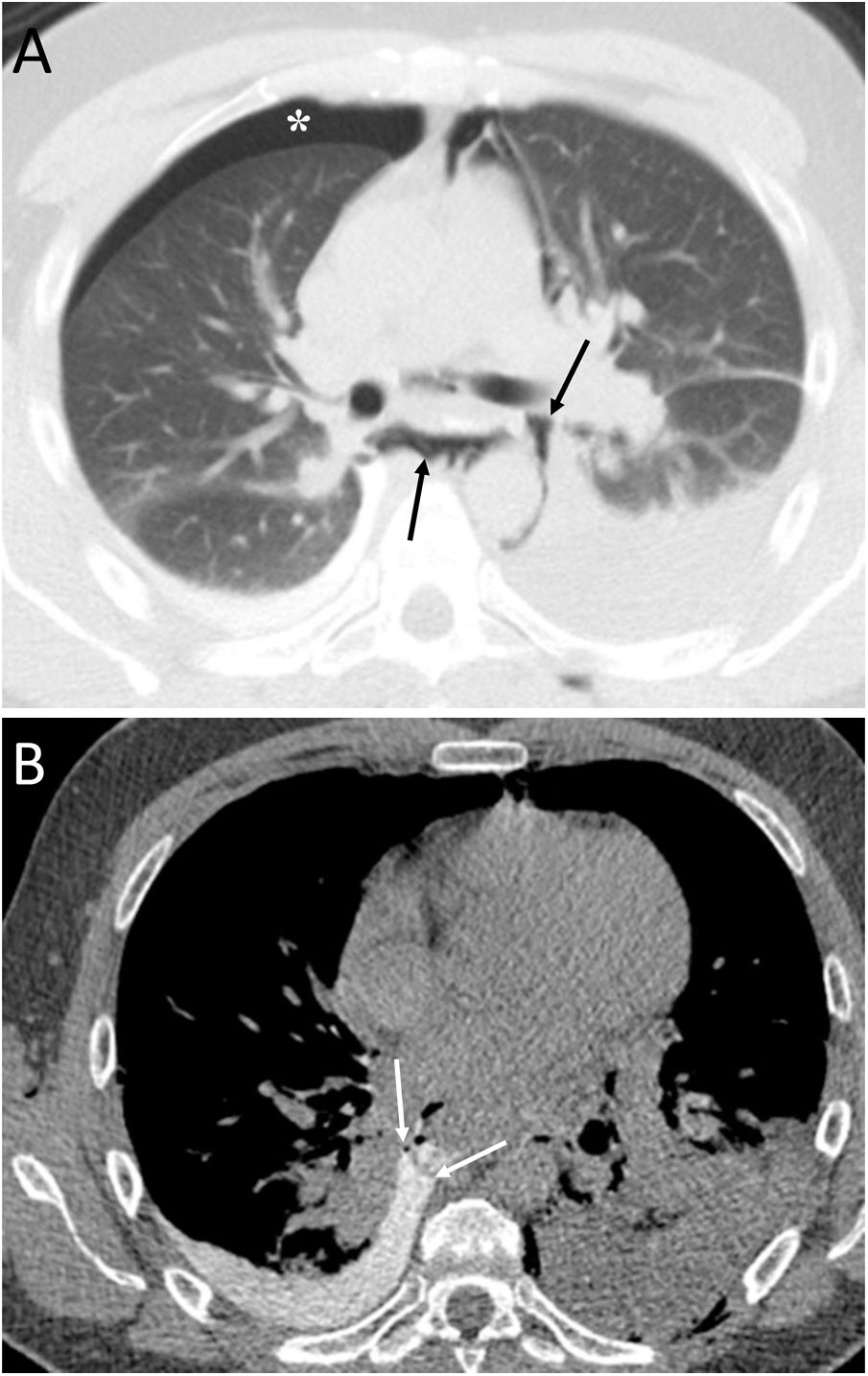
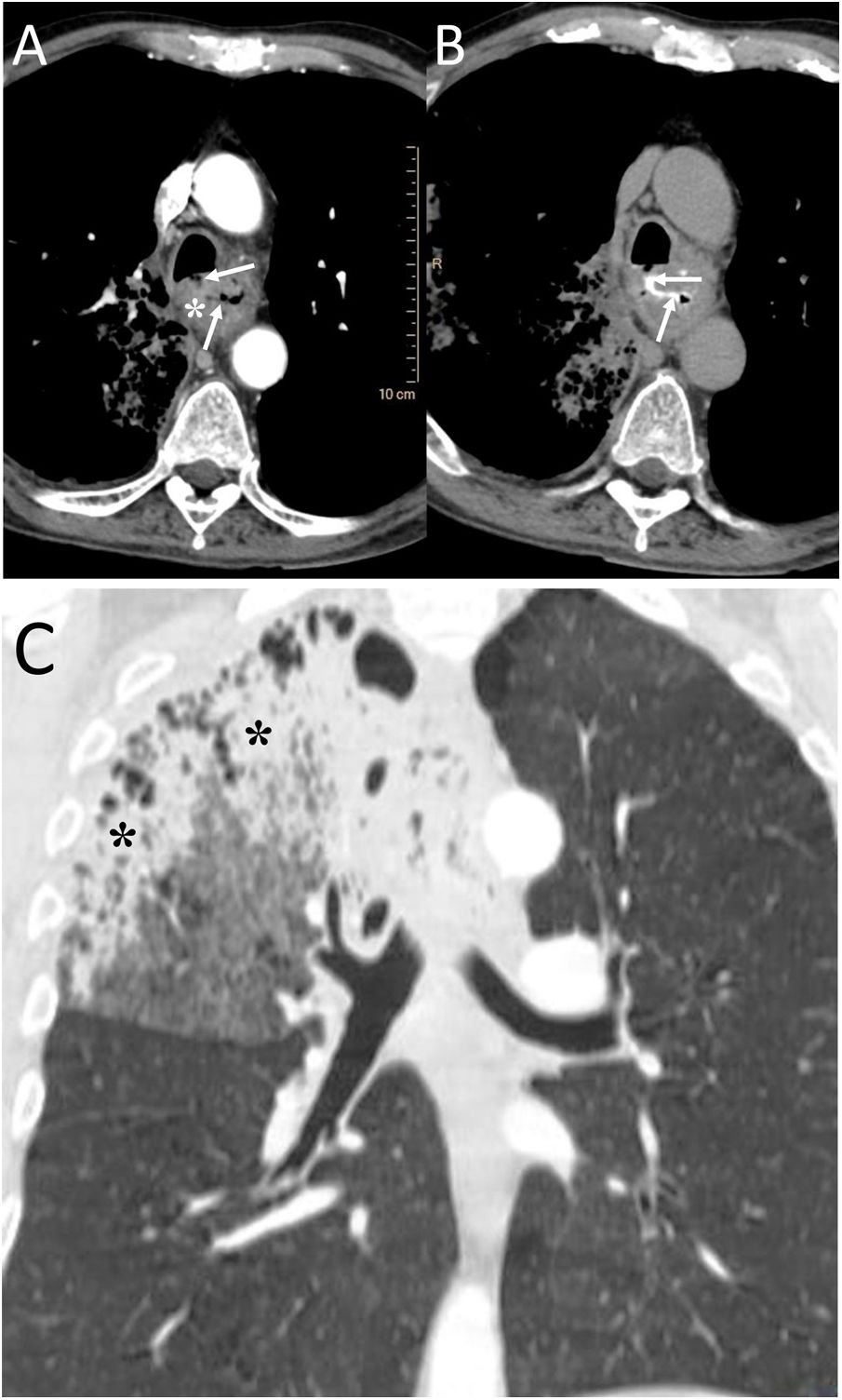
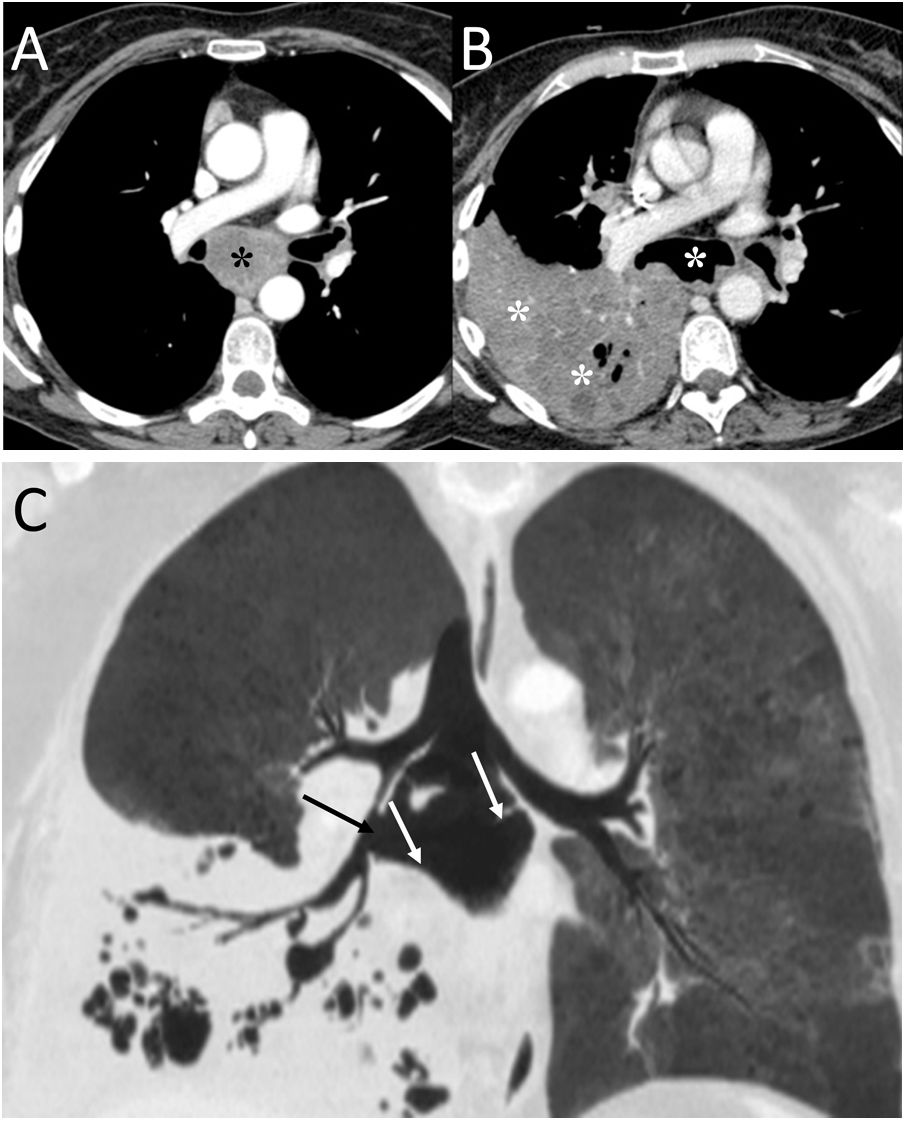
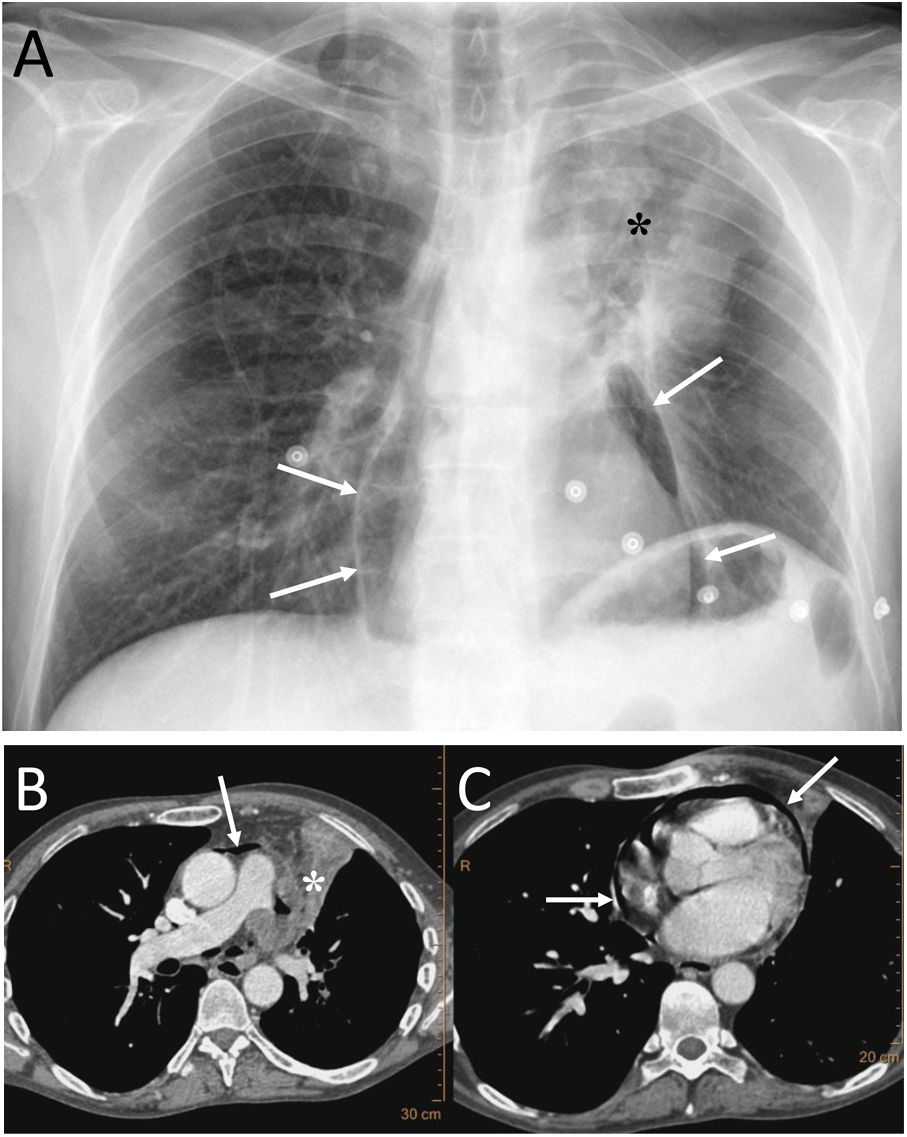
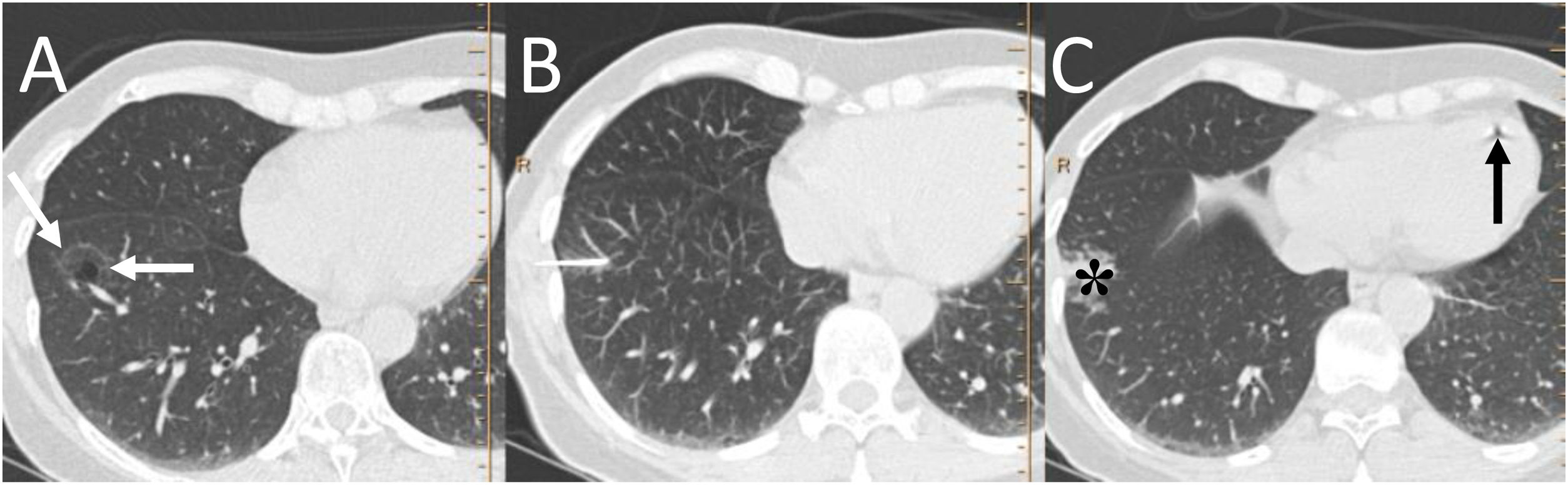
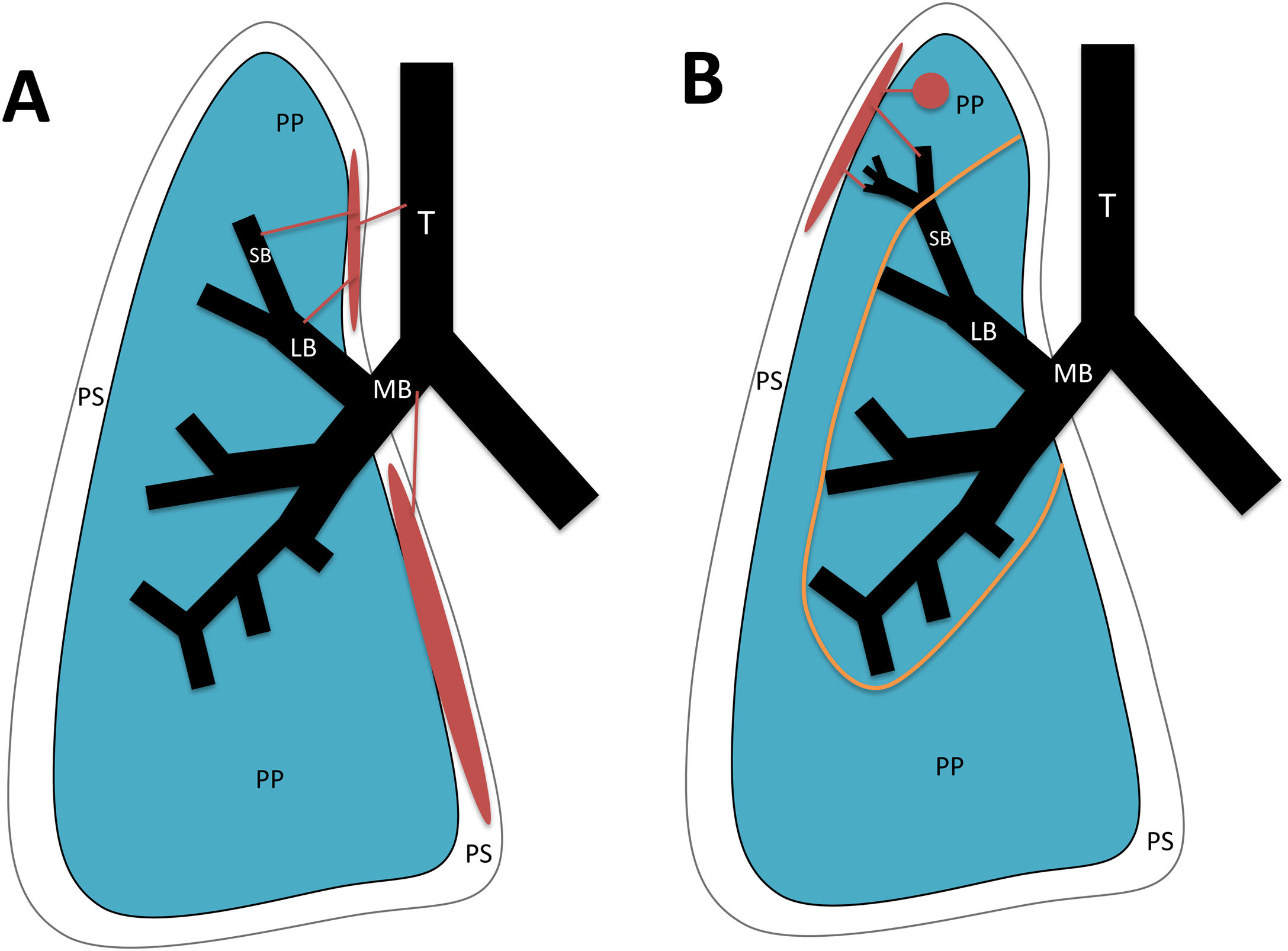
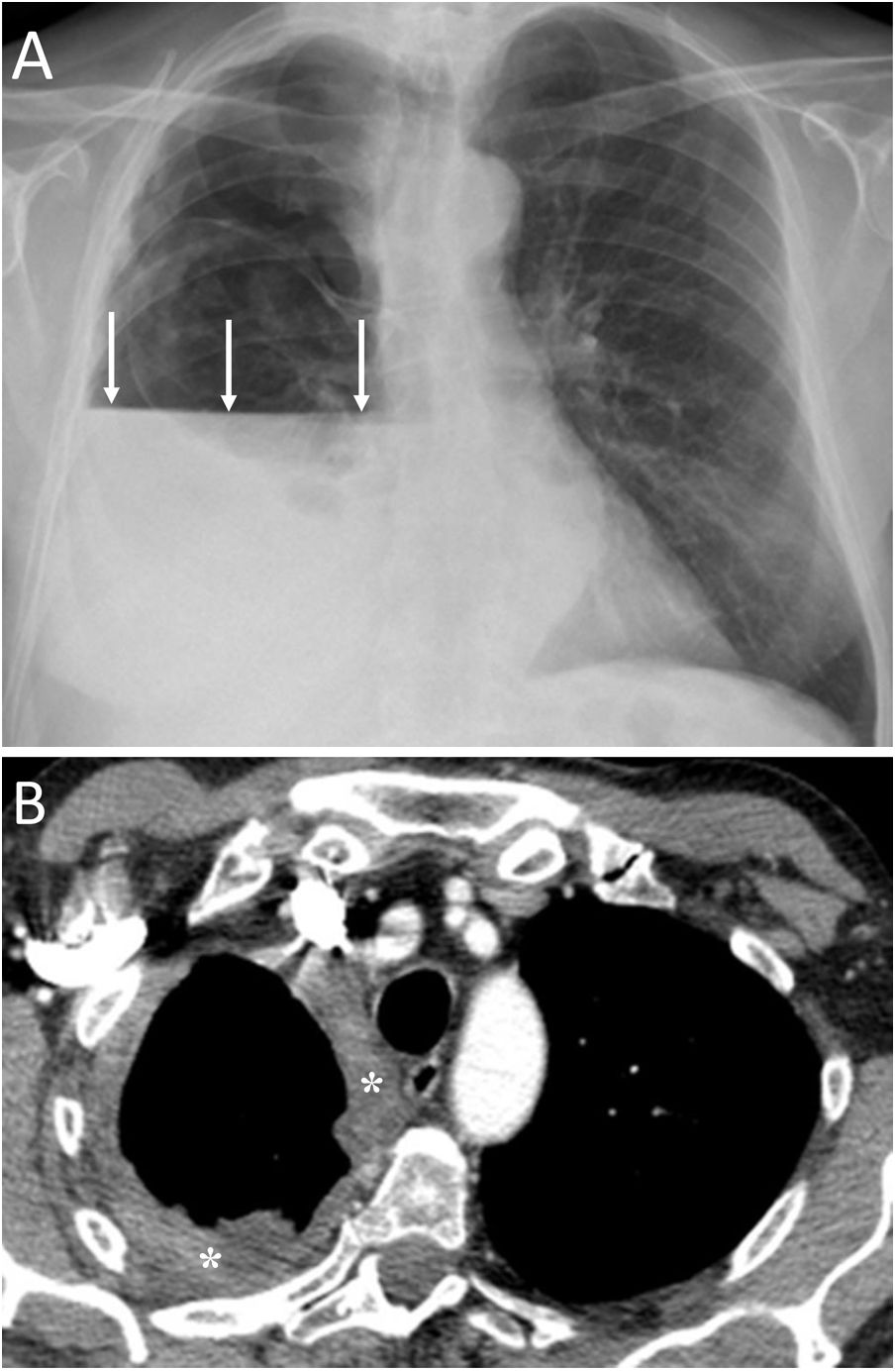
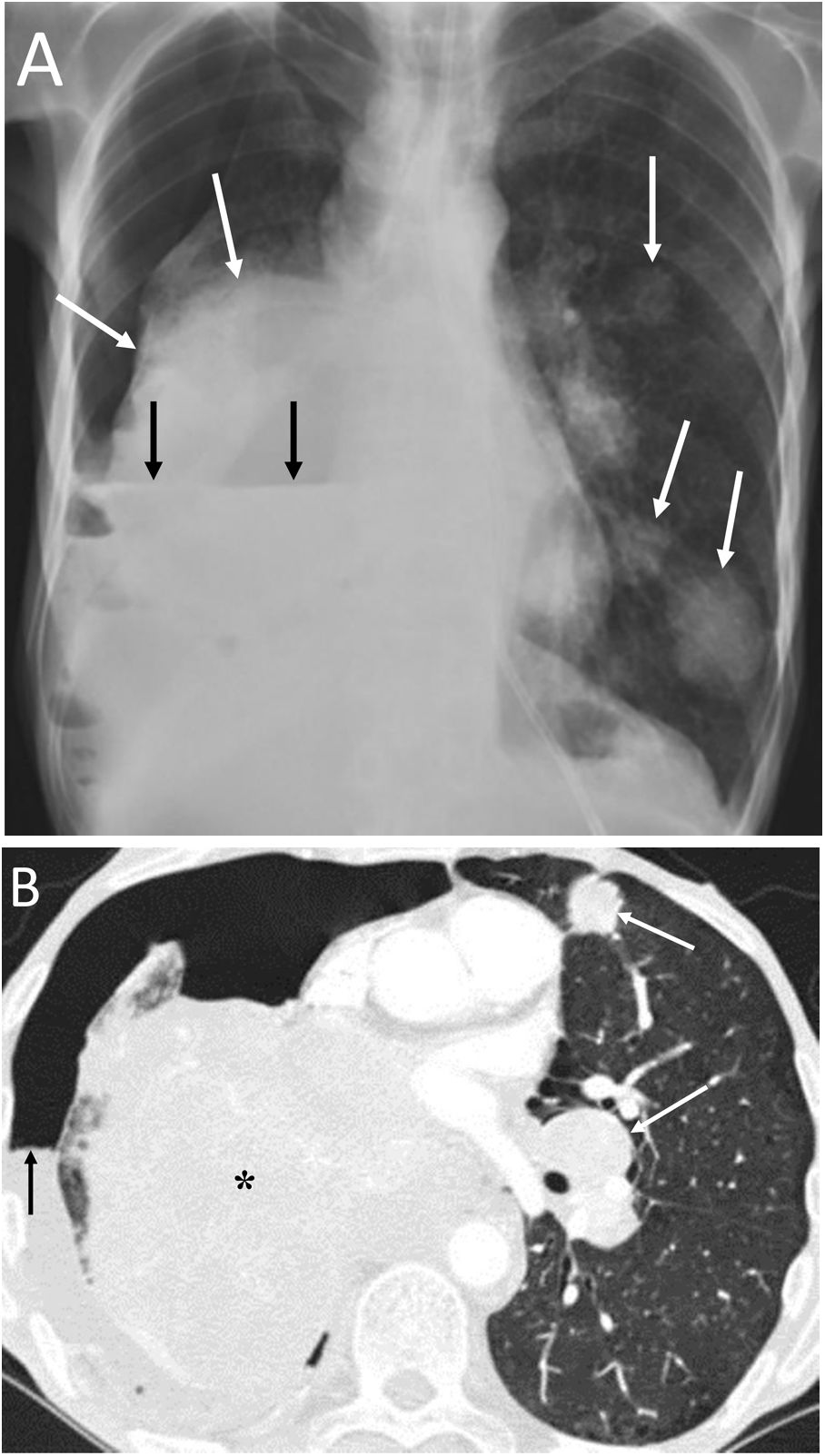
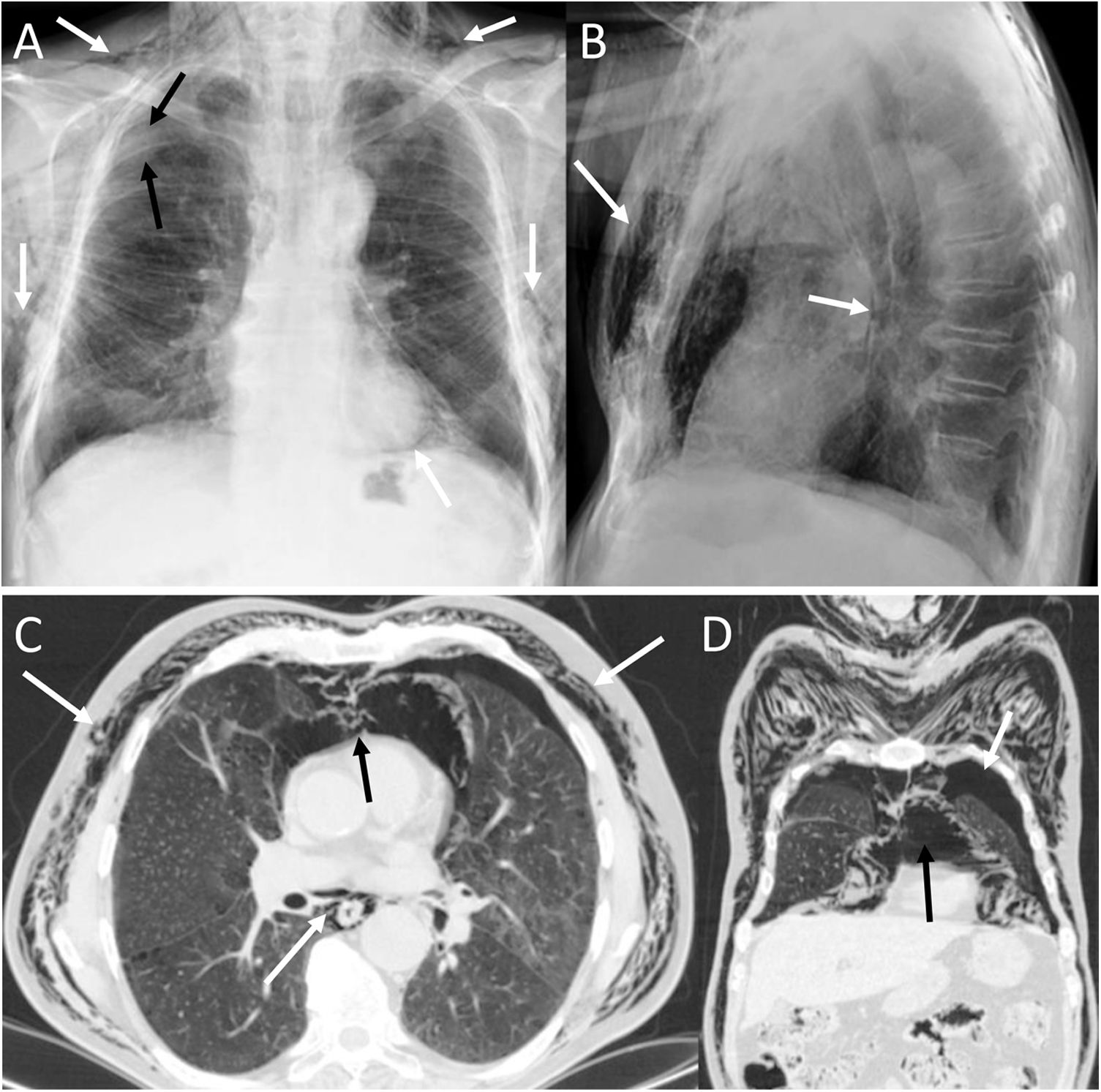
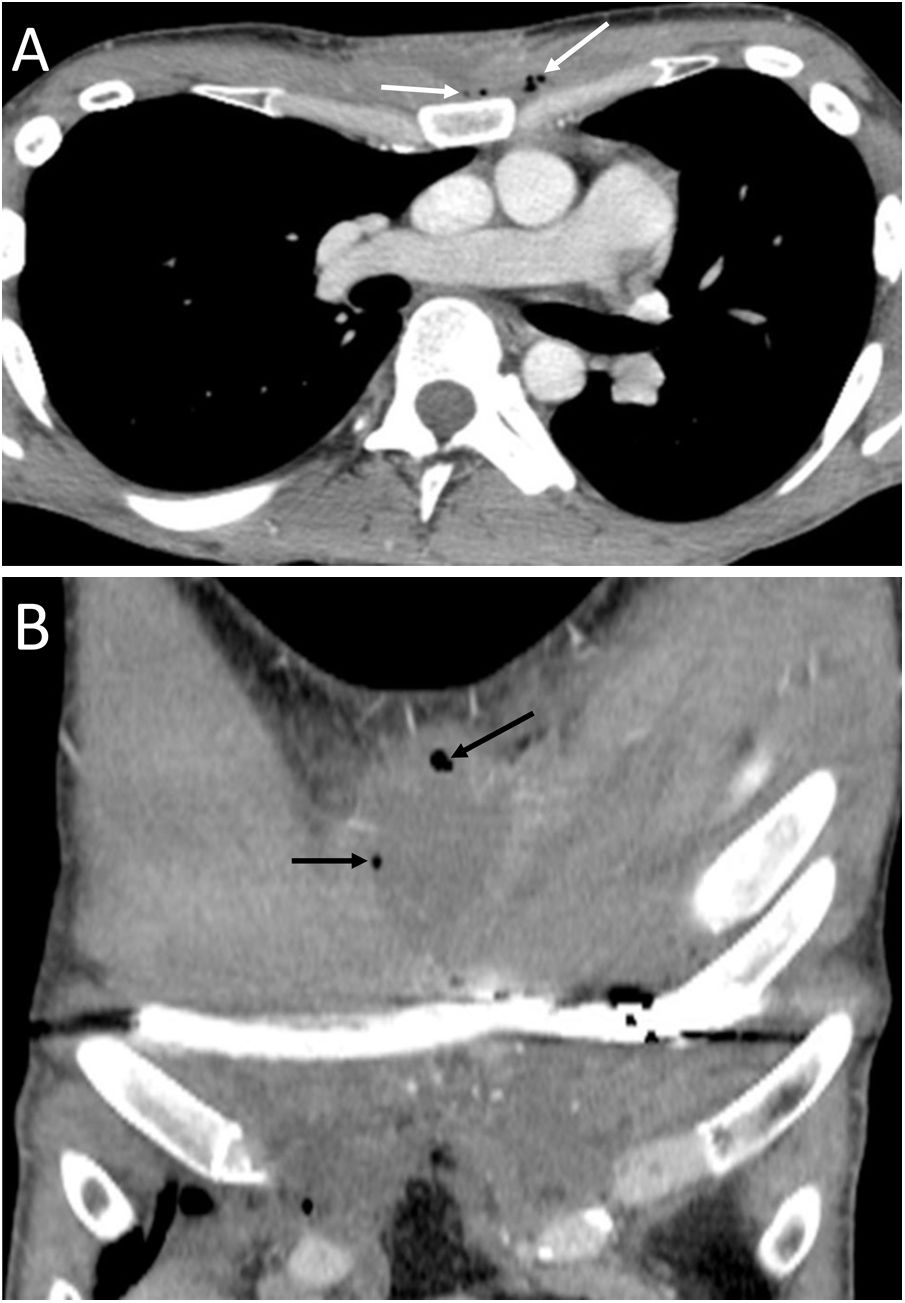
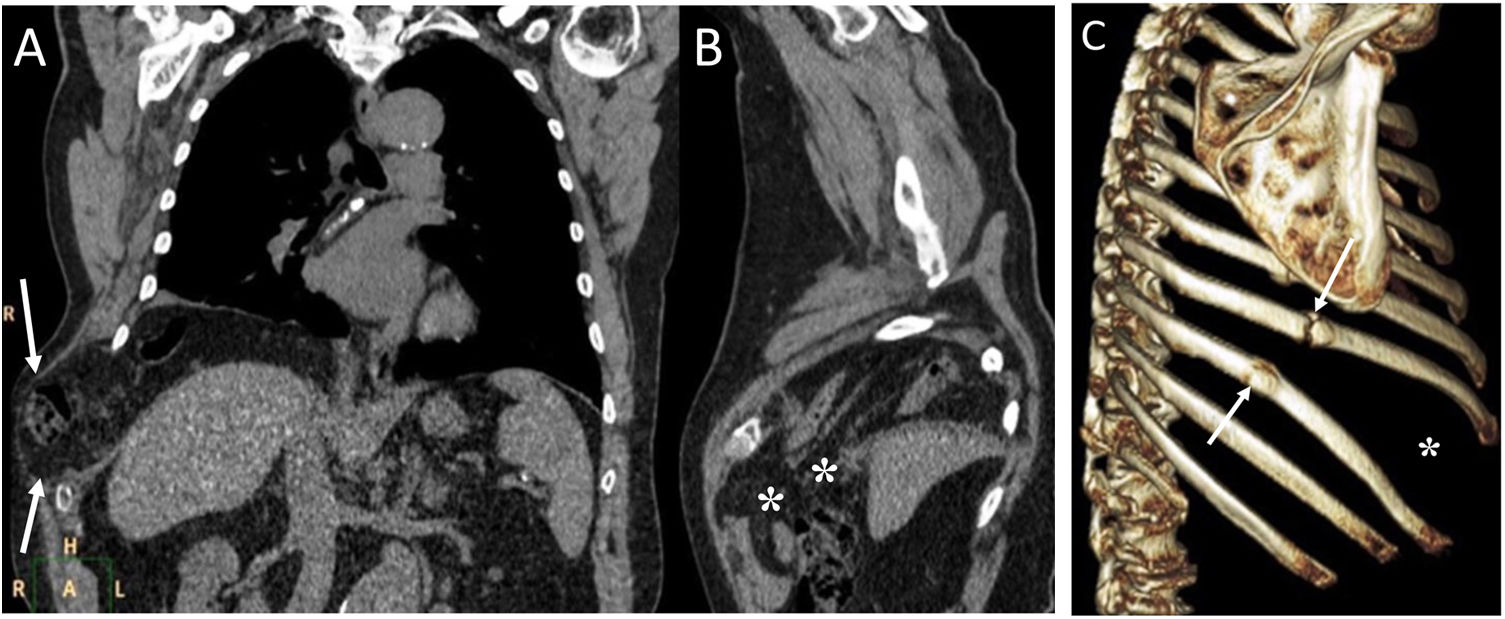
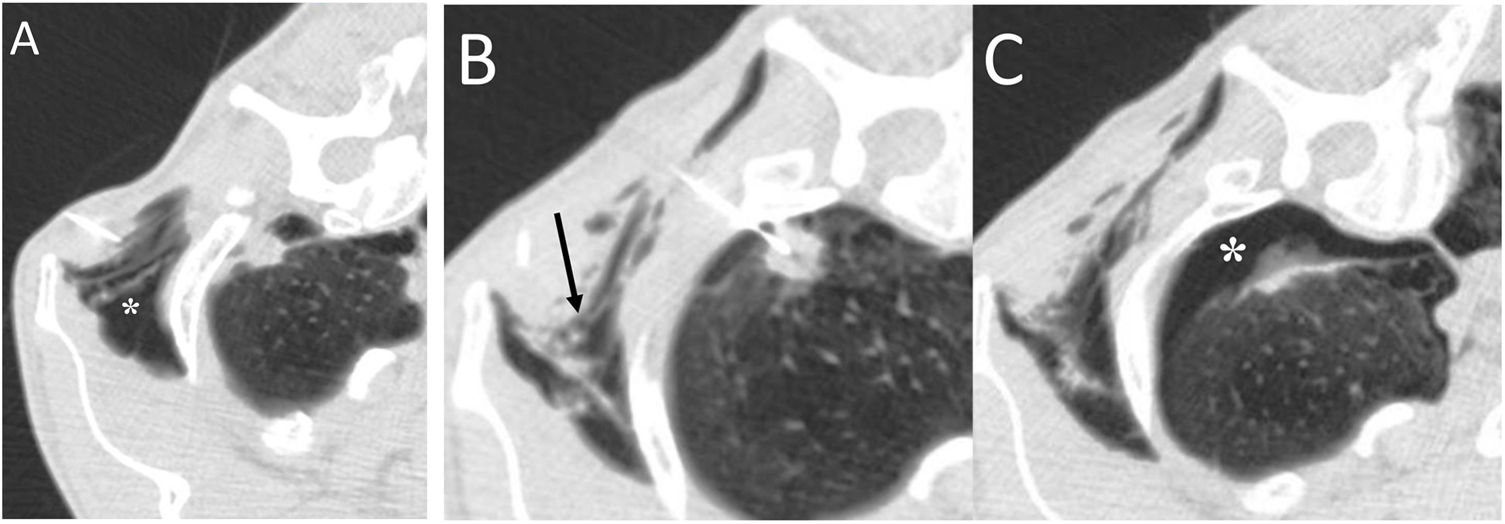
To describe the radiologic findings of extrapulmonary air in the chest and to review atypical and unusual causes of extrapulmonary air, emphasizing the importance of the diagnosis in managing these patients.
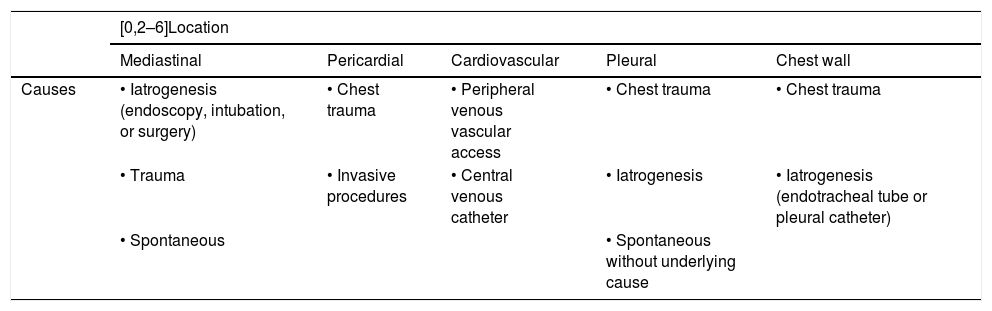
ConclusionIn this article, we review a series of cases collected at our center that manifest with extrapulmonary air in the thorax, paying special attention to atypical and uncommon causes. We discuss the causes of extrapulmonary according to its location: mediastinum (spontaneous pneumomediastinum with pneumorrhachis, tracheal rupture, dehiscence of the bronchial anastomosis after lung transplantation, intramucosal esophageal dissection, Boerhaave syndrome, tracheoesophageal fistula in patients with esophageal tumors, bronchial perforation and esophagorespiratory fistula due to lymph-node rupture, and acute mediastinitis), pericardium (pneumopericardium in patients with lung tumors), cardiovascular (venous air embolism), pleura (bronchopleural fistulas, spontaneous pneumothorax in patients with malignant pleural mesotheliomas and primary lung tumors, and bilateral pneumothorax after unilateral lung biopsy), and thoracic wall (infections, transdiaphragmatic intercostal hernia, and subcutaneous emphysema after lung biopsy).
Describir los hallazgos radiológicos y revisar las causas atípicas e inusuales de aire torácico extrapulmonar, incidiendo en la importancia del diagnóstico para el manejo de estos pacientes.
ConclusiónEn este artículo revisaremos una serie de casos recogidos en nuestro centro que se manifiestan como aire torácico extrapulmonar, con especial atención a las causas atípicas e infrecuentes. Según su localización anatómica, las clasificaremos en: localización mediastínica (neumomediastino espontáneo con neumorraquis, rotura traqueal, dehiscencia de sutura bronquial en trasplante pulmonar, disección intramucosa esofágica, síndrome de Boerhaave, fístula traqueoesofágica en neoplasia esofágica, perforación bronquial y fístula esofagorrespiratoria por rotura de ganglio linfático, y mediastinitis aguda), localización pericárdica (neumopericardio en neoplasia pulmonar), localización cardiovascular (embolia venosa aérea), localización pleural (fístulas broncopleurales, neumotórax espontáneo en mesotelioma pleural maligno y neoplasia pulmonar primaria, y neumotórax bilateral posbiopsia pulmonar unilateral) y localización en pared torácica (infecciones, hernia intercostal transdiafragmática y enfisema subcutáneo posbiopsia pulmonar).