La cirugía de la catarata asistida con el láser femtosegundo (FLACS) se ha considerado un avance tecnológico en la cirugía moderna de la catarata. Tras los años de experiencia, se ha observado que los resultados clínicos presentan más complicaciones de las esperadas al inicio. Con este estudio queremos comparar los beneficios e inconvenientes de la técnica FLACS con la cirugía de catarata convencional.
MétodoUtilizamos las plataformas PubMed y Web of Science para la búsqueda de la literatura científica.
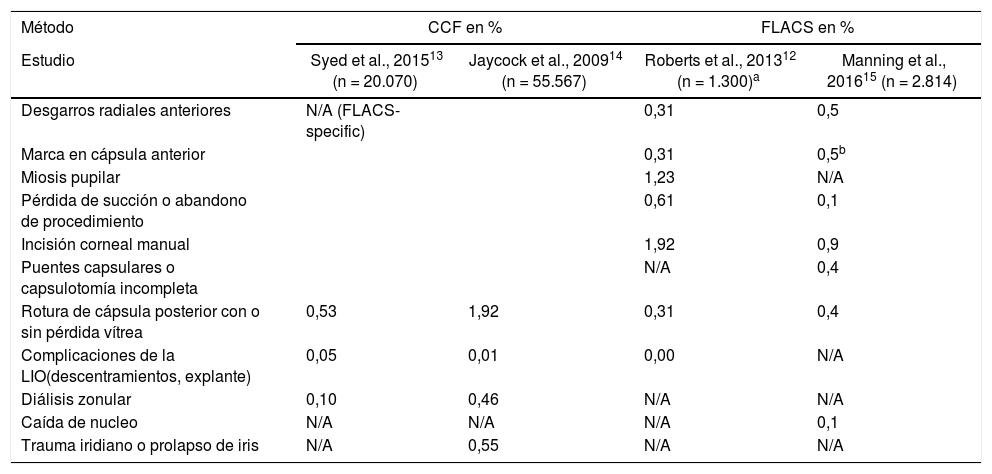
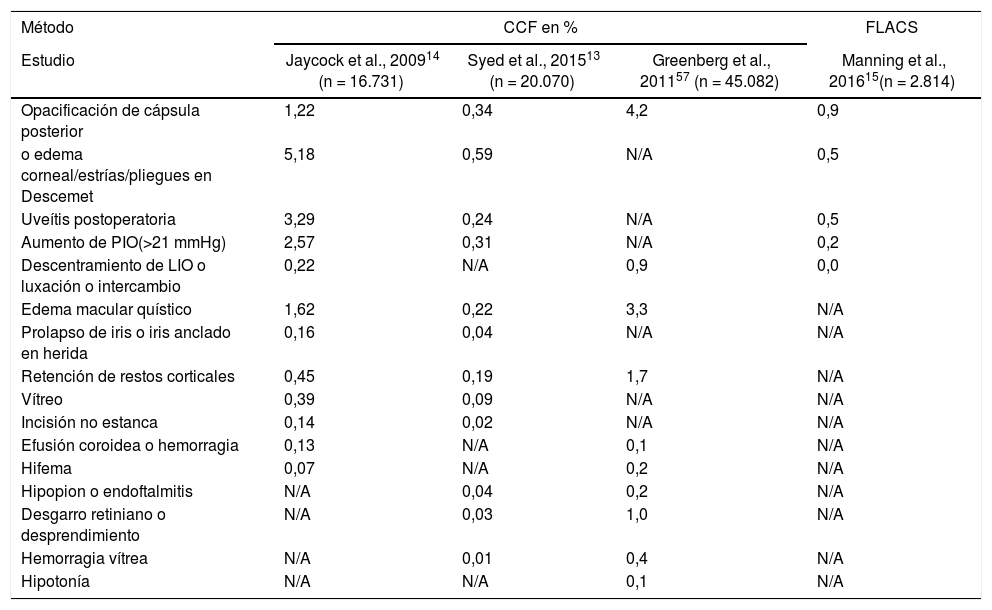
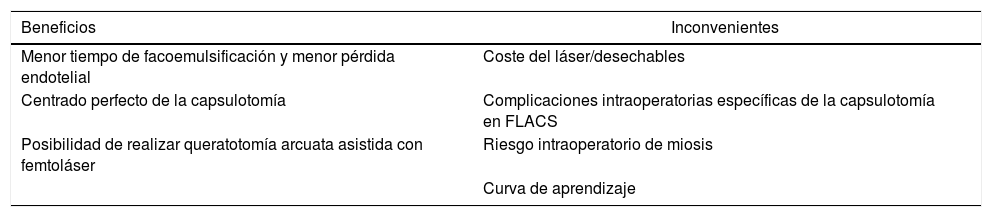
ResultadosActualmente, el FLACS ha mejorado la técnica quirúrgica en cuanto al menor tiempo de ultrasonidos empleado y a la menor pérdida de células endoteliales. Asimismo, el centrado de la capsulotomía y la corrección del astigmatismo con las incisiones arqueadas han mejorado. Como inconvenientes destacan el alto coste del láser, las complicaciones intraoperatorias sobre la cápsula, la inducción de miosis intraoperatoria y la curva de aprendizaje de la técnica.
ConclusionesConsideramos la técnica FLACS beneficiosa para casos concretos como pacientes con cirugía premium programada o con bajo recuento de células endoteliales. No obstante, creemos que, dado el coste tecnológico, no es una técnica rentable para la mayoría de los casos de nuestra práctica clínica diaria, que son casos estándares.
Femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery (FLACS) has been considered a technological advance in modern cataract surgery. After years of experience, it has been observed that clinical outcomes had more complications than expected at the beginning. The aim of this study is to compare the benefits and disadvantages of the FLACS technique with conventional cataract surgery.
MethodThe PubMed and Web of Science platforms were used to search for scientific literature.
ResultsThe FLACS has currently improved the surgical technique in terms of the shorter ultrasound time used and the lower loss of endothelial cells. Likewise, the centration of capsulotomy and the correction of astigmatism with arcuate incisions have also been improved. As disadvantages, are the high cost of the laser, the intraoperative capsular complications, the induction of intraoperative myosis, and the learning curve of the technique.
ConclusionsThe FLACS technique is considered beneficial for specific cases, such as patients with scheduled premium surgery, or with low endothelial cell count. However, it is believed that given the technological cost it is not a cost effective technique for most standard cases in our daily clinical practice.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora