Los problemas de alimentación ocurren en el 80% de niños que presentan algún retraso del desarrollo debido a condiciones médicas crónicas, y pueden presentarse en diferentes grados y formas. Los niños con trastornos de la deglución (TD) pueden manifestar síntomas en todo momento de la alimentación.
ObjetivoDiagnosticar e intervenir TD y/o trastornos de conducta alimentaria (TCA) en niños con patología médica crónica compleja, derivados a un equipo interdisciplinario, durante el año 2017, en un hospital de alta complejidad.
Material y métodosEstudio analítico, prospectivo y longitudinal con intervención de un equipo interdisciplinario. Se realizó evaluación clínica fonoaudiológica de la deglución, ofreciendo pautas de estimulación y modificación de consistencias.
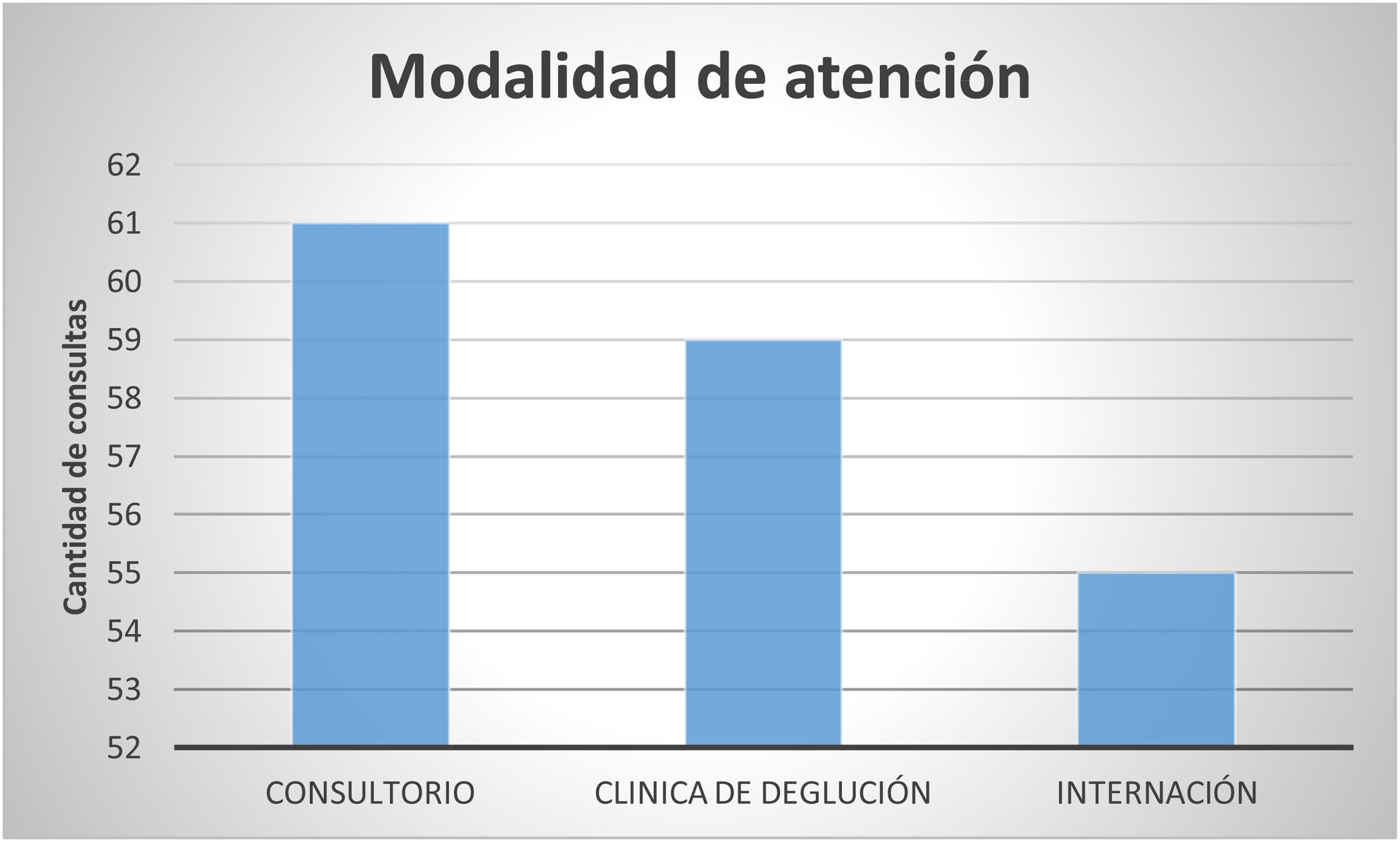
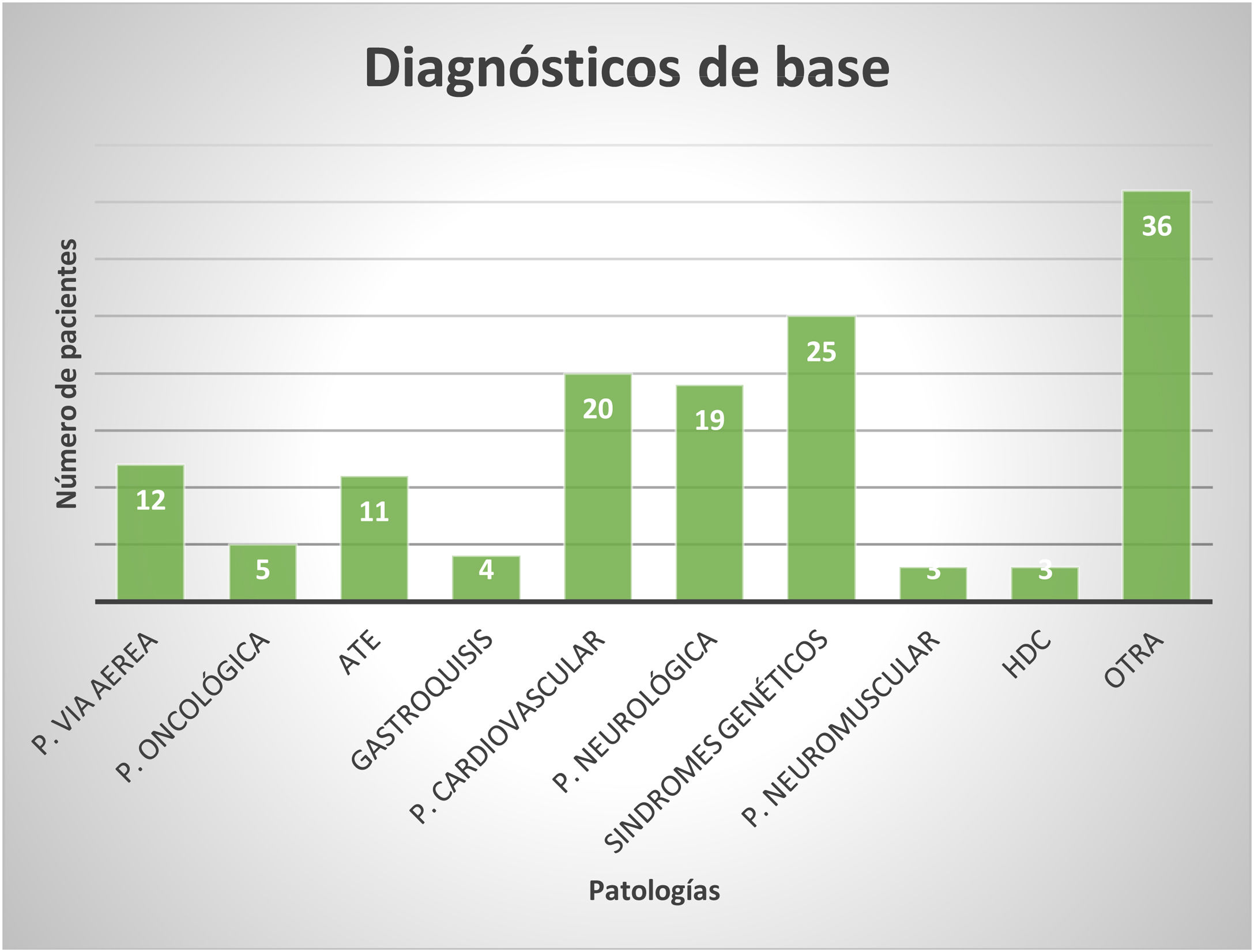
ResultadosSe evaluaron 139 pacientes de entre 2meses y 3años; el 38% eran mujeres, y el 77% con soporte nutricional enteral (SNE). El 73% presentaron TD exclusivamente o asociado a un TCA. El 38% que ingresaron con SNE lograron el destete (sin diferencia significativa entre los que tenían o no TD [p=0,85] y los que tenían o no traqueotomía [p=0,88]), y del grupo que no logró el destete, un 54% aumentaron el aporte por vía oral. Se observó una diferencia estadísticamente significativa en el destete de los pacientes que concurrieron al espacio de la clínica con respecto a los que no (p=0,016) y un mayor tiempo de intervención entre quienes lograron el destete y quienes no: 5,2±3,1 vs 3,45±3,1meses (p=0,0099). El 70% continuqron seguimiento por el fonoaudiólogo.
ConclusiónEn niños con condiciones médicas complejas es esencial el trabajo interdisciplinario y especializado en esta temática. En los casos de TD, la intervención fonoaudiológica se asume como fundamental para la detección precoz y el correcto abordaje de la disfagia.
Children with swallowing disorders (SD) may manifest symptoms at all times during feeding. This clinical entity can present itself in different grades and forms.
ObjectiveTo diagnose and intervene in SD and/or eating behavior (EB) in children with complex chronic medical conditions referred to an interdisciplinary team, during 2017, in a high complexity hospital.
Material and methodsAnalytical, prospective and longitudinal study with the intervention of an interdisciplinary team. Clinical phonoaudiological evaluation of swallowing was performed, offering guidelines for stimulation and consistency modification.
Results139 patients, between 2 month and 3 years old, 38% women, 77% with enteral nutritional support (ENS) were evaluated, 73% presented SD exclusively or associated with an EB. The 38% who entered with ENS achieved weaning (without significant difference between those who had or not SD, P=.85, and those who had or not tracheotomy, P=.88), and of the group that did not achieve weaning, oral contribution increased in 54% of cases. A statistically significant difference was observed in weaning of patients who attended the interdisciplinary space with respect to those who did not (P=.016) and longer intervention time between those who achieved weaning and those who did not, 5.2±3.1 vs 3.45±3.1 months (P=.0099). And 70% off patients continued follow with the speech therapist.
ConclusionInterdisciplinary and specialized work in this subject is essential in children with complex medical conditions. In cases of SD, speech therapy intervention, it is assumed as essential for early detection and correct approach to dysphagia.