The 3rd International Nursing & Health Sciences Students & Health Care Professionals Conference (INHSP) 2019
Más datosTo compare the effectiveness of respiratory muscle exercise (RME) and incentive spirometry exercises (ISE) to improve lung function after mechanical ventilation.
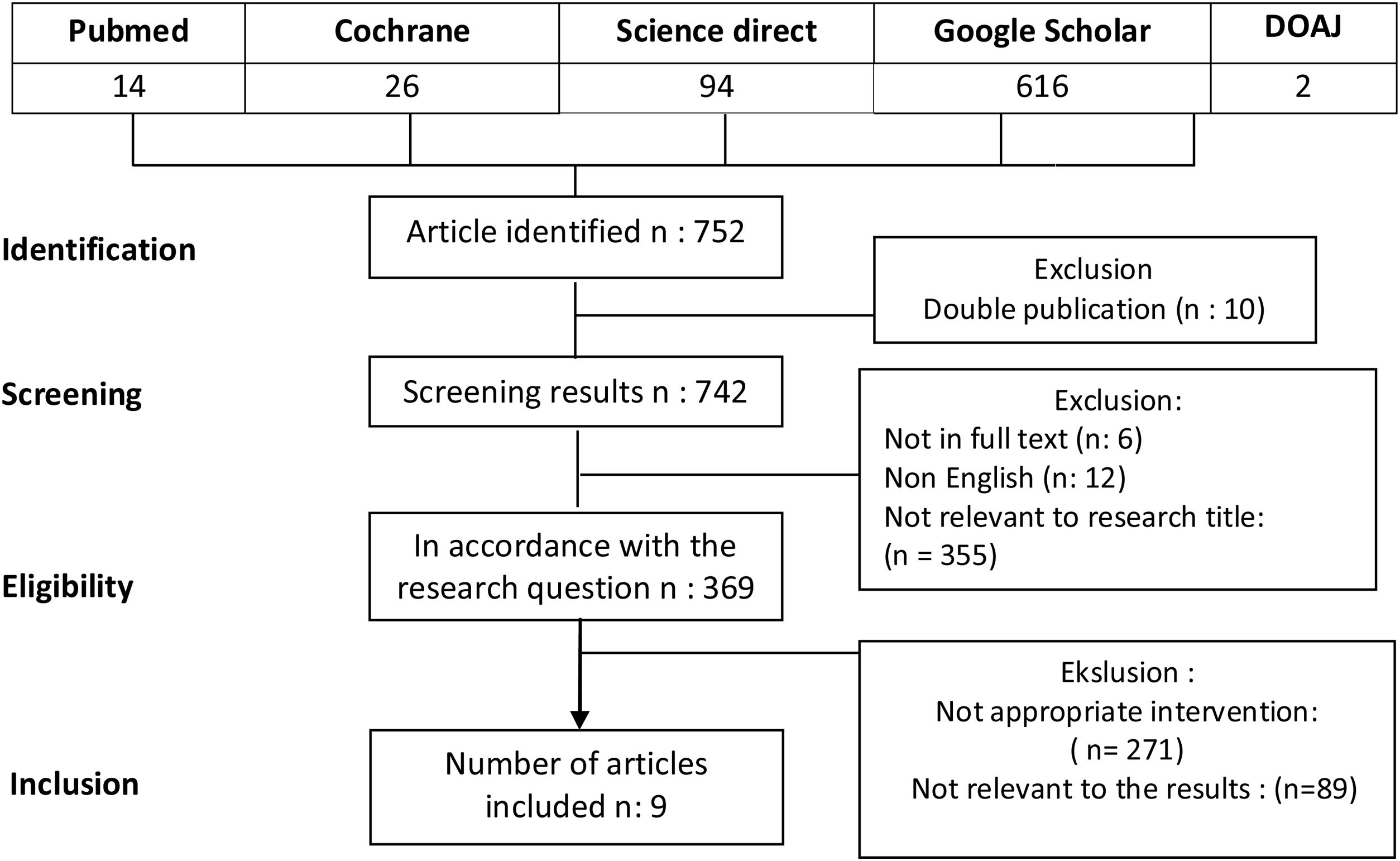
MethodsThis was a systematic literature review by searching through a database; PubMed, Cochrane, Science Direct, Google Scholar, and DOAJ.
