INTRODUCTION
Piroxicam is a widely used anti-inflamatory drug. Most adverse reactions affect gastrointestinal system, liver and skin. Fixed drug eruption, although unusual, has also been described1-3, but only with cutaneous involvement.
CASE REPORT
An 49-year-old man, with no previous history of allergy, complained of cutaneous-mucosal lesions appeared during a treatment with oral piroxicam. Two and half years-ago he was taking oral piroxicam (Feldene capsules®, Pfizer S.A., Madrid, Spain) 1 × day, for left knee meniscopathy. At D2 (day 2) pruritus, exanthema and vesicular lesions at glans appeared. He stopped oral piroxicam and the lesions disappeared. 6 months later he was taking oral piroxicam, 1 × day, (Feldene Flas®, Pfizer S.A., Madrid, Spain) for a relapse on his meniscopathy, during 7 days, despite of the beginning of the lesions at glans at D2 of treatment. At D7 he was admitted to the hospital with a suspicion of Behçet Still. Numerous mucosal ulcers at glans and mouth, and at the skin of the groins and intergluteal sulcus were present. All immunological studies performed to diagnose Behçet Still resulted negatives and the patient was discharged after treatment with oral corticoisteroids and colchicine. Four months later the patient was treated again with oral piroxicam, 1 × day, (Sasulen capsules®, FAES Lab., Madrid, Spain) for muscle spasm in his left scapula. At D3, he developed mucosal ulcers at glans and mouth. Piroxicam was withdrawn and treatment with oral corticosteroids was started. At present the patient has no residual lesion, nor pigmenting at the areas of fixed eruption. After the last reaction oral diclofenac has been well tolerated.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
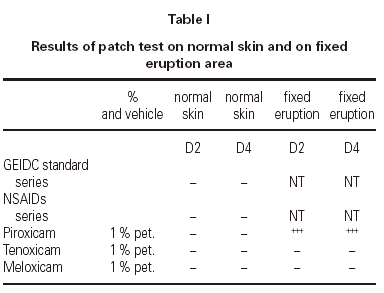
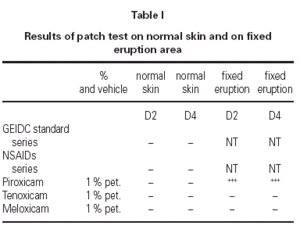
He was patch tested on normal skin with the GEIDC standar series, an NSAIDs series (salicylic acid 1 %, bufexamac 5 %, naproxen 5 %, ibuprofen 5 %, phenylbutazone 1 %, diclofenac 1 %, paracetamol 5 %, indometacine 5 % and ketoprofen 2,5 %, all in pet. Lab. Bial-Aristegui, Bilbao, Spain), and with piroxicam, meloxicam and tenoxicam (all 1 % pet). He was also patch tested on intergluteal sulcus with piroxicam, meloxicam and tenoxicam.
Oral challenge test was not performed due to the severity and reproducibility in previous reactions.
RESULTS
Results are shown on table I.
DISCUSSION
Taking into account all the features of this clinical case, we consider necessary to emphasize the importance to perform an exact diagnosis of adverse drug reaction (ADR) as soon as possible with an accurate clinical history. Sometimes is not an easy work, because of the variability of clinical symptoms (even simulating an autoimmune disease in this case) of the ADR. It's important to point up the diagnosis validity of patch test on fixed eruption area.
To our knowledge, this is the 1st report of non-pigmenting fixed drug eruption with cutaneous-mucosal involvement due to piroxicam. Croos-reactivity between oxicams could not be demonstrated by patch test on fixed eruption.