El daño cerebral adquirido es un importante problema de salud pública y la principal causa de muerte y discapacidad, la cual abarca no solo aspectos motrices, sino también del lenguaje, habla, memoria y/o habilidades cognitivas que afectan de manera sustancial la vida de quienes la padecen.
ObjetivoAnalizar y describir causas y efectos del daño cerebral adquirido traumático y no traumático.
Material y métodosEstudio analítico transversal retrospectivo; se seleccionaron expedientes de pacientes (2011 a 2015) conformando un total de 736. Se calcularon medias, desviaciones estándar, porcentajes y frecuencias; con la finalidad de evaluar si existía diferencia significativa entre variables se calculó χ2 y dependencia estadística mediante análisis de probabilidad condicional.
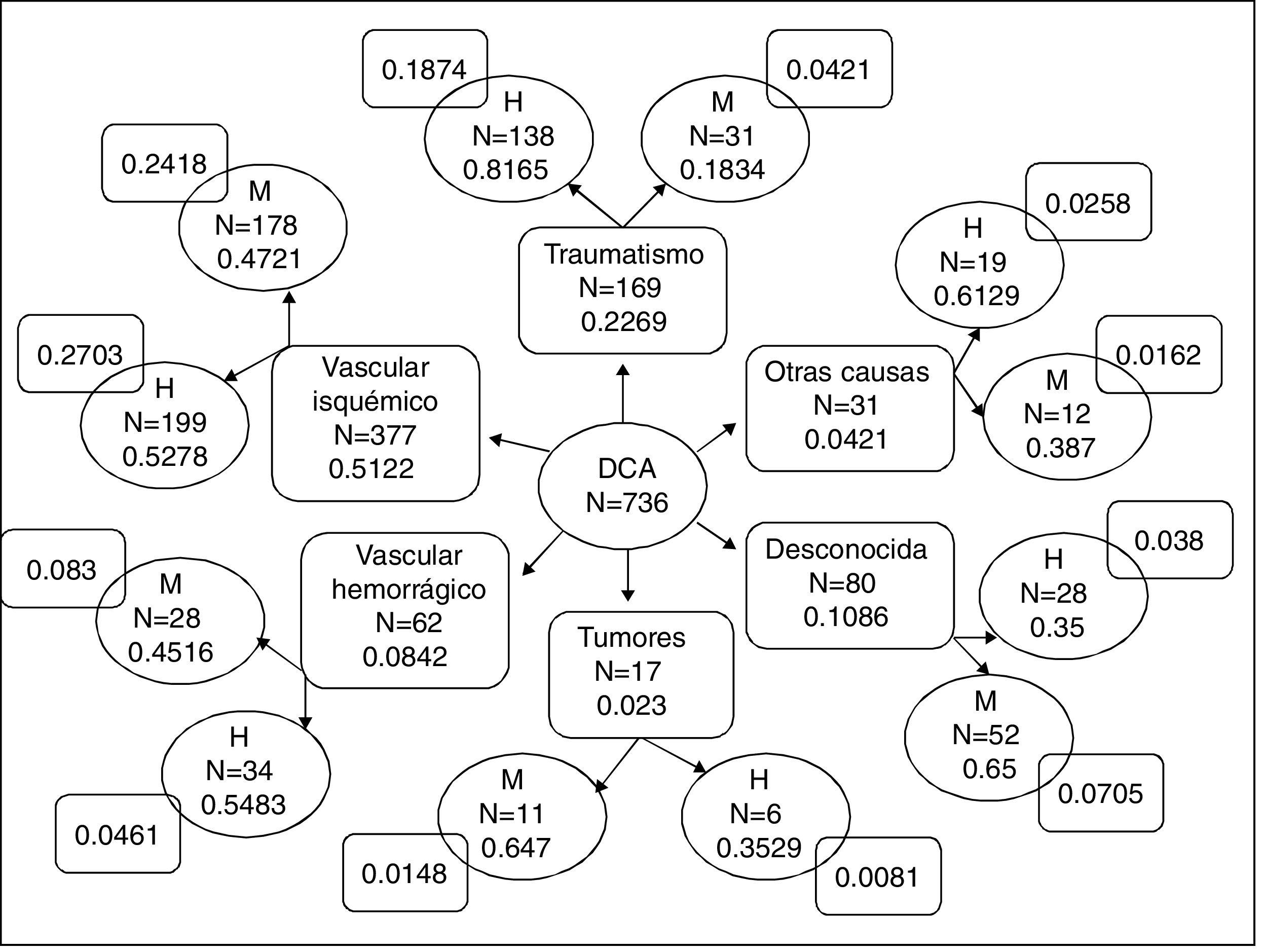
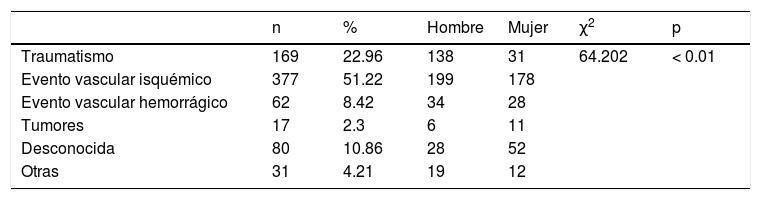
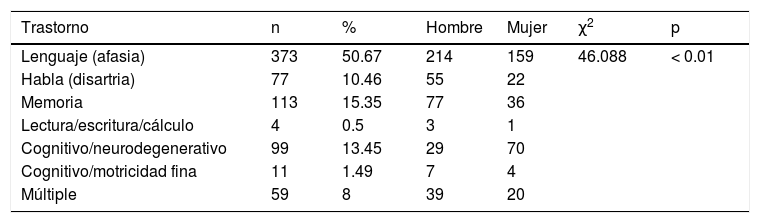
ResultadosEl daño cerebral de origen traumático se presentó en 169 (22.9%) pacientes (138 hombres y 31 mujeres). Las causas principales fueron accidentes automovilísticos (27.8%) y caídas (24.8%); 567 (77%) pacientes (286 hombres, 281 mujeres) presentaron daño por etiología no traumática, principalmente por evento vascular isquémico (377 pacientes, 51.22%). Los diagnósticos establecidos con mayor frecuencia fueron los trastornos del lenguaje y de memoria.
ConclusionesLa enfermedad vascular cerebral se está convirtiendo en un problema de salud, por lo que es necesario generar campañas preventivas e informativas sobre la adecuada atención y tratamiento con la finalidad de disminuir la incidencia y la gravedad de la discapacidad de los pacientes afectados.
Acquired brain damage is a major public health problem and the main cause of death and disability, which encompasses not only motor aspects, but also language, speech, memory and/or cognitive abilities that substantially affect the lives of those suffering from them.
ObjectiveTo analyze and describe causes and effects of traumatic and non-traumatic acquired brain damage.
Materials and methodsThis is a retrospective cross-sectional analytical review. Patient files were selected (2011 to 2015), making a total of 736. Means, standard deviations, percentages and frequencies were calculated; with the purpose of evaluating if there was a significant difference between variables was calculated and statistical dependence through conditional probability analysis.
ResultsAcquired brain injury of traumatic origin occurred in 169 (22.9%) patients (138 men and 31 women). The main causes were car accidents (27.8%) and falls (24.8%); 567 (77%) patients (286 men and 281 women) presented damage due to non-traumatic etiology, mainly due to ischemic vascular event (377 patients, 51.22%). The most commonly established diagnoses were language and memory disorders.
ConclusionsCerebral vascular disease is becoming a health problem, so it is necessary to create preventive and informative campaigns about the adequate care and treatment in order to reduce the incidence and severity of the disability of affected patients.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora