As a follow-up to the article published in your journal entitled “Streptococcus pyogenes infections in Spanish children before and after the COVID pandemic. Coming back to the previous incidence”,1 we would like to add some comments regarding Group A Streptococcus (GAS) infections incidence during the first semester of 2023.
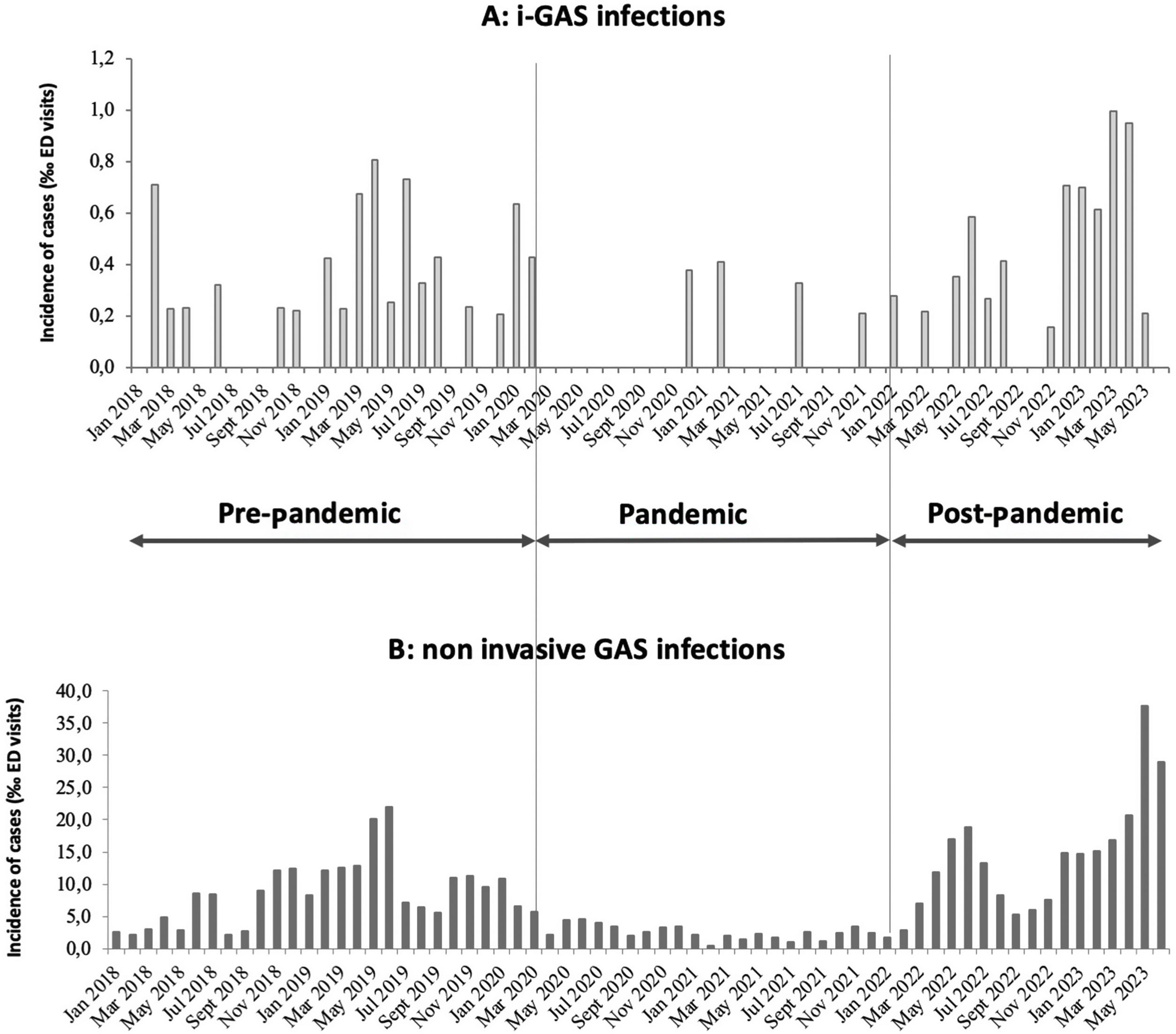
In our series, mild GAS infections (tonsillopharyngitis and scarlet fever) and invasive GAS infections (iGAS) decreased significantly during the pandemic period. Throughout 2022 we observed a reemergence of GAS infections reaching the pre-pandemic levels, but not higher1 than described in the United Kingdom alert published in December 20222 and confirmed in other countries.3 Considering that we may have identified the beginning of the outbreak, we completed the study during the first half of 2023.
Between January and June 2023, our emergency department (ED) attended 625 patients with confirmed GAS infection, 609 mild infections and 16 iGAS infections. The median age of the patients was 6.3 years (RIC: 4.2–8.5); 33.3% were aged 0–4 years, being this age distribution similar to that found in 2019. Fifty-six percent were male (350/625).
The incidence of GAS infections during the first semester 2023 was 22.9/1000 ED visits, reaching double that observed in 2022 (10.2/1000 ED visits) and 2019 (12.4/1000 ED visits) respectively. The incidence of iGAS infections also increased during these first months of 2023 (0.6/1000 ED visits), reaching nearly three times the incidence observed in 2022 (0.2/1000 ED visits) and one and a half times that of 2019 (0.4/1000 ED visits) (Fig. 1). These findings are like those published in Europe during the last months of 2022.4–6
The most frequent invasive disease during the first 6 months of 2023 was mastoiditis (7/16 iGAS; 43.8%) of which 4 had local complications, while in 2022 mastoiditis accounted for 18.2% (2/11) of the iGAS. The remaining invasive diseases were 3 pneumonias, 2 meningitis, one sepsis, one epidural abscess, one orbital cellulitis complicated with subperiosteal abscess, and one peritonsillar abscess.
Although we have not serotyped our GAS strains, the study cited here describes a continuous increase in emm type 1 cases throughout 2022, with a peak occurring during the latter part of the year, being the months with the highest number of cases.5 Furthermore, another study focusing on adults with severe pulmonary GAS infections in Scotland observed a significant predominance of the M1UK strain during the ongoing outbreak.7
In our series there were no varicella cases prior to iGAS infections as described by other authors,5,6 but 5 of the 16 patients with invasive infection were associated with co-infection with other respiratory viruses: two influenza, two SARS-CoV-2 and one respiratory syncytial virus. Viral infections may have amplified the resurgence of iGAS infections during these months.5 In our series, we did not have any deaths.
In summary, in our series including the first semester of 2023 as in other countries, GAS infections decreased markedly during the COVID-19 pandemic, but in the post-pandemic period there has been a considerable increase in both mild and severe cases, reaching figures similar to those detected in other European countries. This delay in the increase of streptococcal infections in our region has had a parallel course to influenza infections in Spain during winter 2022–2023.
Maintain a close surveillance of S. pyogenes infections in the coming months and years will be relevant to know the trend and risk factors of these infections, especially invasive ones.
Financial disclosureThe authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.