The aim of this paper is to carry out a systematic literature review about the relationships between quality management, innovation, and performance. For that end, a search was carried out in the Web of Science and Scopus databases, and 172 articles were selected. Results show that there is a positive relationship between quality management, product and process innovation (incremental and radical), and operational and financial performance, and direct and indirect relationships. Based on these results, a set of direct and indirect relationships between these variables is proposed. The study supplements the few previous investigations on these joint relationships.
The purpose of this research is to analyse the state of the art on the relationship between quality management, innovation (incremental and radical product and process innovation) and operational and financial performance. The literature has mainly analysed, on the one hand, quality management and innovation (Sciarelli, Gheith, & Tani, 2020a; Zeng, Zhang, Matsui, & Zhao, 2017) and, on the other, quality management and performance (Khan, Mirza, & Khushnood, 2020; Sila, 2020). Few studies have analysed the relationship between quality, innovation and performance (Mahmud, Hilmi, & Mustapha, 2019; Wilson & Slobodzian, 2019).
Studies on quality and innovation have shown conflicting results (Abrunhosa & Sa, 2008) and have considered innovation from a one-dimensional perspective (Przychodzen, Leyva-de la Hiz, & Przychodzen, 2020; Srimarut & Mekhum, 2020) or from a multidimensional one (Sciarelli, Gheith, & Tani, 2020b). In this latter case, two dimensions have been mostly distinguished: product and process innovation (Escrig-Tena, Segarra-Cipres, Garcia-Juan, & Beltrán-Martín, 2018; Iswanto, Moridu, Inayati, Hudzafidah, & Rapini, 2020) or incremental and radical innovation (Duhaylongsod & De Giovanni, 2019; Sadikoglu & Zeir, 2010). Few authors have jointly considered the four dimensions of innovation in order to analyse the relationship between quality and innovation (Kim, Kumar, & Kumar, 2012). These ideas suggest the need to continue analysing the relationships between quality management and incremental and radical product and process innovation (Khan & Naeem 2018; Mahmud et al., 2019).
Previous literature also indicates that quality management has an influence on operational performance (Chung, Hsu, & Tsai, 2010; Khan et al., 2020) and it may affect financial performance (Abbas, Phan, & Matsui, 2020; Sila, 2020). While the former relationship has been proved in previous studies, the relationship between quality and financial performance is not so clear (Kusumah & Fabianto, 2018; Prado-Román, Del Castillo-Peces, Mercado-Idoeta, & Del Castillo-Peces, 2018). Innovation may also improve performance (Jaskyte, 2020; Srimarut & Mekhum, 2020). However, there are fewer articles considering the various types of innovation (incremental and radical product or process) in this relationship (Saeidi, Othman, Saeidi, & Saeidi, 2018; Xie, Huo, & Zou, 2019).
A few papers go further and analyse the joint relationships between quality, innovation and performance. These studies indicate that quality management has an indirect influence on financial performance through operational performance (Albuhisi & Abdallah, 2018) or innovation (Kafetzopoulos, Gotzamani, & Skalkos, 2019; Sadikoglu & Zehir, 2010).
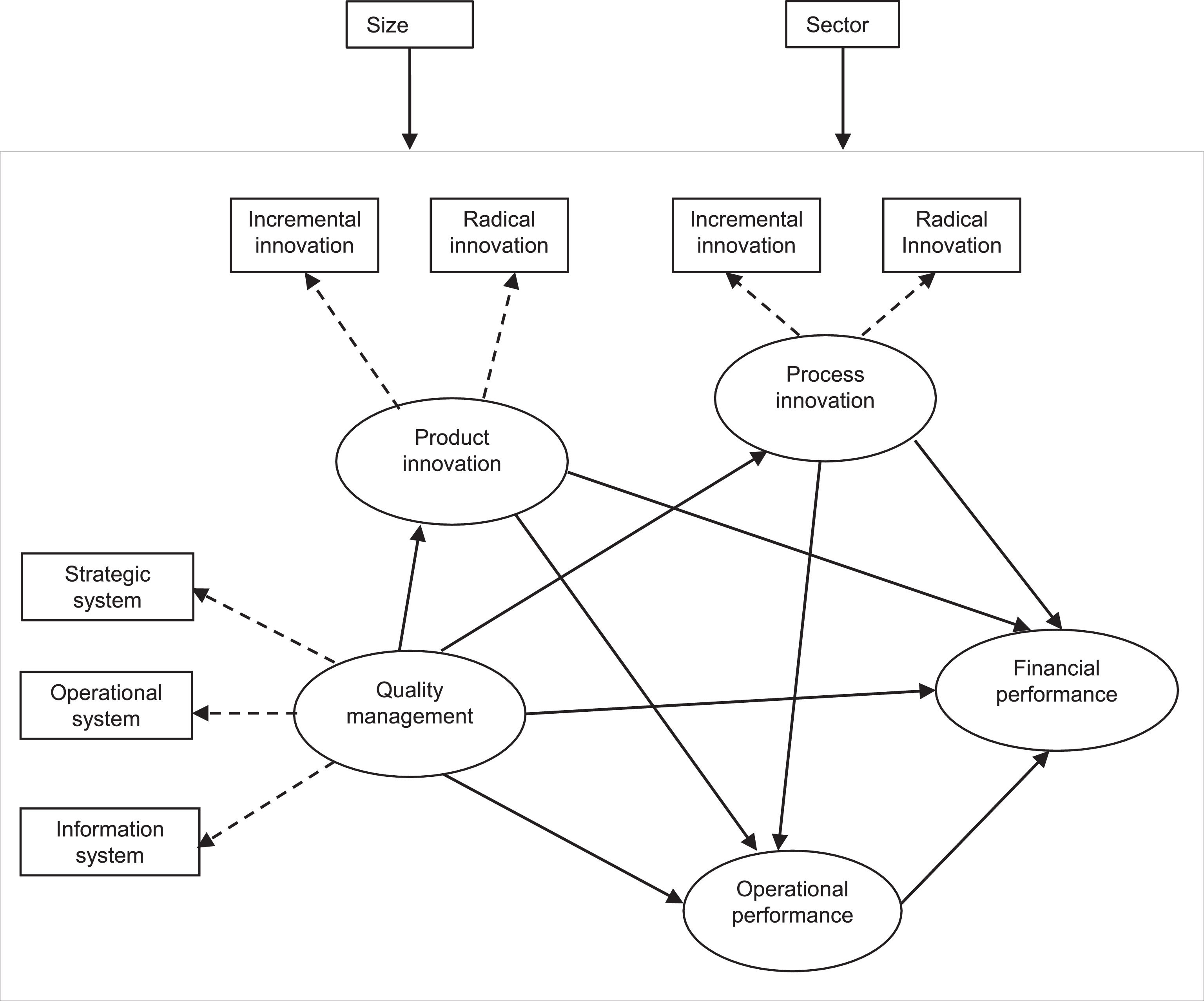
Conflicting results between quality and innovation, and between quality and financial performance, and the few studies jointly analysing quality, innovation and performance suggest that it may be interesting to continue analysing the potential relationships between these variables. The study helps to strengthen the theoretical framework on joint relationships between quality management, incremental and radical product and process innovation, and operational and financial performance, expanding previous studies that have analysed the relationship between quality, innovation and performance. Besides, the research helps to identify the most frequent terms, the research methods used, and the sectors and countries of each paper.
2Theoretical frameworkSome previous works have carried out systematic reviews in the field of quality, analysing the ISO 9001 standard (Heras-Saizarbitoria & Boiral, 2013), the application of the European Foundation for Quality Management excellence model (Doeleman, Have, & Ahaus, 2014; Suárez, Calvo-Mora, Roldán, & Periáñez-Cristóbal, 2017) or the application of quality management to higher education (Manatos, Sarrico, & Rosa, 2014; Tarí & Dick, 2016). Other authors have analysed the relationship between quality (ISO 9001) and product innovation (Manders, de Vries, & Blind, 2016). Alongside these theoretical studies, the empirical studies show the relationships between these variables.
2.1Effects of quality management on innovationAlthough the previous literature shows conflicting results (Khan & Naeem, 2018; Parra, Jimenez-Jimenez, & Martínez-Lorente, 2014; Pinho, 2008), it may be said that quality management practices (leadership, personnel management, customer focus, supplier management, process management, etc.) facilitate innovation. For instance, supplier management allows a firm to exchange information on the product in order to reduce development time and costs and improve the product's innovation capacity (Manders et al., 2016; Miranda, Paulo, Gomes, Filipe, & Lopes, 2014) in an incremental or radical manner (Kim et al., 2012; Parra et al., 2014). Similarly, when the firm measures changes in customer needs, it may introduce small changes in its products, and when leaders identify the changes in the environment, this may facilitate product innovations of a radical nature (Moreno-Luzón, Gil-Marques, & Valls-Pasola, 2013).
Quality management practices may also have a positive influence on process innovation (Perdomo-Ortiz, González-Benito, & Galende, 2006). For instance, quality management practices such as communication, teamwork and people management make it easier for employees to contribute innovations regarding their work processes (Prajogo & Sohal, 2004) in an incremental or radical manner (Kim et al., 2012; Moreno-Luzón et al., 2013; Parra et al., 2014).
2.2Effects of quality management on performanceThe relationship between quality management practices and operational performance has been widely documented in the literature, showing a positive influence (Chatzoglou, Chatzoudes, & Kipraios, 2015; Prajogo, Huo, & Han, 2012). For instance, customer focus may reduce complaints, and therefore improve customer satisfaction (Das, Handfield, Calantone, & Ghosh, 2000). Also, process and supplier management helps to provide a product meeting customers’ specifications, thus improving production standards (Prajogo et al., 2012) and product quality (Grandzol & Gershon, 1998).
Although the relationship between quality practices and financial performance is not a clear one (Kusumah & Fabianto, 2018; Roca-Puig & Escrig-Tena, 2017), it may be said that these practices may improve sales and market share (Powell, 1995). This is the case because practices such as people management, customer focus and supplier relationships affect process management, which leads to improvements in financial performance (Pham, 2020).
2.3Effects of innovation on performanceDifferent authors point out that innovation may improve operational performance. For instance, Kaynak (2003) points out that continuous improvement leads to improved product performance and reduces duplications and errors in the production process, thus improving customer satisfaction (Rahman & Bullock, 2005). In the same way, incremental and radical innovations in products and processes deriving from employees’ ideas for improvement may improve operational performance (Pinho, 2008). The literature also indicates that process and product innovation may improve financial performance (Rahman & Bullock, 2005), in terms of increased sales, market share or profitability (García-Rodríguez, Santos, Sanzo, & Trespalacios, 2008).
2.4Relationships between quality management, innovation and performanceAs has been indicated in previous sections, quality management practices may improve innovation (Moreno-Luzón et al., 2013), and operational and financial performance (Sila, 2020). In turn, innovation can also improve operational and financial performance (Saunila, 2014).
These ideas indicate that relationships may exist between all these variables. However, there is a reduced number of studies relating quality, innovation and performance (Akgün, Ince, Imamoglu, Keskin, & Kocoglua, 2013; Kafetzopoulos et al., 2019). Most of them indicate that innovation is a mediating element between quality management and performance (Akgün et al., 2013; Kafetzopoulos et al., 2019; Sadikoglu & Zehir, 2010; Wilson & Slobodzian, 2019). This small group of studies also includes some authors who do not find any relationships between such variables (Mahmud et al., 2019). Other authors point out that quality practices improve financial performance through operational performance (Lin, Liu, Liu, & Wang, 2013).
3MethodologyLiterature reviews may be quantitative, through meta-analysis, or qualitative, through a narrative review or a systematic review of the literature (Suárez et al., 2017). This paper offers a systematic review of the literature supplementing previous systematic literature reviews performed in the field of quality (Bastas & Liyanage, 2018; Doeleman et al., 2014; Heras-Saizarbitoria & Boiral, 2013; Manders et al., 2016; Suárez et al., 2017; Tarí & Dick, 2016; Tarí, Molina-Azorín, Pereira-Moliner, & López-Gamero, 2020) by analysing the relationships between quality management, incremental and radical product and process innovation, and operational and financial performance, in a joint manner. In this respect, a systematic literature review is performed, based on the stages proposed by Sánchez-Meca (2010) and followed by Suárez et al. (2017). The stages proposed are: (a) formulating the questions, (b) criteria for inclusion and exclusion of articles, (c) article search and selection; and (d) results of the search.
3.1Formulating the questionsThis section shows the questions that may be answered by a systematic literature review, and also introduces the constructs and concepts.
3.1.1Research questions- 1.
Which are the characteristics of the articles analysed (terms most used, type of studies, tools used, sectors and countries)?
- 2.
Does quality management have a positive relationship with innovation?
- 3.
Does quality management have a positive relationship with operational and financial performance?
- 4.
Does innovation have a positive relationship with operational and financial performance?
- 5.
Which are the joint relationships between quality management, innovation and operational and financial performance?
The concepts analysed in this paper are: quality management, innovation and operational and financial performance. Quality management is an integrated organizational management philosophy that includes a set of practices. According to the literature, the most common practices are (Molina-Azorín, Tarí, Pereira-Moliner, López-Gamero, & Pertusa-Ortega, 2015; Nair, 2006): leadership, planning, customer focus, people management, process management, supplier management, and information and analysis. These practices may be grouped into three systems (Curkovic, Vickery, & Droge, 2000): strategic system (leadership, quality planning, customer focus), operational system (people management, process management, supplier management), and information system (information and analysis).
Innovation has different dimensions: it may involve products and processes (Moreno-Luzón et al., 2013; Parra et al., 2014) and also be incremental and radical (Cheng & Krumwiede 2012; Kim et al., 2012). In this way, a distinction may be made between incremental product innovation, radical product innovation, incremental process innovation and radical process innovation.
Concerning organizational performance, it can be operational and financial. Operational performance includes increased product quality, productivity, employee satisfaction and a reduction in the costs of quality (Curkovic et al., 2000; Molina-Azorín et al., 2015). Financial performance may include increased sales, increased market share or increased profitability (Kaynak, 2003).
3.2Criteria for inclusion and exclusion of articlesIn this stage, the article inclusion and exclusion criteria are determined in order to carry out the search (Del Río Rama & Martínez Carballo, 2007; Doeleman et al., 2014; Siva et al., 2016):
- 1.
Temporal scope: articles have been included from the year 1990 (1996 in the case of Scopus, as it is since then that data are available) to the year 2020.
- 2.
Quality of Research: articles were selected if published in journals included in JCR (Journal Citation Report by Thomson Reuters) and SJR (SCImago Journal & CountryRank by Scopus).
- 3.
Area of knowledge: the knowledge areas are quality management, innovation and performance.
- 4.
Language of publication: the articles analysed are mainly published in English, with the exception of some of them which were in Spanish in the Scopus database.
- 5.
Keywords: the keywords were “quality management”, “TQM”, “ISO 9000″, “ISO 9001”, and “EFQM”, for the quality management concept. For the innovation concept, “innovation” was used. For the performance concept, the keywords used were “operational performance” and “financial performance”.
- 6.
All non-peer-reviewed articles, and also books and conference papers, were excluded.
This stage consisted in identifying the articles according to the research questions and the inclusion and exclusion criteria:
- 1.
Databases: the most important databases were used regarding coverage and quality of content (Siva et al., 2016): Web of Science and Scopus.
- 2.
Database search strategy: a combination of keywords was performed, by title, between quality management (quality management, TQM, ISO 9000, ISO 9001 or EFQM) and innovation (innovation). The same was done for the quality management search (quality management, TQM, ISO 9000, ISO 9001 or EFQM) and performance (operational performance or financial performance) and for the search for innovation (innovation) and performance (operational performance or financial performance).
Firstly, the search was performed in these two databases, and 478 articles were identified. First, the abstracts were read for each of these 478 articles. In many cases, the full study was read because by reading the abstract it was not clear if the article met the requirements of this study. Then, those articles that fulfilled the inclusion criteria were read in full.
With regard to the relationship between quality management and innovation, 98 articles were obtained from the Web of Science database, from which 48 were valid. The same search was performed in Scopus, where 143 articles were found: 25 considered according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 43 not considered because they also occurred in the Web of Science database, and the rest were excluded. In this way, 73 valid articles were obtained on the relationship between the concepts of quality management and innovation.
With regard to the relationship between quality management and performance, 40 articles were identified in the Web of Science database, from which 33 were considered according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Fifty articles were identified in the Scopus database, from which 12 were considered, as 29 were repeated, and the rest were excluded. For the relationship between quality management and performance, 45 valid articles were finally obtained.
With regard to the relationship between innovation and performance, 56 articles were found in the Web of Science database, from which 31 were considered. As for the Scopus database, 91 articles were obtained, from which 23 were considered, whereas 27 were repeated and 41 were excluded. For the relationship between innovation and performance, 54 valid articles were obtained. Thus, out of the 478 articles identified in the search, 172 have been analysed in detail.
4Results4.1Most used terms in the literatureConcerning the terms most used in the literature in studies on quality management and innovation (Table 1), it may be observed that total quality management (TQM) is the most used term (33 studies). In this respect, TQM is an integrated management system including a set of practices. Then, the term quality management (QM) was found in 16 articles, quality management practices (QMP) was found in 15 and ISO 9000 in 4. The ISO 9000 standards describe the basic concepts and principles of quality management and specify the requirements to adopt a quality management system according to ISO (ISO, 2021). Also, other terms were found, such as EFQM (European Foundation for Quality Management) (3), a world-recognized management framework allowing organizations to measure their weaknesses and identify potential solutions in order to significantly improve their performance (EFQM, 2021). Also, the terms quality (1) and continuous improvement (1) are found. These terms indicate that there are different ways of approaching and implementing quality management principles and practices. With regard to innovation, it may be observed that the terms most used are innovation (38), product and process innovation (18) and other concepts such as incremental and radical innovation (7), technological innovation (5), organizational innovation (3) and administrative innovation (2).
Terms most used in the literature.
| Terms | Works on | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality-innovation | Quality-performance | Innovation-performance | Total | |
| Quality management | ||||
| • TQM | 33 | 15 | 48 | |
| • QM | 16 | 3 | 19 | |
| • QMP | 15 | 10 | 25 | |
| • ISO 9000 | 4 | 10 | 14 | |
| • EFQM | 3 | 3 | ||
| • Quality | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| • Continuous improvement | 1 | 1 | ||
| • Quality awards | 2 | 2 | ||
| • Quality management systems | 1 | 1 | ||
| • Continuous improvement/statistical control | 1 | 1 | ||
| • ISO 9000/TQM | 1 | 1 | ||
| Innovation | ||||
| • Innovation | 38 | 31 | 69 | |
| • Product and process innovation | 18 | 10 | 28 | |
| • Incremental and radical innovation | 7 | 2 | 9 | |
| • Technological innovation | 5 | 9 | 14 | |
| • Organizational innovation | 3 | 3 | ||
| • Administrative innovation | 2 | 2 | ||
| • Other types of innovation | 2 | 2 | ||
| Performance | ||||
| • Financial performance | 17 | 34 | 51 | |
| • Operational performance | 10 | 6 | 16 | |
| • Operational and financial performance | 6 | 6 | ||
| • Other types of performance | 12 | 14 | 26 | |
Concerning the terms most used in the studies on quality management and performance (Table 1), it may be observed that TQM is the most widely used term (15). This is followed by the terms quality management practices (10) and ISO 9000 (10). Also, other terms are found, such as quality management (3), quality (2), quality awards (2), quality management systems (1), continuous improvement and statistical control practices (1), and studies jointly relating ISO 9000 to TQM (1). With regard to performance, the terms most used are financial performance (17), operational performance (10) and operational and financial performance (6).
Concerning the terms most used in the studies on innovation and performance (Table 1), it may be observed that innovation (open, closed, levels, capability) is the term most used in 31 studies. Then, we find the term process and product innovation (10). This is followed by the terms technological, green or environmental innovation (9), incremental and radical innovation (2) and different types of innovation: technological innovation, service innovation or management innovation. With regard to performance, the terms most used are financial performance (34) and operational performance (6).
4.2Qualitative studies, quantitative studies and tools usedConcerning the studies relating quality management and innovation (Table 2), it may be observed that a great majority of them are of a quantitative nature and there are only 10 (13,70%) of a qualitative origin. Out of the 63 quantitative studies, 44 use structural equation models, and 8 out of the 10 qualitative studies use the case method. Concerning those studies relating quality management and performance (Table 3), it may be observed that most are quantitative and only one is quantitative (Hansson & Eriksson, 2002). The structural equation model is used by 16 out of the 44 quantitative studies, and the only qualitative research uses the case method. On the other hand, 25 out of the 54 quantitative studies on innovation and performance (Table 4) use the structural equation model. Among these works, no qualitative study has been found.
Relationships between quality management and innovation.
| Autor/es | Research model | Sector | Country of sample collection | Sample size | Analysis tool | Main contributions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abrunhosa and Sa (2008) | Qualitative | Industry | Portugal | 20 | Case study | The TQM principles are positively associated to the adoption of technological innovation |
| Abu Salim, Sundarakani, and Lasrado (2019) | Quantitative | Industry and services | United Arab Emirates | 190 | Structural equation model | Continuous improvement is positively linked to innovation |
| Aminbeidokhti et al. (2016)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Services | Iran | 253 | Structural equation model | TQM does not have a positive, significant effect on organizational innovation |
| Aoun and Hasnan (2017)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Services | Lebanon | 13 | Structural equation model | Soft TQM had an influence on innovation skills through people-based management |
| Aoun, Hasnan, and Al-Aaraj (2018) | Quantitative | Services | Lebanon | 352 | Structural equation model | Lean practices had a significant influence on innovation skills |
| Arshad and Su (2015) | Quantitative | Services | Pakistan | 190 | Regression analysis | TQM has a positive, significant impact on service innovation |
| Bon and Mustafa (2014) | Quantitative | Services | Malaysia | 191 | Structural equation model | People management has a positive impact on administrative innovation |
| Bourke and Roper (2017)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Northern Ireland | 1358 | Static models: Tobit Models of Innovative Sales of New Products | The adoption of quality management has short-term negative effects and long-term benefits regarding the performance of product innovations |
| Camisón & Puig-Denia (2016)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Spain | 550 | Structural equation model | Results indicate that the level of implementation of quality management practices is not directly related to process innovation performance |
| Chen and Reyes (2017) | Qualitative | Services | USA | 1 | Case study | A quality management focus facilitates the development of innovation |
| Donate et al. (2019)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Spain | 129 | Structural equation model | Social capital is a mediating factor in the relationship between TQM and radical and incremental innovation capabilities, although the effect is not significant when the radical innovation capabilities are considered |
| Escrig-Tena et al. (2018) | Quantitative | Industry and Services | Spain | 173 | Structural equations | The hard dimension of quality management has a direct influence on product and process innovation |
| García-Fernández (2016)⁎⁎ | Qualitative | Industry and services | Spain | 5 | Case study | Quality management has a positive impact on innovation through knowledge management |
| González-Cruz, Roig-Tierno, and Botella-Carrubí (2018) | Qualitative | Services | Spain | 133 | Comparative qualitative analysis | Quality management helps to strengthen the firm's ability to innovate |
| Gutiérrez, Torres, and Morales (2010) | Quantitative | Industry and Services | Spain, Italy, United Kingdom, Switzerland, Austria, Germany, Rumania, Czech Republic, Sweden, Denmark, France and Belgium | 237 | Multiple linear regression | The quality management elements included in the EFQM model have a deeper impact on administrative innovation and technical innovation than the elements included in Quality Control and the ISO Standards. |
| Hoang, Igel, and Laosirihongthong (2006) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Vietnam | 204 | Structural equation model | When TQM is considered as a set of practices, it has a positive impact on the firm's innovation |
| Honarpour, Jusoh, and Nor (2018) | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 190 | Structural equation model | The study supports the positive association between TQM and innovation |
| Hong, Liao, Zhang, & Yu (2019)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | China | 149 | Structural equation model | Quality management practices may improve innovation performance indirectly through quality management capabilities |
| Hung (2007) | Qualitative | Industry | Taiwan | 1 | Case study | A worldwide leading firm generates innovation by solving a problem on TQM practices |
| Hung, Lien, Yang, Wu, and Kuo (2011) | Quantitative | Industry | Taiwan | 223 | Structural equation model | TQM has both a significant and a positive effect on innovation performance |
| Jiménez-Jiménez, Martínez-Costa, and Para-González (2019) | Quantitative | Primary, secondary and tertiary | Spain | 706 | Structural equation model | There is a curvilinear effect between TQM and organizational innovation |
| Kafetzopoulos and Gotzamani (2019)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Greece | 580 | Structural equation model | The EFQM model enablers are directly or indirectly associated with the four types of innovation (product, process, organization and marketing innovation) |
| Kafetzopoulos et al. (2015) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Greece | 433 | Structural equation model | Quality management directly contributes to product and process innovation |
| Kafetzopoulos et al. (2019)* | Quantitative | Industry | Greece | 580 | Structural equations | Innovation performance partially mediates between EFQM and the firm's performance (operational and financial performance) |
| Kanapathy, Bin, Zailani, and Aghapour (2017) | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 106 | Structural equation models | Innovation is mainly influenced by the adoption of soft elements (TQM) and, secondarily, by hard elements (TQM) |
| Kim et al. (2012) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Canada | 242 | Structural equation model | Results show that a set of quality management practices, through process management, has a direct, positive relationship with incremental, radical and administrative innovation |
| Kim, Kwon, & Park, 2015⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Korea | 330 | Structural equation model | A basic level of ISO 9000 implementation has a positive effect on process innovation and on information technology. An advanced level of ISO 9000 implementation has a negative effect on process innovation and on information technology |
| Leavengood, Anderson, and Daim (2014) | Qualitative | Forest product manufacturers | USA | 2 | Case study | Firms focusing on quality saw innovation as an end and not as the means to reach other objectives |
| Lee et al. (2015b, 2015a)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 258 | Multiple linear regression | Strategic planning, customer focus and human resource management lead to greater technological innovation. Organizational learning mediates between process management, information and analysis and technological innovation |
| Lee et al. (2010) | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 125 | Structural equation model | Leadership, strategic planning, customer focus, information and analysis, human resource management and process management are positively associated to the performance of product innovations |
| Li, Zhao, Zhang, Chen, and Cao (2018)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | China | 407 | Generalised estimating equations | Quality management has significant negative effects on the likelihood of implementing green technological innovation and green management innovation |
| Llach, Casadesus, and Marimon (2011) | Quantitative | Industry | Spain | 151 | Maximum likelihood method | The level of quality management has a positive relationship with the implementation of organizational innovations |
| Long, Aziz, Kowang, and Ismail (2015) | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 123 | Multiple regression and correlation analysis | TQM has a positive impact on innovation performance as shown by five practices measured: customer focus, leadership, process management, strategic planning and people management |
| Mahmud et al. (2019)* | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 124 | Structural equation model | TQM had a significant impact on innovation (both organizational and technological) and on performance (both operational and financial) |
| Maistry, Hurreeram, & Ramessur (2017)* | Quantitative | Agriculture | Mauricio | 60 | Structural equation model | There is a positive relationship between TQM, innovation (administrative and technological) and performance (operational and financial performance) |
| Mangiarotti and Riillo (2014) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Luxemburg | 1140 | Logit Model | ISO 9000 may promote innovation by adopting definitions capturing the sector-specific features of innovation |
| Martínez-Costa and Martínez-Lorente (2008) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Spain | 451 | Structural equation model | TQM promotes innovation (both product and process) within firms |
| Mohammed Yusr, Mohd Mokhtar, and Rahim Othman (2013) | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 139 | Structural equation model | TQM improves innovation performance |
| Moreno-Luzón et al. (2013)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Spain | 72 | Structural equation model | TQM does not directly affect radical innovation, but there is a significant positive relationship with incremental innovation |
| Ooi, Lin, and Teh (2012) | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 206 | Multiple regression analysis | TQM has a positive, significant relationship with innovation performance |
| Palm, Lilja and Wiklund (2016)⁎⁎⁎ | Qualitative | Services | Sweden | 2 | Multiple case study | Present quality management practice is perceived as st&ardization, which leads to less room for innovation |
| Perdomo-Ortiz et al. (2006) | Quantitative | Industry | Spain | 102 | Multiple regression analysis | There are TQM dimensions accounting for the generation of innovation capabilities |
| Perdomo-Ortiz et al. (2009a) | Quantitative | Industry | Spain | 106 | Bivariate correlation analysis and multiple regression analysis | Direct influence of the positive effects of teamwork on technological innovation |
| Perdomo-Ortiz, González-Benito, and Galende (2009b) | Quantitative | Industry | Spain | 105 | Multiple regression analysis | The commercial practices suggested by TQM in technological innovation may be better understood by considering the firms’ innovation capabilities |
| Pinho (2008)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Portugal | 135 | Structural equation model | No statistical evidence was found confirming the effect of TQM on innovation |
| Prajogo and Sohal (2003) | Quantitative | Industry | Australia | 194 | Structural equation model | TQM is positively and significantly related to product innovation performance |
| Prajogo and Sohal (2004) | Quantitative | Industry | Australia | 194 | Structural equation model | Leadership and people management are positively related to product innovations |
| Prajogo and Sohal (2006)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Australia | 194 | Structural equation model | TQM does not have a significant relationship with innovation |
| Roldán Bravo, Lloréns Montes, and Ruiz Moreno (2017) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Europe | 270 | Hierarchical regression analysis | The negative effects of quality management on innovation performance may be overcome through the learning style |
| Ruiz Moreno, Haro, and Ortega (2011) | Quantitative | Services | Spain | 202 | Regression analysis | Firms that have implemented TQM systems have a greater orientation towards innovation, especially in service firms |
| Ruiz-Moreno, Haro-Domínguez, Tamayo-Torres and Ortega-Egea (2016) | Quantitative | Industry and Services | Spain | 202 | Structural equation model | Those organizations implementing quality management programmes are characterized by a greater orientation towards innovation |
| Sa and Abrunhosa (2007) | Qualitative | Industry | Portugal | 16 | Case study | TQM is more supportive of the type of innovation applied in industry (incremental technological / process). |
| Sadikoglu and Zeir (2010)* | Quantitative | Industry | Turkey | 373 | Structural equation model | Innovation is a mediating factor between TQM and operational performance |
| Sahoo (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | India | 134 | Structural equation model | Quality management practices promote product and process innovation |
| Sciarelli et al. (2020a)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Services | Italy | 449 | Structural equation model | There are positive relationships between quality management practices and innovation. Some quality management practices have an impact on innovation through people management and processes |
| Sciarelli et al. (2020b) | Quantitative | Services | Italy | 356 | Structural equation model | Quality practices improve innovation |
| Sefatian, Klidbari, and Shojaie (2016) | Quantitative | Industry | Iran | 30 | Equation modelling | By increasing the level of total quality management, it is possible to increase firms’ innovation rate |
| Silva, Gomes, Lages and Pereira (2014)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Portugal | 112 | Structural equation model | Product design capability helps towards product innovation. The TQM culture has a direct influence on improved processes and in product design capabilities, but not on product innovation |
| Taddese (2017) | Qualitative | Industry | Japan, India and Thailand | 17 | Case study | TQM facilitates the development of innovation capabilities (both product and process) |
| Taddese and Osada (2010) | Qualitative | Industry | India | 8 | Case study | TQM affects process technoinnovation |
| Terziovski and Guerrero (2014)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry and Services | Australia | 220 | Structural equation model | ISO 9000 certification does not have a statistically significant relationship with measures of product innovation performance |
| Urban and Toga (2017) | Quantitative | Industry | South Africa | 183 | Multiple regression analysis | Customer focus and leadership account for a significant part of product innovations, but not process innovation |
| Vahidnia, Bavarsad, and Senoubari (2013) | Quantitative | Industry | Iran | 95 | Structural equation model | TQM has a positive, significant effect on innovative performance |
| Vujović et al. (2017) | Quantitative | Industry and Services | Montenegro | 119 | Ordinary least squares regression | ISO 9000 has a positive influence on innovation performance |
| Wang (2014) | Quantitative | Industry | Taiwan and China | 607 | Generalized estimating equation | Results show that there is a reverse, U-shaped relationship between innovation competence and quality management |
| Wu, Chen, and Chuang (2011) | Quantitative | Industry | Taiwan | 15 | Diffuse analytic hierarchy process. Spearman's rank correlation | Competent leadership and the capability for management, research and development helps high-technology firms to promote innovation |
| Wu, Wu, and Harrigan (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | China | 497 | Regression model | Quality management provides an important foundation for internal controls in firms on their innovation activities |
| Yusr (2016)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 147 | Structural equation model | TQM practices do not have a positive impact on innovation performance |
| Yusr, Mokhtar, and Othman (2014) | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 105 | Structural equation model | There is a positive effect when applying TQM practice on technological innovation capabilities. |
| Yusr et al. (2017)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 147 | Structural equation model | The relationships between TQM and innovation performance were not supported |
| Zeng, Chi and Matsui (2015)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | USA, Japan, Italy, Sweden, Austria, Korea, Germany and Finland | 238 | Structural equation model | The hard aspects of quality management positively affect (directly and indirectly) innovation performance through their effect on quality performance. Soft aspects of quality management have an indirect effect on innovation performance through their effect on hard aspects |
| Zeng et al. (2017) | Quantitative | Industry | USA, Japan, Italy, Sweden, Austria, Korea, Germany and Finland | 238 | Structural equation model | The hard aspects of quality management have a direct influence on how fast new products are introduced, while the soft aspects of quality management have a direct influence on product innovation |
| Zhou, Gu, and Zhao (2018) | Quantitative | Services | China | 184 | Structural equation model | TQM has a direct, positive effect on innovation |
Relationships between quality management and performance.
| Author(s) | Research model | Sector | Country of sample collection | Sample size | Analysis tool | Main contributions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbas et al. (2020) | Quantitative | Industry | Iraq | 140 | Correlation analysis | TQM has a positive impact on financial performance |
| Agus and Sagir (2001)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 127 | Structural equation model | TQM practices have a positive influence on financial performance through competitive advantage |
| Agus et al. (2000)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 127 | Structural equation model and Cluster | TQM practices have a positive influence on customer satisfaction and, ultimately, on financial performance |
| Akgün et al. (2014)* | Quantitative | Industry | Turkey | 193 | Structural equation model | TQM positively affects innovation. Innovation affects financial performance |
| Albuhisi and Abdallah (2018)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Jordan | 197 | Structural equation model | Customer focus has a significant mediating role between soft TQM and financial performance |
| Anh and Matsui (2011) | Quantitative | Industry | Japan | 167 | Variance and regression analysis | Quality management practices (exchanging information and communication at workshop and between function) significantly affect the various dimensions of operational performance |
| Ataseven et al. (2014) | Quantitative | Industry and Services | Australia and New Zealand | 321 | Structural equation model | The internalization of the ISO 9000 standards improves commercial processes |
| Augustyn, Elshaer, and Akamavi, (2021) | Quantitative | Services | Egypt | 288 | Structural equation model | Interconnected quality management practices (top management leadership, employee management, customer focus, supplier management, process management, quality data and reports) may improve financial performance |
| Baird et al. (2011)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry and Services | Australia | 364 | Multiple regression analysis | Quality management practices (supplier's quality management, process management and quality data and reports) help to reach operational performance goals. Product design has no relationship |
| Benner & Veloso (2008)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | USA | 75 | Regression model | Firms who are late adopters of ISO 9000 no longer obtain financial benefits |
| Chapman et al. (1997) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Australia | 75 | Correlation analysis | Quality improvement is connected to financial performance |
| Chatzoglou et al. (2015)⁎⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Agriculture, industry and services | Greece | 168 | Structural equation model | ISO 9000 implementation is closely associated to improved financial performance. Besides, it was discovered that ISO implementation is directly associated to quality awareness, execution of operations, market share, customer satisfaction and income from sales |
| Chung, Hsu, & Tsai (2010)⁎⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Taiwan | 73 | Variance analysis (ANOVA) | The degree of implementation of TQM activities has a significant influence on operational performance (quality performance, financial performance and inventory management performance) |
| Gotzamani, Longinidis, and Vouzas (2010) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Greece | 300 | Student t and conglomerate analysis | Quality performance has a positive relationship with financial performance for external providers of logistics firms |
| Hansson and Eriksson (2002) | Qualitative | Industry and Services | Sweden | 17 | Case study | The study indicates that winners of Swedish quality awards have better financial performance then the other firms |
| Hendricks and Singhal (2001) | Quantitative | Agriculture, Industry and Services | USA | 435 | Anova, Ancova, Student t and Multiple regression analysis | Smaller firms obtain significantly better performance than larger firms. Those forms that have won independent awards obtain significantly better performance than those obtaining rewards from providers |
| Herzallah, Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, and Munoz (2014)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Palestine | 202 | Structural equation model | Results from this study show that TQM practices have an indirect, positive, significant relationship with financial performance through competitive strategies |
| Ionaşcu, Ionaşcu, Săcărin, and Minu (2017) | Quantitative | Services | Romania | 67 | Regression models | ISO 9001 is directly related to its financial performance |
| Khan et al. (2020) | Quantitative | Services | Pakistan | 150 | Regression analysis | TQM practices have a positive influence on operational performance in hotels in the context of developing countries |
| Kober et al. (2012)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry and services | Australia | 3776 | Categorical regression analysis | No evidence was found that of TQM improving financial performance |
| Kusumah and Fabianto (2018)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Indonesia | 27 | McNemar Test and Cochran Q | There was no significant impact of ISO 9000 on financial performance before and after implementation (McNemar). All the firms in the sample with more consistency became more efficient and fast, and thus increased financial performance (Cochran Q) |
| Lee and Park (2016) | Quantitative | Agriculture, Industry and Services | Worldwide | 443 | Structural equation model | Quality management practices may improve operational performance |
| Maqsood, Hussain, and Al Arab (2019) | Quantitative | Services | Pakistan | 150 | Regression analysis lineal | TQM practices have a positive, statistically significant relationship with non-financial performance |
| Martí-Ballester and Simon (2017) | Quantitative | Agriculture, Industry and Services | Spain | 76 | Partial least squares analysis | The level of integration of quality systems procedures has a positive, significant relationship with corporate financial performance |
| Merino-Díaz de Cerio (2003) | Quantitative | Industry | Spain | 965 | Multiple regression analysis | Quality management practices related to product design and development, alongside human resources, are the most significant predictors of operational performance |
| Modgil and Sharma (2016)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | India | 254 | Factor analysis, route model and structural equation model | TQM has a direct and indirect effect on operational performance |
| Mokhtar, Karbhari, and Naser (2005) | Quantitative | Agriculture, industry and services | Malaysia | 162 | Correlation and regression analysis | ISO 9000 is associated to firms’ performance (financial performance) |
| Nair & Choudhary, 2016⁎⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Services | Qatar | 331 | Structural equation model | The results have indicated that top management leadership, organizational learning, quality information management and supplier management have a significant influence on endogenous variables (operational and financial performance). |
| Naveh and Marcus (2007) | Quantitative | Services | USA | 40 | Hierarchical linear models | Safety performance of certified carriers was significantly better after ISO 9000 than before, and was also significantly better than non-certified carriers |
| O'Neill, Sohal, and Teng (2016) | Quantitative | Industry | Australia | 1154 | Univariate Ancova procedure, multivariant discriminant analysis, Mancova analysis | A firm's orientation towards quality management provides a statistically significant financial performance advantage |
| Pantouvakis and Dimas (2010) | Quantitative | Industry | Worldwide | 18 | Regression analysis | ISO-certified ports are more financially efficient than their non-certified competitors |
| Parvadavardini, Vivek and Devadasan (2016)⁎⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | India | 152 | Structural equation model | Positive relationship between quality management practices and quality performance and financial performance |
| Pham (2020)⁎⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Agriculture, Industry and Services | Vietnam | 211 | Structural equation model | TQM has a positive effect on financial and operational performance. Operational performance has a positive effect on financial performance. Operational performance does not mediate in the relationship between TQM and financial performance |
| Phan et al. (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | Vietnam | 120 | Correlation analysis and hierarchical regression analysis | Quality management practices in the supply chain have a significant connection to operational performance |
| Prajogo et al. (2012)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Agriculture, industry and services | Australia | 321 | Structural equation model | Process management (supplier) is positively related to operational performance. However, process management (customer) is not positively related to operational performance |
| Roca-Puig and Escrig-Tena (2017)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Services | Spain | 168 | Polynomic regression analysis | In high levels of quality management, additional investments aimed at improving quality will not lead to financial benefits |
| Saleh, Sweis, and Mahmoud (2018) | Quantitative | Industry | Jordan | 40 | Simple and multiple linear regression analysis | The results showed that continuous improvement and process statistical control practices play an important role in obtaining operational performance results |
| Samson and Terziovski (1999) | Quantitative | Industry | Australia and New Zealand | 1024 | Factor analysis, correlations and multiple regression analysis | The leadership, people management and customer service categories were the most important predictors of operational performance. |
| Sharma (2005) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Singapore | 70 | Regression analysis | ISO 9000 certification improves financial performance |
| Sharma and Modgil (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | India | 262 | Structural equation model | TQM practices have a direct impact on operational performance |
| Sila (2020)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry and Services | Turkey | 156 | Structural equation model | TQM also has direct and indirect positive effects (through corporate social performance) on financial and market performance |
| Wali and Boujelbene (2011)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Agriculture, Industry and Services | Tunis | 70 | Structural equation model | TQM has a direct, significant negative effect on ROA and ROS |
| Wayhan et al. (2002) | Quantitative | Agriculture, Industry and Services | USA | 48 | Manova, Anova | ISO 9000 has a very limited impact on financial performance |
| Wayhan, McCallum, and Golyer (2013) | Quantitative | Industry | USA | 93 | T Tests and Mancova | TQM has a direct, statistically significant link with financial performance |
| Youssef and Youssef (2018) | Quantitative | Industry | USA, Canada, México and Saudi Arabia | 2961 | Anova, Kruskal-Wallis H test, ordinal logistic regression | Plants integrating ISO 9000 and TQM made faster progress in order to have better operational performance in terms of quality management, inventory management, time-based performance and competitiveness |
Relationships between innovation and performance.
| Autor/es | Research model | Sector | Country of sample collection | Sample size | Analysis tool | Main contributions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aas and Pedersen (2011) | Quantitative | Industry and Services | Norway | 4707 | Mann –Whitney –Wilcoxon non-parametric test (Z tests) | The effects of service innovation depend on the indicators analysed for financial performance |
| Abdallah, Phan, and Matsui, (2016) | Quantitative | Industry | Austria, Finland, Germany, Italy, Japan, Korea and United States | 214 | Regression analysis | Results show that technological innovation significantly and positively affects operational performance |
| Aguilera-Caracuel and Ortiz-de-Mandojana (2013)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, The Netherlands, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Japan, China, South Korea and Taiwan | 140 | Matched pair analysis and multiple and moderate regression analysis | Green innovative firms do not show better financial performance compared to non-green innovative firms. By focusing on green innovative firms, it may be observed that the intensity of green innovation is positively related to the firm's profitability |
| Al-Sa'di et al. (2017) | Quantitative | Industry | Jordan | 207 | Hayes SPSS mediation process | Process innovation has a significant positive effect on operational performance, while product innovations do not |
| Beyhan Yasar, Sezen, and Karakadilar, 2019⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Turkey | 384 | Structural equation models | Continuous improvement has a mediating effect on the relationship between innovation and financial performance |
| Bigliardi (2013) | Quantitative | Industry | Italy | 98 | Regression analysis | An increase in the level of innovation leads to an increase in financial performance. |
| Bistrova, Lace, Tamošiūnienė, and Kozlovskis (2017) | Quantitative | Primary, Secondary and Tertiary | Central and Eastern Europe, including Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia Latvia and Lithuania | 2672 | Cluster and linear regression lineal | Substantial investments in innovation (over 10%) lead to greater profitability |
| Bockova and Zizlavsky (2016) | Quantitative | Industry | Czech Republic | 169 | Mann-Whitney U test | Investment in innovation is closely related to financial performance |
| Cegarra-Navarro, Reverte, Gómez-Melero, and Wensley (2016) | Quantitative | Services | Spain | 133 | Structural equation model | An innovation culture linked to the economic dimension of social responsibility leads to improved financial performance |
| Černe, Jakličerne, and Šernekerlavaj (2015) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Slovenia, Spain and South Korea | 604 | Structural equation models | Innovation in management is the mechanism allowing firms to fully benefit from their technological discoveries in order to obtain higher financial performance |
| Chen and Chiu (2018) | Quantitative | Services | China | 317 | Lisrel model | The innovation strategy used has a positive relationship with operational performance |
| Cortez and Cudia (2011) | Quantitative | Industry | China | 20 | Regression analysis | Automotive companies show a positive impact of green innovation on income, assets, debt and long-term capital. Electronics firms only show an impact on income and long-term debt |
| de Oliveira and da Silva (2018)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Brazil | 2810 | Structural equation model | Innovation performance had a negative influence on future financial performance |
| Duhaylongsod and De Giovanni (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | Europe (10 countries) | 173 | Structural equation models | Incremental product innovation strategy improves the relationship between operational performance |
| García Vidales, Maldonado Guzmán, and Alvarado Carrillo (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | Mexico | 300 | Structural equation model | Open innovation has a positive, significant effect on financial performance |
| Gök and Peker (2017)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry and services | Turkey | 305 | Structural equation model | Innovation has a direct negative relationship with financial performance |
| Ho, Nguyen, Adhikari, Miles, and Bonney, (2018) | Quantitative | Primary | Vietnam | 190 | Structural equation model | Innovation has a direct positive relationship with financial performance |
| Hsueh and Tu (2004) | Quantitative | Industry and Services | Taiwan | 1047 | Regression analysis | Innovative action had a greater impact on increased sales, while fostering an innovative atmosphere and the ability to innovate within the organization had a greater impact on profits |
| Iswanto et al. (2020) | Quantitative | Industry | Indonesia | 303 | Structural equation model | Results indicate that process, product and management innovation have a positive, significant effect on firms’ financial performance. |
| Jaskyte (2020)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Services | USA | 103 | Multiple regression analysis | Technological innovation was not a significant predictor of financial performance. Organizational innovation was a significant predictor of total assets and total income |
| Khanh, Chau, and Adhikari (2018) | Quantitative | Agriculture | Vietnam | 190 | Structural equation model | Innovation has a positive relationship with financial performance |
| Kostopoulos, Papalexandris, Papachroni, and Ioannou (2011) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Greece | 461 | Structural equation model | The absorption capacity directly and indirectly contributes to innovation and financial performance |
| Lee, Cho, and Shin 2015a⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Worldwide | 28 | Multiple regression analysis | Open innovation has mid-term and long-term positive effects on financial performance, but no short-term effects |
| Lee, Park, and Song (2009) | Quantitative | Industry | Korea | 215 | Regression analysis | A closed innovation strategy, represented by the family control over an SME, is positively related to financial performance |
| Leyva-de la Hiz, Ferron-Vilchez, and Aragon-Correa (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | Worldwide | 216 | Hausman (Fixed effects model) | High levels of deficiencies in resources reduce the existing positive relationship between focused environmental innovations and financial performance |
| Liao (2018) | Quantitative | Industry and services | China | 366 | Structural equation model | The environmental innovation dimensions promote financial performance |
| Liao and Rice (2010)** | Quantitative | Industry | Australia | 449 | Structural equation model | Innovation improves financial performance through transformation results |
| Lin, Cheah, and Azali (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | Worldwide | 163 | Generalized method of moments | A green innovation strategy had a positive influence on financial performance |
| Manresa, Bikfalvi, and Simon (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | Spain | 169 | Binomial logistic regression model (logit) | Development practices aimed at creativity and innovation have positive results on financial performance |
| Mejía Vallejo and Arias-Pérez, (2017)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Colombia | 85 | Cluster and Anova | The development of integrated circuits for products and processes does not guarantee improved results in terms of increased sales and market share |
| Muharam et al. (2020) | Quantitative | Industry | Indonesia | Structural equation model | A positive relationship exists between firms’ process innovation, market innovation and financial performance | |
