Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSAS) or Apnea-Hypoapnea Syndrome (SAHS) is one of the most prevalent sleep disorders in the general population. It is associated with an increase in the prevalence of difficult orotracheal intubation and postoperative complications. The application of validated early detection tests, such the STOPbang test in English (STBC), is recommended; a test of high methodological quality, sensitivity and specificity in the early detection of SAHS in both surgical and general populations.
ObjectiveThe validation, translation, cross-cultural adaptation of the STBC to the Spanish population.
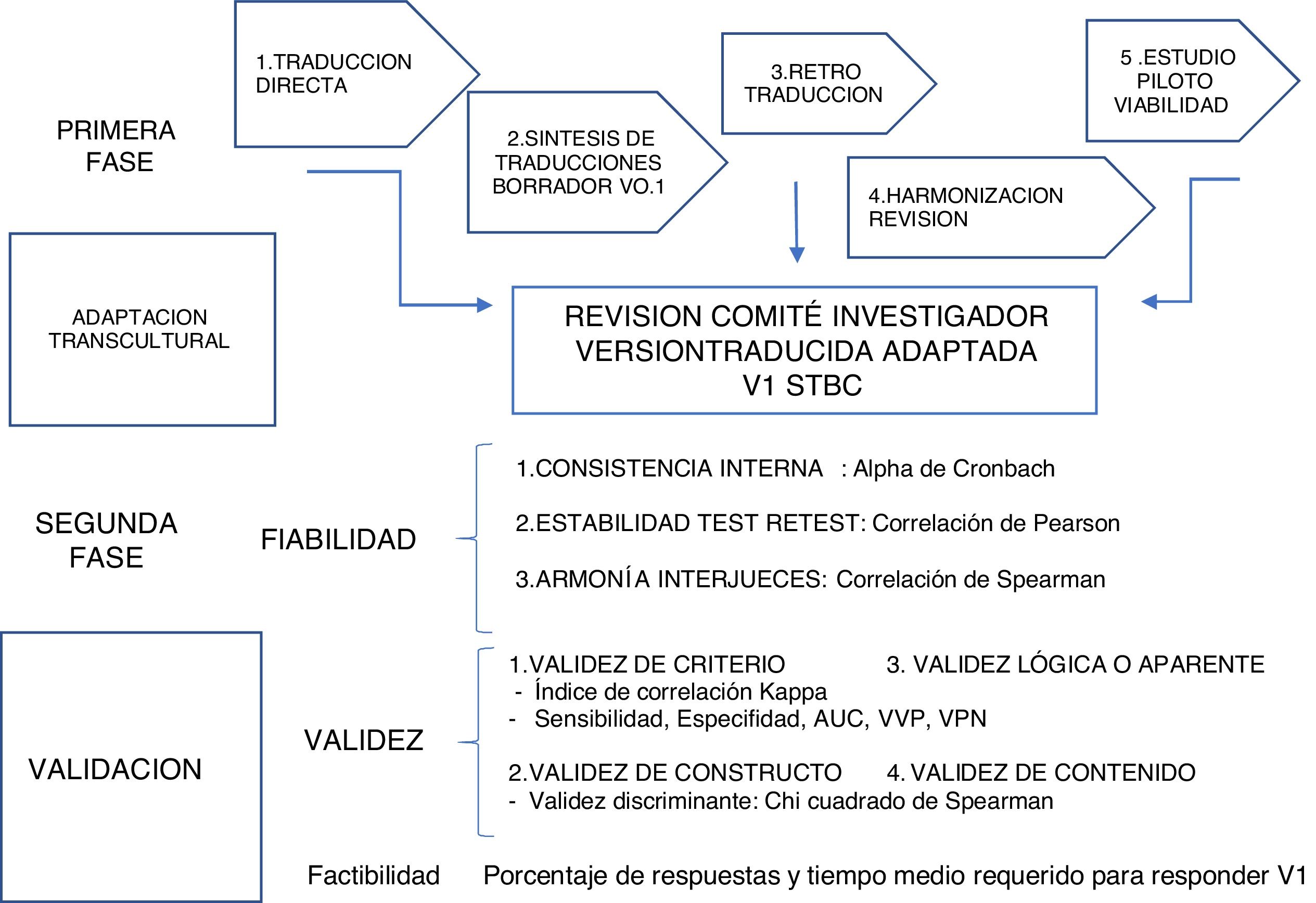
Material and methodsThe transcultural adaptation of the STBC to Spanish was carried out and a subsequent validation study with 77 consecutive patients was carried out. The statistical analysis evaluated the reliability, validity and feasibility of the translated and culturally adapted version.
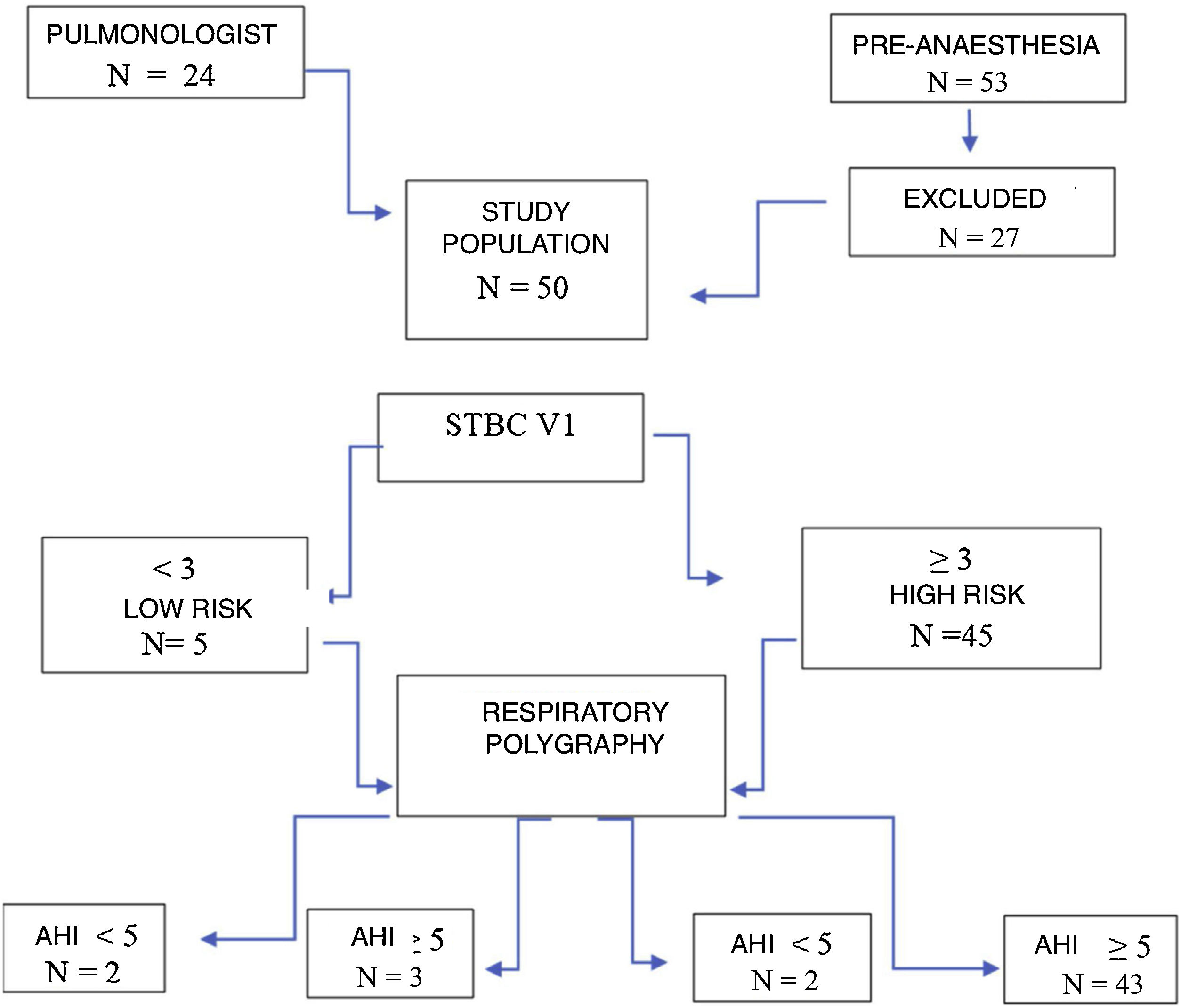
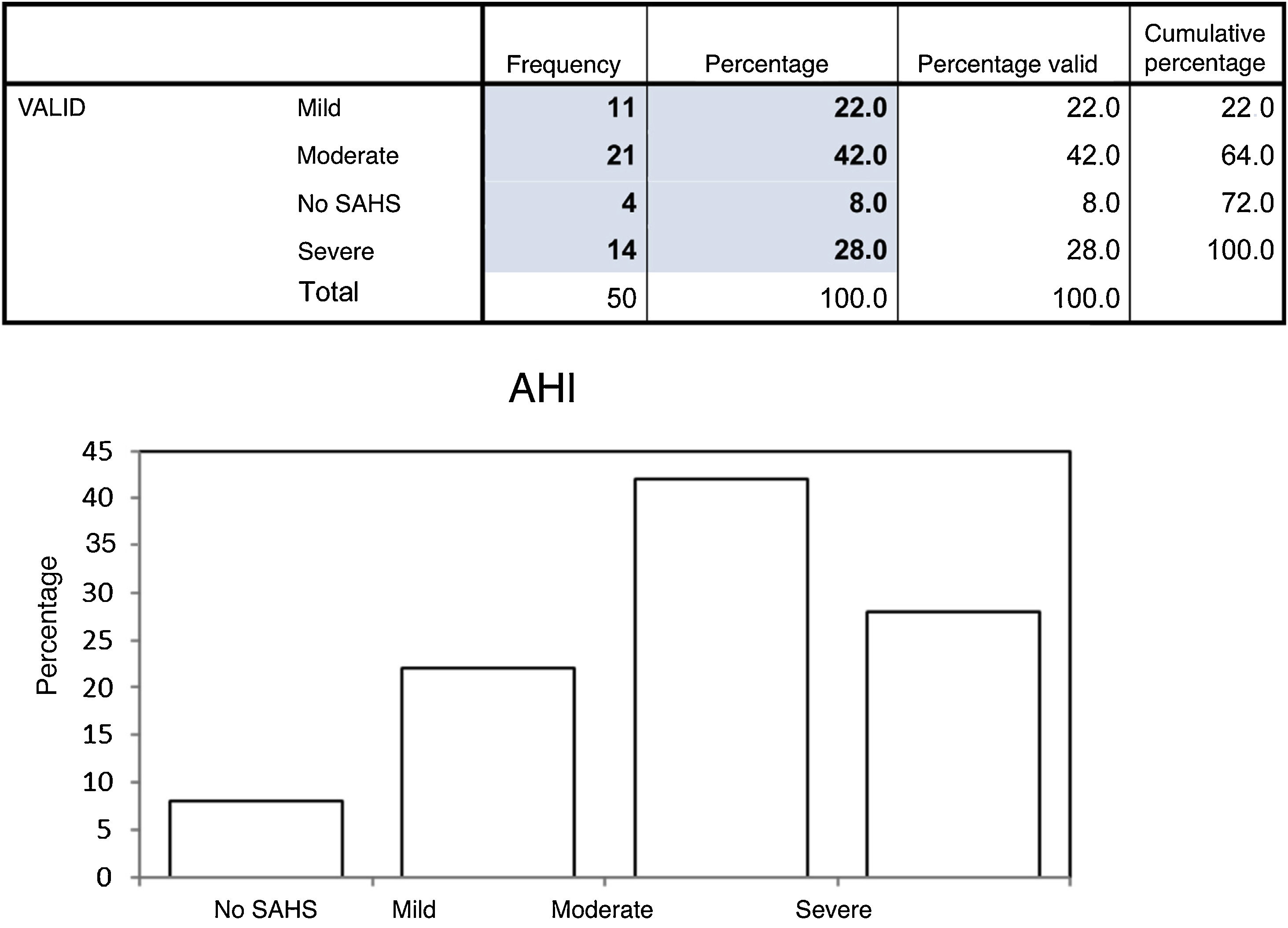
Results44% of women and 56% of men were included, with a mean age of 53.58 ± 12.88 years. The reliability results were: a Cronbach's Alpha Coefficient of 0.767, a Pearson correlation r = 0.777 (P < .001) and a Sperman correlation rho = 0.455 (P = .044). The feasibility of the study was 100%. Criterion validity was evaluated using the Kappa coefficient, which was 0.444. For a score >3 of the questionnaire adapted to Spanish, the results of sensitivity, specificity according to the different cut-off levels of the apnea hypopnea index (AHI) >5, >15, >30) were: Sensitivity 87%, 91% and 100% respectively and Specificity of 50%, 31% and 22%.
ConclusionsThe STBC questionnaire translated, adapted and validated into Spanish, evaluated in the present study, is reliable and valid with respect to the original design of the questionnaire. It is a useful tool that is easy to understand and implement, which can be used rigorously to stratify surgical risk and carry out adequate perioperative planning of those patients at risk of SAHS.
El Síndrome de Apnea Obstructiva del Sueño (SAOS) o Síndrome de Apnea-Hipoapnea (SAHS) es uno de los trastornos del sueño más prevalentes en la población general. Está asociado a un aumento en la prevalencia de Intubación orotraqueal difícil y de las complicaciones postoperatorias. Se recomienda la aplicación de tests de detección precoz validados como el test en inglés de STOPbang (STBC); un test de alta calidad metodológica, sensibilidad y especificidad en la detección precoz del SAHS tanto en la población quirúrgica como general.
ObjetivoLa validación, traducción y adaptación cultural del test STBC a la población española.
Material y metodosSe realizó la adaptación transcultural del STBC al español y un estudio de validación posterior con 77 pacientes consecutivos. El análisis estadístico evaluó la fiabilidad, validez y factibilidad de la versión traducida y adaptada culturalmente.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 44% de mujeres y 56% de hombres con una edad media de 53,58 ± 12,88 años. Los resultados en la fiabilidad fueron: un Coeficiente Alpha de Cronbach de 0,767, una correlación de Pearson r = 0,777 (P <,001) y una correlación de Sperman rho = 0,455 (P =,044). La factibilidad del estudio fue del 100%. La validez de criterio se evaluó mediante el coeficiente Kappa que fué de 0,444. Para una puntuación > 3 del cuestionario adaptado al español los resultados de sensibilidad, especificidad según los distintos niveles de corte del índice apnea hipoapnea (IAH) >5, >15, >30) fueron: Sensibilidad del 87%, 91% y 100% respectivamente y de Especificidad del 50%, 31% y 22%.
ConclusionesEl cuestionario STBC traducido, adaptado y validado al español evaluado en el presente estudio, es fiable y válido con respecto al diseño original del cuestionario. Es una herramienta útil de fácil comprensión e implementación, que puede utilizarse con rigor para estratificar el riesgo quirúrgico y realizar una adecuada planificación perioperatoria de aquellos pacientes con riesgo de SAHS.