Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant disease that causes the abnormal formation of connective tissue, which alters its distensibility. It is generally associated with osteoarticular, cardiologic and ocular manifestations. Less frequently, it can affect the respiratory tract and cause different alterations, the most frequent of which is spontaneous pneumothorax.1,2
Marfan syndrome patients have a risk for spontaneous pneumothorax that is 10 times higher than the general population,3 with an associated prevalence that is between 4 and 11%.1,2,4
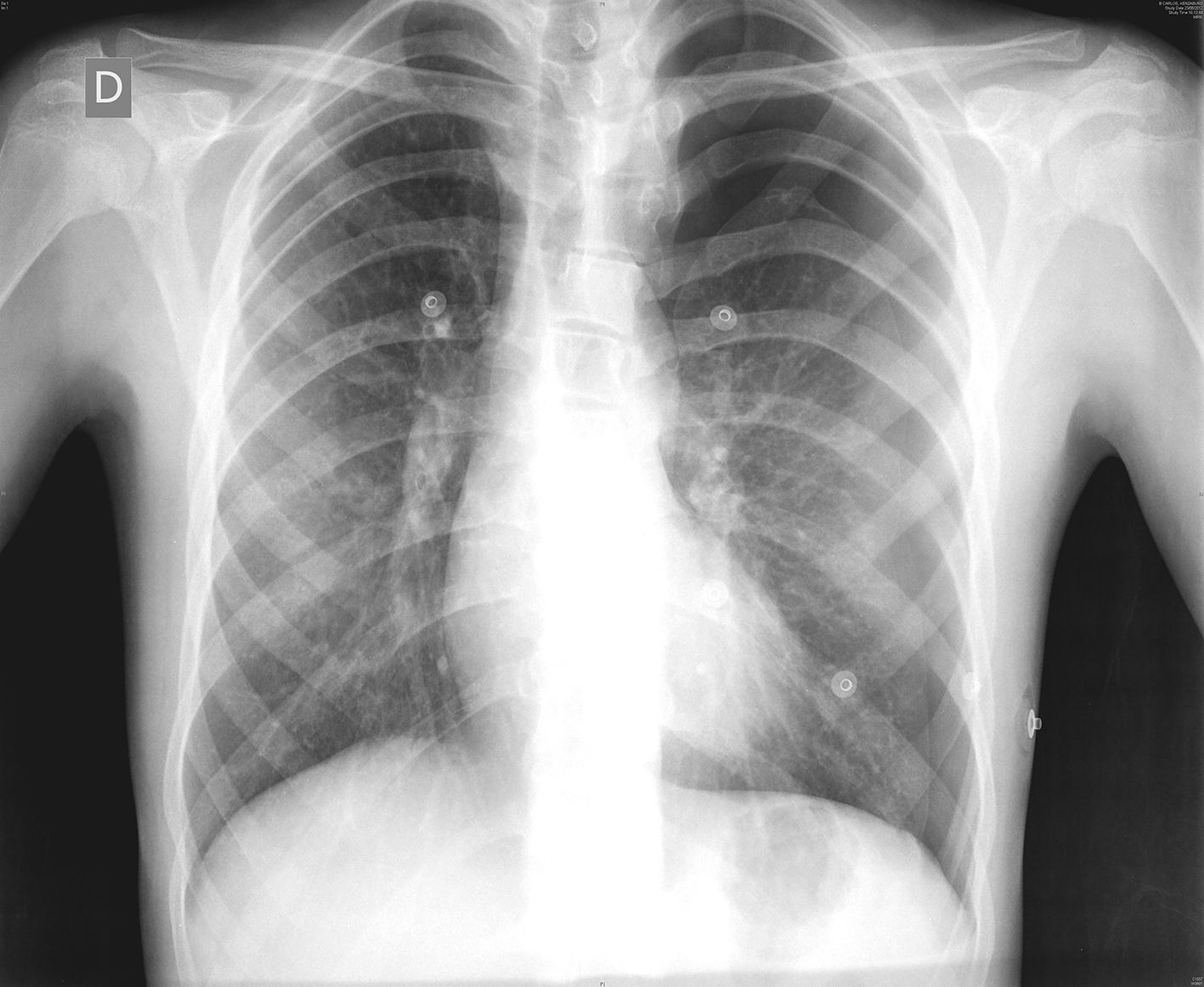
Case ReportOur patient is a 14-year-old male diagnosed with Marfan syndrome at the age of 5. Symptoms included aneurysmal dilatation of the thoracic aorta, myopia with no lens involvement and toe syndactyly. His father had died due to ischaemic heart disease secondary to this syndrome. The patient came to our Emergency Department with sharp pleuritic pain in the left hemithorax that had been progressing over the previous 2 days and was accompanied by mild dyspnoea. Oxygen saturation was 94%. Auscultation detected apical hypophonesis in the left lung. There was no subcutaneous emphysema. Posteroanterior chest radiograph demonstrated pneumothorax of more than 30% (Fig. 1). A 16 FR chest tube was inserted in the left fifth intercostal space on the anterior axillary line, which resolved this condition within 5 days of hospitalisation. The pleural drain was withdrawn and the patient was discharged.
