students studying this topic. These analyses will help a scientist to review the trend topics investigated, the top-cited articles in this issue (maybe the ones that should be read), the journals that have more articles, the top-cited journals, the journals that could be used as a guide about this issue, and the topics that were investigated the most over the years. In addition, the results of this study will give an idea about the potential new research topics.
There was a significant correlation between publication productivity and GDP values of the countries. Although there is a contribution of some developing or underdeveloped countries, generally developed counties had contributions to publication productivity. International collaborations were in small clusters, and generally, the geographical location was effective in international collaborations. Therefore, multidisciplinary new studies including developing or underdeveloped countries (samples from different societies) should be planned and shed light on new developments.
Authors’ contributionsDr. Doğan, and Dr. İpek conceptualized and designed the study, collected data, carried out the initial analyses, wrote the manuscript, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Ethical approvalThis article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consentFor this type of study formal consent is not required.
FundingThe study had no funding source.
Conflict of interestAuthors declare that he has no conflict of interest.