Este estudio analiza, en una muestra de niños españoles, las diferencias en el temperamento entre niños que tartamudean y niños con un desarrollo típico, con el objetivo de relacionar dichas diferencias con la aparición de la tartamudez.
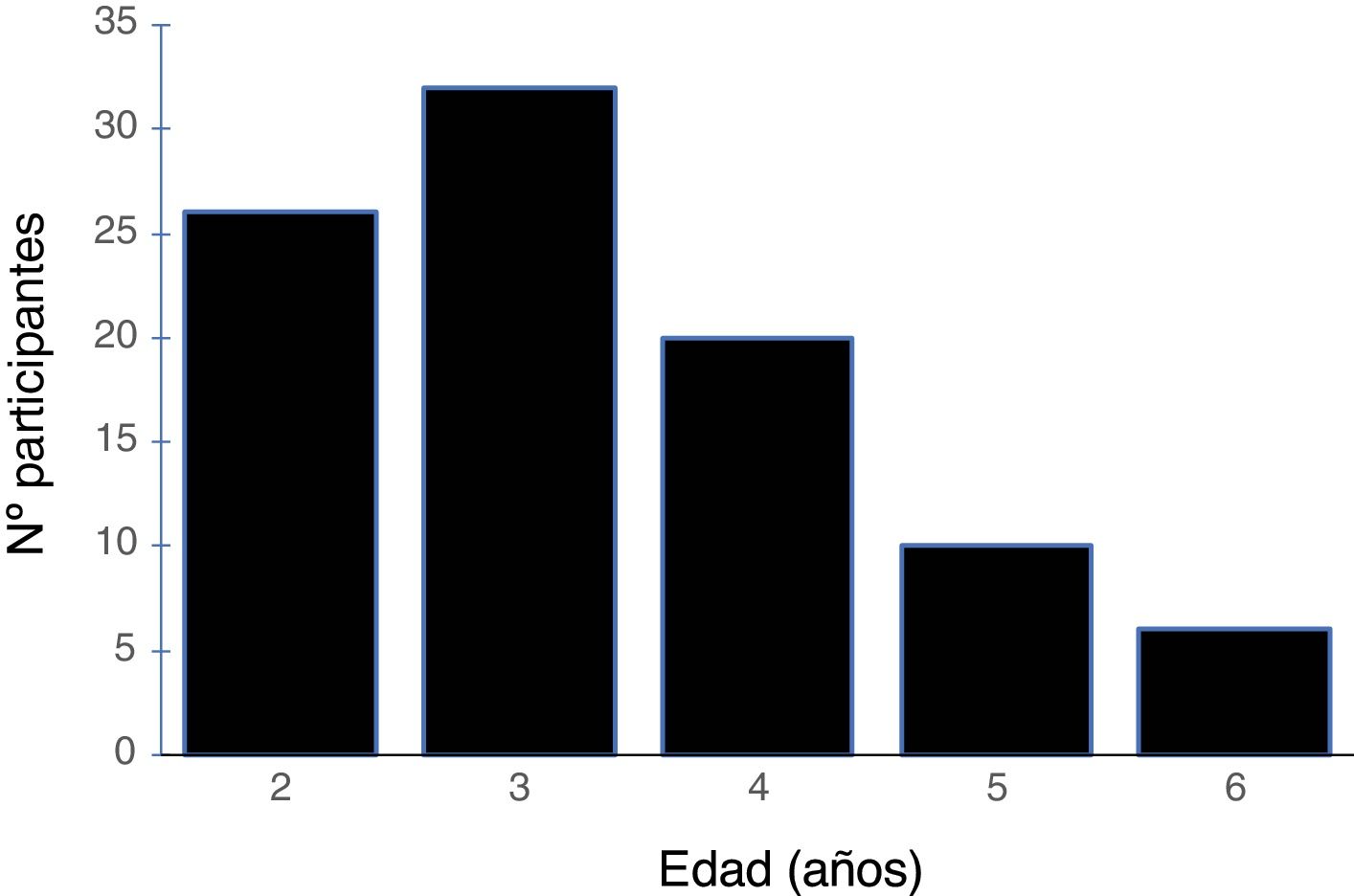
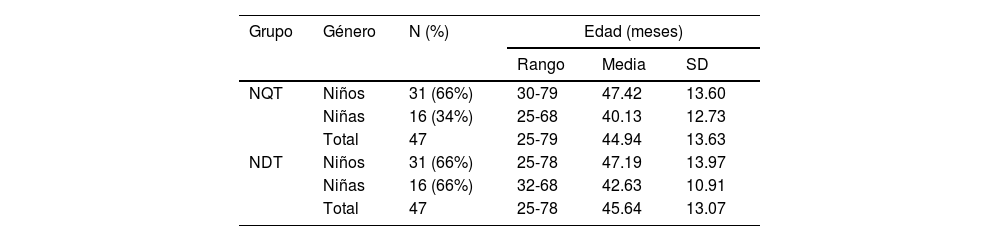
MetodologíaParticiparon 47 niños con tartamudez y 47 niños con desarrollo típico de entre 2 y 6 años, igualados en género y edad (± 2 meses). Para valorar el temperamento se utilizó la adaptación española del Children's Behavioral Questionnaire (CBQ) en su versión corta, que es una prueba informada por los padres.
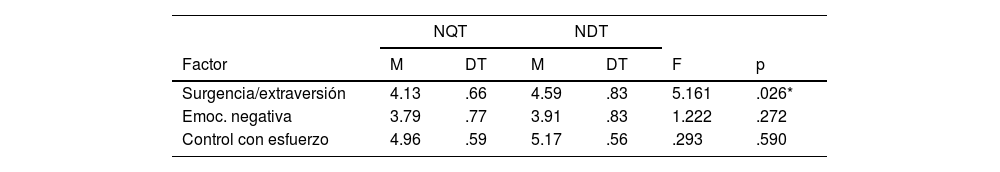
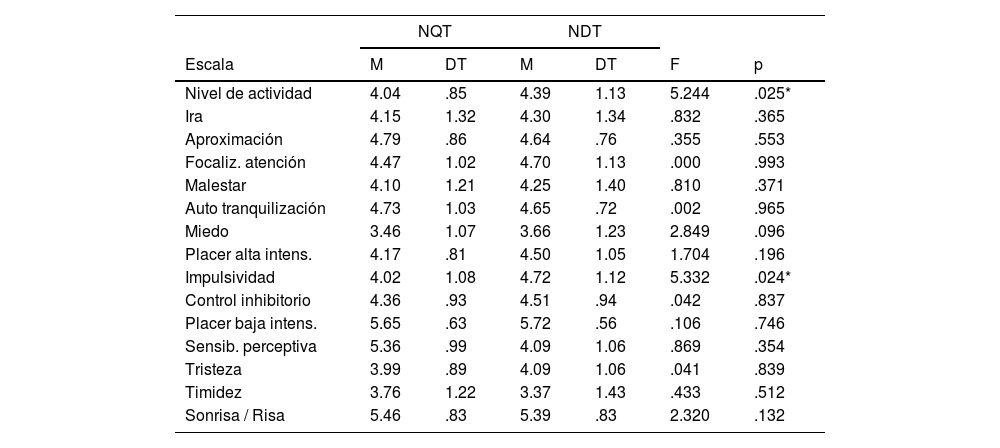
ResultadosLos niños que tartamudean obtuvieron puntuaciones más bajas que los niños con desarrollo típico en nivel de actividad (4.04 frente a 4.39) y en impulsividad (4.02 frente a 4,72). Los niños que tartamudean también puntuaron más bajo en el factor general de surgencia/extraversión (4.14 frente a 4.59).
ConclusiónAparecieron diferencias en el temperamento entre ambos grupos en 2de las 15 escalas del CBQ, al contrario que en estudios de otros países donde hubo mayores diferencias. Se hipotetiza que estos hallazgos podrían deberse a un efecto de la edad, ya que la mayoría de los participantes contaban entre 2 y 4 años, indicando que a edades tempranas no hay una relación clara entre características temperamentales y la tartamudez.
This study analyzes, in a Spanish-speaking sample, differences in temperament between children who stutter and typically-developing children, aiming to establish a relation between such differences and stuttering onset.
MethodologyParticipants consisted of 47 children who stutter and 47 typically-developing children aged 2–6 years, matched in gender and age (±months). Temperament was assessed using the Spanish version of the short form of the Children's Behavior Questionnaire (CBQ), a parent rating scale.
ResultsChildren who stutter scored lower compared to their typically-developing matches in activity level (4.04 vs. 4.39) and impulsivity (4.02 vs. 4,72). Children who stutter also scored significantly lower in the general surgency factor (4.14 vs. 4.59).
ConclusionTemperamental differences between both groups emerged in 2of the 15 scales of the CBQ, unlike in studies from other countries where such differences were more pronounced. It is hypothesised that these findings could be due to an age effect, as most of the participants were between 2 and 4 years old, indicating that at young ages there is no clear relationship between temperamental characteristics and stuttering.