The objective of this study was to evaluate safety and efficacy of Privigen®, a 10% intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), in a particular group of paediatric patients (highly sensitive to previous IVIG infusion) affected with Primary Immunodeficiencies (PID).
Material and methodsPatients (n=8) from 3 to 17 years old diagnosed of PID who often suffered from adverse events related to the infusion to previous IVIG were switched to Privigen® in an open protocol. Data were prospectively collected regarding Privigen® administration: infusion, safety and efficacy. In parallel, data on safety and tolerance were retrospectively collected from medical charts regarding the previous 10% IVIG product used.
Results50% of the patients required premedication with previous IVIG. At the end of the study none required premedication with Privigen®. The infusion rate was lower than that recommended by the manufacturer. All patients had suffered through adverse events during previous IVIG infusion being severe in three patients and recurrent in the rest. With Privigen® only three patients suffered from an adverse event (all cases were milder than previous related). Trough levels of IgG remained stable. None suffer from any episode of bacterial infection.
ConclusionThe present work shows that Privigen® was safe in a group of hypersensitive paediatric patients who did not tolerate the administration of a previous 10% liquid IVIG by using a particular infusion protocol slower than recommended. The number of adverse effects was smaller than published, and all cases were mild. No premedication was needed. Privigen® was also effective in this small group.
Gammaglobulin is a standard and life-saving therapy in primary immunodeficiencies (PID) as well as in diseases dealing with immunoglobulin dysregulation such as neoplasia or autoimmune disorders.1
The discovery, 50 years ago, that immunoglobulin replacement therapy decreased the susceptibility to infection in patients with PID has led to ongoing efforts to develop better, safer and more comfortable formulations.2 Replacement of missing IgG antibodies has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of infections.3–5
There are currently a number of products that provide chemically unmodified lyophilised powders or liquid concentrates of polyclonal IgG; these products are produced from plasma recovered from whole blood donations, or more commonly from a large number of plasmapheresis donors.6 Although all these intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) end products are composed of high IgG concentrations, variations in manufacturing processes lead to unique product characteristics.7 In recent years, new formulations with IgG concentration of 10% have appeared aiming at decreasing the time of administration. Indeed, the rate at which IVIG can be administered can have a significant impact on patient time saving and health service use.8 Likewise, liquid IVIG, as opposed to lyophilised products which require reconstitution,9,10 are gaining support. Comparative studies between liquid and lyophilised formulations of IVIG have been published.11 They concluded that liquid formulations were therapeutically equivalent and equally well tolerated to lyophilised formulations but in a more convenient ready-to-use dosage form that may also reduce preparation errors.11
Despite the clear benefit of IVIGs for patients, concern exists about adverse events that keep being reported.3 Most of these are infusion reactions that are related to the rate of infusion. When evaluating different formulations,2,8,12 it was found that IgG dimers were associated with infusion reactions,9,13–15 and clinical tolerability of IVIG products was improved by reducing the presence of IgG dimers in IVIG formulations.
Privigen® is a 10% liquid preparation of polyvalent human IgG for intravenous administration. It was licensed in Europe in 2008.16 Stabilisation with l-proline at pH 4.8 is a unique feature of this formulation, in that it minimises the formation of IgG dimers and preserves IgG functional activity without refrigeration.13,14,17,18
Over the last five years, our institution has been using two 10% IVIG with different product characteristics: Privigen® has been used from June 2009 onwards. Previously a different 10% IVIG was used, which used glycine as a stabiliser. Both are in liquid form.19 IgG levels and subclass distribution are similar in both products, as well as IgA and IgM levels.19,20
A subgroup of patients who are being followed in our outpatient clinic for primary immunodeficiencies and who are highly sensitive to previous IVIG, have been treated sequentially with the two IVIG products. The objective of the present study was to evaluate safety and efficacy of the 10% liquid immunoglobulin preparation for intravenous use (Privigen®) in this particular group of paediatric patients affected with Primary Immunodeficiencies using a particular infusion protocol slower than recommended (and retrospectively compare the results to a different IVIG formulation).
Materials and methodsProductPrivigen® is a ready-to-use 10% liquid formulation of polyvalent human IgG for intravenous administration that is stable at room temperature for its entire shelf-life. The naturally occurring amphiphilic amino acid l-proline (250mmol/L=28.8mg/mL) is used as stabiliser at pH 4.8. Privigen® has an IgG content of 99.2%, with more than 99.8% monomers and dimers (dimer content is typically 6%). The IgG fraction from plasma is purified by a combination of cold ethanol fractionation, octanoic acid precipitation and anion exchange chromatography. The manufacturing process includes two dedicated viral clearance steps (pH 4 incubation and nanofiltration) and two partitioning steps with validated viral clearance characteristics. Privigen® contains no preservative, has a low sodium content (≤1mmol/L) and osmolality (320±9mOsm/kg) is in the physiological range. Only trace amounts of IgA are present (8.6±1.8μg/mL).18
The previous IVIG used was also a 10% liquid form, but glycine was used as stabiliser instead. The maximum IgA content was 140μg/ml and the IgG content was at least of 98%. It required be stored in a refrigerator (2–8°C).19
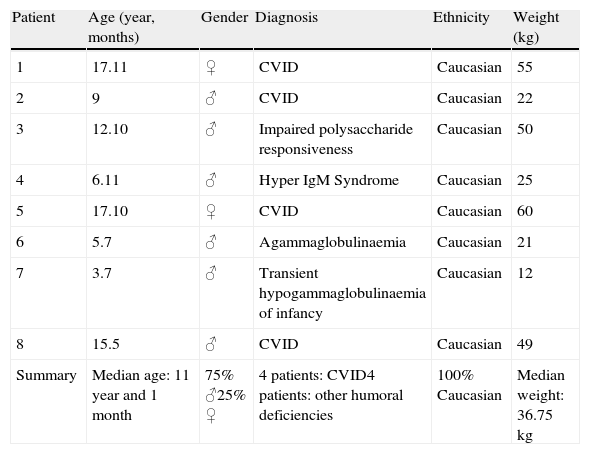
PatientsThe present work was undertaken in the Paediatric Allergy and Clinical Immunology Department of Hospital Sant Joan de Déu, a Tertiary-level Multi-speciality Mother and Child Hospital. Eight patients were included (Table 1). They had a diagnosis of Primary Immune Deficiency, according to the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee classification 21: Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) (four patients), and other humoral deficiencies (four patients). All of them had been switched from the previous 10% IVIG formulation to Privigen® in an open protocol due to severe and/or recurrent adverse events, despite premedication and reduction of infusion rate.
Demographic patient characteristics.
| Patient | Age (year, months) | Gender | Diagnosis | Ethnicity | Weight (kg) |
| 1 | 17.11 | ♀ | CVID | Caucasian | 55 |
| 2 | 9 | ♂ | CVID | Caucasian | 22 |
| 3 | 12.10 | ♂ | Impaired polysaccharide responsiveness | Caucasian | 50 |
| 4 | 6.11 | ♂ | Hyper IgM Syndrome | Caucasian | 25 |
| 5 | 17.10 | ♀ | CVID | Caucasian | 60 |
| 6 | 5.7 | ♂ | Agammaglobulinaemia | Caucasian | 21 |
| 7 | 3.7 | ♂ | Transient hypogammaglobulinaemia of infancy | Caucasian | 12 |
| 8 | 15.5 | ♂ | CVID | Caucasian | 49 |
| Summary | Median age: 11 year and 1 month | 75% ♂25% ♀ | 4 patients: CVID4 patients: other humoral deficiencies | 100% Caucasian | Median weight: 36.75kg |
Data were prospectively collected regarding Privigen® administration: infusion (dose, rate, total time, and interval), safety (interview with parents and patients about adverse events during the infusion and, by telephone, 72h later; use of premedication or rescue medication) and efficacy (measurement of trough levels before first administration and after three doses of Privigen®; clinical efficacy was assessed by questionnaire and chart review – use of antibiotics and severe infections while under Privigen®). In parallel, data on safety and tolerance were retrospectively collected from medical charts regarding the previous 10% IVIG product used.
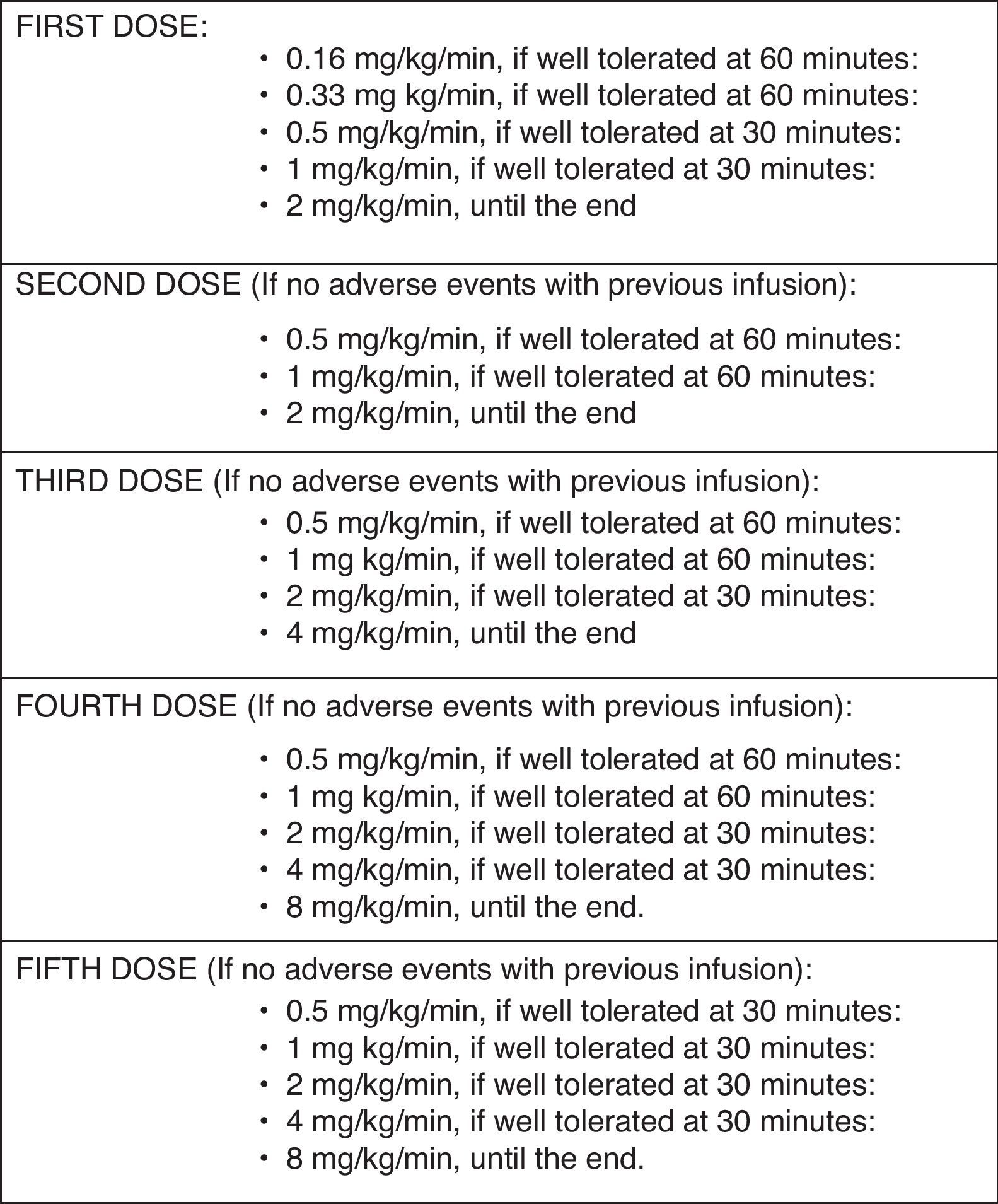
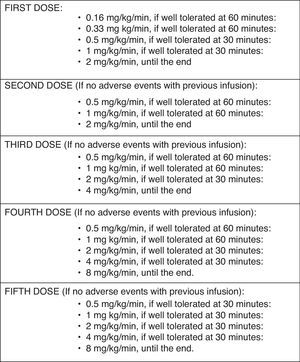
Administration protocolThe infusion rate used for this particularly susceptible group of patients was lower than the recommended by the manufacturer (Fig. 1): in the first administration, the initial rate was 0.16mg/kg/min (instead of the recommended 0.5mg/kg/min). The rate was increased 60min later to 0.33mg/kg/min if no reaction been observed, and was kept for 60min. Then an increase to 0.5mg/kg/min, 1 and 2mg/kg/min in 30min intervals, followed, if tolerated. If no reaction was observed 72h after administration, the second infusion was started at 0.5mg/kg/min, and increased to 1 and 2mg/kg/min (maximum rate) every 60min. The third and fourth infusions were started at 0.5mg/kg/min, which were doubled every 60min to a maximum of 4mg/kg/min and 8mg/kg/min, respectively. After the fifth infusion, the rates were increased every 30min, if tolerated.
Premedication useThe patients who were routinely given premedication with the previous 10% IVIG, were given the same premedication with the first dose of Privigen®. Premedication was stopped if Privigen® was well tolerated.
ResultsEight patients with humoral PID (Table 1) were followed for a minimum of six months under Privigen®. Median age was 11 years old (3.5–17.9 years), and 75% were male. Four patients carried a diagnosis of CVID.
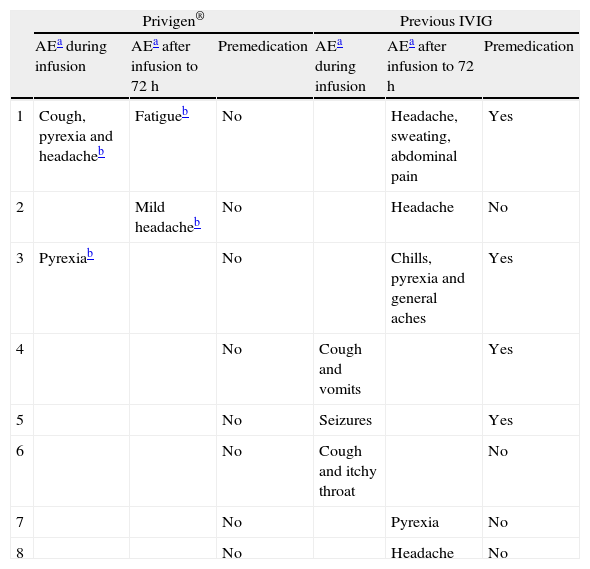
All patients had previously been under IVIG treatment with another 10% liquid formulation for a minimum of one year and a maximum of three years. A median of 23.6 doses per patient had been administered (range: 14–34doses/patient). IVIG replacement dose was 475mg/kg/dose (range 300–600mg/kg/dose), every four weeks for all patients except one (every three weeks). All patients had suffered adverse events during IVIG infusion (Table 2), being severe in three patients (seizures, severe headache and anaphylactic-like reactions), and recurrent in the rest (headache, vomits, cough). In five patients (62.5%) adverse events also occurred 24–48h after infusion, and included headache (three patients), pyrexia (two patients), general aches (one patient) and abdominal pain (one patient). 50% of the patients received premedication systematically.
Summary of adverse events.
| Privigen® | Previous IVIG | |||||
| AEa during infusion | AEa after infusion to 72h | Premedication | AEa during infusion | AEa after infusion to 72h | Premedication | |
| 1 | Cough, pyrexia and headacheb | Fatigueb | No | Headache, sweating, abdominal pain | Yes | |
| 2 | Mild headacheb | No | Headache | No | ||
| 3 | Pyrexiab | No | Chills, pyrexia and general aches | Yes | ||
| 4 | No | Cough and vomits | Yes | |||
| 5 | No | Seizures | Yes | |||
| 6 | No | Cough and itchy throat | No | |||
| 7 | No | Pyrexia | No | |||
| 8 | No | Headache | No | |||
All patients were switched to Privigen® in an open protocol due to severe or repeated adverse events related to IVIG infusion. The same dose and interval were used with the two different formulations. Premedication was given before the first Privigen® infusion to those patients that were receiving it with the previous IVIG. After the second infusion, this premedication could be withdrawn in all patients. A median of 6.6 doses per patient (range 5–9 doses/patient) was administered during the follow up.
Adverse events were registered in three patients (37.5%): two patients during the first Privigen® infusion (pyrexia and headache) (Table 2). In all cases, symptoms were mild and were controlled with the use of acetaminophen and dexchlorpheniramine, and they ceased in subsequent infusions.
Two other patients had reactions 24–48h after the infusion. One referred a mild headache that resolved in 30min without medication. The other referred fatigue for 24h, but was able to perform regular activity. She had had serious adverse events under the previous IVIG. In summary, all reactions (during and or after Privigen®) were mild and did not need premedication.
At the end of the study, the median time of administration was 3.3h/dose/patient (range 2.5–4h/dose/patient), with a median infusion dose of 6.4mg/kg/min (range of 3.3–8mg/kg/min), shorter than that to previous IVIG. No patient was in need of premedication. Five patients reached the maximum recommended dose of 8mg/kg/min.
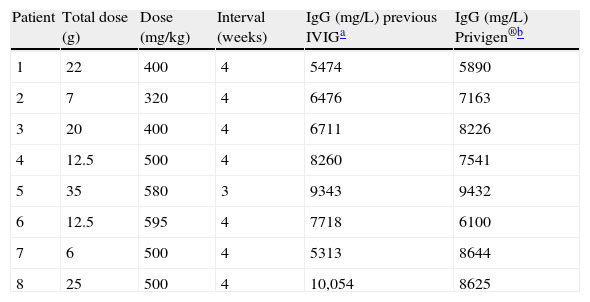
During the six-month-follow-up on Privigen®, no patient developed a severe infection requiring hospitalisation. No antibiotics were needed to treat mild infections. Median IgG trough levels after the third dose of Privigen® were similar to those reached with the previous IVIG (median IgG 7700mg/L and 7400mg/L, respectively) (Table 3), with the same dose being administered for both products. In all patients, trough levels were above 5500mg/L.
Dose and interval of IVIG. Serum levels of IgG.
This study confirmed both safety and efficacy of Privigen® for paediatric use in PID. Also, to our understanding, this is the first study to evaluate the use of Privigen® in a subgroup of paediatric PID patients who are highly sensitive (that do not tolerate previous IVIG infusions). We show that Privigen® is suitable for these patients with low tolerance to other IVIG products. Furthermore, this product would also be convenient as a starting replacement therapy.
Most patients included in the study were diagnosed of CVID. This is in accordance with a recent survey by the Immune Deficiency Foundation which indicated that patients with CVID and agammaglobulinaemia represent approximately 77% of PID patients currently receiving IVIG replacement therapy.22 Doses and administration intervals were also as per current practice.
In this work we have devised an open and adapted infusion protocol for this especially sensitive group of patients to IVIG products: the infusion rate was slower than recommended by the manufacturer. This protocol was effective: indeed, all patients suffered only from very mild adverse reactions, none needed premedication, and in five patients, the maximum infusion rate recommended by the manufacturer (8mg/kg/min) could be reached. Median time needed to administer Privigen® doses was 3.3h (range 2.5–4h/dose/patient), which was significantly reduced compared to the previous IVIG.23 This reduction in the time of administration was particularly appreciated by patients and parents to decrease school and work absenteeism, respectively.
The number of patients suffering adverse events during Privigen® (11.3%), was not only reduced compared to the previous 10% IVIG, but also compared to what is published related to Privigen® (21%) 8,10,24 and other IVIG products (24.9% and 29.1%),25,26 despite reaching maximum infusion rates. Besides, the reactions referred were all mild (low pyrexia, headache), compared to the severe reactions the same patients had had with the previous IVIG, that were all limiting to their daily lives. These reactions all disappeared in the following injections, as expected,27 and no patient needed premedication after the second Privigen® infusion. The most frequent adverse event was headache, as published with Privigen® in another group of patients 10 and with other IVIG products.25,26
This study has a clear limitation in that the retrospective data obtained from the previous 10% IVIG product cannot be directly compared to the prospective data collected for Privigen®. Besides, the protocol is open and not double blinded. Despite these limitations, this adapted infusion protocol with Privigen® shows a clear tendency towards a safer profile compared to the previous IVIG, at least in these first six months of follow-up.
As for efficacy, it is general consensus that IgG trough levels should be above 5000mg/L,6,28–30 as is observed in all of our patients, after using a standard infusion dose of 400–600mg/kg every 3–4 weeks. These trough levels were even slightly higher compared to the previous IVIG, using the same replacement dose and interval (median trough IgG 7700mg/L and 7400mg/L, for Privigen® and previous IVIG, respectively).
ConclusionsThe present work shows that this novel 10% liquid IVIG was safe in a special group of paediatric patients who did not tolerate the administration of a previous 10% liquid IVIG. The number of adverse effects was smaller than published, and all cases were mild. No premedication was needed. Privigen® was also effective in this small group, with IgG trough levels being stable and in the higher range, along with no infections clinically. The combination of well-tolerated high infusion rates and convenience of use due to liquid presentation and room temperature storage would be potentially advantageous for both patients and healthcare personnel.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this investigation.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
This work was partially supported by an IgMAPS grant from CSL Behring.