Despite limited published evidence, robotic-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (RATS) for anatomic lung resection in early-stage lung cancer continues growing. The aim of this study is to evaluate its safety and oncologic efficacy compared to video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS).
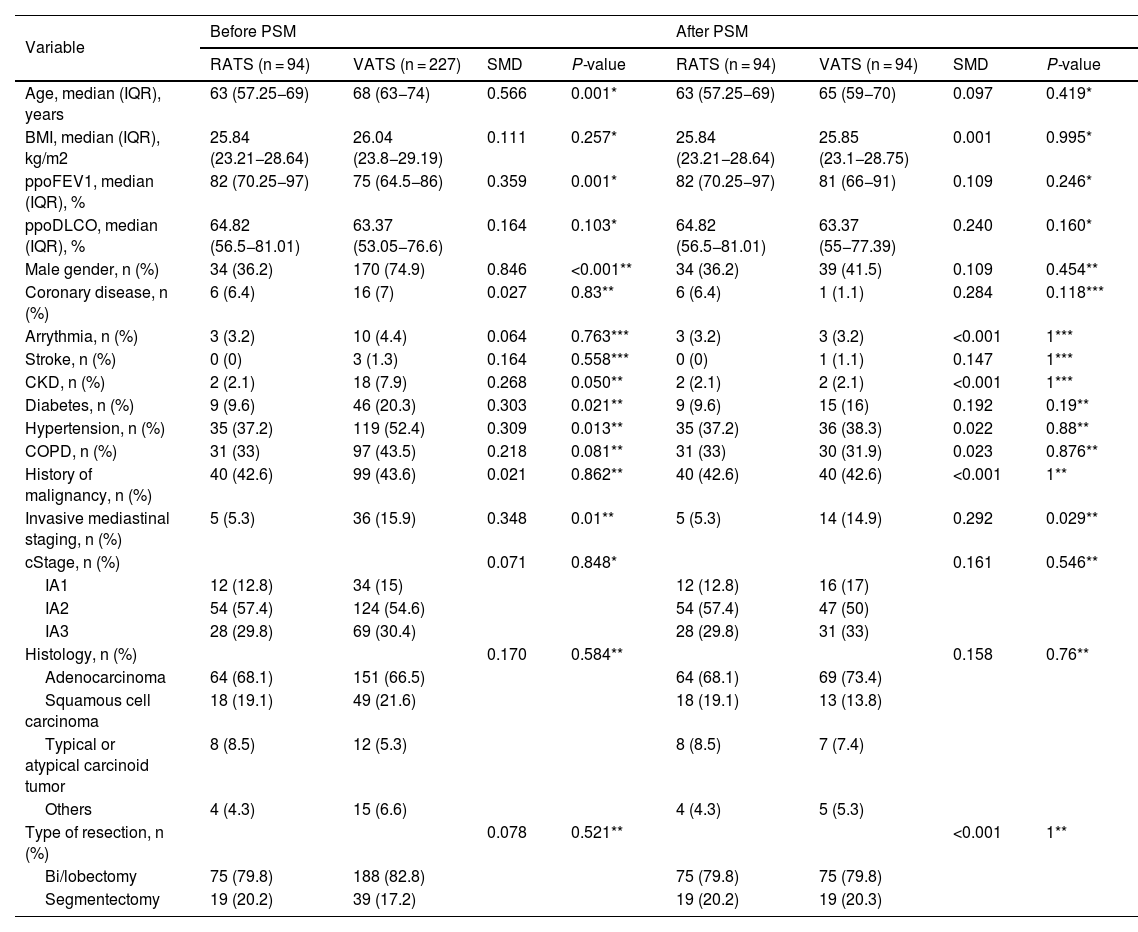
MethodsSingle-centre retrospective study of all patients with resected clinical stage IA NSCLC who underwent RATS or VATS anatomic lung resection from June 2018 to January 2022. RATS and VATS cases were matched by propensity scoring (PSM) according to age, sex, histology, and type of resection. Short-term outcomes were compared, and the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test were used to evaluate the overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS).
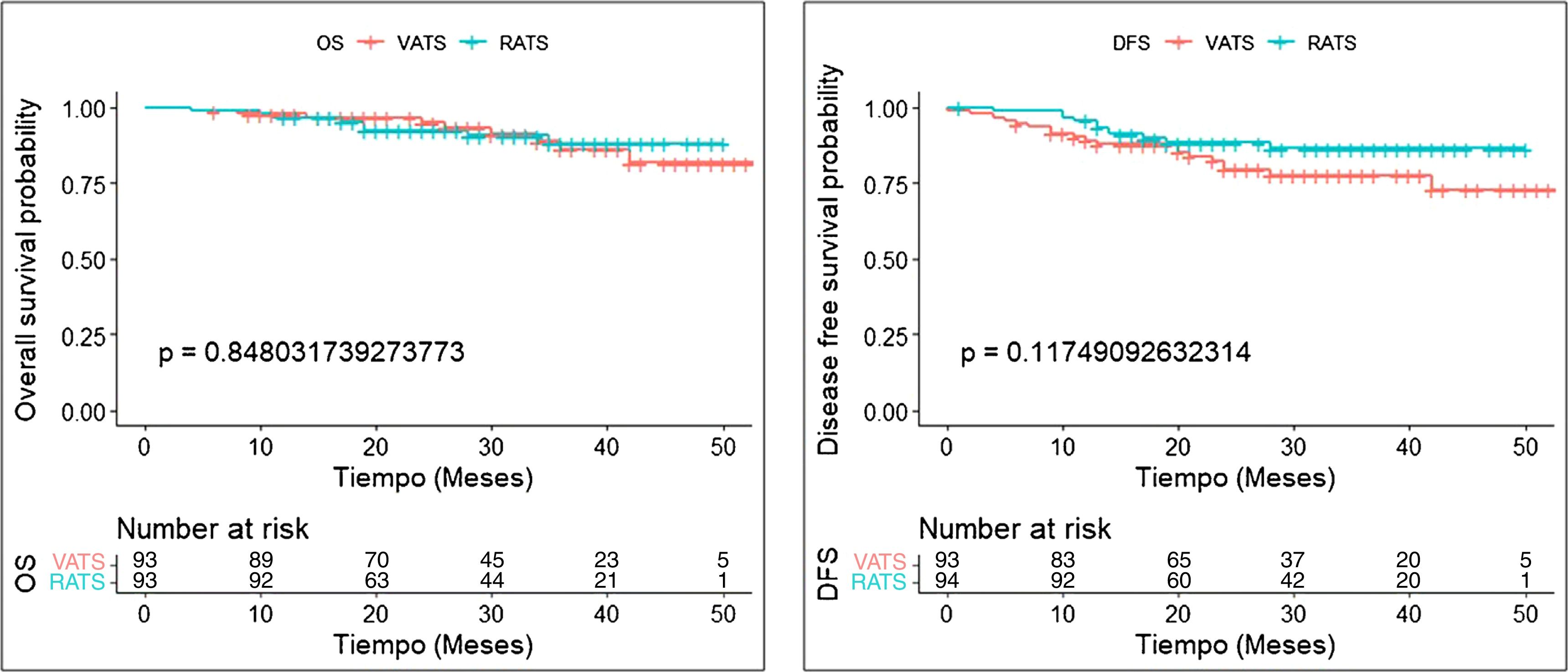
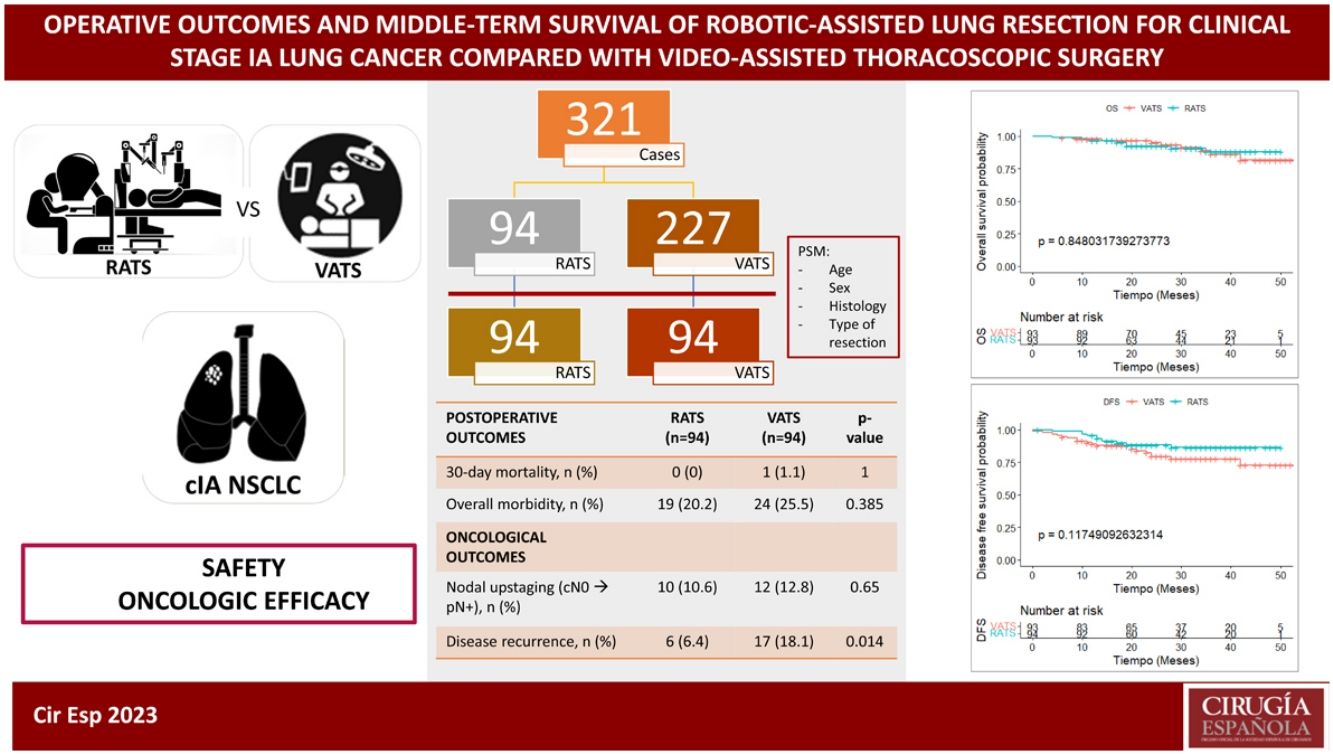
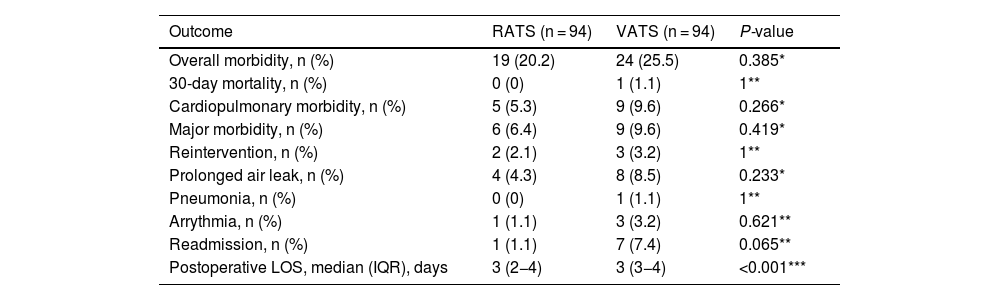
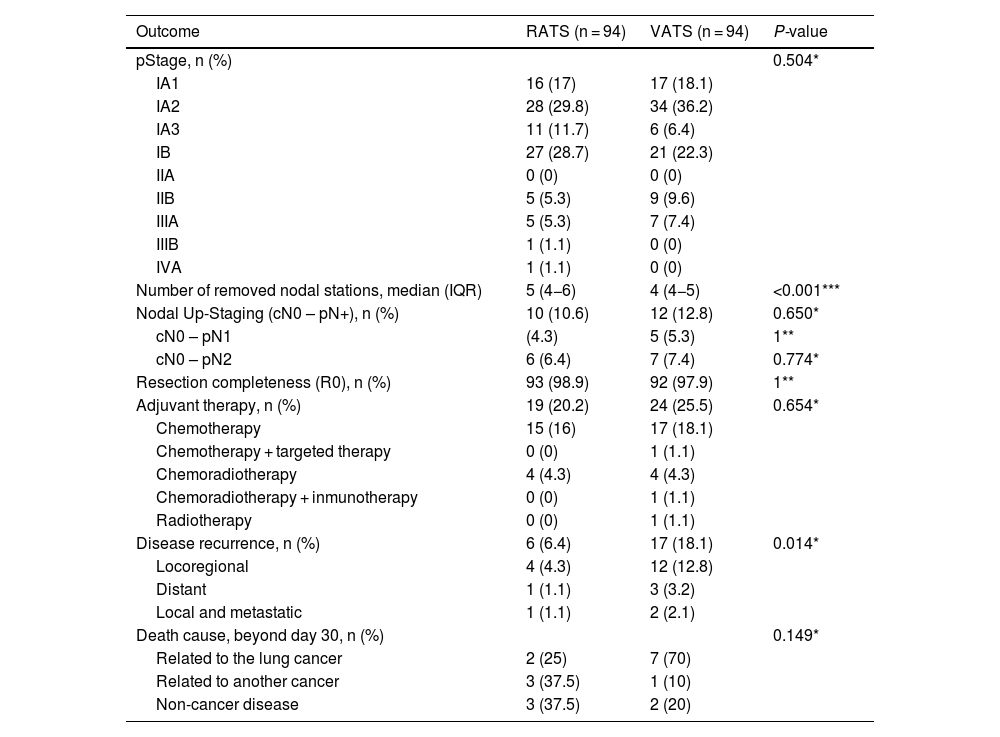
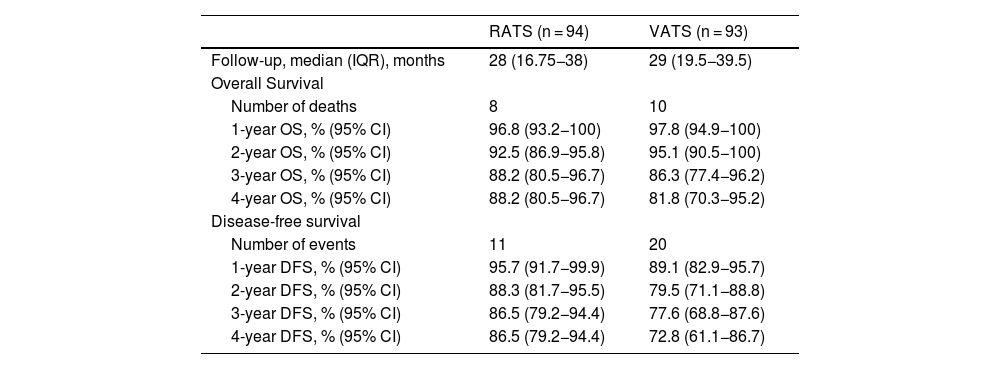
Results321 patients (94 RATS and 227 VATS cases) were included. After PSM, 94 VATS and 94 RATS cases were compared. Demographics, pulmonary function, and comorbidity were similar in both groups. Overall postoperative morbidity was comparable for RATS and VATS cases (20.2% vs 25.5%, P = 0.385, respectively). Pathological nodal upstaging was similar in both groups (10.6% in RATS and 12.8% in VATS). During the 3.5-year follow-up period (median: 29 months; IQR: 18–39), recurrence rate was 6.4% in RATS group and 18.1% in the VATS group (P = 0.014). OS and DFS were similar in RATS and VATS groups (log rank P = 0.848 and P = 0.117, respectively).
ConclusionRATS can be performed safely in patients with early-stage NSCLC. For clinical stage IA disease, robotic anatomic lung resection offers better oncologic outcomes in terms of recurrence, although there are no differences in OS and DFS compared with VATS.
A pesar de la limitada evidencia disponible, el uso de la RATS en resecciones pulmonares anatómicas por cáncer continúa creciendo. El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar su seguridad y eficacia oncológica en comparación con la VATS.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo unicéntrico en el que se incluyeron todos los pacientes con CPNM en estadio cIA sometidos a resección pulmonar anatómica RATS o VATS entre junio de 2018 y enero de 2022. Los casos se emparejaron mediante puntuación de propensión (PSM) según edad, sexo, histología y tipo de resección. Se compararon los resultados a corto plazo y la supervivencia global (OS) y libre de enfermedad (DFS) mediante el método de Kaplan-Meier y la prueba de rangos logarítmicos.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 321 pacientes (94 RATS y 227 VATS). Tras el PSM, se compararon 94 VATS y 94 RATS. La morbilidad global fue comparable en ambos grupos (20.2 % en RATS vs 25.5 % en VATS, P = 0.385). El upstaging ganglionar fue similar en ambos abordajes (10.6% en RATS y 12.8% en VATS). Durante los 3.5 años de seguimiento, la tasa de recurrencia fue del 6.4 % en RATS y del 18.1 % en VATS (P = 0.014). OS y DFS fueron similares en los dos grupos (rango logarítmico P = 0.848 y P = 0.117, respectivamente).
ConclusiónLa RATS se puede realizar de forma segura en pacientes con CPNM en estadio inicial. Para la enfermedad en estadio cIA, el abordaje robótico ofrece mejores resultados en términos de recurrencia, aunque no hay diferencias en la OS y la DFS en comparación con la VATS.