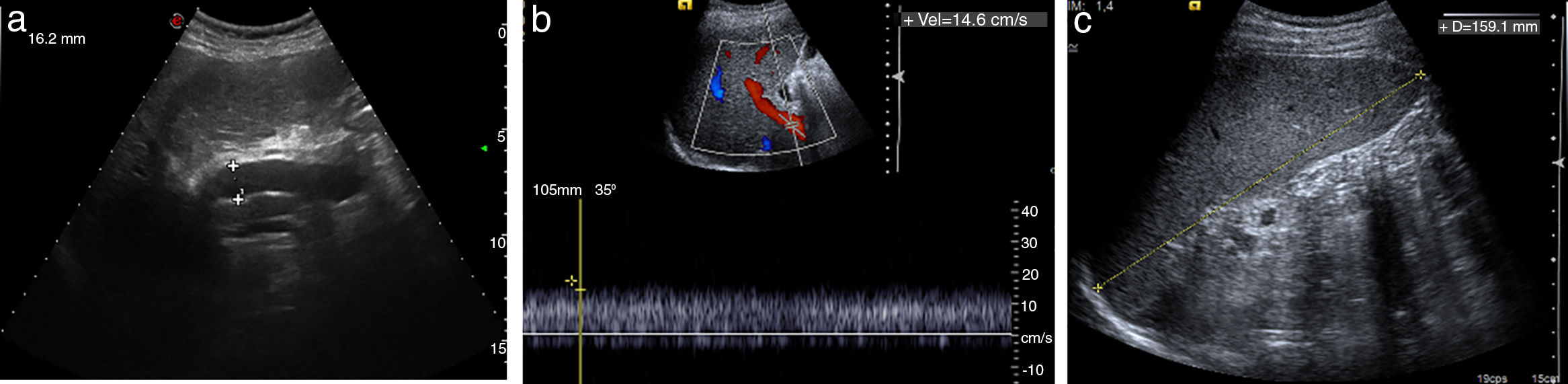
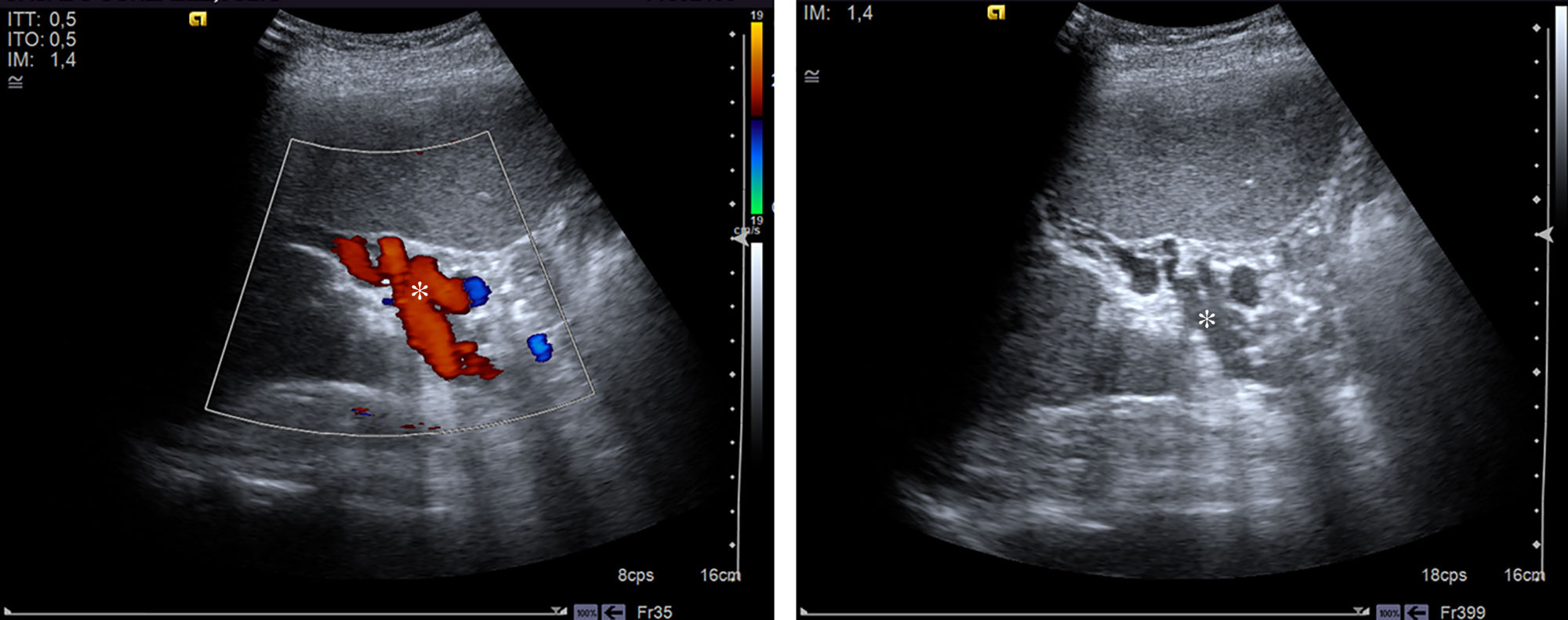
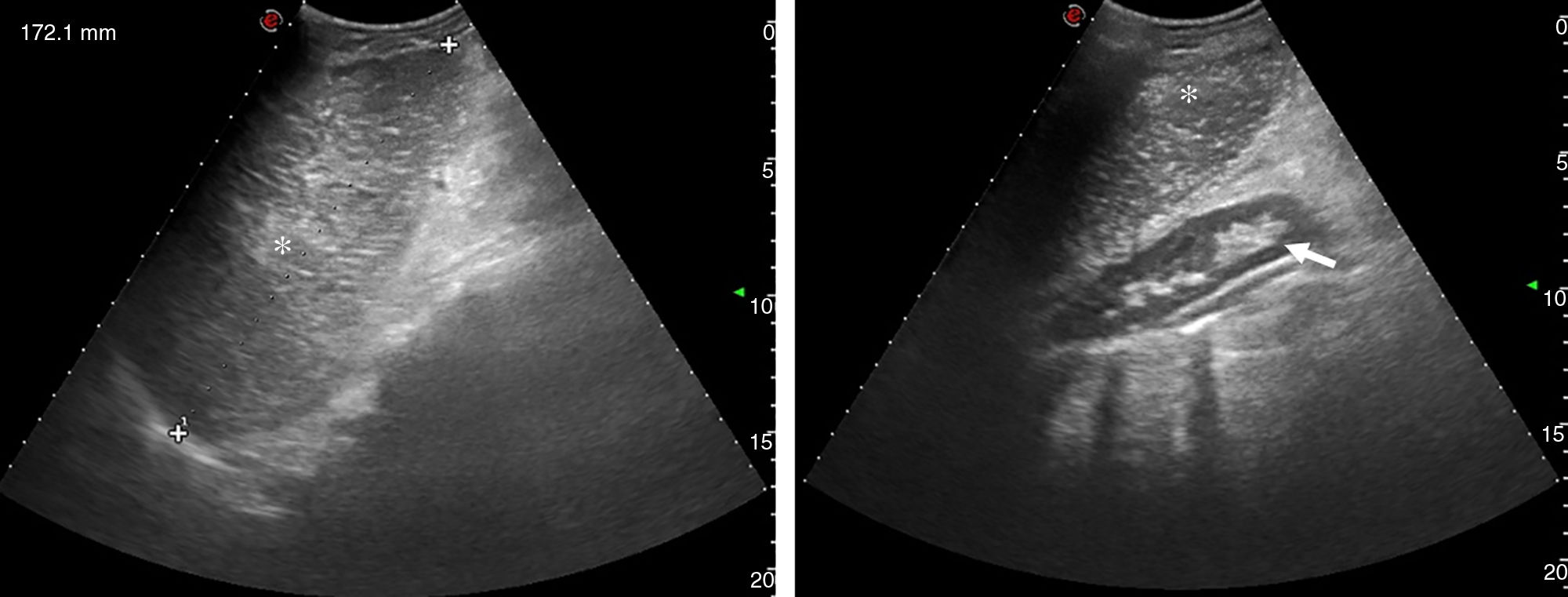
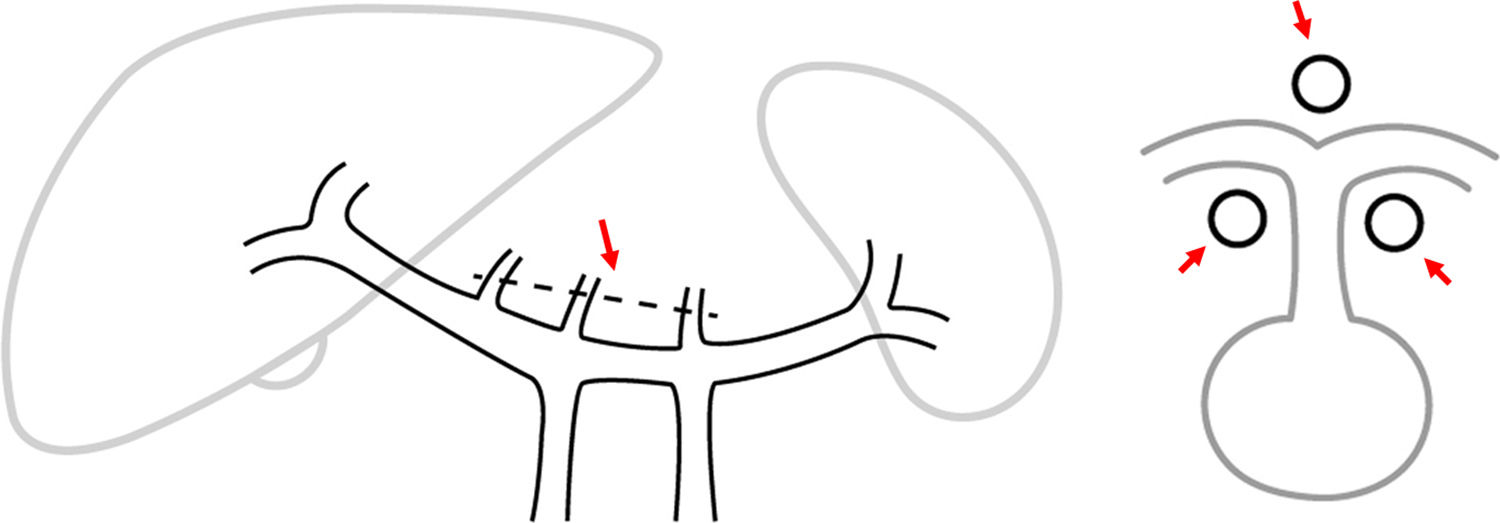
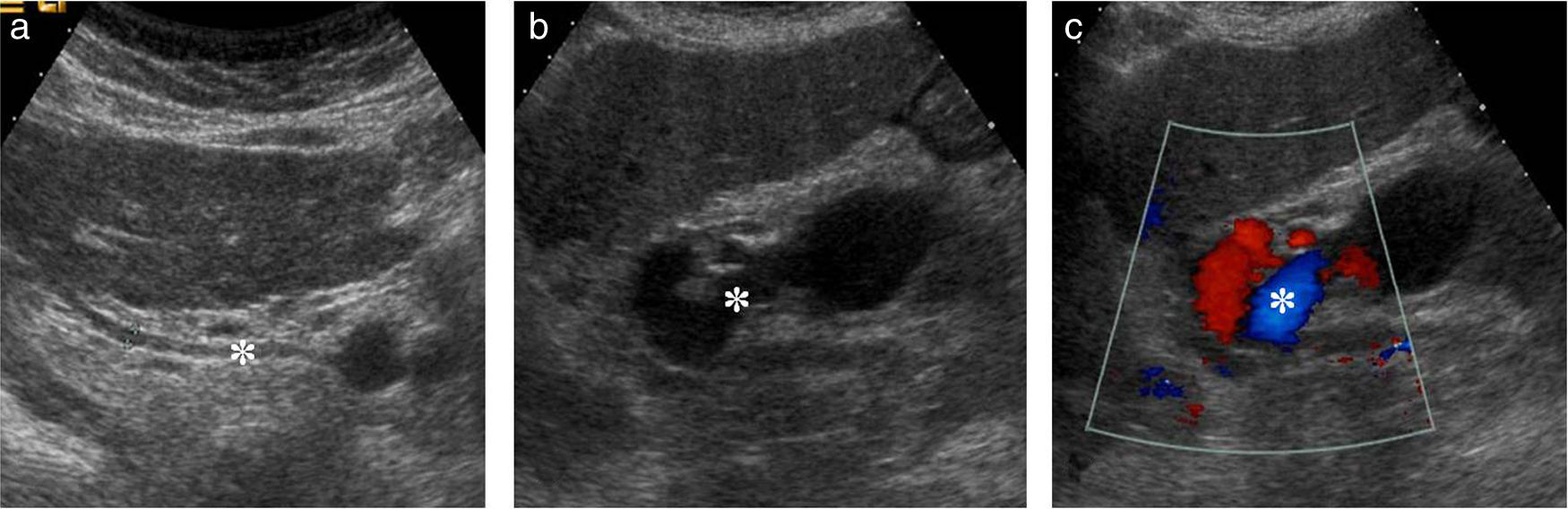
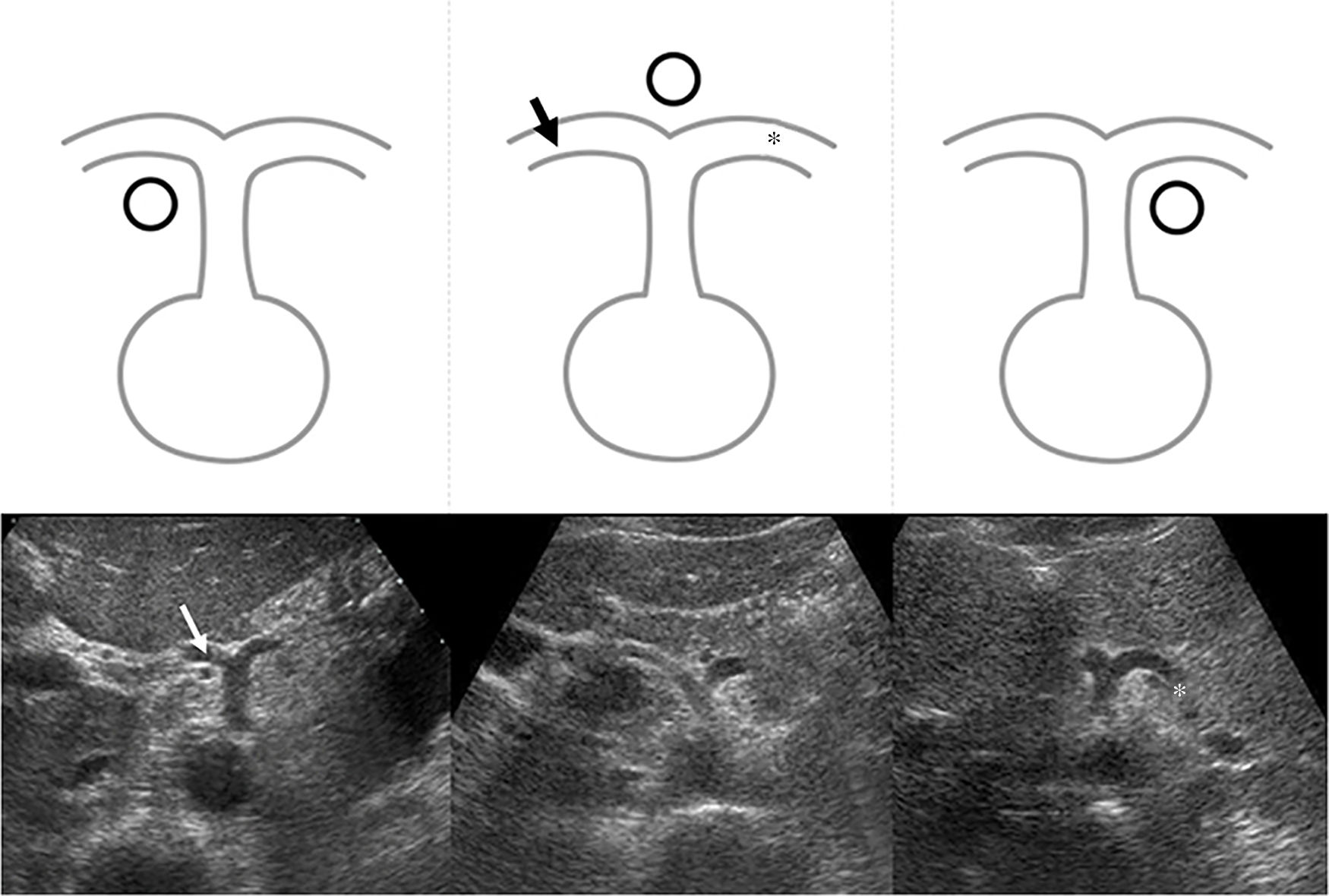
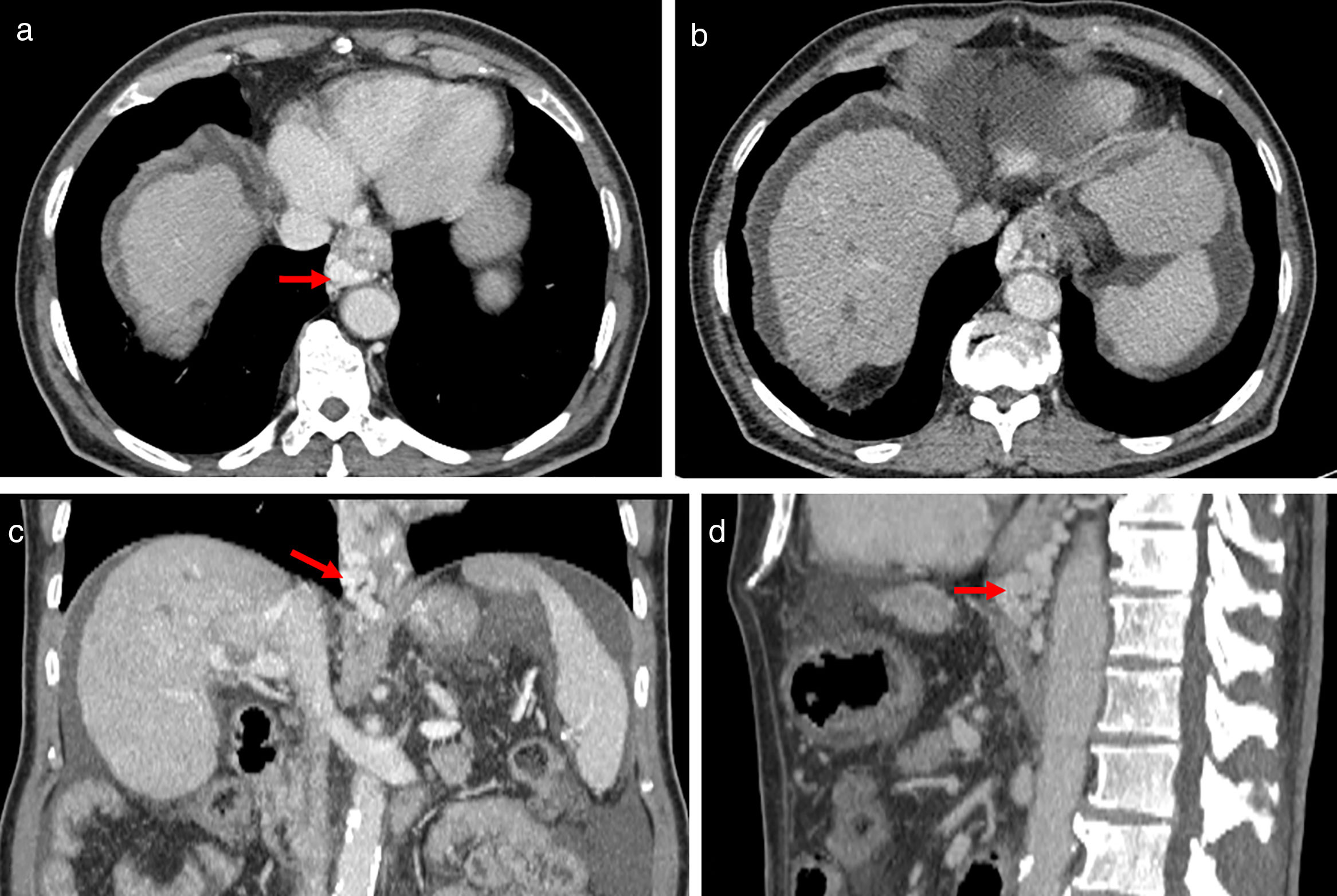
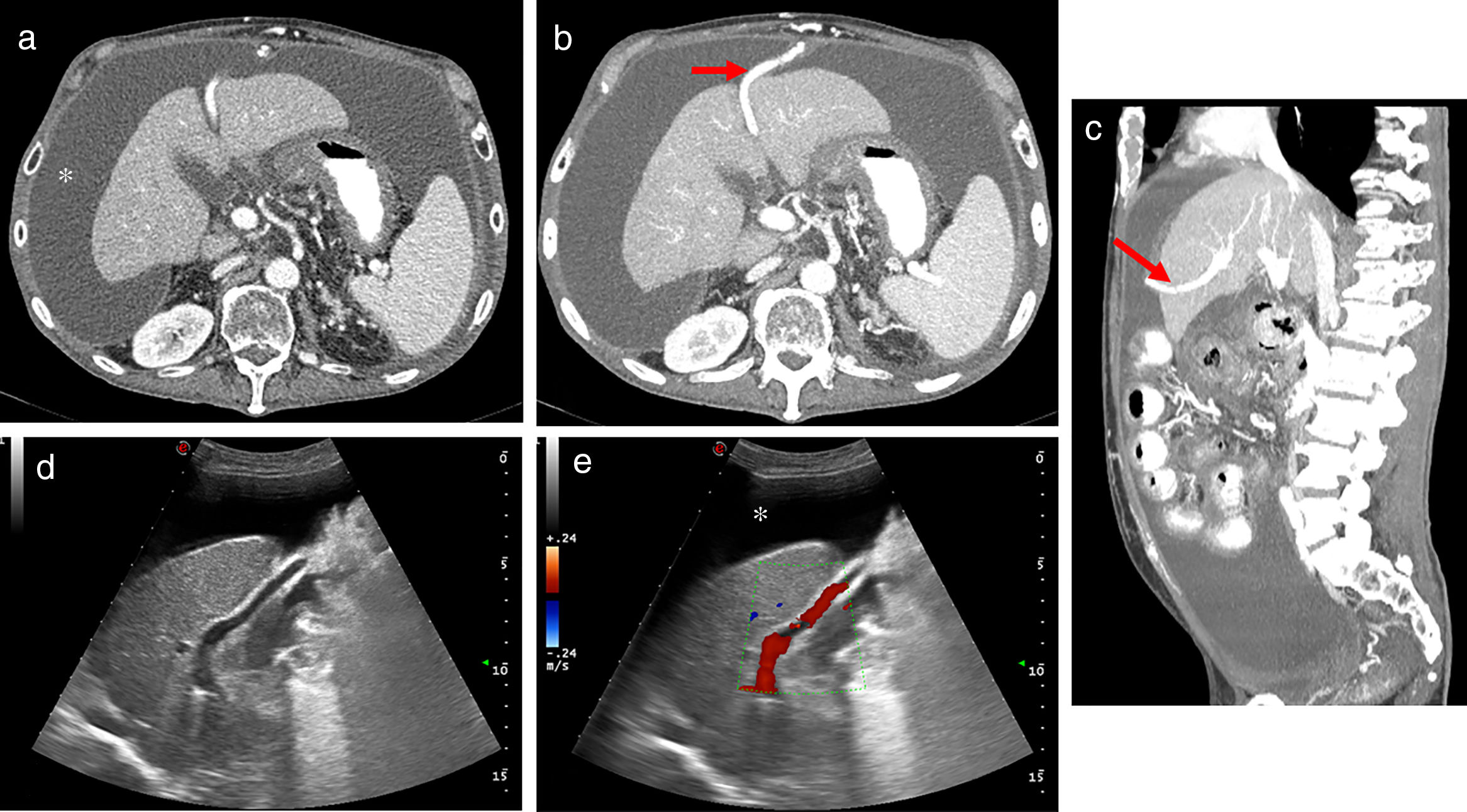
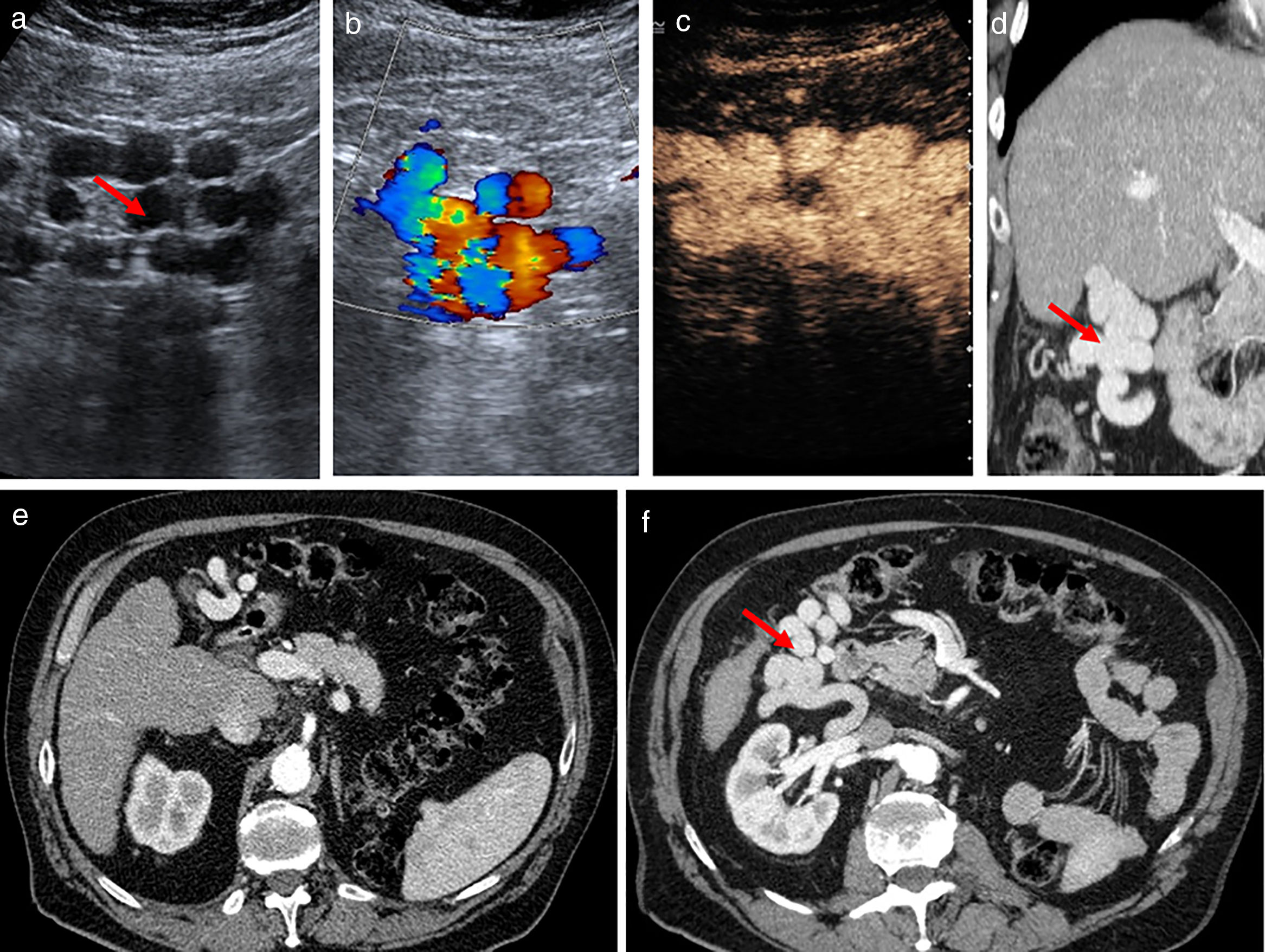
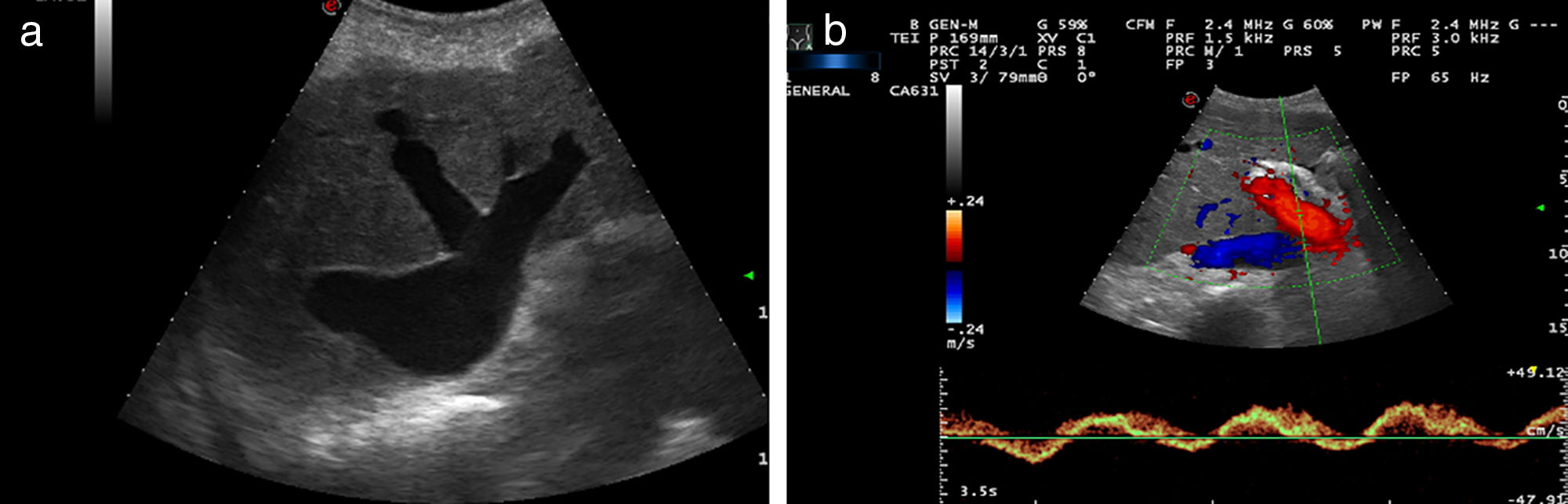
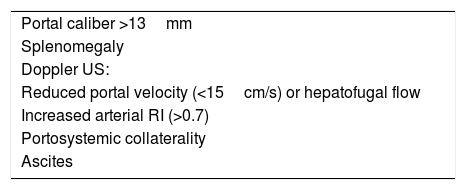
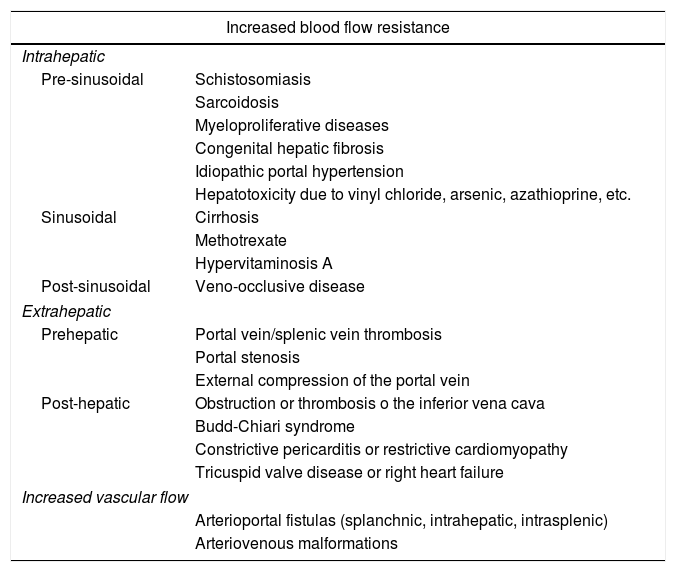
Portal hypertension (PHT) is a clinical entity defined when hydrostatic pressure >5mm Hg in the portal venous territory, being clinically significant if it reaches ≥10mm Hg. At this threshold, complications can develop, such as the bleeding of esophageal varices, the appearance of ascites, or hepatic encephalopathy. Imaging modalities play an important role here as non-invasive methods to determining whether PHT is present or not. This article analyzes various imaging findings that can be suggestive of PHT and contributes to define its etiology, severity, and possible complications.
La hipertensión portal (HTP) es una condición clínica definida por una presión hidrostática >5mmHg en el territorio venoso portal, siendo clínicamente significativa cuando es ≥10mmHg. A partir de este umbral pueden desarrollarse complicaciones, como sangrado de varices esofágicas, aparición de ascitis o encefalopatía hepática. Las técnicas de imagen tienen un papel importante como método no invasivo para determinar la presencia de HTP. En este artículo se analizan varios hallazgos radiológicos que pueden sugerir HTP y contribuir a definir su etiología, gravedad y posibles complicaciones.