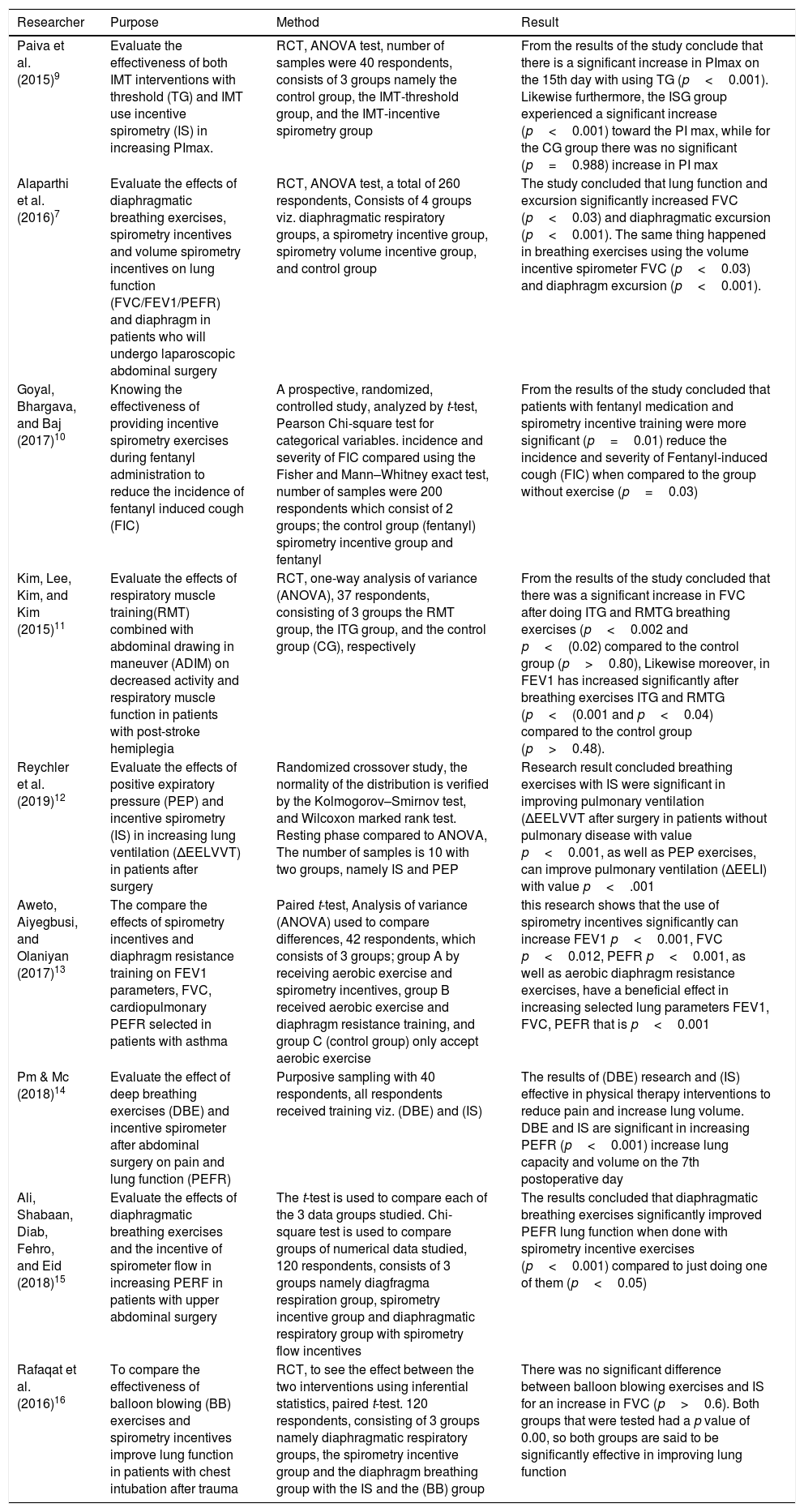
ResultsNine articles were identified according to eligibility criteria, and all of them evaluated the effectiveness of breathing exercises with ISE. Such exercise has been significant in improving lung function; three articles that evaluate related to the direct title, namely RME with diaphragmatic breathing and ISE, the results are significant for improvement in lung function.
ConclusionsSeveral studies have concluded that breathing exercises (BE) by training diaphragmatic breathing muscles include RME and ISE, significantly improve lung function.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora