Estudiar la correlación entre la existencia de residuo posmiccional (rp) con otros parámetros urodinámicos.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo. 121 pacientes (33V, 88M). Edad=68,22 y S=12,904 (16–90 años) que presentaban rp realizándose estudio videourodinámico completo. Se excluyeron disfunciones neurógenas vésicouretrales y posradioterapia pélvica. Se estudiaron correlaciones estadísticas entre residuo y síntomas, parámetros urodinámicos y hallazgos de la exploración física. Se ha realizado estadística descriptiva y correlaciones (rho de Spearman y comparación de medianas [chi cuadrado]).
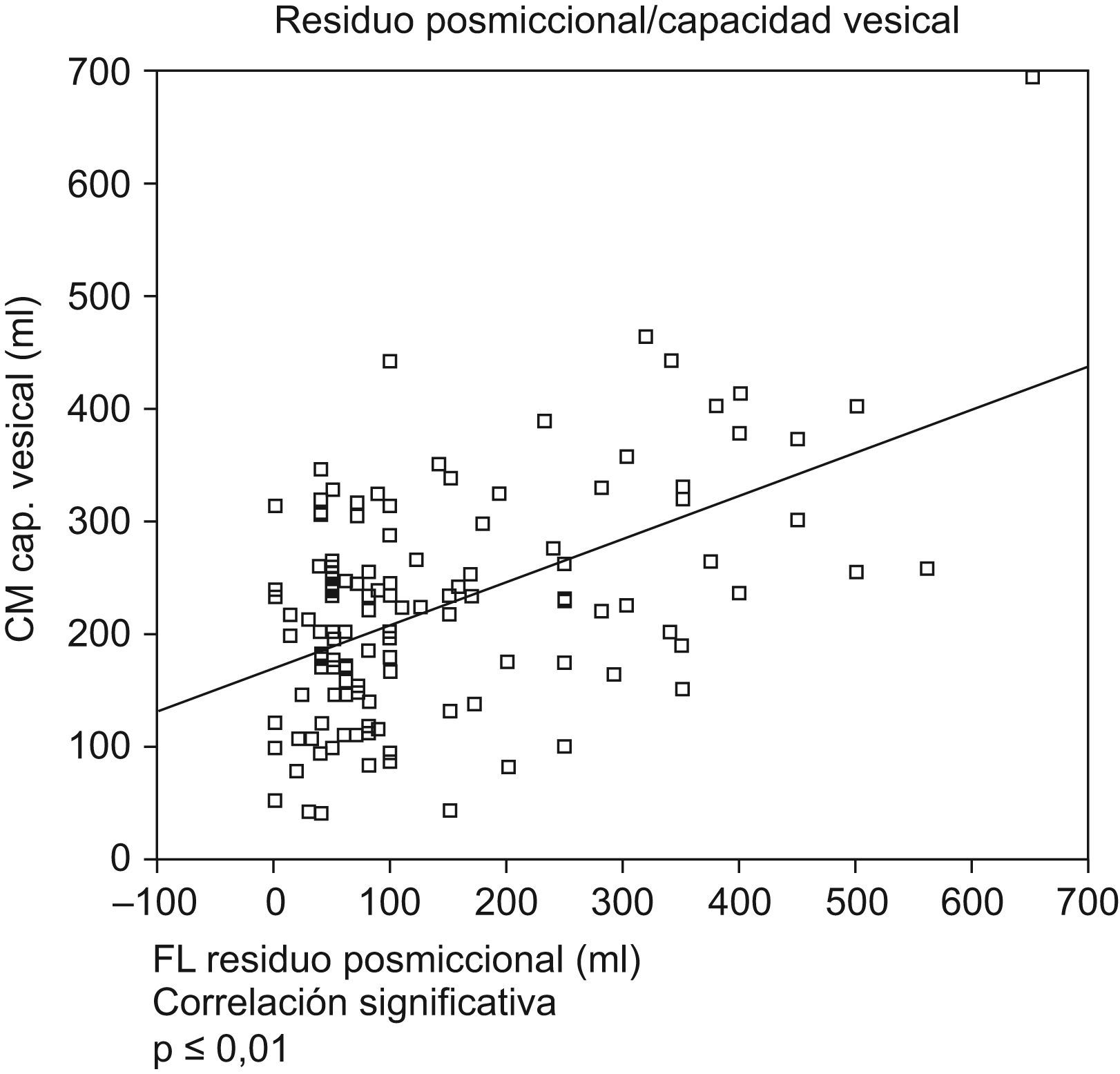
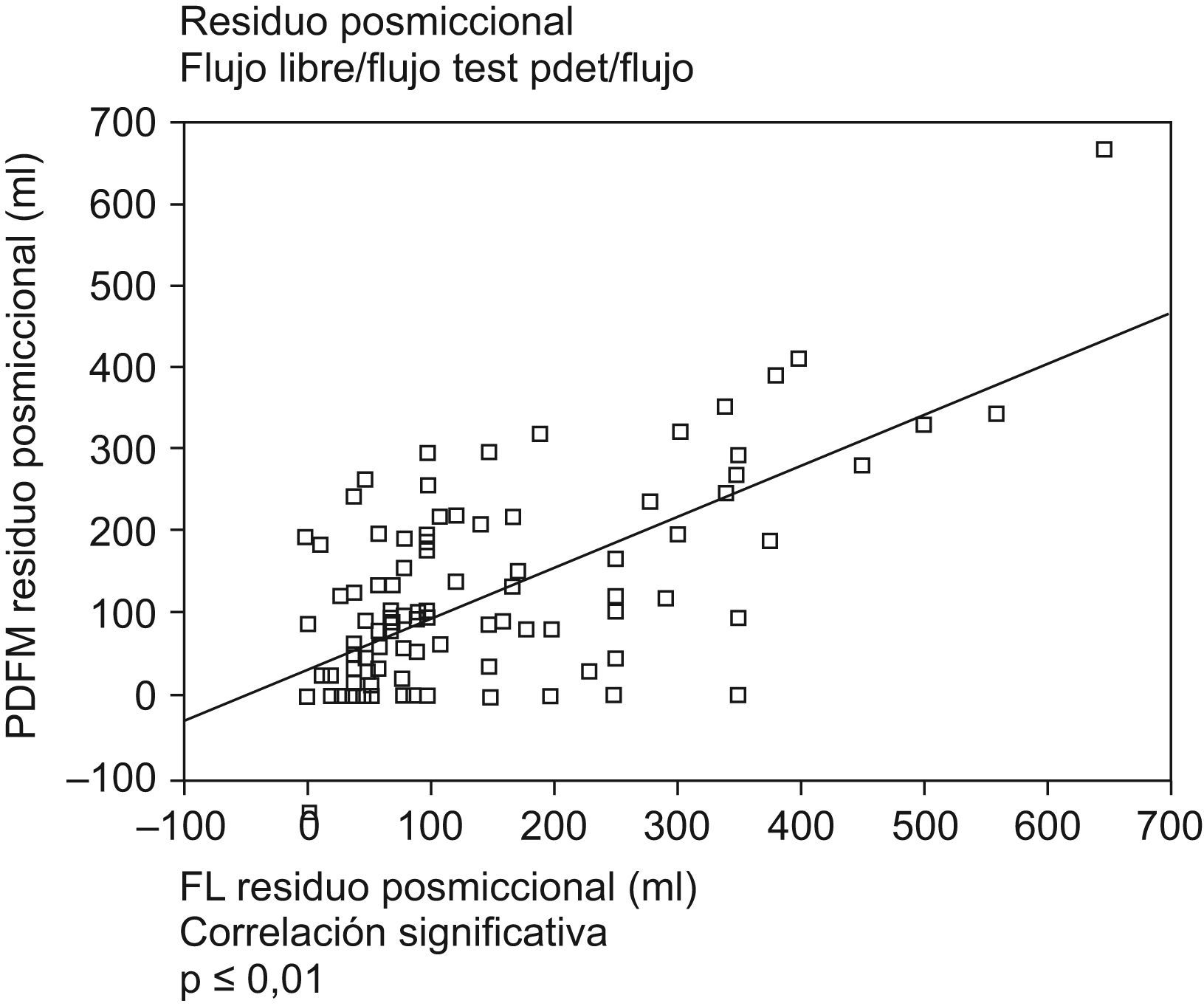
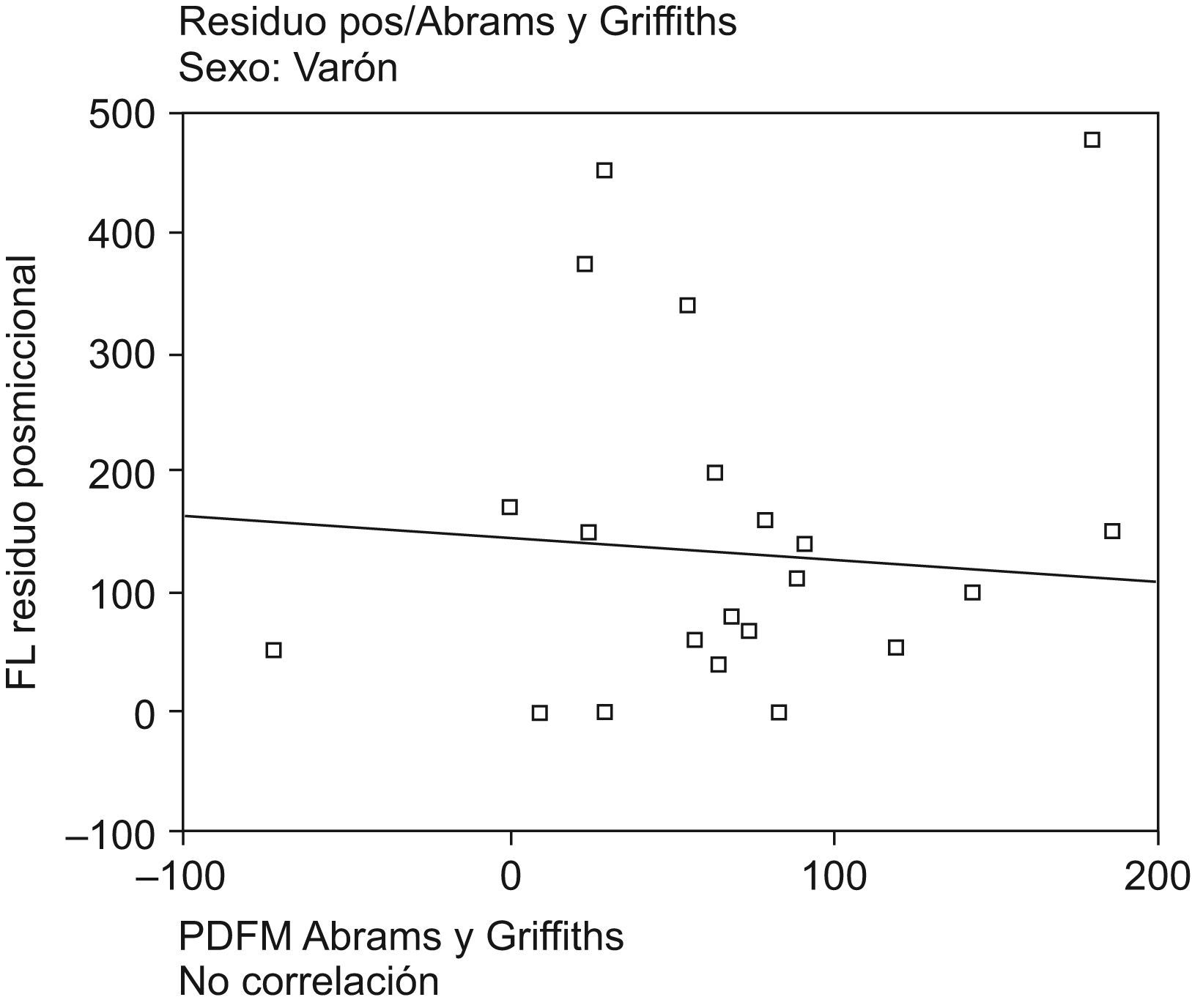
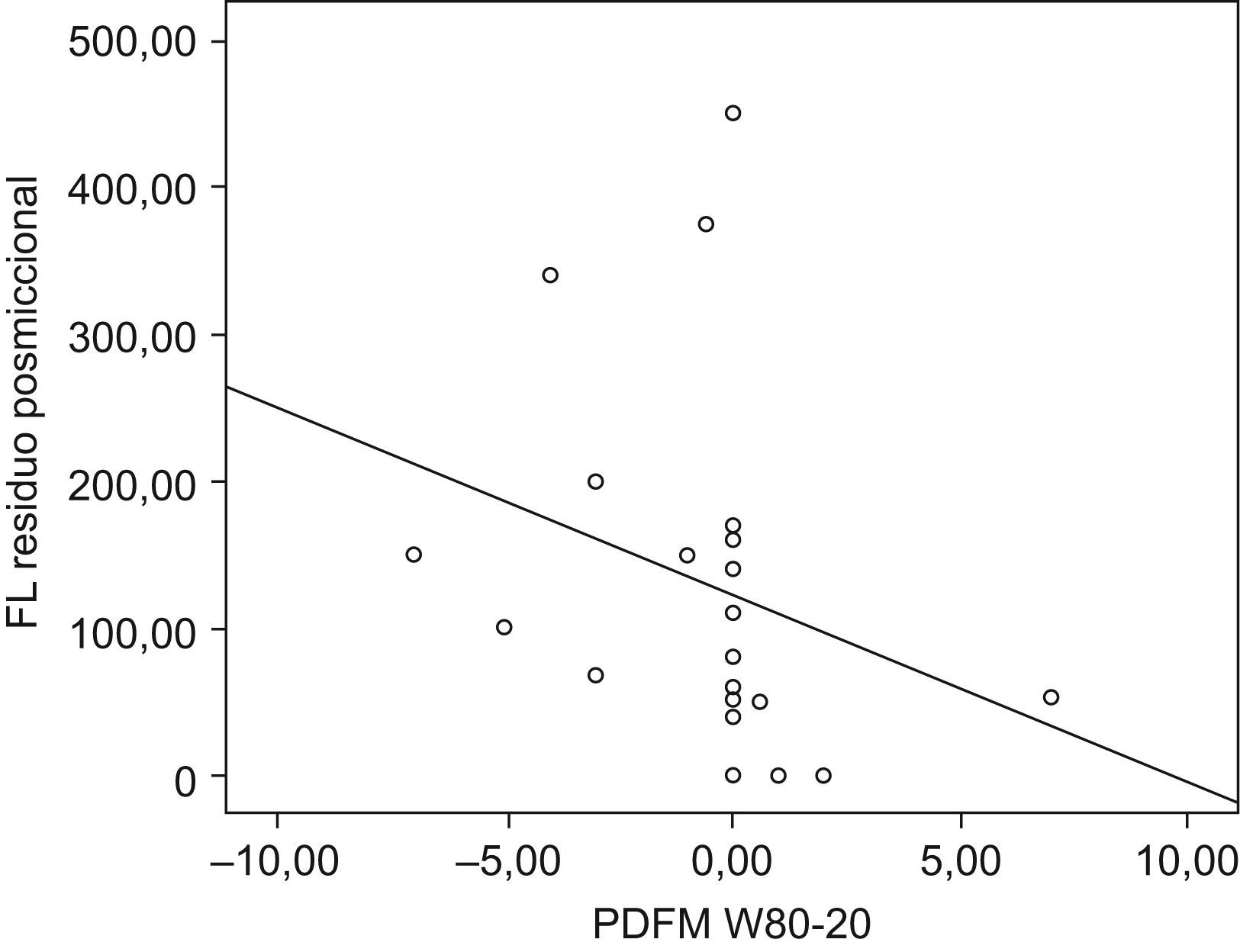
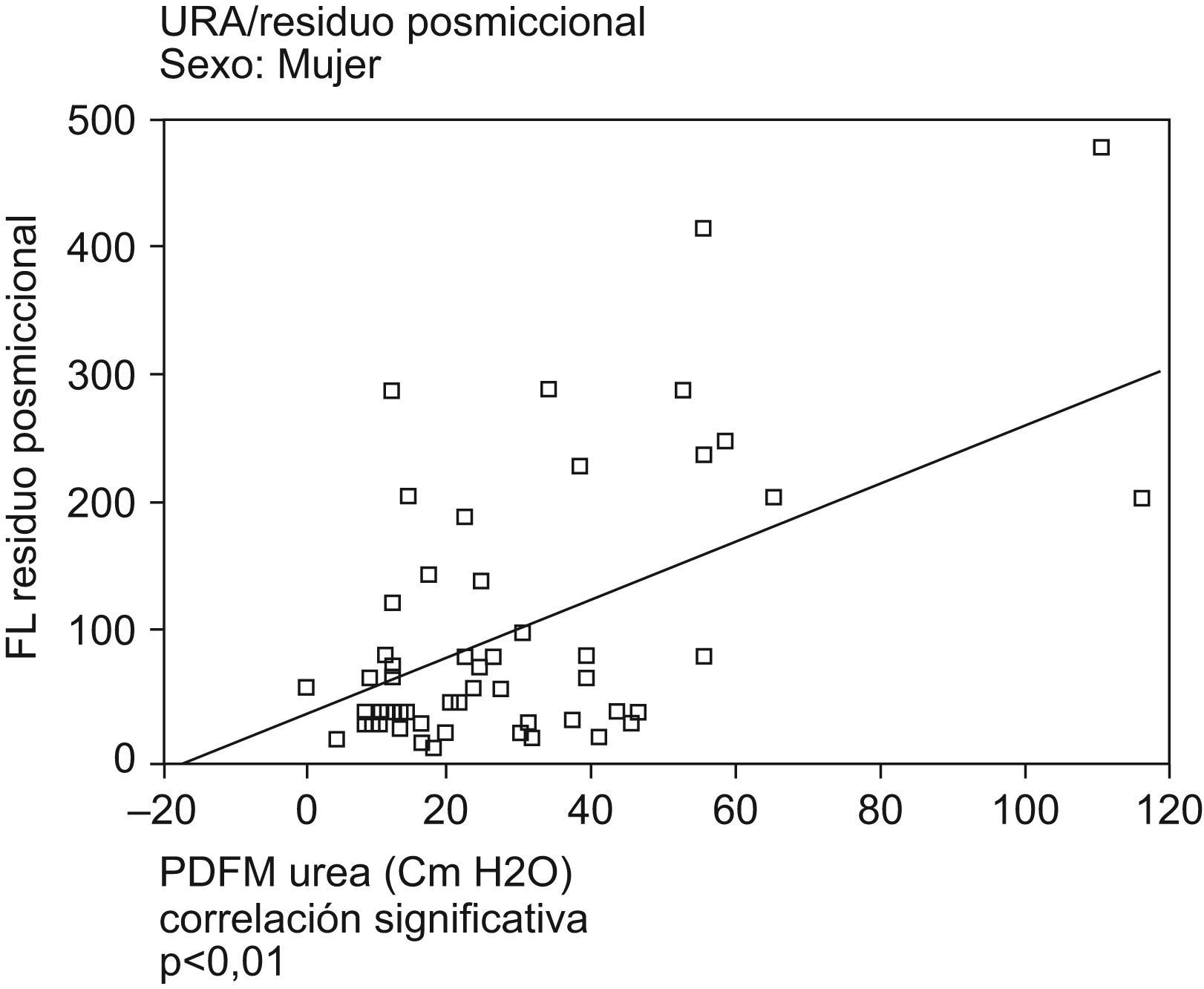
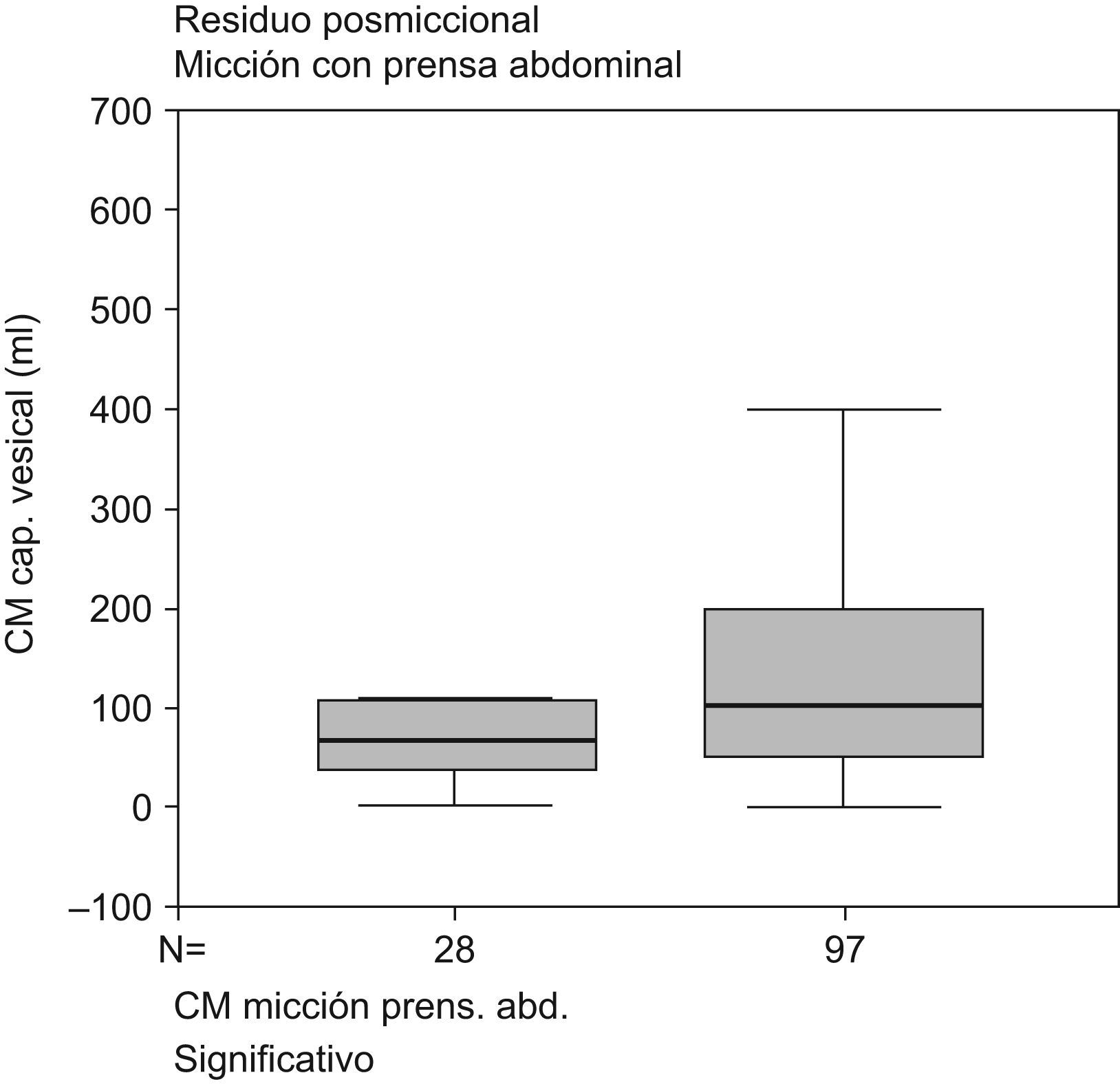
ResultadosSe encontró correlación positiva (hombres y mujeres) entre rp y capacidad vesical (p=0,001), entre rp (flujometría libre) y el rp (test pdet/flujo) (r=0,450 p=0,001). En mujeres entre rp y resistencia uretral (p=0,001) y entre rp y micción con prensa abdominal (p<0,05) Se encontró correlación negativa (hombres) entre rp y parámetros de contracción istotónica del detrusor (W80–W20) (p<0,05). No se ha encontrado correlación entre rp y parámetros cistomanométricos, ni con el diagnóstico urodinámico de obstrucción, semiología radiológica asociada, vejiga hiperactiva, ni síntomas funcionales de vaciamiento en el hombre.
ConclusionesEl rp urodinámicamente se comportó más como un parámetro de medida de contractilidad del detrusor que como un parámetro de obstrucción del tracto urinario inferior. El rp no presentó ninguna semiología clínica ni radiológica asociada específica.
To study the possible correlation between the existence of postmicturition residual (PR), both in men as in women, with other urodynamic parameters.
Material and methodsA retrospective study in a series of 121 patients (33 male, 88 female), age X=68.22 and SD=12.904 (16–90 years), with a significative PR had been underwent a videourodynamic study. All cases of neurogenic vesicourethral dysfunctions and post pelvic radiotherapy were excluded. Statistical study was performed between the PR and the presence of urinary symptoms, urodynamic data, and findings of physical examination. The study was conducted, both descriptive and with statistical correlations. We used the Spearman Rho and compared with the median chi-square.
ResultsWe found a positive correlation (men and women), between the PR and bladder capacity (p=0.001) and between the PR free flowmetry and PR test pdet/flow (r=0.450 p=0.001). In women, a positive correlation was found between the PR and the urethral resistance (URA) (p=0.001), and between PR and voiding by abdominal pressure (p<0,05). We found a negative correlation in men between the PR and the parameters of detrusor contraction (W80–W20) (p<0.05). Not found statistically significant correlation between the PR and cystometry, nor with the urodynamic diagnosis of obstruction, associated radiological semiology, hyperactive bladder and emptying symptoms in men.
ConclusionsThe PR behaved more as a parameter measurement of detrusor contractility, than a parameter of the lower urinary tract obstruction. The PR was not associated with any clinic or associated radiologic semiology.