El trastorno del desarrollo del lenguaje (TDL) implica la afectación de una o varias dimensiones lingüísticas. Se ha observado que estos niños y niñas presentan dificultades en las narraciones orales a nivel de microestructura y macroestructura, aunque existe mucha disparidad en las herramientas de evaluación empleadas en la investigación. El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar las habilidades narrativas de niños y niñas hispanohablantes con TDL mediante el análisis de las narraciones orales atendiendo a la microestructura y macroestructura narrativa y a los errores fonológicos y morfológicos.
MétodoLa muestra está formada por 24 niños/as: 12 con TDL y 12 con desarrollo típico (DT) de entre 7 y 11años. Se les administraron CELF-5, Raven's2 Matrices Progresivas y Test Peabody de Vocabulario en Imágenes para conocer el nivel de competencia lingüística y cognitiva y el Multilingual Assessment Instrument for Narratives (MAIN). Estas narraciones orales fueron transcritas y analizadas con las herramientas del proyecto CHILDES y codificadas con el sistema PREP-CORP.
ResultadosSe observaron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre ambos grupos en el número de enunciados, en la longitud media de enunciado y en el número de eventos narrados, así como en la frecuencia de errores morfológicos y fonológicos.
ConclusionesLas narraciones orales de los niños con TDL usando el instrumento MAIN son más cortas y menos detalladas que las del DT, así como con un mayor número de errores fonológicos y morfológicos. Por lo tanto, el MAIN podría ser una adecuada herramienta clínica para la evaluación de las habilidades narrativas de los sujetos con TDL.
Developmental language disorder (DLD) involves the impairment of one or more linguistic dimensions. It has been observed that these children present difficulties in oral narratives at the microstructure and macrostructure levels, although there is much disparity in the assessment tools used in research. The aim of this study is to assess the narrative skills of Spanish-speaking children with DLD by analyzing oral narratives in terms of narrative microstructure and macrostructure and phonological and morphological errors.
MethodThe sample consisted of 24 children: 12 with DLD and 12 with typical development (TD) aged between 7 and 11years. They were administered CELF-5, Raven's 2, and Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test to assess the level of linguistic and cognitive competence and the Multilingual Assessment Instrument for Narratives (MAIN), a narrative assessment tool. These oral narratives were transcribed and analyzed with the CHILDES project tools and coded with the PREP-CORP system.
ResultsStatistically significant differences were observed between both groups in the number of utterances, mean utterance length and number of events narrated, as well as in the frequency of morphological and phonological errors.
ConclusionsOral narratives of DLD children using the MAIN tool are shorter and less detailed than those of TD, as well as with a higher number of phonological and morphological errors. Therefore, the MAIN could be a suitable clinical tool for the assessment of the narrative skills of DLD children.
El trastorno del desarrollo del lenguaje (TDL) es un trastorno del neurodesarrollo que puede afectar a uno o más dominios del lenguaje tanto a nivel de producción como de comprensión del lenguaje oral y escrito (Bishop et al., 2017). El DSM-5 (APA, 2014) lo define como un trastorno del neurodesarrollo sin una causa específica, que no puede explicarse por una deficiencia auditiva o una discapacidad intelectual, sensorial o física. El único estudio realizado en España, concretamente en Andalucía, establece la prevalencia del TDL en torno al 8.27 por mil (Villegas, 2022) en niños y niñas de entre 6 y 12años escolarizados en Educación Primaria en esa región, mientras que se sitúa aproximadamente en el 7% de la población en otros países, como Estados Unidos (Nitin et al., 2022) o Inglaterra (Norbury et al., 2016). Además, el TDL se considera un trastorno complejo, persistente, dinámico y heterogéneo, más frecuente en niños que en niñas, con una proporción de 4.8:1 (Norbury et al., 2016), donde la perspectiva actual sobre su etiología plantea una combinación de factores tanto genéticos como ambientales (Rice, 2020).
Tradicionalmente, se consideraba que la morfología y la sintaxis eran los dominios más afectados en los niños con TDL, independientemente de la lengua (Auza et al., 2018). Sin embargo, existen numerosas evidencias que muestran que los niños con TDL presentan un déficit en sus habilidades narrativas orales, más allá de la morfología y la sintaxis, en comparación con niños con desarrollo típico (DT) (Botting, 2002; Fichman et al., 2022; Mäkinen et al., 2014; Norbury y Bishop, 2003; Taha et al., 2021). Esto podría deberse a que la narración oral es una actividad compleja que precisa de todas las dimensiones lingüísticas y que se organiza en torno a dos niveles: la microestructura y la macroestructura (Bliss et al., 1998). La microestructura narrativa hace referencia a la cohesión, que se corresponde con el orden lógico y fluido de los sucesos de la historia. La longitud y la complejidad de las oraciones, los marcadores discursivos de progresión empleados y la diversidad léxica conformarían este nivel (Camus et al., 2022). Por otro lado, la macroestructura narrativa se relaciona con la estructura global o trama de la historia y su coherencia, y hace referencia a los personajes de la historia y las escenas, episodios y eventos que tienen lugar a lo largo de la misma (Paradis et al., 2013).
Concretamente, se ha observado que los niños con TDL producen narraciones orales más pobres a nivel de microestructura (vocabulario limitado, oraciones más cortas y gramaticalmente menos complejas) y de macroestructura (menos escenas, eventos, episodios y personajes, menos componentes gramaticales, menor organización, coherencia y calidad general) comparado con sus iguales con DT (Acosta et al., 2013; Blom y Boerma, 2016; Boerma et al., 2016; Botting, 2002; Coloma et al., 2016; Del Valle et al., 2018; Duinmeijer et al., 2012; Fey et al., 2004; Fichman et al., 2022; Norbury y Bishop, 2003; Pearce et al., 2010; Vandewalle et al., 2012; Xue et al., 2022). Estas diferencias parecen depender, además, de la edad de los sujetos y de la tarea solicitada. En el estudio de Blom y Boerma (2016) de 129 niños holandeses con una media de 5;9años en la primera evaluación, el grupo con TDL obtuvo peores resultados que el grupo con DT tanto en comprensión como en producción narrativa, pero un año después los grupos obtuvieron puntuaciones similares en la tarea de comprensión. En otro estudio en español, a la edad de 4años no se observaron diferencias en la complejidad sintáctica de las narraciones entre los niños con TDL y con DT, aunque a la edad de 6años los primeros produjeron narraciones menos complejas (Pavez et al., 2015). Así pues, los niños con TDL tienden a producir narraciones que carecen de una estructura narrativa adecuada a nivel de microestructura y macroestructura, lo que les condiciona la elaboración de un relato coherente y cohesionado.
Además, en las narraciones orales cometen un mayor número de errores lingüísticos que los niños de su misma edad con DT (Fey et al., 2004; Guo et al., 2008; Norbury y Bishop, 2003). Son frecuentes tanto los errores morfosintácticos (Blom y Boerma, 2016; Pavez et al., 2015) que afectan a la estructura de las oraciones o concordancia en género o número de las palabras, como los errores fonológicos, que se corresponden con dificultades en la pronunciación de los fonemas o sonidos que forman las palabras (Schwartz, 2017). Por otra parte, también se ha observado que los niños con TDL utilizan significativamente más pausas, repeticiones de palabras y frases, reformulaciones y falsos comienzos y enunciados inacabados que los niños con DT en sus narraciones (Guo et al., 2008).
Por ello, la evaluación de las habilidades narrativas orales se ha propuesto como un buen indicador de la competencia lingüística y comunicativa en todos los dominios (morfosintaxis, fonología, semántica y habilidades pragmáticas del discurso) (Norbury y Bishop, 2003), un adecuado predictor del desarrollo del lenguaje oral (Acosta et al., 2014) y ha permitido aumentar la sensibilidad diagnóstica de los niños con TDL (Paradis et al., 2013). A pesar de ello, se observa cierta divergencia metodológica en la evaluación de las mismas en el TDL, tanto por el tipo de tarea solicitada para la producción de las narraciones orales como por los instrumentos y materiales de evaluación empleados.
La tarea de cuento mediante imágenes, frente a la de recuento con apoyo en imágenes, ha sido la más utilizada en las investigaciones con TDL (Acosta et al., 2013; Botting, 2002; Blom y Boerma, 2016; Delgado-Cruz et al., 2022; Fey et al., 2004; Iuliu y Martínez, 2021; Marini et al., 2008; Norbury y Bishop, 2003; Pearce et al., 2010; Taha et al., 2021). Otro tipo de material, que se podría utilizar en la evaluación e intervención de las habilidades narrativas del TDL serían los programas de televisión y de dibujos de eventos complejos, y películas de dibujos animados sin lenguaje verbal, que ya se han empleado con otros trastornos del neurodesarrollo asociados a síndromes genéticos (Diez-Itza et al., 2018; McDuffie et al., 2017; Miles et al., 2006). Independientemente de la tarea utilizada (Botting, 2002; Vandewalle et al., 2012), se ha observado que los niños con TDL presentan dificultades, aunque cada tarea narrativa exige diferentes capacidades cognitivas, como la atención auditiva sostenida y la memoria de trabajo verbal (Duinmeijer et al., 2012).
En cuanto al instrumento empleado para la elicitación de las narraciones orales de los niños con TDL, el libro ilustrado Frog, where are you? (Mayer, 1969) y sus versiones ha sido el más utilizado (Acosta et al., 2013; Botting, 2002; Duinmeijer et al., 2012; Norbury y Bishop, 2003; Pearce et al., 2010; Taha et al., 2021) junto con el instrumento normalizado de evaluación The Renfrew Bus Story Test (Glasgow y Cowley, 1994). No obstante, sería necesaria una herramienta clínica con suficiente validez ecológica que proporcione información sobre el uso del lenguaje en un contexto natural para evaluar las dificultades narrativas del TDL (Gagarina et al., 2016). Este es el caso de la herramienta Multilingual Assessment Instrument for Narratives (MAIN) (Gagarina et al., 2012, 2015, 2019), que, si bien no es un instrumento normalizado, su aplicación incluye un procedimiento estandarizado para evaluar a niños de entre 3 y 12años. El MAIN, cuya versión original está en inglés, adaptado al castellano (Ezeizabarrena y García del Real, 2020) ha sido diseñado para evaluar las habilidades narrativas de niños que han adquirido más de una lengua, y se ha utilizado en estudios con población con y sin TDL (Blom y Boerma, 2016; Boerma et al., 2016; Bohnacker y Gagarina, 2020; Bohnacker y Gagarina, 2022; Fichman et al., 2022; Gagarina y Bohnacker, 2022; Lindgren et al., 2023; Pesco y Kay-Raining, 2016; Pham et al., 2019). Sin embargo, hasta lo que sabemos, esta herramienta no ha sido empleada para evaluar las habilidades narrativas de niños hispanohablantes con TDL, considerando el análisis de la microestructura y macroestructura narrativa, aunque sí se ha empleado en el caso de niños hispanohablantes con DT (Ezeizabarrena y García del Real, 2020).
Las ventajas que podría proporcionar esta herramienta, frente a otras herramientas de evaluación narrativa, son varias. En primer lugar, los participantes no conocerían la historia, puesto que si los cuentos o historias son conocidos por los niños, las narraciones a nivel macroestructural y microestructural del grupo con TDL podrían ser similares a las del DT (Iluz-Cohen y Walters, 2012). En segundo lugar, el material que se utiliza para las tareas de narración es visual, lo que reduciría las demandas cognitivas, que supondría un gran beneficio para los sujetos con TDL (Washington y Warr-Leeper, 2013), favoreciendo las características lingüísticas de las narrativas. Por último, es un instrumento formado por material libre de licencia, ampliamente utilizado por la comunidad científica y cuyo protocolo de evaluación ha sido traducido a 92 lenguas (https://main.leibniz-zas.de), lo que permitiría hacer comparaciones translingüísticas fiables, puesto que todos utilizarían el mismo material, donde el número de eventos que forman cada historia no es muy amplio.
Por todo ello, el objetivo principal de este estudio era evaluar las habilidades narrativas orales de un grupo de niños y niñas hispanohablantes con TDL a partir de la narración de una de las historias del MAIN, usando medidas lingüísticas de microestructura productiva y de complejidad, y macroestructura (estructura narrativa) comparándolas con las de niños con desarrollo típico de misma edad cronológica. Un objetivo secundario era analizar los errores fonológicos y morfológicos producidos por los niños con TDL en estas narraciones orales comparándolos con los del DT, así como el tiempo de narración, la frecuencia de reformulaciones de palabras y frases, pausas y repeticiones de palabras.
MétodoParticipantesLa muestra está formada por 24 niños y niñas con un rango de edad de 7 a 11años, escolarizados en Educación Primaria del Principado de Asturias. Doce de ellos (9 niños y 3 niñas) con una edad cronológica media de 9.46 años (DT=1.09) y con una edad lingüística media de 8.26 años (DT=1.54), están diagnosticados de trastorno del desarrollo del lenguaje (TDL), y otros doce (también 9 niños y 3 niñas), con una edad cronológica media de 9.48 años (DT=1.05) y con una edad lingüística media de 10.17 años (DT=1.29), con desarrollo típico (DT) y sin dificultades lingüísticas. Los sujetos del grupo con TDL y del DT fueron emparejados por edad cronológica y sexo.
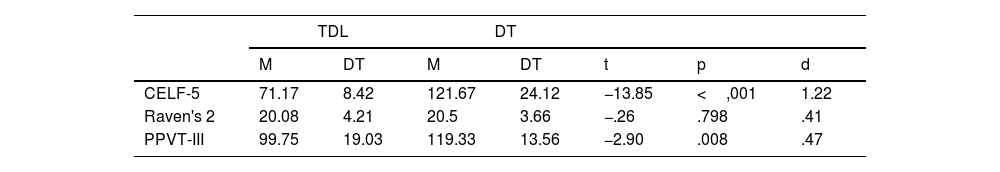
Para confirmar el diagnóstico de los niños y niñas del grupo con TDL se administró el CELF-5, en el que todos los participantes se situaron por debajo de 85, puntuación límite que indica un trastorno del lenguaje. Se empleó el Raven's2 para descartar un bajo funcionamiento cognitivo como posible causa del TDL, y además se administró el Test de Vocabulario en Imágenes Peabody (PPVT-III) para conocer la edad lingüística de todos los participantes. Se observa que hay diferencias estadísticas entre los grupos en las puntuaciones del CELF-5 con un tamaño del efecto grande y en las del PPVT-III con un tamaño del efecto mediano. Por otro lado, no se observan diferencias en la puntuación del Raven's2 (tabla 1).
MaterialesDurante el proceso de evaluación de la muestra se utilizaron tres herramientas estandarizadas para conocer sus habilidades lingüísticas y cognitivas. En primer lugar, la CELF 5: Evaluación Clínica de los Fundamentos del Lenguaje (Wiig et al., 2018), que tiene como objetivo la identificación y diagnóstico de los trastornos del lenguaje y comunicación. Realiza un análisis exhaustivo acerca de las dimensiones lingüísticas de sujetos de entre 5 y 15 años y es la herramienta diagnóstica empleada para la detección del TDL. Además, se administró el Raven's2 Matrices Progresivas (Raven, 2018), que realiza una estimación del funcionamiento cognitivo general de personas de entre 4 y 69 años. Por último, se empleó el Test de Vocabulario en Imágenes Peabody (PPVT-III) (Dunn et al., 2010), que valora el vocabulario a nivel receptivo entre 2 años y medio y 90 años.
También se administró la versión traducida y adaptada al castellano del Multilingual Assessment Instrument for Narratives (MAIN) (Ezeizabarrena y García del Real, 2020; Gagarina et al., 2019), que evalúa la comprensión y la producción de narraciones en distintos modos de elicitación (cuento modelo, recuento y cuento) con el objetivo de obtener información acerca de las habilidades narrativas orales en una o más lenguas. El MAIN se compone de cuatro historias análogas con una secuencia de seis imágenes cada una de ellas, en las que se ha controlado el nivel de complejidad cognitiva y lingüística, la equivalencia macroestructural y microestructural, así como la idoneidad cultural. Como se recoge en el propio manual de aplicación (Gagarina et al., 2012), este instrumento se compone de cuatro secuencias de imágenes impresas en color: Pajaritos, Cabritillos, Gato y Perro, cuatro guiones/textos estímulo para cada una de las cuatro historias y hoja de puntuación para el análisis de la macroestructura, los términos de estado interno y las preguntas de comprensión. Las imágenes deben descargase de la web del MAIN (www.leibniz-zas.de/en/service-transfer/main). Asimismo, en el protocolo se explica cómo se deben preparar los materiales para evaluar y las instrucciones que debe seguir el investigador para evaluar a los participantes.
Para este estudio se ha empleado la tarea de cuento de una de las cuatro historias gráficas que se compone el MAIN, concretamente la historia «Perro». Esta cuenta con una escena y tres episodios, y cada episodio se conforma de once eventos, que fueron codificados para determinar la calidad de la estructura de las narraciones.
ProcedimientoLas condiciones y las características del presente estudio han sido aprobadas por el Comité de Ética en la Investigación de la Universidad de Oviedo en la resolución con referencia 19_RRI_2022, y de acuerdo con el mismo se han recogido de todas las familias los correspondientes documentos de consentimiento informado de participación en el estudio.
En primer lugar, se reclutó al grupo de niños y niñas con TDL a través de la Asociación de Trastorno Específico del Lenguaje, un Hospital Universitario, varios centros y diversas clínicas de logopedia de la región asturiana. Una vez firmado el consentimiento informado por parte de las familias, se llevaron a cabo las evaluaciones de forma individual, en dos sesiones de una hora y media cada una. En la primera sesión se administraron el CELF-5 y el Raven's2, y en la segunda, el Test Peabody y el MAIN. La evaluación se realizó de forma individualizada, en una sala libre de distractores y ruidos externos.
Las narraciones obtenidas del MAIN fueron recogidas con un equipo de grabación compuesto por un micrófono profesional AUDIX-HT2P y una grabadora ZOOM H4n Handy Recorder. Posteriormente, las narraciones fueron transcritas en formato CHAT y analizadas con el programa CLAN del Proyecto CHILDES (MacWhinney, 2000). Por último, las narraciones se codificaron mediante el sistema de etiquetado pragmático de corpus clínicos de lengua oral PREP-CORP (Fernández-Urquiza et al., 2017), una práctica habitual en este campo. Este instrumento realiza una cuantificación precisa de las habilidades pragmáticas tanto en conversaciones espontánea como semiestructurada, lo cual permite diseñar intervenciones lingüísticas específicas y adaptadas según el perfil de habilidades pragmáticas de los participantes (Fernández-Urquiza et al., 2017). Cada narración fue transcrita y codificada por una de las autoras y revisada por otra, para garantizar su fiabilidad. Las dificultades detectadas, tanto en la transcripción como en la codificación, eran analizadas conjuntamente y las discrepancias eran resueltas entre las tres autoras.
Análisis de datosEn la microestructura se consideraron las siguientes medidas:
- -
Número total de enunciados (UTT), número total de palabras (tokens [TOK]) y número total de cláusulas (CLA) que se corresponden con la productividad de la microestructura.
- -
Longitud media de los enunciados en palabras (LMEp), número total de palabras diferentes (types: TYP), número total de marcadores del discurso (MRK) y sus tipos (Inicio Discursivo [IND], Continuidad [CON], Adición [ADI] y Cierre Discursivo [CRD]), que corresponden con la complejidad de la microestructura. La clasificación de los tipos de marcadores usada para este estudio parte de la establecida por Casado-Velarde (1993).
Respecto a la macroestructura se evaluó:
- -
Número total de episodios (EPI).
- -
Número total de eventos no repetidos (EVT).
- -
Número total de personajes (PER).
La codificación de la macroestructura se basa en el Protocolo Rápido de Evaluación Pragmática (PREP-CORP) (Fernández-Urquiza et al., 2017), que permite codificar la estructura narrativa en tres niveles: a)Escenarios: nivel básico o general, correspondiente a las localizaciones o espacios en los que tienen lugar el suceso iniciador, la complicación, el punto álgido y la resolución de la historia. b)Episodios: nivel intermedio o integrado, correspondiente a conjuntos de acciones cuya secuenciación constituye la trama de la historia. c)Eventos: nivel complejo o detallado, correspondiente a la secuencia de acciones individuales que componen la historia. En el caso de este estudio solo se han codificado dos de los tres niveles, puesto que solo hay un escenario en la historia del MAIN.
Por último, se analizaron los errores morfológicos (MOR) y errores fonológicos (FON) producidos en las narraciones orales por ambos grupos, así como el tiempo de narración, la frecuencia de reformulaciones de palabras y frases, pausas y repeticiones de palabras.
Con el fin de determinar la existencia de diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre ambos grupos, se utilizó la prueba paramétrica t de Student para dos muestras independientes para las variables de la microestructura y de la macroestructura y del tiempo de narración, la frecuencia de reformulaciones de palabras y frases, pausas y repeticiones de palabras, mediante el software estadístico JASP0.17.2, puesto que estos datos presentan una distribución normal según la prueba de normalidad de Shapiro-Wilks (p<.05). Mientras que para los errores fonológicos y morfológicos se empleó la prueba no paramétrica de Mann-Whitney porque los datos no presentan una distribución normal. También se calculó el tamaño del efecto, mediante el indicador de la d de Cohen (Cohen, 1988), donde <.5 es un tamaño del efecto pequeño; entre .5 y .8, un tamaño del efecto medio, y >.8, un tamaño del efecto grande.
ResultadosLos resultados se agrupan en tres apartados. El primero y el segundo, con el fin de analizar las habilidades narrativas orales del grupo con TDL y con DT a partir de la narración de una de las historias del MAIN, recogen los estadísticos descriptivos, las diferencias de medias y el tamaño del efecto de las medidas lingüísticas de microestructura productiva y de complejidad, y de macroestructura. En tercer lugar, se analizan los errores fonológicos y morfológicos producidos por los niños con TDL en estas narraciones orales, comparándolos con los del DT, así como el tiempo de narración, la frecuencia de reformulaciones de palabras y frases, pausas y repeticiones de palabras.
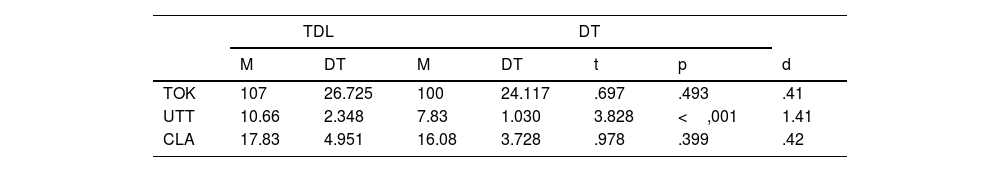
Microestructura productiva y de complejidadA partir de los resultados en las medidas microestructurales de productividad se pueden observar diferencias estadísticamente significativas en el número de enunciados (UTT), con mayor número de UTT en el grupo TDL que en el grupo DT, con un tamaño del efecto grande. Aunque la diferencia no es significativa, también se ha observado que el grupo con TDL produce un mayor número de palabras (TOK) y de cláusulas (CLA) que el grupo con DT (tabla 2).
Estadísticos descriptivos, valor de t y su significación y tamaño del efecto (d) en las medidas de la microestructura a nivel de productividad del TDL y DT
| TDL | DT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | DT | M | DT | t | p | d | |
| TOK | 107 | 26.725 | 100 | 24.117 | .697 | .493 | .41 |
| UTT | 10.66 | 2.348 | 7.83 | 1.030 | 3.828 | <,001 | 1.41 |
| CLA | 17.83 | 4.951 | 16.08 | 3.728 | .978 | .399 | .42 |
CLA: cláusulas; TOK: tokens; UTT: enunciados.
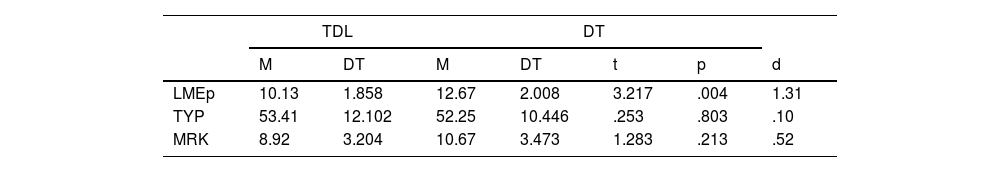
En cuanto a la complejidad de la microestructura, los resultados indicaron diferencias estadísticamente significativas en longitud media de los enunciados en palabras (LMEp), con una longitud mayor en el grupo DT que en el grupo con TDL, donde el tamaño del efecto es grande. Se observa que el grupo con TDL produjo más palabras diferentes (TYP) que el grupo con DT, aunque las diferencias no fueron estadísticamente significativas. A pesar de que en los MRK no se obtuvieron diferencias, se puede observar que los sujetos del grupo con TDL produjeron menos marcadores que el grupo con DT (tabla 3).
Estadísticos descriptivos, valor de t y su significación y tamaño del efecto (d) en las medidas de la microestructura a nivel de complejidad del TDL y DT
| TDL | DT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | DT | M | DT | t | p | d | |
| LMEp | 10.13 | 1.858 | 12.67 | 2.008 | 3.217 | .004 | 1.31 |
| TYP | 53.41 | 12.102 | 52.25 | 10.446 | .253 | .803 | .10 |
| MRK | 8.92 | 3.204 | 10.67 | 3.473 | 1.283 | .213 | .52 |
LMEp: longitud media de enunciado en palabras; MRK: marcadores discursivos; TYP: types.
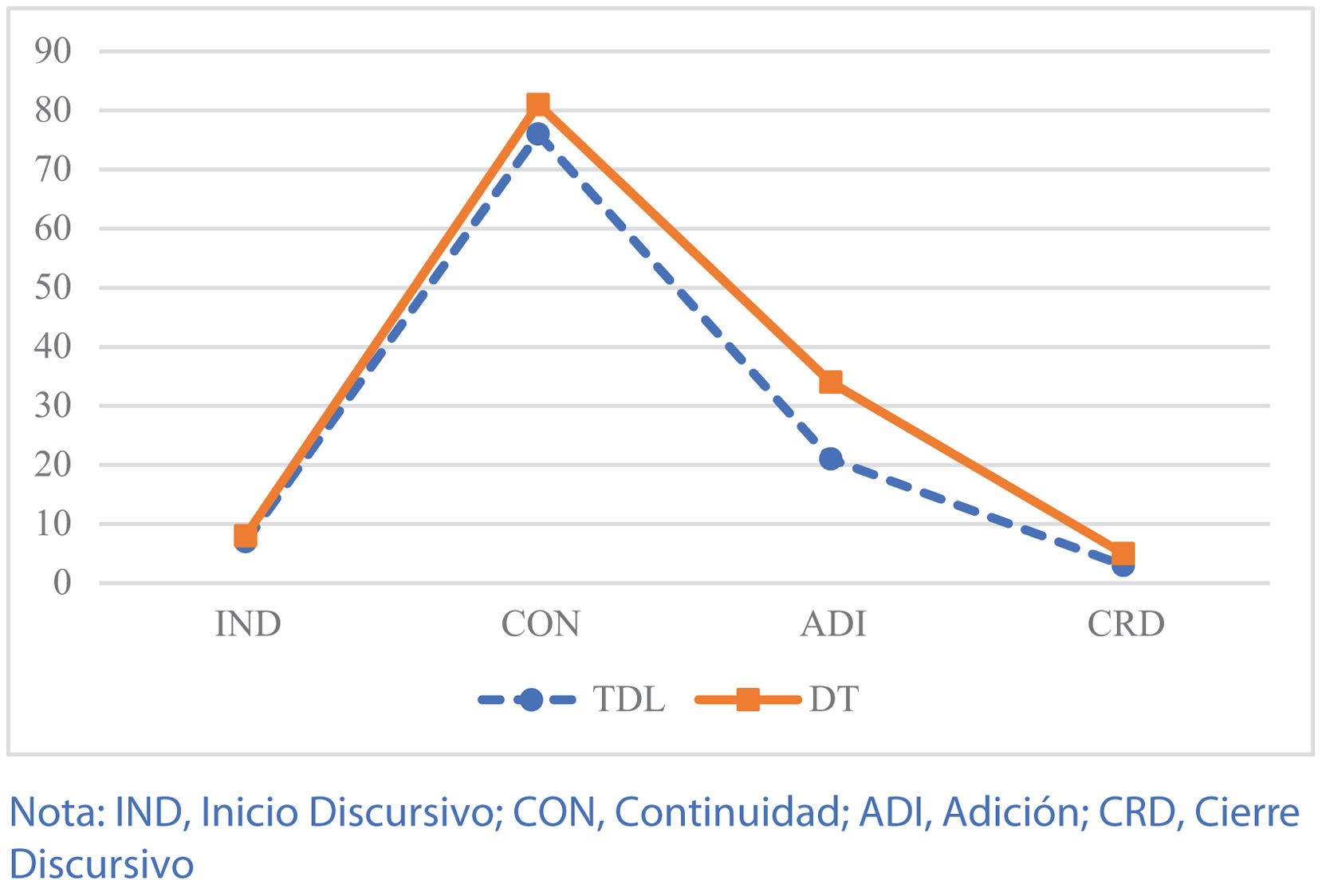
En cuanto a los tipos de MRK, en la figura 1 se observa la frecuencia absoluta de cada uno de los cuatro tipos de marcadores (Inicio Discursivo [IND], Continuidad [CON], Adición [ADI] y Cierre Discursivo [CRD]). Ambos grupos emplearon mayor frecuencia de marcadores CON que de otro tipo en sus narraciones orales. Por otro lado, aunque se observa que los niños con DT empleaban más los marcadores ADI que los niños con TDL, estas diferencias no son significativas. Los marcadores empleados con menor frecuencia por ambos grupos fueron los IND y CRD.
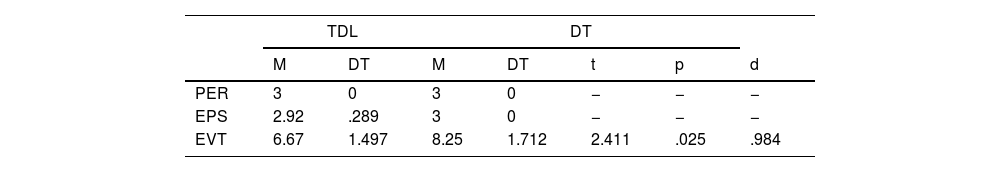
Macroestructura (estructura narrativa)En lo que respecta a la macroestructura, se observa un efecto techo en los personajes (PER) en ambos grupos, de ahí que no haya valores en t, en p y en d en la tabla 4. Por su parte, los participantes del grupo DT producen los tres episodios (EPS) de la estructura narrativa, mientras que los del grupo con TDL producen de media 2.92 episodios. Tampoco en esta variable se obtienen valores de t, puesto que la desviación típica en el grupo con DT es 0. Se observan diferencias estadísticamente significativas en el número de eventos (EVT) con un tamaño del efecto grande, con un mayor número de eventos producidos por el DT (tabla 4).
