This study explored the correlation between nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI) and family functioning among adolescents aged 12 to 17 years with mood disorders.
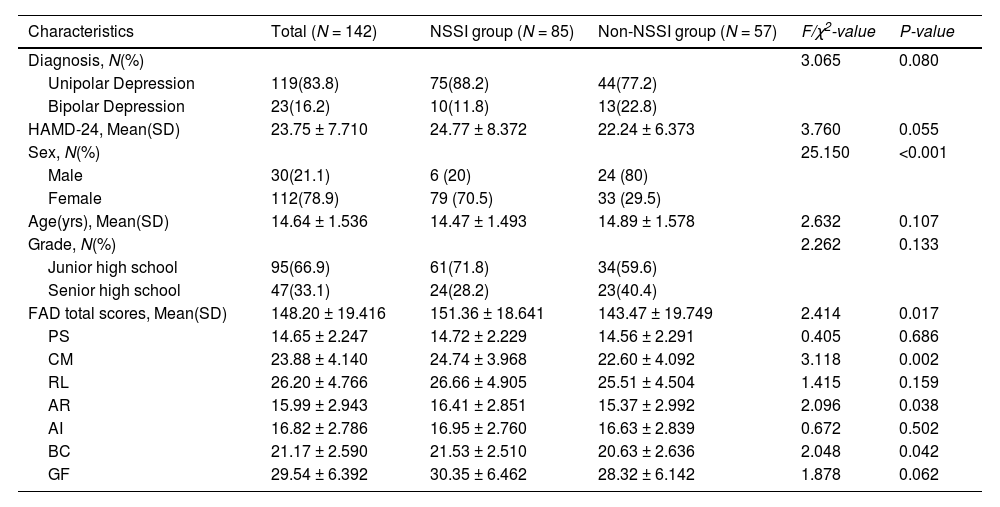
MethodsA total of 142 participants were clinically assessed for NSSI, with 85 in the NSSI group and 57 in the non-NSSI group. The correlation between NSSI and family functioning was compared and a regression prediction model was constructed to determine the risk probability of NSSI.
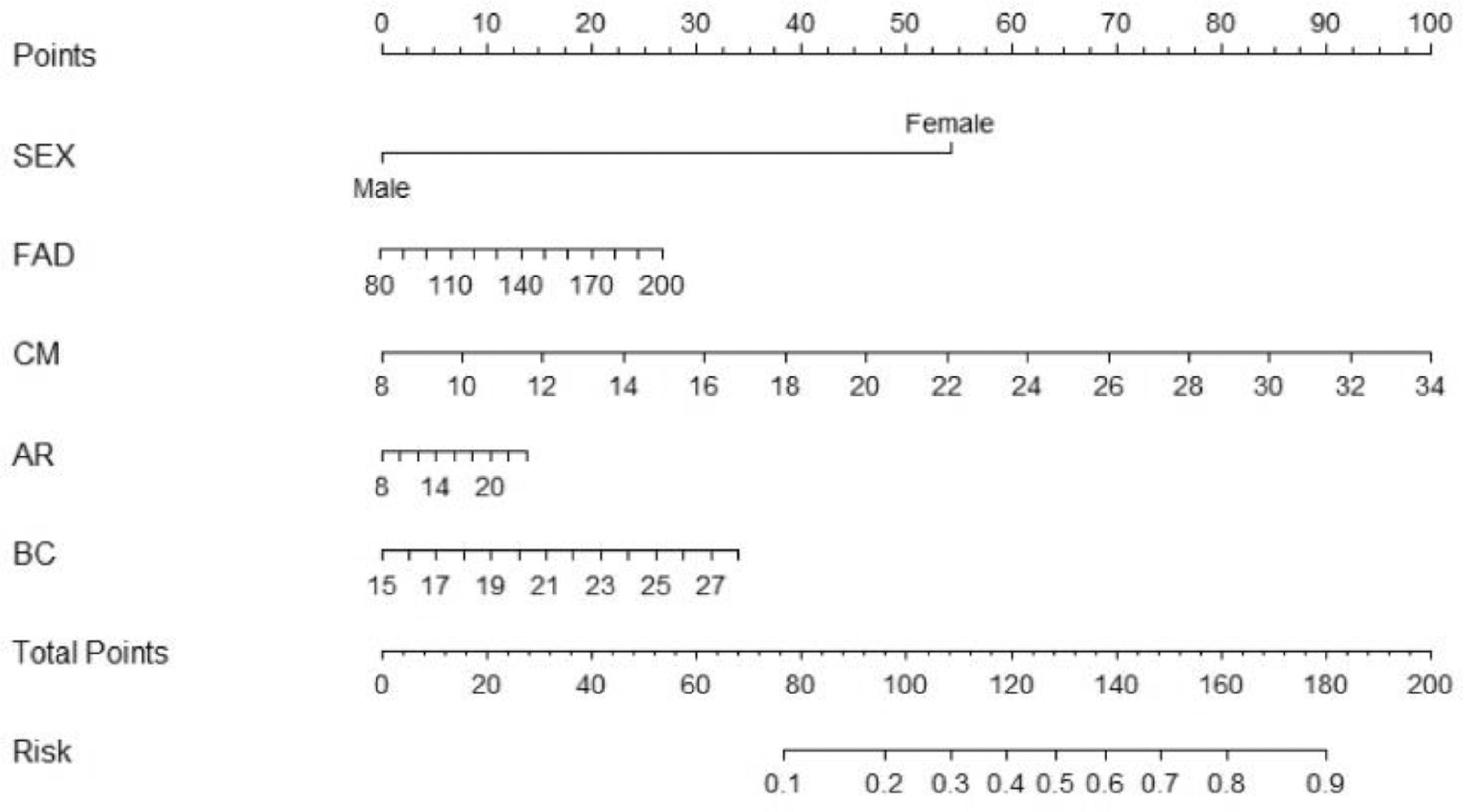
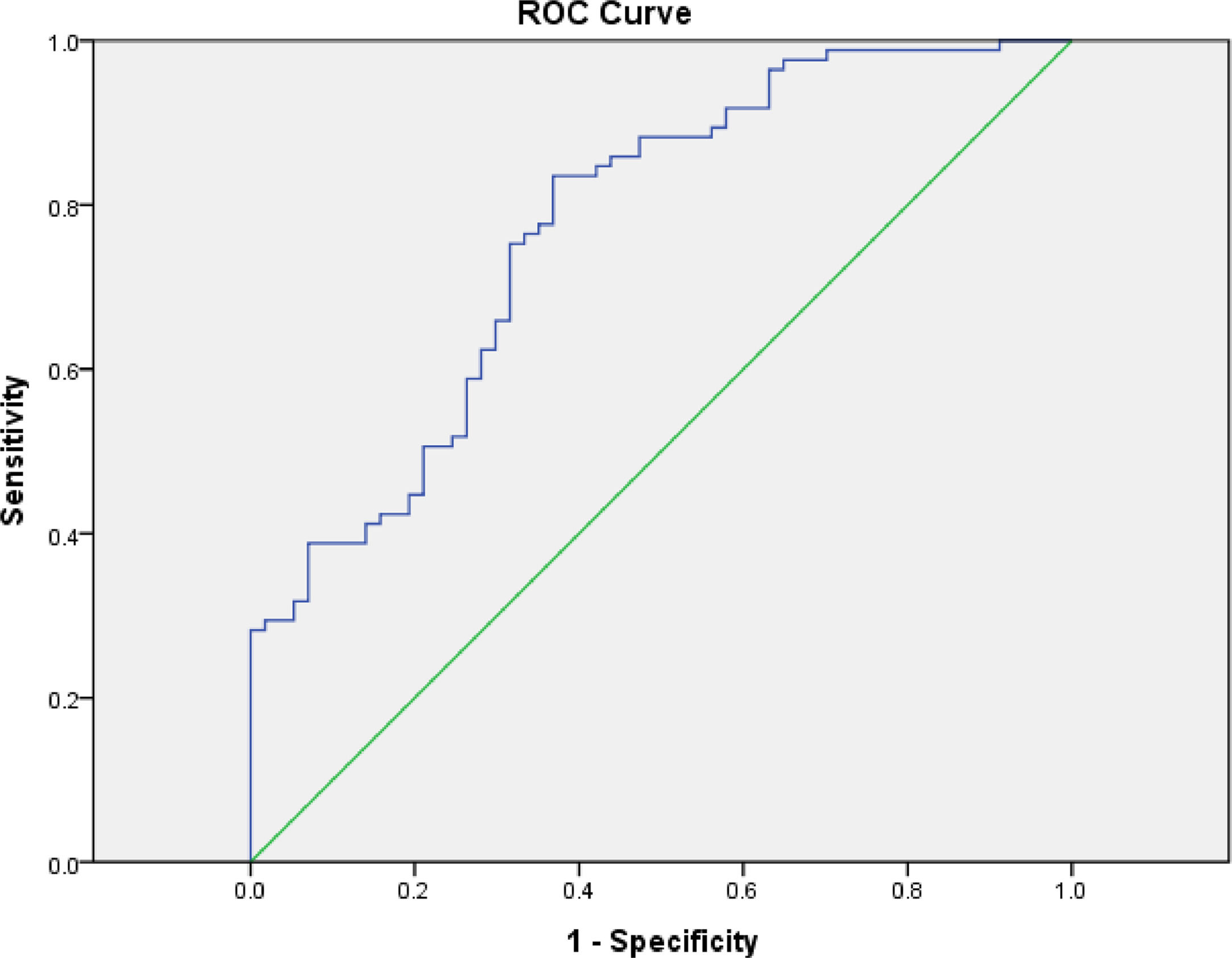
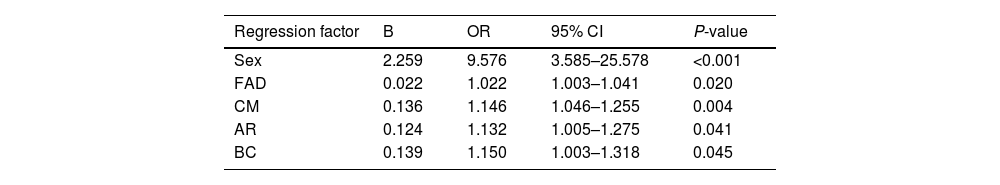
ResultsA significant association was found between family functioning and NSSI (P = 0.017). The correlation between adolescents with NSSI and gender, communication, affective responsiveness, and behaviour control was statistically significant. A nomogram graph and ROC curve were constructed, with an AUC of 0.772.
ConclusionThe findings support the notion that family functioning is associated with a higher risk for NSSI among adolescents with mood disorders. Furthermore, gender, communication, affective responsiveness, and behaviour control may be contributing factors.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora