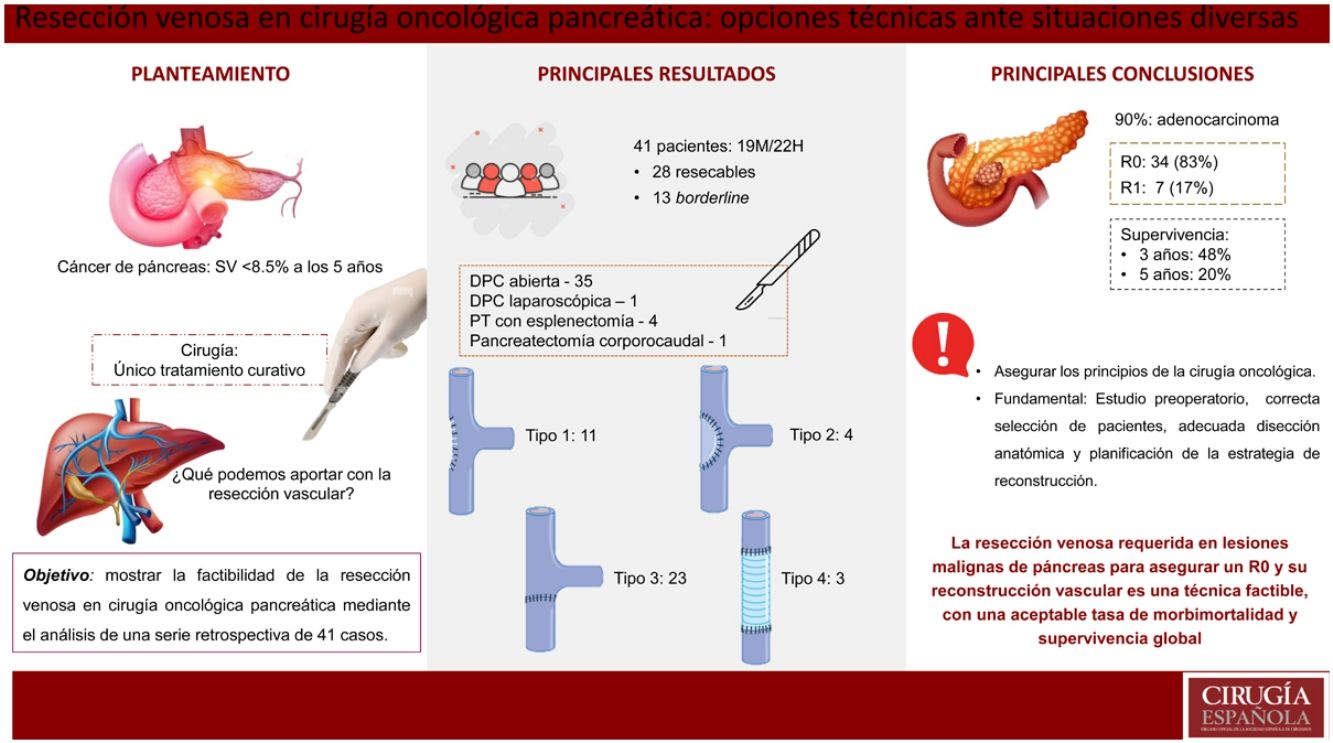
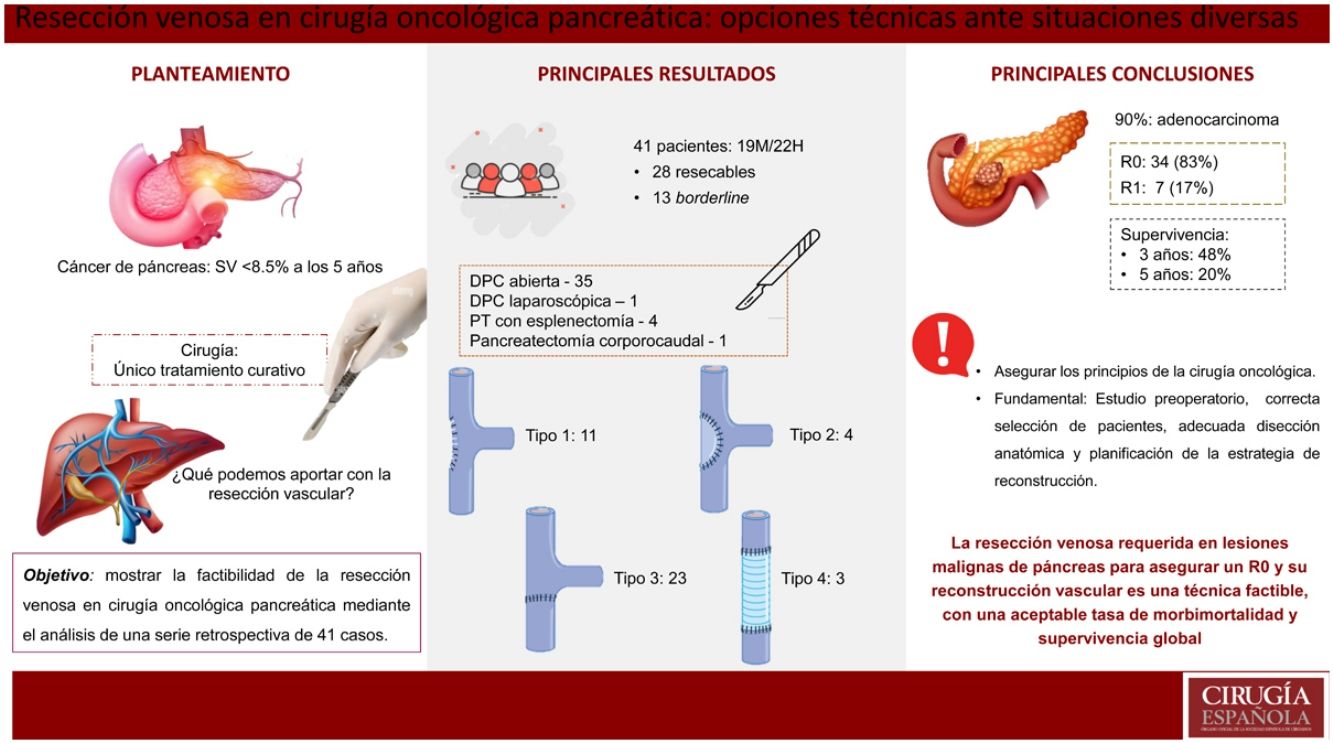
Análisis de los resultados de resección venosa en cirugía pancreática oncológica de 2 centros de referencia. Se analiza el tipo de intervención realizada, los tipos de reconstrucción vascular, el estudio anatomopatológico, la morbimortalidad postoperatoria y la supervivencia a 3 y 5 años.
MétodosAnálisis retrospectivo, transversal y comparativo. Se incluyen 41 pacientes intervenidos de lesiones neoplásicas pancreáticas desde 2003 hasta 2021 que requirieron resección venosa por afectación vascular.
ResultadosLa técnica quirúrgica más frecuente fue la duodenopancreatectomía cefálica tipo Whipple, realizada en 35 de los 41 pacientes (85%). Uno de los casos se realizó por acceso laparoscópico. La reconstrucción vascular tipo 1 (sutura simple) se realizó en 11 pacientes (27%), la tipo 2 (patch de falciforme) en 4 casos (10%), la tipo 3 (sutura término-terminal) en 23 casos (56%) y la reconstrucción tipo 4 (injerto autógeno) en 3 casos (7%). La longitud media del segmento venoso resecado fue de 21mm (11-46) y el tiempo quirúrgico medio fue de 290min (220-360). El 90% (37/41) fueron adenocarcinoma de páncreas. El 83% se consideraron R0 y hubo afectación en el tramo vascular resecado en el 41% de los casos. Hubo morbilidad Clavien-Dindo>3 en 4 pacientes y no hubo ningún caso de mortalidad postoperatoria. La supervivencia a 3 años fue del 48% y a 5 años del 20%.
ConclusionesLa resección venosa con reconstrucción para asegurar una resección R0 es una técnica factible, con una aceptable tasa de morbimortalidad y supervivencia global.
To report the clinical results of patients with malignant pancreatic lesions who underwent oncological surgery with vascular resection. The type of intervention performed, the types of vascular reconstruction, the pathological anatomy results, postoperative morbidity and mortality, and survival at 3 and 5 years were analysed.
MethodsRetrospective, cross-sectional and comparative analysis. We include 41 patients with malignant pancreatic lesions who underwent surgery with vascular resection due to vascular involvement, from 2013 to 2021.
ResultsThe most performed surgery was the cephalic pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure) using median laparotomy, in 35 of the 41 patients (85%). One of the cases in the series was performed laparoscopically. Type 1 reconstruction (simple suture) was performed in 11 (27%) patients, type 2 in 4 (10%) cases, type 3 (T–T suture) in 23 (56%) cases, and type 4 reconstruction by autologous graft in 3 (7%) cases. The mean length of the resected venous segment was 21 (11–46)mm and the mean surgical time was 290 (220–360)min. 90% (37/41) were pancreatic adenocarcinoma. 83% were considered R0 and there was involvement in the resected vascular section in 41% of the cases. Four patients had Clavien-Dindo morbidity>3 and there were no cases of postoperative mortality. Survival at 3 years was 48% and at 5 years was 20%.
ConclusionsThe aggressive surgical treatment with venous resection in pancreatic malignant lesions to ensure R0 and its vascular reconstruction is a feasible technique, with an acceptable morbid-mortality rate and overall survival.
El cáncer de páncreas es uno de los tumores con peor pronóstico, con una tasa de supervivencia menor del 8,5% a los 5 años1. Hoy en día, la cirugía continúa siendo el único tratamiento curativo, pero su comportamiento hace que únicamente el 20% de los pacientes sean resecables en el momento del diagnóstico2.
Clásicamente, se consideraba una contraindicación para la cirugía aquellos tumores que contactaban la vena mesentérica superior (VMS) o la vena porta (VP).
En 1951, Moore et al. describieron la primera cirugía con resección de VP y VMS para el tratamiento de un adenocarcinoma pancreático localmente avanzado3. Desde entonces se han desarrollado distintas técnicas de reconstrucción vascular, como las prótesis de politetrafluoroetileno, el injerto vascular autógeno y la confección de patch con ligamento falciforme o vaina posterior de músculo recto del abdomen4.
Presentamos el análisis de una serie retrospectiva de 41 casos intervenidos con resección vascular, valorando sus resultados clínicos, así como la descripción de los diferentes métodos de reconstrucción vascular.
Pacientes y métodosDiseñoSe analizan de forma retrospectiva sobre una base de datos prospectiva los pacientes intervenidos de cáncer de páncreas con resección vascular desde septiembre de 2003 a enero de 2021 en 2 hospitales (Hospital Universitario Germans Trias i Pujol desde 2017 a 2021 y Hospital Universitario Mútua Terrassa desde 2003 a 2021). El registro incluye variables de acuerdo con los datos demográficos, el tipo de tumor, el tratamiento quimioterápico y quirúrgico, los datos patológicos y la supervivencia.
Pacientes y métodosLos criterios de inclusión fueron hombres y mujeres mayores de 18 años diagnosticados de neoplasia de páncreas resecable o borderline, que hubieran sido valorados en comité multidisciplinar y hubieran firmado el consentimiento informado para la cirugía. El diagnóstico radiológico y la afectación vascular se realizó mediante TC siguiendo las guías del National Comprehensive Cancer Network de 20215. Se indicó tratamiento neoadyuvante según el protocolo hospitalario en todos los pacientes borderline resecables y planificamos una posible resección y reconstrucción vascular con TC preoperatoria.
Técnica quirúrgica- a)
Fase de resección y valoración de la invasión vascular
Se realiza una laparotomía subcostal bilateral y se expone la arteria mesentérica superior con una maniobra de Kocher amplia hasta la vena renal izquierda o a través del mesocolon a la altura del ángulo de Treitz. Tras asegurar la no afectación de la arteria mesentérica superior se realiza: sección gástrica a nivel del antro con 2 endograpadoras; disección del hilio hepático y sección de la vía biliar por encima del conducto cístico; pinzamiento y sección de la arteria gastroduodenal en su origen; paso retropancreático por encima de la VMS/VP y sección del páncreas; sección de la primera asa yeyunal y descruzamiento duodenal; disección del mesopáncreas separando la VMS y la VP, momento en el cual se valora la invasión venosa y su posible resección.
- b)
Fase de reconstrucción vascular
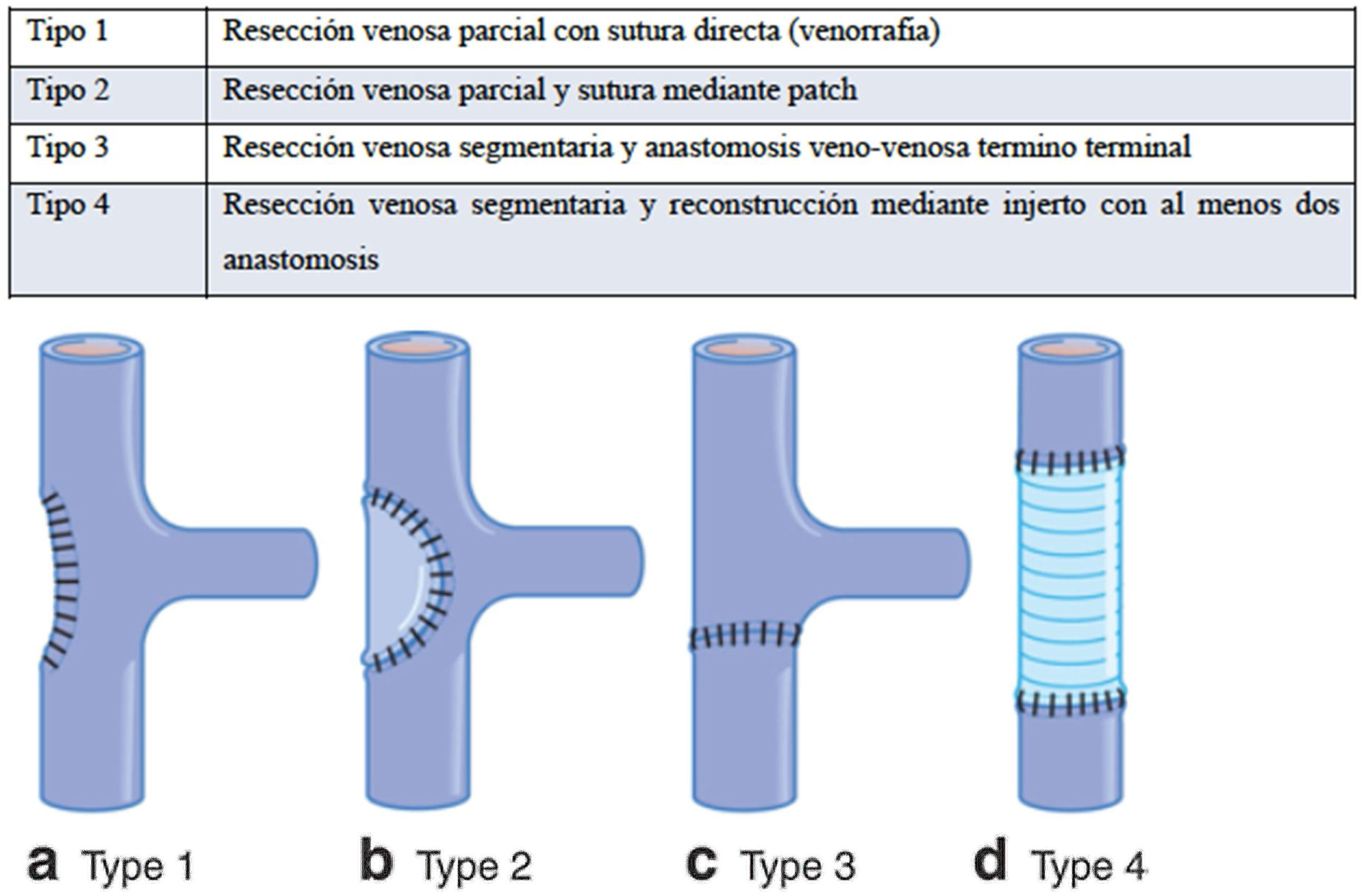
La reconstrucción vascular se realiza siguiendo la clasificación del International Study Group on Pancreatic Surgery para la resección venosa y su reconstrucción5 (fig. 1).
El objetivo de la reconstrucción vascular es asegurar una reparación sin tensión. Para lograrlo, la liberación temporal de separadores hepáticos puede ser útil, así como la movilización hepática completa o la realización de una incisión a nivel de la raíz mesentérica para facilitar su ascenso. Estas maniobras pueden posibilitar la reconstrucción mediante anastomosis término-terminal, incluso en resecciones de hasta 5cm6.
No obstante, la técnica elegida para la reconstrucción debe individualizarse en cada caso, valorando la localización del tumor, la afectación venosa y la longitud de vena, así como el calibre de la reconstrucción para evitar zonas estenóticas y una posible disminución del flujo portal.
A continuación se describen los diferentes tipos de reconstrucción venosa:
- •
Tipo 1: Resección vascular parcial mediante pinzamiento lateral de la VP o VMS. Para su reconstrucción se realiza rafia primaria con prolene 4/0 o 5/0 (fig. 2A).
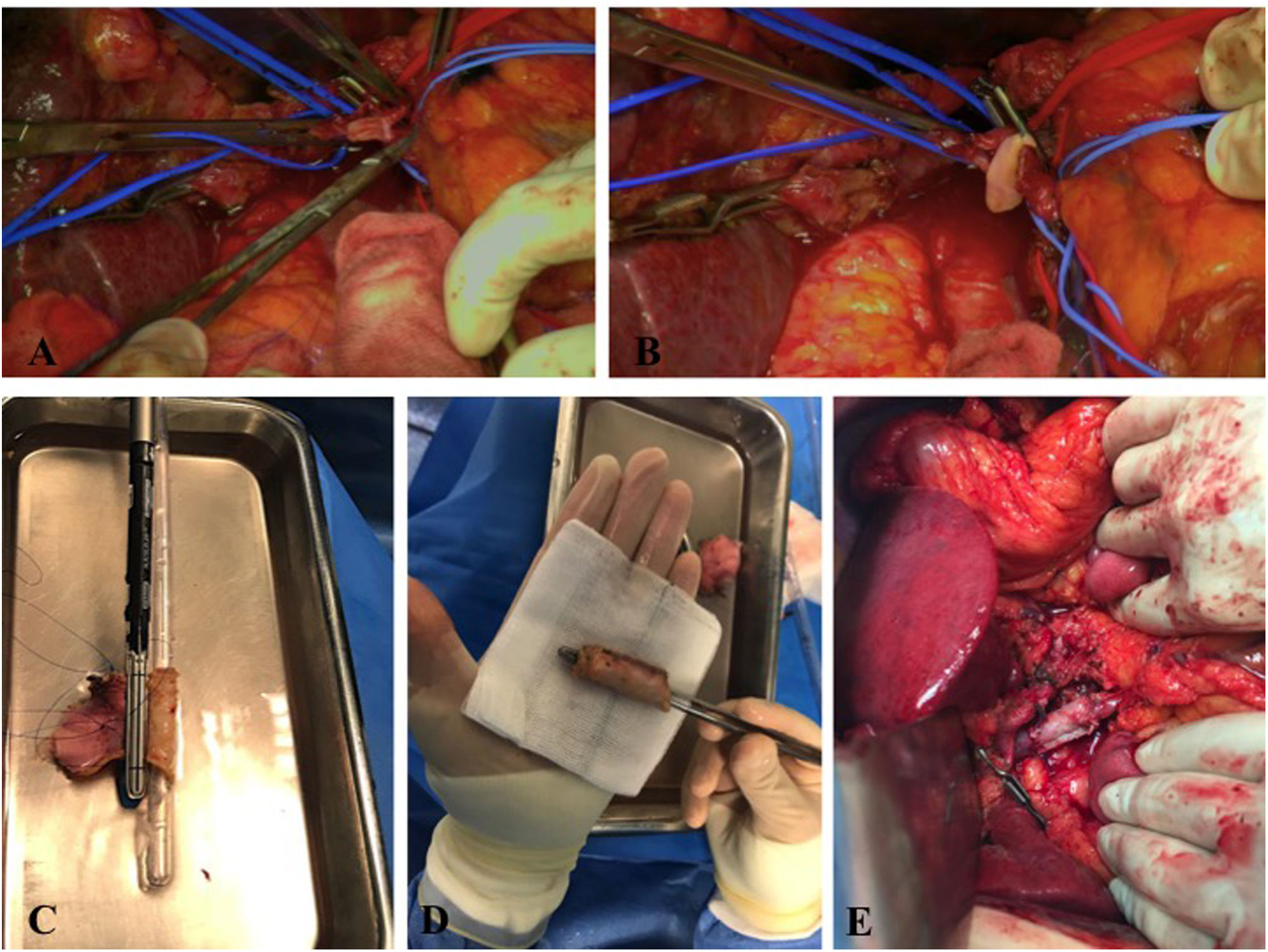
Figura 2.A: Imagen intraoperatoria. Vena porta seccionada en su porción lateral. B: Imagen intraoperatoria. Reconstrucción mediante patch de falciforme. C: Reconstrucción tipo 4. Confección mediante injerto autógeno de peritoneo mediante endograpadora lineal con carga vascular. D: Visión final de injerto autógeno confeccionado con peritoneo y vaina posterior del músculo recto anterior del abdomen. E: Imagen final de reconstrucción vascular tipo 4 con injerto autógeno mediante 2 suturas continuas semicirculares de prolene 4/0 y growth factor a la pared del vaso.
(0.39MB). - •
Tipo 2: Resección parcial y reconstrucción mediante patch para evitar una anastomosis con tensión, acodada o torsionada. La reconstrucción con patch se realiza con una plastia lateral autógena de ligamento falciforme utilizando sutura continua de prolene 5/0 (fig. 2B).
- •
Tipo 3: Resección vascular completa/segmentaria y reconstrucción veno-venosa término-terminal. La anastomosis se realiza mediante una sutura continua de prolene 5/0 en la cara posterior y anterior, incorporando el factor de crecimiento o growth factor durante la misma. Se retiran las pinzas vasculares y se revisa la hemostasia. La ecografía intraoperatoria ayuda a evaluar la correcta permeabilidad de la anastomosis.
- •
Tipo 4: Resección vascular completa/segmentaria y reconstrucción mediante injerto con al menos 2 anastomosis. Este tipo de reconstrucción suele ser necesaria en resecciones mayores de 3cm7 y se han descrito múltiples opciones para la misma (vena renal, vena yugular interna, peritoneo y vaina posterior del músculo recto del abdomen, prótesis sintética). En nuestra serie se utiliza la vaina posterior del músculo recto anterior del abdomen. Se marca la cara peritoneal para que quede orientada hacia el interior del injerto, se introduce en una solución de glutaraldehído al 2,5% durante 5min para endurecer el injerto y se aclara en suero fisiológico durante 2min. Para la confección del injerto tubular, se usa una sonda rectal (CH 32) de un calibre similar al del vaso a reconstruir y se sutura lateralmente con una endograpadora lineal (fig. 2C y D). Finalmente, se realiza la anastomosis con 2 suturas continuas de prolene 4/0 (fig. 2E).
Las consideraciones técnicas a tener cuenta son las siguientes:
- A)
Conocimiento exhaustivo del sistema venoso portal y variantes. Para facilitar el reconocimiento anatómico de las estructuras, el sistema venoso hepatopancreatobiliar se puede dividir en 5 zonas: 1) hilio hepático; 2) ligamento hepatoduodenal; 3) confluencia vena esplénica/VP; 4) VMS infrapancreática y su confluencia, y 5) vena esplénica.
- B)
El uso de injertos autógenos o sintéticos como el politetrafluoroetileno se puede reservar para resecciones completas venosas en las que la reconstrucción vascular no puede realizarse sin tensión.
- C)
Maniobras como la liberación de retractores y la movilización del hígado de sus inserciones diafragmáticas pueden facilitar la realización de una anastomosis sin tensión.
- D)
La reconstrucción venosa debe asegurar un calibre adecuado y sin torsiones.
- E)
El tiempo total de exclusión vascular y reanastomosis debería ser menor de 20min8.
- c)
Fase reconstructiva visceral
Se finaliza la intervención con la realización de las anastomosis según técnica de Child en un solo asa:
- 1.
Anastomosis pancreatoyeyunal ducto-mucosa con sutura continua barbada 3/0 y ducto-mucosa con tutor perdido con PDS® 5/0 puntos sueltos. En caso de no apreciarse el conducto de Wirsung se realiza una anastomosis pancreatogástrica con una doble corona de sutura barbada 3/0.
- 2.
Anastomosis hepaticoyeyunal con PDS® 4/0 puntos sueltos o, en caso de que el diámetro de la vía biliar sea mayor de 1cm, se realiza sutura continua con Stratafix™ 3/0.
- 3.
Anastomosis gastroentérica con puntos sueltos de Vicryl® 3/0.
Todos los pacientes fueron extubados en quirófano e ingresaron en la Unidad de Reanimación. Se retira la sonda nasogástrica al día siguiente, iniciándose tolerancia a dieta líquida progresiva y la movilización del paciente.
En caso de estabilidad hemodinámica se traslada al paciente a planta convencional de Cirugía General. Por protocolo se dejan 2 drenajes abdominales (a nivel de anastomosis pancreatoyeyunal y hepaticoyeyunal), por los que se analizan las amilasas los días 1, 3 y 5 postoperatorios. En caso de débitos<300cc en 24h y amilasas<150U/L, los drenajes se retiran desde el primer día postoperatorio. Todos los pacientes reciben de forma profiláctica heparina de bajo peso molecular.
Análisis de variablesSe analiza el tipo de intervención quirúrgica y la reconstrucción vascular. Desde el punto de vista postoperatorio se analiza la morbilidad postoperatoria según la clasificación de Clavien-Dindo y la mortalidad postoperatoria a los 30 y 90 días. Desde el punto de vista patológico se analiza el y/pTNM, la radicalidad de la resección (R0/R1) y la afectación de los márgenes pancreáticos, retroperitoneal, vascular y circunferencial, según el protocolo propuesto por Verbeke y Gladhaug9.
Finalmente, se analiza el tipo de recidiva, la supervivencia libre de enfermedad y la supervivencia global.
Análisis estadísticosLos datos categóricos se expresan como frecuencias y porcentajes, y los datos cuantitativos como media y desviación estándar. El análisis de supervivencia se evaluó con el método de Kaplan-Meier. Los análisis se llevaron a cabo utilizando el SPSS® versión 15.0 para Windows.
ResultadosDesde septiembre de 2003 hasta enero de 2021 se intervinieron de forma electiva 41 pacientes (19M/22H) en el Hospital Universitario Germans Trias i Pujol (2017-2021) y en el Hospital Universitario Mútua Terrassa (2003-2021).
Más de la mitad de los pacientes (58%) se intervinieron entre 2017 y 2021.
Desde septiembre de 2003 hasta enero de 2021 se realizaron 520 resecciones pancreáticas, de las cuales en 41 ocasiones hubo que asociar resección y reconstrucción vascular. En los últimos 4 años se han intervenido 24 pacientes (58% del total). La mediana de edad de los pacientes fue de 62 años (39-81) y el IMC de 25 (19-33). El 66% de los pacientes (27/41) fueron clasificados como ASA II, un paciente fue ASA I y 13 ASA III. El 93% de los casos (38/41) fueron tumores de cabeza pancreática, mientras que los 3 casos restantes fueron: uno de cola, uno de cuerpo de páncreas y un colangiocarcinoma localizado en colédoco distal.
Fueron considerados resecables 28 casos (68%) y 13 (32%) fueron clasificados como borderline resecables. De estos 13 pacientes, 11 presentaron histología positiva, por lo que se efectuó quimioterapia/radioterapia neoadyuvante, siendo el esquema FOLFIRINOX el más utilizado (tabla 1). Se colocó prótesis biliar en 12 pacientes de la serie, en 11 mediante colangiografía pancreática retrógrada endoscópica y en un caso por colangiografía transparietohepática.
Características clínicas y diagnóstico
| Sexo (mujeres/hombres) | |
| 19/22 | |
| Edad (años), mediana (rango) | |
| 62 (39-81) | |
| IMC, mediana (rango) | |
| 25 (19-33) | |
| ASA, n (%) | |
| I | 1 (2) |
| II | 27 (66) |
| III | 13 (32) |
| Drenaje biliar, n (%) | |
| Sí | 12 (30) |
| No | 29 (70) |
| Método colocación de prótesis, n (%) | |
| CPRE | 11 (92) |
| CTPH | 1 (8) |
| Tipo de prótesis, n (%) | |
| Plástica | 4 (33) |
| Metálica no cubierta | 6 (50) |
| Metálica cubierta | 2 (17) |
| Ca 19.9, mediana (rango) | |
| 186 (4-18.680) | |
| Localización tumoral, n (%) | |
| Cabeza páncreas | 38 (93) |
| Cuerpo páncreas | 1 (2,3) |
| Cola páncreas | 1 (2,3) |
| Colédoco distal | 1 (2,3) |
| Diagnóstico TC preoperatoria, n (%) | |
| Resecable | 28 (68) |
| Borderline | 13 (32) |
| QT/RT neoadyuvante, n (%) | |
| Sí | 11 (27) |
| No | 30 (73) |
| Tipo QT neoadyuvante, n (%) | |
| FOLFIRINOX | 6 (55) |
| Gemcitabina+paclitaxel | 4 (36) |
| Estreptozocina+5FU+doxorrubicina | 1 (9) |
ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists; CPRE: colangiografía pancreática retrógrada endoscópica; CTPH: colangiografía transparietohepática; IMC: índice de masa corporal; QT: quimioterapia; RT: radioterapia; TC: tomografía computarizada; 5FU: 5-fluorouracilo.
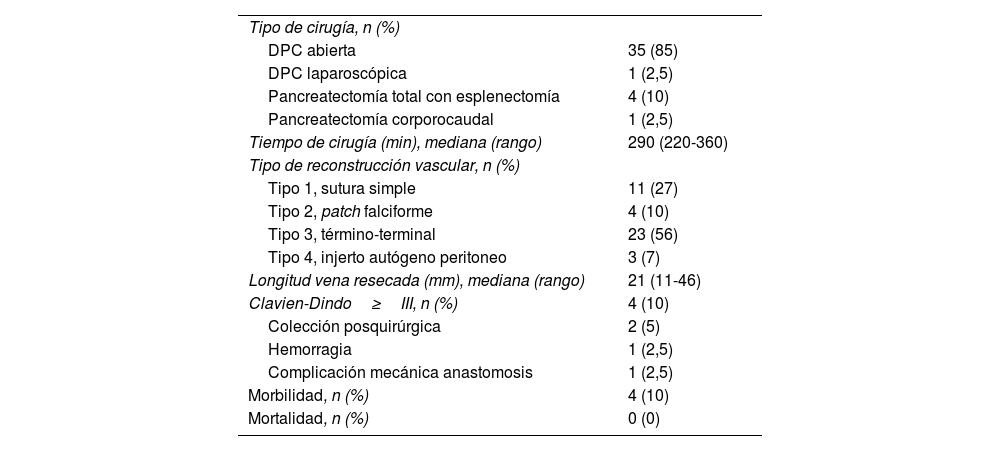
La técnica quirúrgica más realizada fue la duodenopancreatectomía cefálica (DPC) tipo Whipple, en 35 de 41 pacientes (85%).
La reconstrucción vascular tipo 1 se realizó en 11 pacientes (27%), la tipo 2 mediante patch de falciforme en 4 casos (10%), la tipo 3 en 23 casos (56%) y la reconstrucción tipo 4 mediante injerto autógeno en 3 casos (7%). La longitud media del segmento venoso resecado fue de 21mm (11-46) y el tiempo quirúrgico medio fue de 290min (220-360) (tabla 2).
Procedimiento quirúrgico y morbilidad
| Tipo de cirugía, n (%) | |
| DPC abierta | 35 (85) |
| DPC laparoscópica | 1 (2,5) |
| Pancreatectomía total con esplenectomía | 4 (10) |
| Pancreatectomía corporocaudal | 1 (2,5) |
| Tiempo de cirugía (min), mediana (rango) | 290 (220-360) |
| Tipo de reconstrucción vascular, n (%) | |
| Tipo 1, sutura simple | 11 (27) |
| Tipo 2, patch falciforme | 4 (10) |
| Tipo 3, término-terminal | 23 (56) |
| Tipo 4, injerto autógeno peritoneo | 3 (7) |
| Longitud vena resecada (mm), mediana (rango) | 21 (11-46) |
| Clavien-Dindo≥III, n (%) | 4 (10) |
| Colección posquirúrgica | 2 (5) |
| Hemorragia | 1 (2,5) |
| Complicación mecánica anastomosis | 1 (2,5) |
| Morbilidad, n (%) | 4 (10) |
| Mortalidad, n (%) | 0 (0) |
DPC: duodenopancreatectomía cefálica.
De los 41 pacientes, 3 presentaron fístula pancreática grado A (7%) y 2 grado B (5%). En 4 pacientes (10%) hubo morbilidad Clavien-Dindo>3: 2 pacientes presentaron una colección retrogástrica y requirieron de drenaje percutáneo, y 2 pacientes fueron reintervenidos, uno por sangrado a nivel de la cava que se solucionó con una sutura simple, y otro en el que, tras un íleo paralítico prolongado, se objetivaron en TC signos compatibles con torsión de la anastomosis gastroentérica, por lo que se reintervino y se realizó una nueva anastomosis y reconstrucción en Y de Roux.
No hubo ningún caso de mortalidad postoperatoria a los 30 y 90 días. Se describieron 2 casos (5%) de trombosis venosa por recidiva tumoral y un caso (2%) de estenosis portal focal asintomática en TC de control.
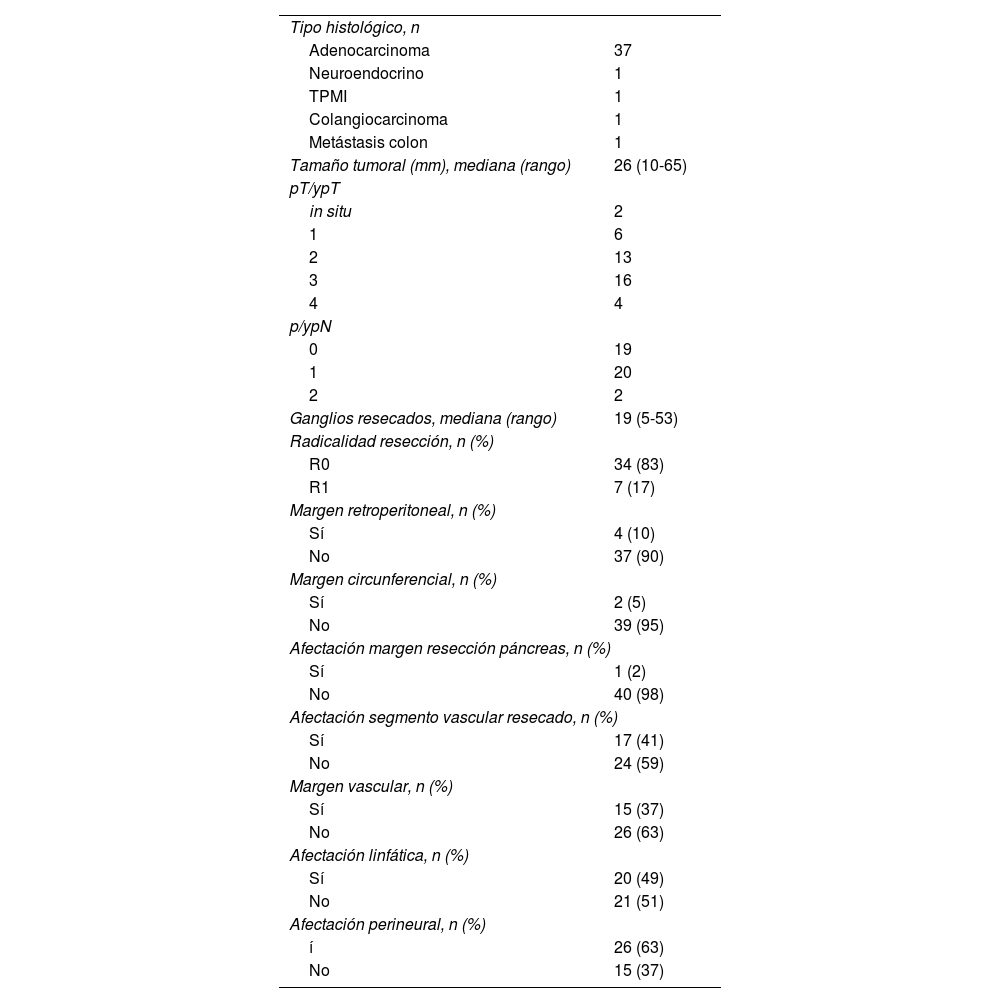
En cuanto al análisis histológico, el 90% (37/41) fueron adenocarcinomas de páncreas. El tamaño medio tumoral fue de 26mm (10-65), el 83% se consideraron R0 y hubo afectación en el tramo vascular resecado en 17 casos (41%) (tabla 3). La supervivencia media fue de 29 meses y la supervivencia libre de enfermedad de 28 meses (tabla 4).
Resultados histopatológicos
| Tipo histológico, n | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 37 |
| Neuroendocrino | 1 |
| TPMI | 1 |
| Colangiocarcinoma | 1 |
| Metástasis colon | 1 |
| Tamaño tumoral (mm), mediana (rango) | 26 (10-65) |
| pT/ypT | |
| in situ | 2 |
| 1 | 6 |
| 2 | 13 |
| 3 | 16 |
| 4 | 4 |
| p/ypN | |
| 0 | 19 |
| 1 | 20 |
| 2 | 2 |
| Ganglios resecados, mediana (rango) | 19 (5-53) |
| Radicalidad resección, n (%) | |
| R0 | 34 (83) |
| R1 | 7 (17) |
| Margen retroperitoneal, n (%) | |
| Sí | 4 (10) |
| No | 37 (90) |
| Margen circunferencial, n (%) | |
| Sí | 2 (5) |
| No | 39 (95) |
| Afectación margen resección páncreas, n (%) | |
| Sí | 1 (2) |
| No | 40 (98) |
| Afectación segmento vascular resecado, n (%) | |
| Sí | 17 (41) |
| No | 24 (59) |
| Margen vascular, n (%) | |
| Sí | 15 (37) |
| No | 26 (63) |
| Afectación linfática, n (%) | |
| Sí | 20 (49) |
| No | 21 (51) |
| Afectación perineural, n (%) | |
| í | 26 (63) |
| No | 15 (37) |
TPMI: tumor papilar mucinoso intraductal.
Seguimiento y supervivencia
| Recidiva, n (%) | |
| Sí | 28 (70) |
| No | 9 (22) |
| N/S | 4 (8) |
| Tipo recidiva, n | |
| Local | 16 |
| M1 hepáticas | 12 |
| M1 pulmonares | 3 |
| Carcinomatosis | 1 |
| Seguimiento (meses), mediana (rango) | 24 (9-55) |
| Supervivencia libre de enfermedad (meses), mediana (rango) | 28 (4-71) |
| Supervivencia global (meses), mediana (rango) | 29 (6-138) |
| Exitus, n (%) | |
| Sí | 25 (61) |
| No | 16 (39) |
N/S: no sabe.
Desde que Moore et al. reportaron el primer caso en 19513, la resección de VP/VMS ha sido aplicada para el tratamiento del cáncer pancreático. En el caso del cáncer de páncreas borderline, la actitud terapéutica, siguiendo las guías del National Comprehensive Cancer Network5, debe incluir el tratamiento neoadyuvante con quimioterapia. El grupo de Mellon et al.10 describió una tasa media de supervivencia de 33,5 meses en pacientes intervenidos que recibieron quimioterapia previa frente a los 23,1 meses de los pacientes que recibieron únicamente adyuvancia.
Esta estrategia clínica, combinada con el desarrollo y mejoría de las técnicas de imagen, la optimización de la técnica quirúrgica y la prehabilitación a la cirugía, ha permitido la realización de técnicas y abordajes quirúrgicos intensivos, ofreciendo así una resección curativa a pacientes inicialmente no tributarios de cirugía.
Así, varios autores han descrito tasas de supervivencia tras la DPC con resección vascular similares a las de la DPC convencional, sin observar un aumento en la morbilidad en centros experimentados11,12. En nuestra serie se observan supervivencias del 20% a 5 años, acorde con lo esperado13,14.
El metaanálisis publicado por Zhou et al.1, con 2.247 pacientes incluidos, concluye que no hay diferencias en la morbimortalidad ni en la supervivencia a los 5 años en pacientes con resección de VP en comparación con los que no se sometieron a resección venosa. Tseng et al.15, del MD Anderson Center, no encontraron diferencias en la tasa de supervivencia entre los 2 grupos, y el grupo de Yekebas16 describió tasas de morbimortalidad postoperatoria similares entre ambos grupos.
En nuestra serie, más de la mitad de los casos corresponden a pacientes intervenidos en los últimos 4 años, lo que demuestra que una actitud quirúrgica más agresiva permite rescatar pacientes que antes no se operaban o en los que se dejaba margen vascular afecto, empeorando así la supervivencia17. Asimismo, el documento de consenso publicado en 2014 por la International Study Group on Pancreatic Surgery18 indica que la evidencia científica hasta la fecha justifica la resección venosa en casos de cáncer pancreático, si bien recomienda que la realización de la cirugía sea en centros de referencia.
En 2015 Landi et al.19 publicaron una serie de 78 pacientes, de los cuales 10 requirieron resección de vena mesentérica superior por afectación tumoral. La tasa de complicaciones en el grupo de resección venosa fue significativamente inferior a la de la DPC estándar (63 vs. 30%; p=0,04), reportando 9 casos con complicaciones Clavien-Dindo>3 en el grupo DPC estándar (p=0,115). En nuestra serie de 41 pacientes sometidos a resección vascular, describimos 4 pacientes con una morbilidad Clavien-Dindo>3. No obstante, consideramos que estos pacientes que reciben un tratamiento quirúrgico intensivo requieren de una vigilancia estrecha y de una actitud proactiva, para anticiparse a las posibles complicaciones y realizar el tratamiento oportuno de manera precoz.
Valorando los resultados de nuestra serie y los datos publicados con anterioridad, la afectación venosa aislada no es una contraindicación para la resección pancreática como parte de un abordaje multidisciplinario y multimodal del cáncer de páncreas localizado. La resección y reconstrucción vascular se puede realizar de forma segura y no afecta la supervivencia de los pacientes.
ConclusiónLas resecciones vasculares con reconstrucción deben asegurar los principios de la cirugía oncológica. Una gran variedad de abordajes quirúrgicos y de procedimientos vasculares se han descrito para asegurar la extirpación tumoral segura y exitosa. La cirugía del cáncer de páncreas asociada a resección vascular por afectación tumoral es una técnica segura y reproducible por cirujanos expertos. No obstante, un estudio y preparación preoperatoria exhaustiva, una correcta selección de pacientes, así como una adecuada disección anatómica y planificación de la estrategia de reconstrucción resultan fundamentales para el éxito de esta cirugía.
Conflicto de interesesLos autores declaran no tener ningún conflicto de intereses.