Errores lingüísticos y tiempo de narración, reformulaciones, repeticiones y pausasRespecto al objetivo secundario, analizar los errores fonológicos y morfológicos cometidos por ambos grupos en las narraciones orales, se ha observado que el grupo con TDL produce un mayor número de errores fonológicos que el grupo DT (MTDL=9.75; DT=10.89; MDT=.92; DT=2.39), siendo la diferencia significativa (U=17.5000; p=.001; d=.757). En el caso de los errores morfológicos, el grupo DT no produjo ningún error, mientras que en el grupo con TDL la media de errores morfológicos es de 1.167 (DT=1.946).
Si bien se ha observado que los niños con TDL necesitan más tiempo para narrar las seis viñetas de la historia que los niños con DT (MTDL=70.83; DT=17.903 vs MDT=46.75; DT=11.274), realizan más reformulaciones (MTDL=1.75; DT=1.865 vs MDT=.91; DT=1.165), repeticiones de palabras (MTDL=2.66; DT=1.969 vs MDT=.83; DT=1.115), y pausas (MTDL=2.33; DT=1.614 vs MDT=3.66; DT=2.807), solo en el caso del tiempo de narración (t=3.943; p <.001; d=−1.610) y de las repeticiones (t=2.806; p=.010; d=−1.146) las diferencias son estadísticamente significativas con un tamaño del efecto grande en ambas variables.
DiscusiónEl objetivo principal de este estudio era evaluar las habilidades narrativas orales de un grupo de niños y niñas hispanohablantes con TDL a partir de la narración de una de las historias del MAIN, usando medidas lingüísticas de microestructura y macroestructura productiva y de complejidad comparándolas con las de niños con DT de misma edad cronológica. Los resultados reflejaron que los participantes del grupo con TDL obtuvieron puntuaciones más bajas en las medidas lingüísticas de la microestructura y la macroestructura de las narraciones orales, tal y como se ha observado en otras investigaciones (Acosta et al., 2013; Botting, 2002; Coloma et al., 2016; Del Valle et al., 2018; Duinmeijer et al., 2012; Fichman et al., 2022; Lindgren et al., 2023; Pham et al., 2019; Vandewalle et al., 2012; Xue et al., 2022), lo que repercutiría negativamente en el desarrollo social y académico del niño, ya que la habilidad para construir narraciones es esencial para el proceso de aprendizaje (Acosta et al., 2014; Favot et al., 2020; Fichman et al., 2022).
En cuanto a la microestructura narrativa a nivel de productividad y complejidad, los niños y las niñas del grupo con TDL, aunque emitieron significativamente un mayor número de enunciados que el grupo DT, la longitud media de los mismos era más corta (Mäkinen et al., 2014; Marini et al., 2008; Xue et al., 2022). Esta diferencia en los enunciados a favor del grupo con TDL podría deberse a que produjeron significativamente más perseveraciones, mayor número de enunciados reformulados y pausas, rasgos característicos de las narraciones de los niños con TDL (Guo et al., 2008), los cuales ha sido considerados como marcadores clínicos (Taha et al., 2021). Por tanto, la variable microestructural clásica de la longitud del relato parece menos útil para determinar las diferencias entre ambos grupos, que la del LMEp, según estos resultados.
Por otro lado, a pesar de que los participantes con DT emplearon más marcadores discursivos en sus narraciones que los participantes con TDL, esta diferencia no fue significativa, resultado que también ha sido observado en un grupo de niños chilenos de 7 años con TDL (Asenjo y Nazar, 2020). No obstante, los participantes de ambos estudios difieren en la frecuencia de uso de los tipos de marcadores; nuestros participantes usaron más marcadores de continuidad, mientras que los niños chilenos emplearon en mayor frecuencia los de adición (Asenjo y Nazar, 2020). Sin embargo, no todas las investigaciones en español muestran ausencia de diferencias. Así, Delgado-Cruz et al. (2022) observaron que el grupo con TDL usaba significativamente menor número de conectores intra-sentencia y extra-sentencia que los niños con DT. Ello podría deberse a las diferencias de edad cronológica de los participantes, puesto que los de la investigación de Delgado-Cruz et al. (2022) estaban en un rango de edad menor (5;2-6;3 años) que los participantes del presente estudio. Parece, pues, que los recursos para conectar cláusulas son un logro de desarrollos tardíos del lenguaje (Tolchinsky, 2004).
En otras medidas a nivel microestructural de productividad (TOK, CLA) y complejidad (TYP) no se observaron diferencias significativas; incluso los niños con TDL mostraron un rendimiento mejor que los niños con DT en todas ellas. También Marini et al. (2008) observaron que los niños con TDL produjeron una cantidad de palabras comparable a la producida por el grupo con DT, aunque estas contenían muchas omisiones y sustituciones de morfemas ligados y libres, lo que indicaría problemas para acceder a los niveles de lema y lexema del procesamiento léxico. Por tanto, los datos no avalan que los niños con TDL produzcan un menor número de cláusulas (Mäkinen et al., 2014), de palabras diferentes (Fey et al., 2004) y más problemas de cohesión (Fichman et al., 2022; Norbury y Bishop, 2003) que los niños con DT. Estas diferencias podrían deberse a las características de tarea empleada, a la edad de los participantes y/o al idioma de la investigación. Aunque todas las investigaciones utilizaron una tarea de cuento, el material empleado era diferente; así, Mäkinen et al. (2014) y Norbury y Bishop (2003) emplearon un libro en imágenes; Fey et al. (2004), una historia de elaboración propia formada por tres imágenes, y Fichman et al. (2022), las historias del Gato y el Perro del MAIN. En cuanto a la edad, excepto en el estudio de Norbury y Bishop (2003), todos tienen menos de 8 años.
Respecto a la macroestructura narrativa, los participantes de ambos grupos introdujeron los tres personajes y mencionaron los tres episodios en los que se había dividido la narración. Sin embargo, el grupo con TDL produjo menos eventos que el DT, es decir, explicó con menor detalle la historia, lo que afectaría a la estructura narrativa a pesar de emplear más tiempo en la narración (Blom y Boerma, 2016; Boerma et al., 2016; Pham et al., 2019; Xue et al., 2022). Esto confirmaría que los niños con TDL en una tarea de narración, a partir de material visual, como es el MAIN, tienden a omitir ciertos sucesos de la misma, lo que daría lugar a que sus narraciones sean más descriptivas, a la vez que usan menos conectores. No se han recogido datos sobre la complejidad de la macroestructura, lo que hubiera proporcionado información sobre si la historia seguía la secuencia lógica de los eventos recogidos en los dibujos. Ambas medidas serían necesarias para tener una imagen completa y concluyente de cómo los niños con TDL elaboran la estructura narrativa de la historia evaluada con el MAIN (Lindgren et al., 2023).
Respecto al objetivo secundario, el análisis de los errores morfológicos y fonológicos que producían los niños con TDL en sus narraciones orales, se observó que producían significativamente más errores de ambos tipos en comparación con el DT. La presencia de errores morfológicos en las narraciones del grupo con TDL confirmaría que estos niños son menos precisos gramaticalmente que los niños con DT (Acosta et al., 2014; Blom y Boerma, 2016; Del Valle et al., 2018; Duinmeijer et al., 2012; Fichman et al., 2022; Guo et al., 2008; Marini et al., 2008; Norbury y Bishop, 2003). Además, el grupo con TDL produjo un mayor número de errores fonológicos que el DT, al igual que se observó en el estudio de Marini et al. (2008), lo que afectaría a la inteligibilidad de sus narraciones. Estos datos confirmarían que algunos de los participantes presentan un retraso en su desarrollo fonológico teniendo en cuenta que los niños castellanoparlantes culminan el mismo a la edad de 7 años (Bosch, 2004).
LimitacionesAlgunas de las limitaciones de este estudio son el número de participantes, pues un aumento en la muestra de estudio proporcionaría unos resultados más robustos y consistentes. Además, y a pesar de que los grupos eran homogéneos en cuanto a la edad cronológica y sexo, en futuras investigaciones se sugiere contar con un grupo emparejado por edad lingüística con el grupo con TDL, para conocer si las habilidades narrativas de estos niños se equipararían a las de los niños más pequeños, o si estos presentarían un perfil narrativo idiosincrático.
ConclusionesEl presente estudio sugeriría que el MAIN es un fiable instrumento para evaluar las habilidades narrativas oral de los niños hispanohablantes con TDL analizando la microestructura y la macroestructura de sus narraciones. Se ha podido confirmar que estos niños presentan una competencia narrativa menor que los niños con desarrollo típico de su misma edad cronológica, puesto que producen historias menos detalladas y con oraciones más cortas. Además, se confirma que las narraciones son un buen indicador de la competencia lingüística a nivel de fonología y morfosintaxis, donde se ha observado que ambos dominios estaban especialmente afectados en los niños con TDL.
Este estudio avalaría la importancia de la evaluación de las habilidades narrativas a través de un instrumento con validez ecológica como el MAIN, lo que le otorga relevancia para la práctica logopédica, siendo adecuado para la identificación de las dificultades narrativas a nivel de microestructura y de macroestructura de los niños con TDL. Por tanto, el MAIN permite a investigadores y logopedas examinar, de forma exhaustiva, la competencia narrativa, mediante una evaluación dinámica.
Conflicto de interesesLas autoras declaran que no existe conflicto de intereses en este estudio.
A todas las familias que han participado en el estudio. A la Asociación TELAsturias, Hospital Universitario de Cabueñes, Colegio Santa María del Naranco de Oviedo y clínicas privadas de logopedia por su ayuda en el reclutamiento de participantes. A la Biblioteca de la Universidad de Oviedo por prestarnos los instrumentos de evaluación.