Comprobar la eficacia predictora de dificultades de lectura del Test para la detección temprana de las dificultades en el aprendizaje de la lectura y escritura y de la Batería de iniciación a la lectura (BIL3-6).
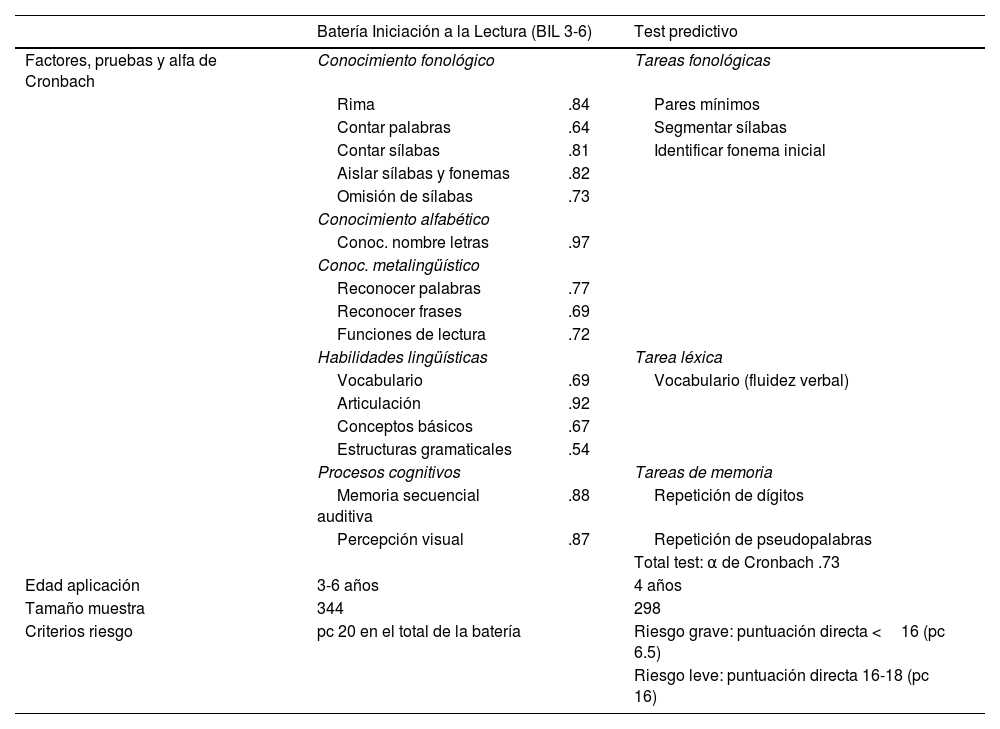
MétodoSe aplicaron ambos instrumentos a alumnado de 2.° curso de Educación Infantil (107 participantes para el Test de detección temprana de las dificultades en el aprendizaje de la lectura y escritura y 211 para la BIL3-6), y dos años más tarde se evaluó su lectura por medio de la Lectura de Palabras y Pseudopalabras del Prolec-R y del Texto IB del TALE. También se obtuvo del profesorado una valoración del aprendizaje de los participantes.
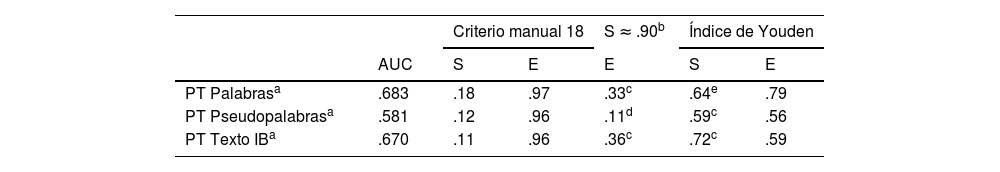
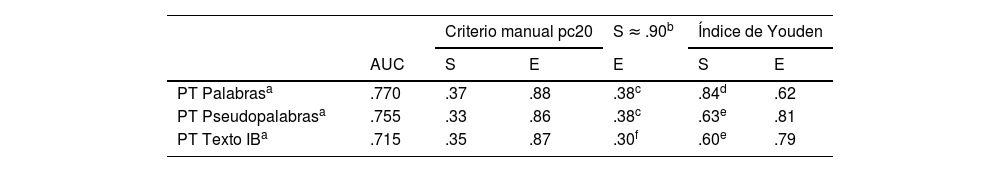
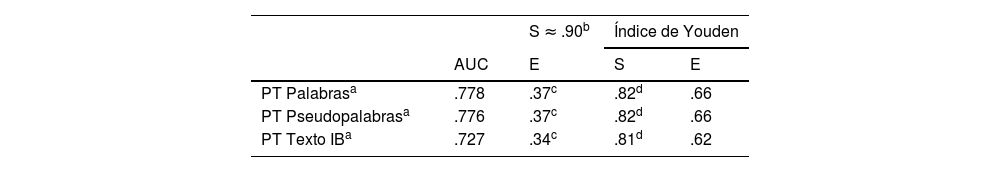
ResultadosSe calculó la sensibilidad (S) y la especificidad (E) de ambos instrumentos basándose en los agrupamientos del alumnado en función de los resultados en las tres tareas de lectura: buenos y malos lectores a partir del pc16. Ninguno de los dos instrumentos examinados alcanza unos valores adecuados de S y E. Si se toma a priori un valor adecuado de S para asegurar que se identifica al alumnado con riesgo de dificultades, entonces la E es muy baja y, por tanto, la cantidad de falsos positivos hace imposible adoptar decisiones educativas acertadas. La valoración general del profesorado sobre el aprendizaje de cada participante muestra similar capacidad predictiva que ambos instrumentos.
To check the predictive efficacy of subsequent reading difficulties of the Test for the early detection of difficulties in learning to read and write and the Battery for initiation to reading (BIL3-6).
MethodBoth instruments were applied to students in the 2nd year of Preschool (107 participants for the Early Detection Test and 209 for the BIL3-6), and 2 years later their reading was evaluated by reading Words and Pseudowords of the Prolec-R and Text IB of the TALE. An assessment of the participants’ learning was also obtained from the teachers.
ResultsThe sensitivity (S) and specificity (E) of both instruments were calculated based on the groupings of the students based on the results in the 3 reading tasks: good and poor readers from pc16. Neither of the two instruments examined reach appropriate values of S and E. If an appropriate value of S is taken a priori to ensure that students at risk of difficulties are identified, then the E is very low, and therefore the number of false positives makes it impossible successful educational decisions. The general assessment of the teaching staff on the learning of each participant shows a similar predictive capacity as both instruments.