INTRODUCTION
Peroxinorm is a commercial form of superoxide dismutase (orgotein) administered in local injections for its anti-inflammatory properties. It has been gradually withdrawn from some European countries due to reported allergic reactions. Orgotein is obtained from bovine liver by heat treatment, enzymatic digestion of other proteins and purification to homogeneity by molecular sieve and ion exchange chromatography (1, 2). According to the manufacturer it is only 80 % pure, the contaminants identified are albumin and chymotrypsin but there may be other waste products. We report an anaphylactic shock probably caused by impurities contained in this drug.
CASE REPORT
A 50 year old woman, suffering from a sore shoulder, was being treated weekly with intra-articular injections of orgotein (Peroxinorm) and mepivacaine. Five minutes after the third injection she developed dyspnea, generalized urticaria and hypotension. She was immediately treated with epinephrine and corticoids and one hour later was admitted to the Emergency Room. She received parental antihistamines and corticosteroids and was kept under observation for 24 hours. Twelve hours later she developed a new anaphylactic episode and was readmitted to hospital.
The patient had never eaten cow liver. She did not usually drink milk but tolerate milk by-products. She had never been treated with other bovine extracted drugs.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Peroxinorm powder was dissolved in saline phosphate buffer at 2 mg/ml for in vitro assays. Samples of 2, 0.2 and 0.02 mg/ml of sterilized solutions were prepared for the skin prick test. Mepivacaine at 3 % (Scandicain, Scandinibsa Labs.) was prick-tested and subcutaneously challenged. We prick-tested milk, meat and cow epithelium extracts, all for them at 5 % W/V from Abello Laboratory, 10 mg/ml BSA (Sigma) and 2 mg/ml chymotrypsin (Cusi Lab). Liver extract was prepared in our laboratory as follows: 100 g of cow liver was homogeneized in 25 ml of PBS and stirred at 4 °C for 18 hours. It was then centrifuged at 40,000 x g for 20 minutes. Supernatant was dialysed and filtered through a 0.2 mm Millipore filter. It was stored at 20 °C until later use for in vivo and in vitro assays.
Tryptase serum levels, were determined by RIA (Tryptase RIACT Pharmacia) from serum samples obtained 3, 24 hours and 15 days after the anaphylactic shock.
Specific serum IgE to Peroxinorm (2 mg/ml), BSA (10 mg/ml), chymotrypsin and cow liver were assessed by ELISA. Briefly, 100 microliters of each protein were applied in duplicate to a 96 well microtiter plate for 18 h at 4 °C. The wells were blocked with 200 ml of human serum albumin (5 %) for 1 hour at 37 °C. After thorough washing 100 ml of patient's or control's sera were applied for 2 hours at 37 °C. After washing, gout anti-human IgE peroxidase labelled (1:500) was added for 1 hour at 37 °C. Substrate was applied and the plate was read at 492 nm in an ELISA reader after 15 minutes. Milk and cow epithelium specific IgE were measured by CAP (Pharmacia).
A twelve percent SDS-Page (3) was performed with Peroxinorm, BSA, chymotrypsin and cow liver. Proteins were transferred to an immobilon P membrane in Twin Buffer (4). The membrane was blocked with 3 % human serum albumin and serum was applied for 2 hours. After thorough washing, goat antihuman IgE labelled alkaline phosphatase was added for 1 hour. Nitroblue tetrazolium and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate in DMF (BIORAD) was used as the substrate.
RESULTS
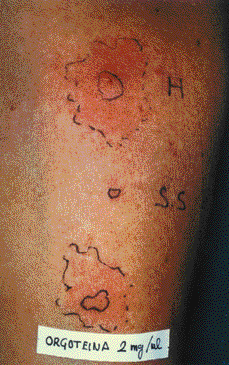
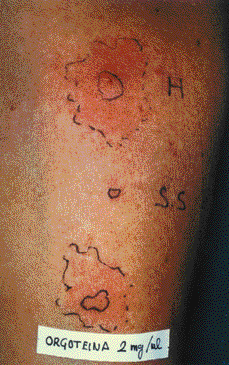
Skin prick test produced a 9 x 6 mm papule pseudopods to Peroxinorm at 2 and 0.2 mg/ml (fig. 1), BSA (7 x 7 mm) and to cow liver extract (7 x 4 mm) but resulted negative with chymotrypsin, milk, meat and cow epithelium extracts. Prick tests and subcutaneous challenge with mevipacaine 3 % were negative.
