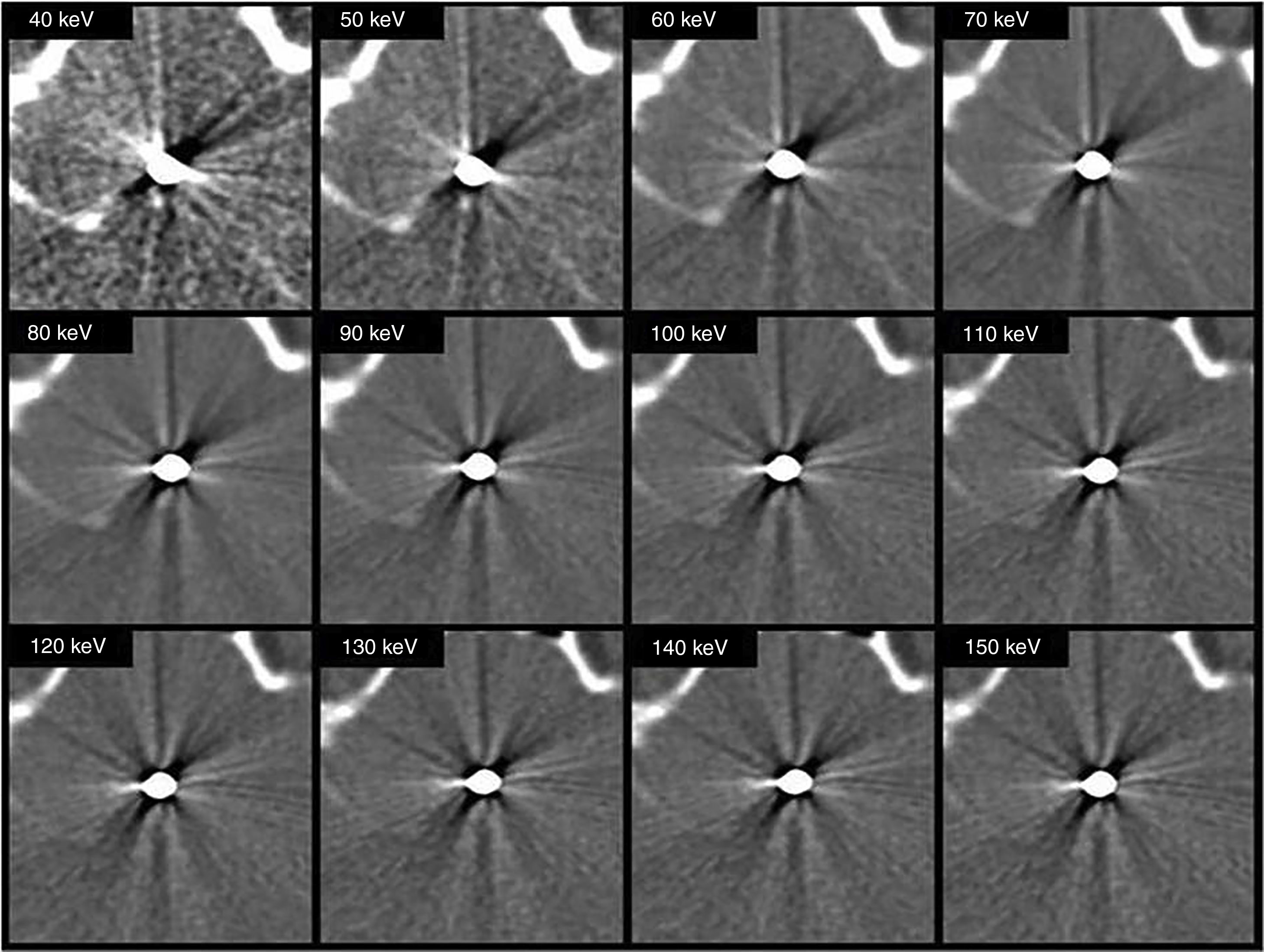
To assess the ability of dual-energy CT (DECT) to reduce metal-related artifacts in patients with clips and coils in head CT angiography, and to analyze the differences in this reduction between both type of devices.
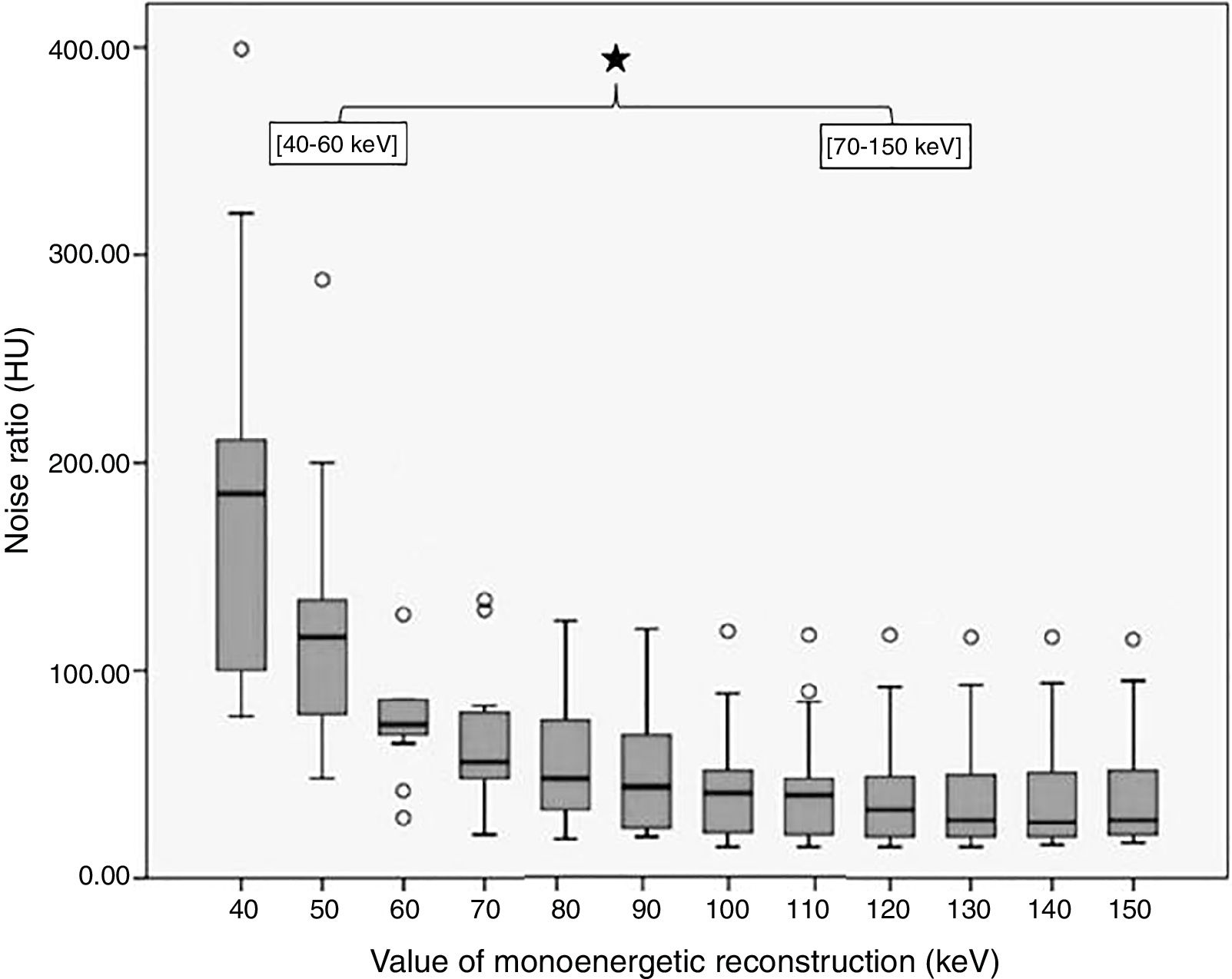
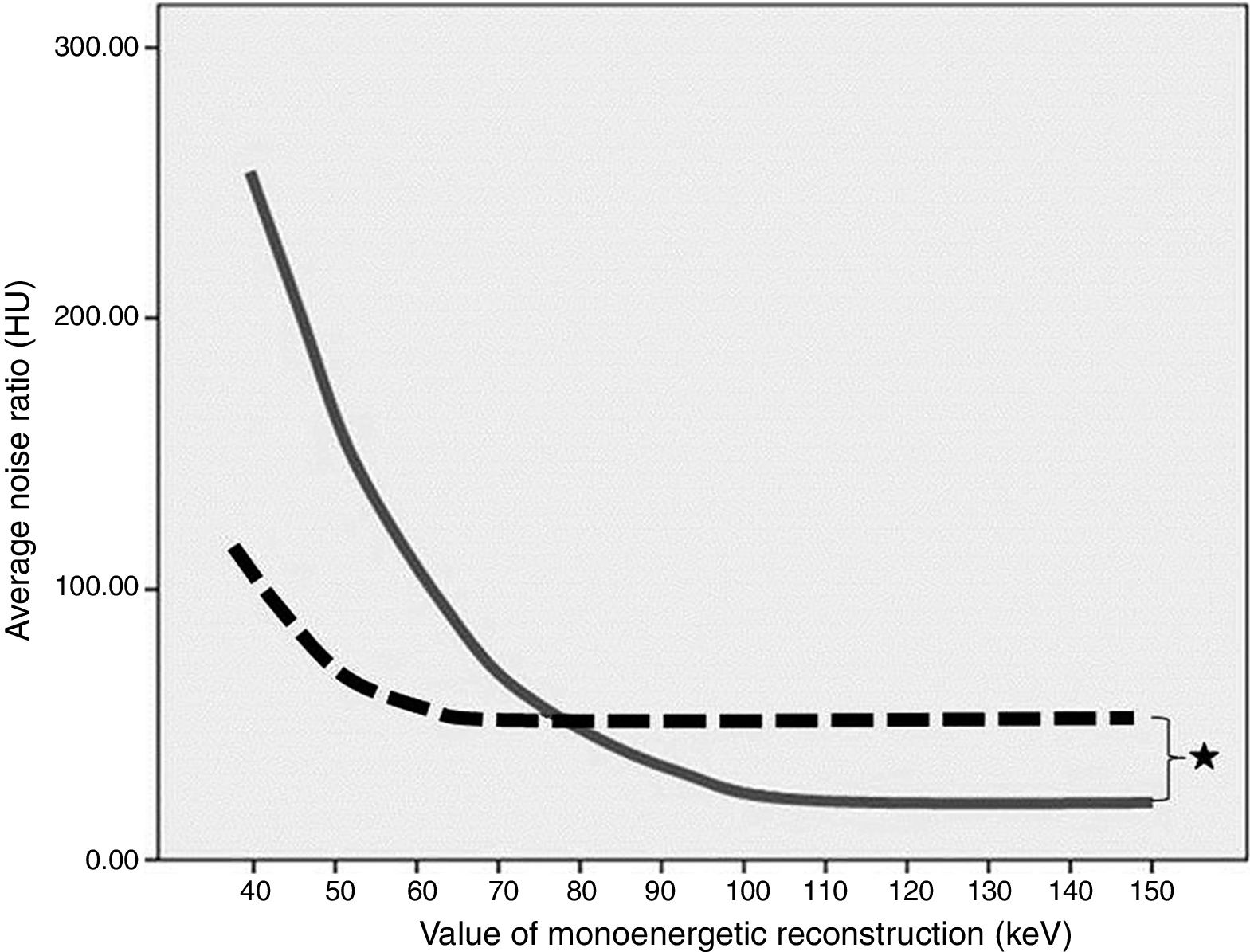
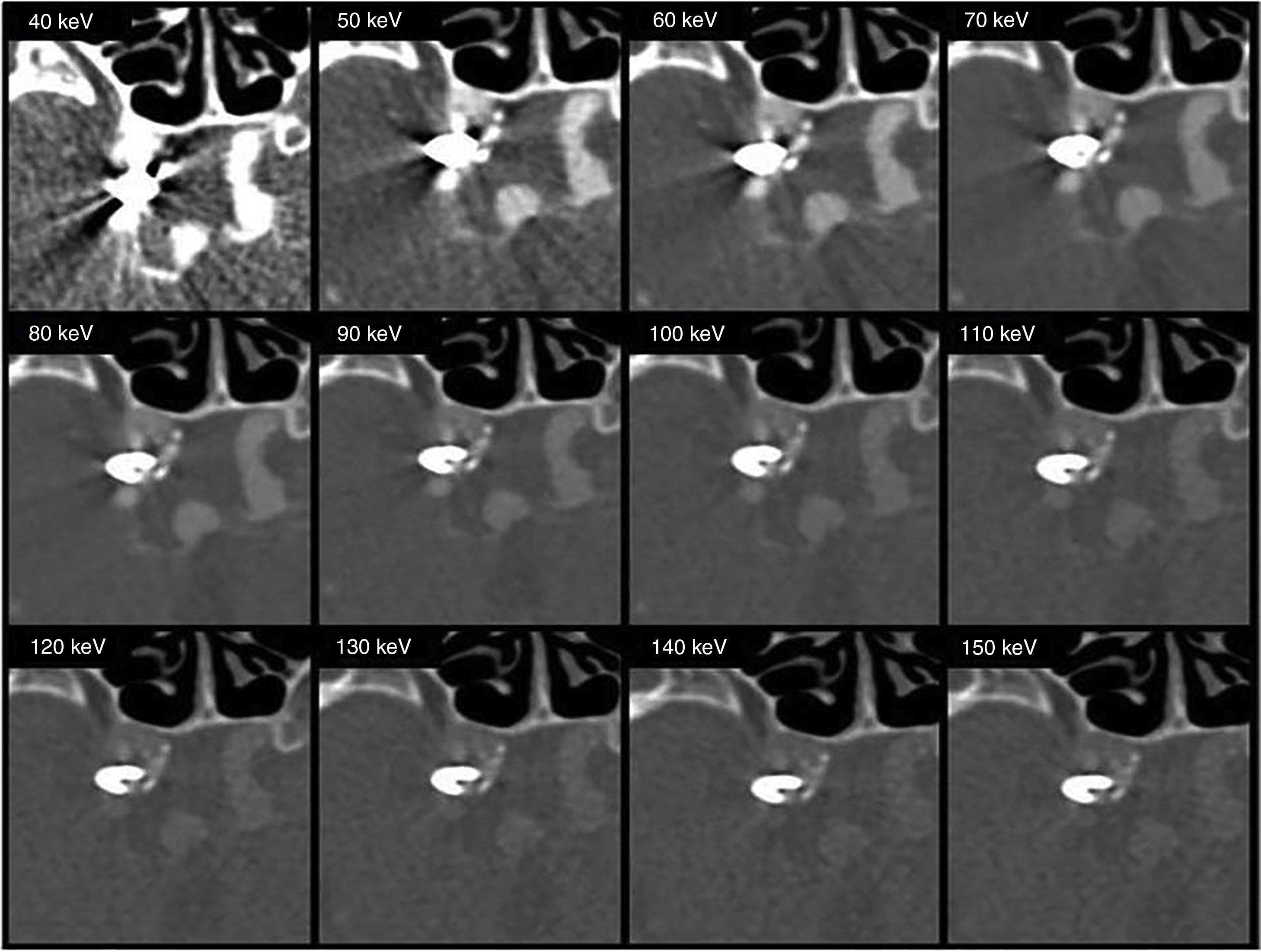
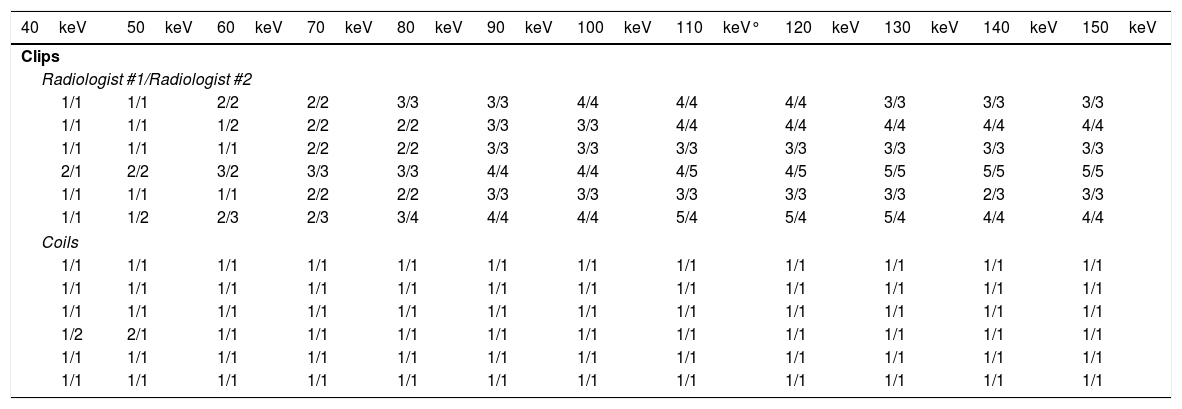
Materials and methodsThirteen patients (6 clips, 7 coils) were selected and retrospectively analyzed. Virtual monoenergetic images (MEI) with photon energies from 40 to 150keV were obtained. Noise was measured at the area of maximum artifact. Subjective evaluation of streak artifact was performed by two radiologists independently. Differences between noise values in all groups were tested by using the ANOVA test. Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare the differences between clips and coils. Cohen's κ statistic was used to determine interobserver agreement.
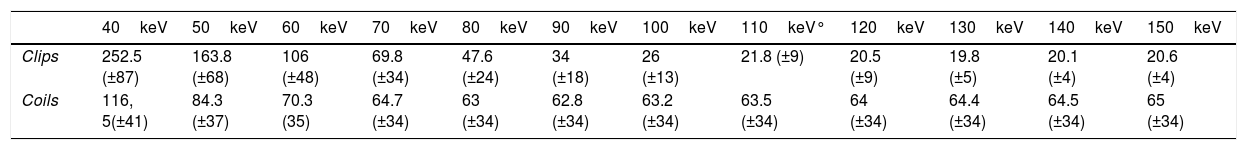
ResultsThe lowest noise value was observed at high energy levels (p<0.05). Noise was higher in the coil group than in the clip group (p<0.001). Interobserver agreement was good (κ=0.72).
ConclusionsTCED with MEI helps to minimize the artifact from clips ands coils in patients who undergo head CT angiography. The reduction of the artifact is greater in patients with surgical clipping than in patients with endovascular coiling.
Evaluar la capacidad de la TC de energía dual (TCED) para reducir el artefacto metálico en pacientes con clips y coils intracraneales en estudios de angio-TC cerebral, y analizar el diferente impacto que dicha reducción tiene en función del tipo de dispositivo estudiado.
Material y métodosSe analizaron retrospectivamente 13 pacientes (6 clips, 7 coils). Se obtuvieron imágenes virtuales monoenergéticas (IVM) en un rango de 40 a 150 keV. Se midió el ruido dentro del área de máximo artefacto. La evaluación subjetiva del ruido fue realizada independientemente por dos radiólogos. Las diferencias encontradas se evaluaron mediante el test ANOVA. El test Mann-Whitney se utilizó para comparar las diferencias entre clips y coils. Se determinó el grado de concordancia interobservador (coeficiente κ).
ResultadosEl ruido fue más bajo en los niveles energéticos más altos (p<0,05). El ruido fue mayor en pacientes con coils (p<0,001). La correlación interobservador fue buena (κ=0,72).
ConclusionesEl uso de TCED con reconstrucciones virtuales monoenergéticas ayuda a minimizar el artefacto producido por clips y coils intracraneales en estudios de angio-TC cerebral. La reduccción del artefacto conseguida es mayor en el grupo de pacientes con clips que en el grupo de pacientes con coils.