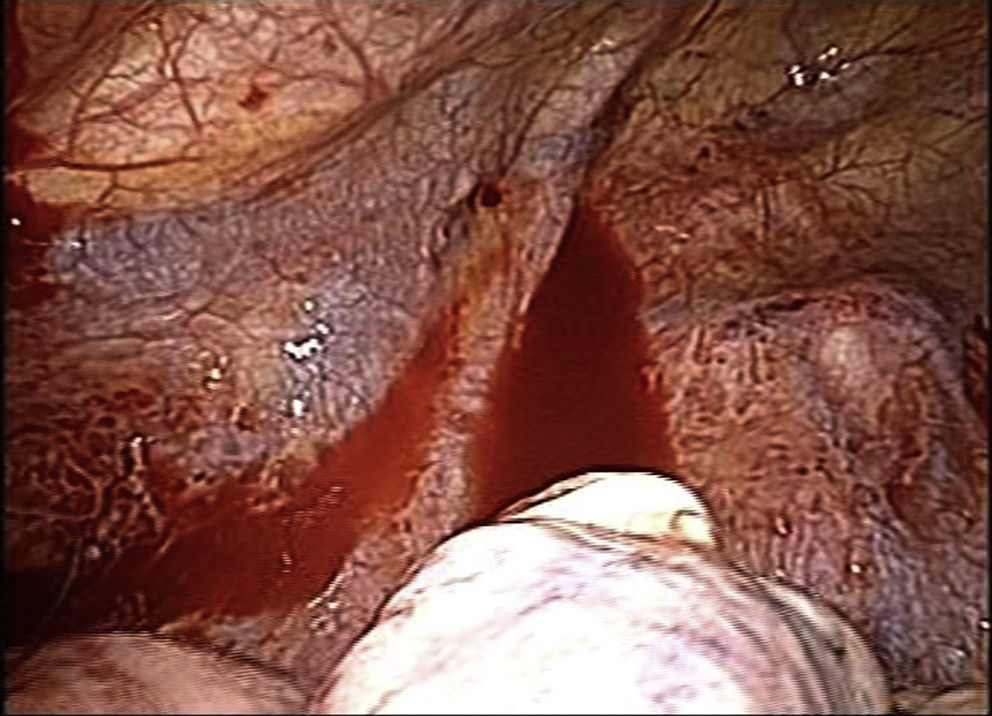
Three days later, the patient once again came to the Emergency Department due to pain of similar characteristics. Chest radiograph revealed a recurrence of the pneumothorax, and another pleural drain was inserted in the same location as the first. During hospitalisation, the patient presented a persistent air leak, requiring exploratory thoracoscopy (Fig. 2), which detected an air leak in the apex of the left lung. Atypical apical segmentectomy was performed, and the patient was discharged on the fifth day, with no further complications.
DiscussionMarfan syndrome involves altered collagen fibre synthesis, which causes reduced elasticity and tensile strength of the terminal bronchioles and leads to the appearance of blebs, lung cysts and ampullae.3 These lesions entail a greater risk for the appearance of spontaneous pneumothorax (including its bilateral presentation), its recurrence and persistent air leak.5
Therefore, the therapeutic management of these patients should be more aggressive, including early indication for surgery. As in the general population, thoracoscopy is the surgical approach of choice.
There is no international consensus about the management of ampullae in asymptomatic patients. In general, conservative treatment is used, although some authors opt for surgical treatment or pleurodesis.3
Please cite this article as: Fortea-Sanchis C, Ángel Yepes V, Priego Jiménez P, Martínez-Ramos D, Escrig Sos J. Neumotórax y síndrome de Marfan. Cir Esp. 2015;93:e87–e88.