Figure 1.--Prick test to orgotein (Peroxinorm) 2 mg/ml. H: Histamine 10 mg/ml. S.S: Saline solution.
Tryptase serum levels determined 3, 24 h and 15 days after the shock measured 6.32, 0.81 and 0.84 U/L respectively.
Detection of specific IgE to Peroxinorm, BSA and chymotrypsin by ELISA was negative and positive to cow liver. Specific IgE (Pharmacia CAP system) to milk and cow ephitelium was negative.
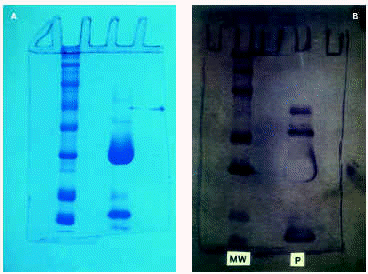
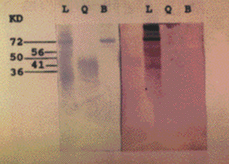
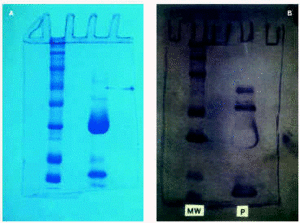
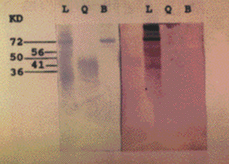
SDS-PAGE with Peroxinorm showed several bands, the most prominent of which corresponded to orgotein (32 kDa) (fig. 2a). Immunoblotting revealed specific IgE bands at an apparent M.W of 67, 51, 56 and 16 kDa (fig. 2b). Immunoblotting with cow liver revealed bands at 72, 56, 50 and 36 kDa; Immunoblot with BSA and chymotrypsin were negative (fig. 3).
Figure 2.--A) SDS-PAGE with Peroxinorm (right). Molecular weight standards (left). B) Immunoblot with Peroxinorm (right), MW standards (left).
Figure 3.--SDS-PAGE (left) and immunoblot (right) with Liver (L), Chymotrypsin (Q) and BSA (B).
DISCUSSION
Peroxinorm injection caused an anaphylactic shock. Immediate hypersensitivity mechanism was demonstrated by positive skin prick test, detection of specific IgE by immunoblotting and an increase in tryptase serum levels after the reaction.
The immunoblotting performed with Peroxinorm did not reveal any band at the M.W of orgotein (32 kDa) which rules out orgotein as the main allergen. We, therefore, focused the study on other cow liver allergens derived from the purification procedure present in the drug as contaminants. Sensitization to BSA was demonstrated by the prick test although the patient did not react to other BSA sources (milk, meat). The band at 67 kDa revealed by immunoblotting with Peroxinorm could easily correspond to BSA (68 kDa), and a similar band was obtained in immunoblotting with the liver extract.
Surprisingly, the immunoblotting with purified BSA was negative.
The 51 and 56 kDa bands present in Peroxinorm western blot are equivalent to other bands present in cow liver (50 and 56 kDa) and may represent two commont allergens of Peroxinorm and bovine liver.
We can speculate that the 16 kDa band in the immunoblotting with Peroxinorm corresponds to chymotrypsin, one of the known contaminants, although we were not able to find an equivalent chymotrypsin band or to detect specific IgE by ELISA.
The reaction relapsed several hours after the first episode probably because of the slow and late access of the compound from the place of injection to the blood.
Previously reported cases (5-7) and other cases informed to the health authorities alerted to the possibility of severe allergic reactions to orgotein. We emphasize the role that 20 % of impurities, unspecified on the labels of the pharmaceutical preparations, may have in immediate hypersensitivity reactions. Although the other cases described had assigned responsibility of the reaction to the orgotein molecule, some reactions could be due to liver contaminants. The main impurity, BSA, a haterologous protein, has already been proven to be a potent allergen which contaminates medical procedures (8-10). The adverse experiences reported with orgotein preparations should teach us to be cautions when administering drugs of partially unknown composition.