Digital tomosynthesis has proven useful in the evaluation of damage to joints. This study aims to describe the most common digital tomosynthesis findings for four rheumatological entities and to compare the usefulness of this technique with that of other imaging techniques.
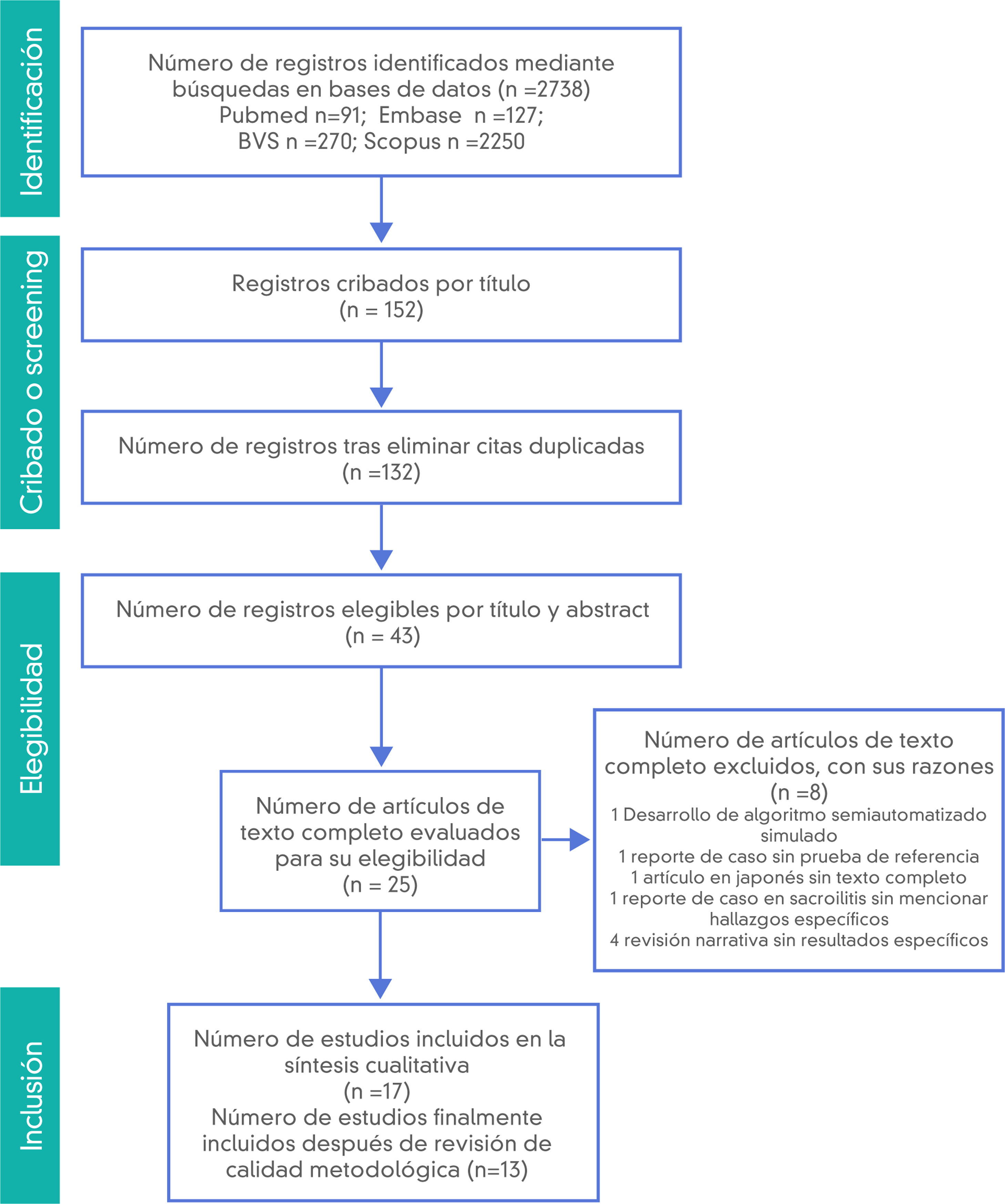
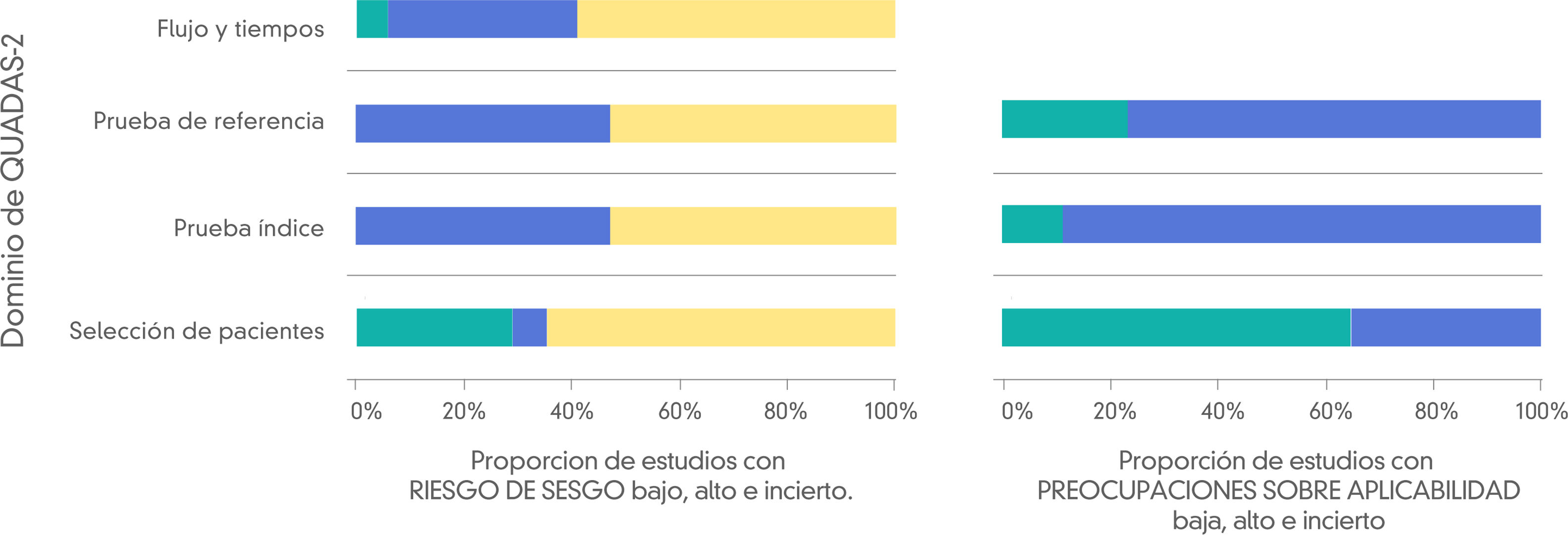
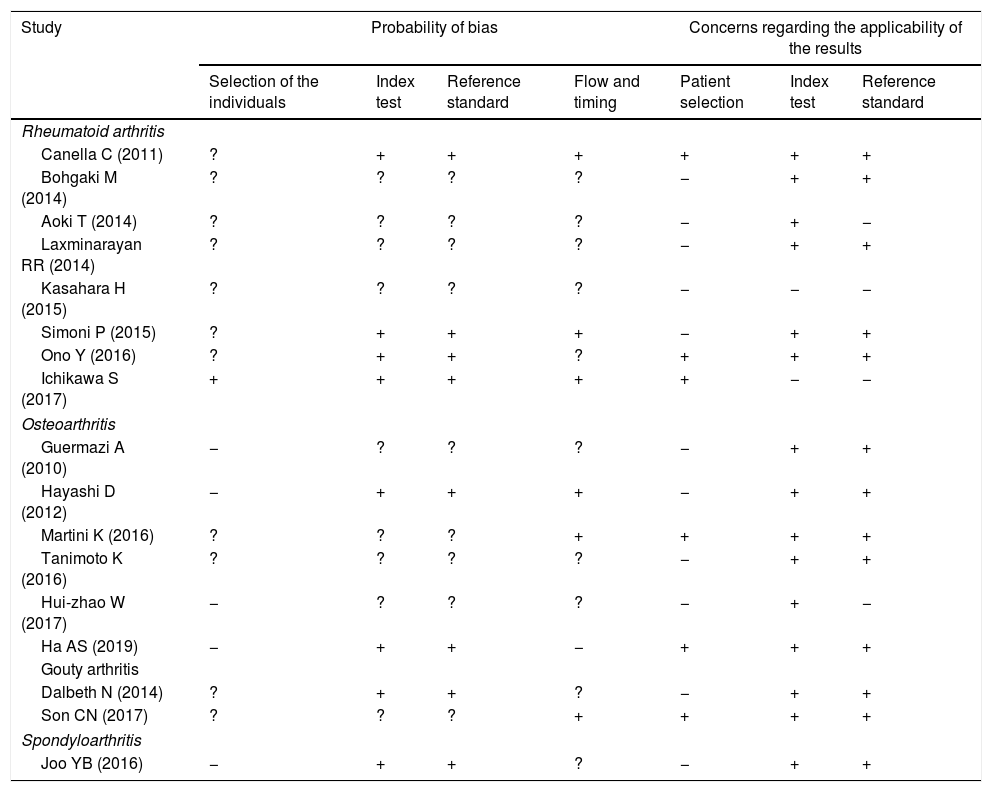
Materials and methodsFollowing the PRISMA guidelines, we systematically searched the literature for articles about the use of digital tomosynthesis in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, spondyloarthritis, and gout. We used the QUADAS-2 (Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies) criteria to evaluate the quality of the articles included.
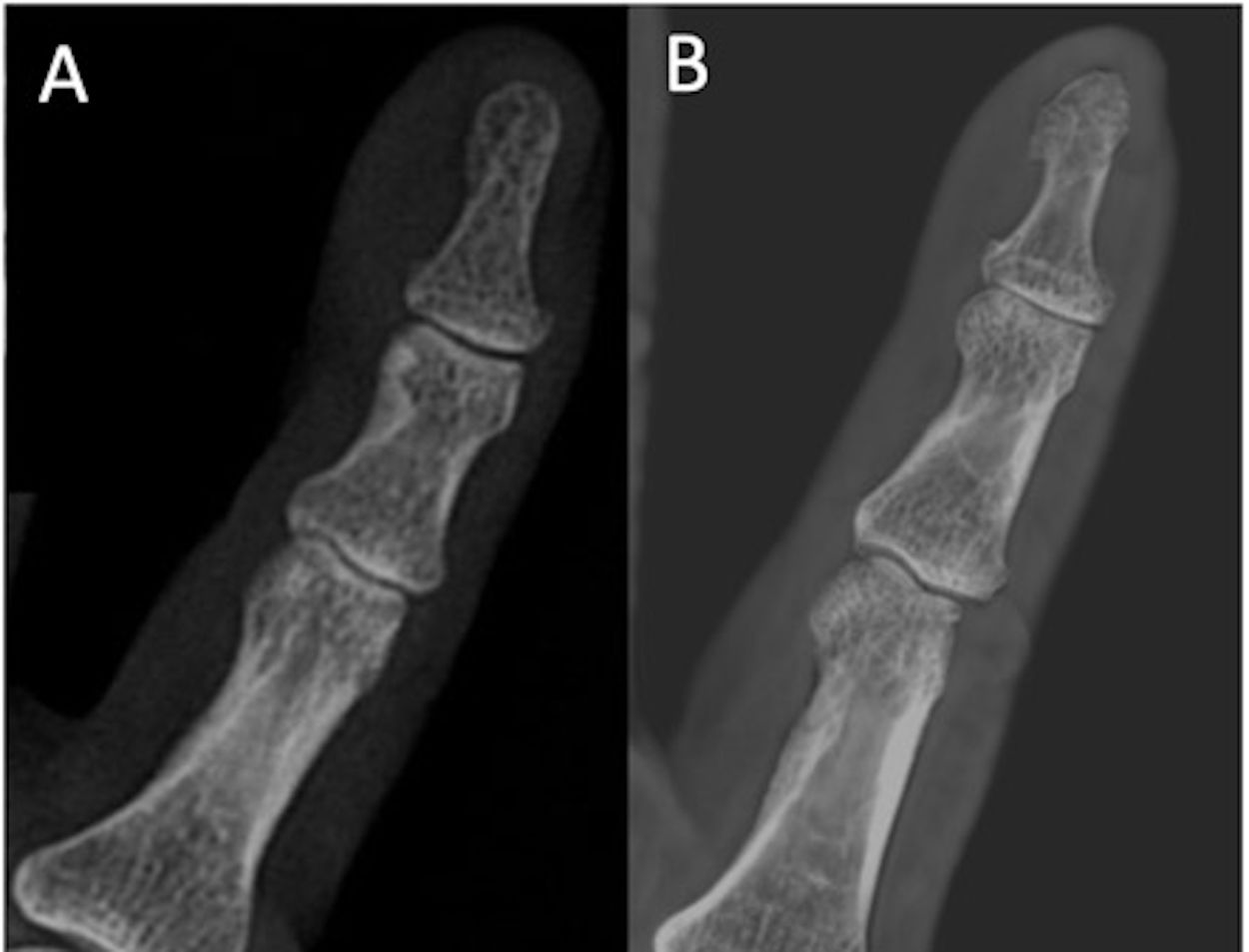
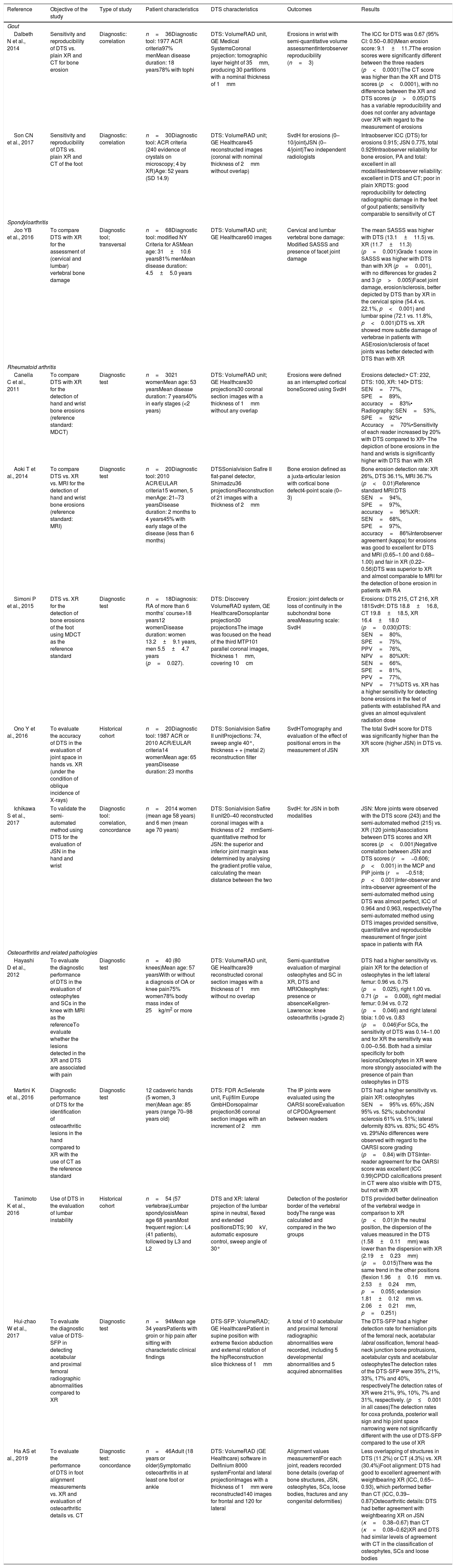
ResultsWe included 13 articles. For rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and spondyloarthritis, digital tomosynthesis detected bone abnormalities better than plain-film X-rays; however, for gout, the results were variable.
ConclusionsDigital tomosynthesis can play an important role in the evaluation of skeletal abnormalities in rheumatological disease, especially compared to plain-film X-rays.
La tomosíntesis digital ha mostrado beneficio en la evaluación del daño articular. El objetivo del estudio es describir los hallazgos frecuentes a través de la tomosíntesis digital en cuatro patologías reumatológicas y comparar su utilidad con otras técnicas de imagen.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó una búsqueda sistemática de la literatura siguiendo las guías PRISMA. La evaluación de la calidad se realizó con los criterios QUADAS-2 (Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies).
ResultadosSe incluyeron 13 artículos. Para la artritis reumatoide, la artrosis y la espondiloartritis, la tomosíntesis digital en comparación con la radiografía simple mostró mayor capacidad de detección de alteraciones óseas; para la artritis gotosa, los resultados fueron variables.
ConclusionesLa tomosíntesis digital puede tener un papel importante en la evaluación de las alteraciones esqueléticas de las enfermedades reumatológicas, especialmente en comparación con la radiografía simple.