| Nybakk and Jenssen (2012) | Quantitative | Industry | Norway | 241 | Structural equation model | An innovation strategy and an innovative working environment improved financial performance |
| Ong, Lee, Teh, and Magsi, (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | Malaysia | 124 | Structural equation model | Innovation and performance at an environmental level are key enablers for the creation of economic value for environmental manufacturing firms |
| Oskouei (2019)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Iran | 278 | Structural equation models | Innovation is inefficient regarding a firm's financial performance |
| Ouedraogo, Salem, and Laid Ouakouak (2020) | Quantitative | Primary, Secondary and Tertiary | Worldwide | 320 | Structural equation model | Innovation performance has a positive relationship with non-financial performance |
| Padgett and Moura-Leite, (2012)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry and services | Worldwide | 2025 | Regression analysis | Innovation with a high social benefit has a negative, significant effect on financial performance |
| Paula and Da Silva, (2018)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Bulgaria, Romania, Italy, Portugal, Spain, Estonia, Lithuania, Croatia, Cyprus, Slovenia, Czech Republic, Hungary, Slovakia and Norway | 15,607 | Structural equation model | Innovation performance had no short-term influence on financial performance |
| Peng, Schroeder, and Shah (2011) | Quantitative | Industry | Finland, Sweden, Germany, Italy, Austria, Japan, Korea and United States | 238 | Regression analysis | Innovation capacity has a variable impact on various dimensions of operational performance |
| Przychodzen and Przychodzen (2015) | Quantitative | Industry and services | Poland | 94 | Equation model estimation | Eco-innovative firms where characterised by better return on assets and equity and less earnings retention |
| Przychodzen et al. (2020)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry and Services | USA | 500 | Multivariate regression model | An excessive focus on innovation, compared to other types of innovating activism, has a negative influence both on accounting and on stock exchange performance. |
| Purwanto, Kamaruddin and Mohamad (2015)* | Quantitative | Industry | Indonesia | 124 | Structural equation model | A firm's innovation capability may account for the effects of industrial clustering and manufacturing flexibility on operational performance |
| Ramanathan, Ramanathan and Bentley (2018) | Quantitative | Industry | United Kingdom | 131 | Regression analysis | Results indicate that innovation capabilities have a significant influence on firms’ financial performance if firms feel that the environmental regulations they face are flexible ones |
| Rezende et al. (2019)⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry and services | Worldwide | 356 | Fixed effects panel regression | The degree of green innovation is not significantly related with financial performance during the first year. The association is a positive one and increases after 2 years. The degree of internationalization has no moderating effect on this relationship. |
| Saeidi et al. (2018) | Quantitative | Industry | Iran | Hierarchical regression analysis | The findings revealed that both process and product innovation are positively related to financial performance, while the effect is significant on product innovations and not significant on process innovation | |
| Saunila (2014)⁎⁎⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Primary, secondary and tertiary | Finland | 2400 | Linear regression | The aspects of innovation capability are more influential on financial performance than operational performance |
| Sivakumar, Roy, Zhu, and Hanvanich, (2011) | Quantitative | Industry | Worldwide | 353 | Structural equation model | As the generation of global innovation increases, financial performance increases until a certain point; after this it has a negative relationship |
| Srimarut and Mekhum (2020)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Thailand | 302 | Structural equation model | With increased innovation, the associated risk also increases, and as a result, firms’ financial performance also increases |
| Sun (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | China | 240 | Multiple regression analysis | Ecological innovation has a positive impact on financial performance |
| Tanideh (2013) | Quantitative | Industry | Iran | 42 | Regression analysis | Innovation capital has a negative, significant relationship with financial performance |
| Tarigan (2018) | Quantitative | Industry | Indonesia | 84 | Structural equations (least partial square) | Process innovation and product innovations affect operational performance |
| Tjahjadi, Shanty and Soewarno (2019)⁎⁎ | Quantitative | Industry | Indonesia | 173 | Structural equation model | Marketing performance has a partial mediating role on the relationship between innovation and financial performance |
| Wilson and Slobodzian, (2019)* | Quantitative | Industry | Canada | 75 | Structural equation model | Customer focus has an influence on financial performance through innovation |
| Xie et al. (2019) | Quantitative | Industry | China | 209 | Regression analysis | Process innovation and ecological products may improve financial performance |
| Xin et al. (2008) | Quantitative | Industry | United States | 78 | Event studies | Radical innovation helps firms to maintain increased sales and return on sales. It does not improve return on assets |
The studies relating quality management to innovation show that 46 studies are based on industry, 13 on industry and services, 12 only on services, one on agriculture and one on a set of sectors (Fig. 1). Concerning studies relating quality management to performance (Fig. 1), 21 regard industry and 7 regard services. Another 8 are performed on industrial and service firms, and 9 on three sectors: agriculture, industry and services. With regard to studies relating innovation to performance (Fig. 1), most are based on industry (36). Ten studies are performed both on industry and on services, 3 only on services and another 3 on three industrial sectors: agriculture, industry and services. Finally, studies were found based on agriculture (2).
4.4CountriesAs for studies relating quality management to innovation, it may be observed that Spain is the country with the highest number of studies (14), followed by Malaysia (12), and in the third place, Portugal (4), China (4) and Australia (4). Concerning the works relating quality management to performance, it may be observed that Australia and the USA are the countries with the highest number of studies (5). These are followed by Spain and Malaysia (3), and then India (2), Turkey (2), Jordan (2), Greece (2), Pakistan (2) and Vietnam (2). Concerning studies relating innovation and performance, it may be observed that the most frequently occurring ones are worldwide studies (7). These are followed by China and Indonesia (5), and in the third place, the USA and Iran (3).
4.5Relationship between quality management and innovationThe review (Table 2) indicates that most studies (60) show a positive relationship between quality management and innovation. Among them, there is a high number relating quality management to process and product innovation (18), and a somewhat lower number relating quality management to incremental and radical innovation (7). A few studies (9) point out that there is no relationship between quality and innovation (Terziovski & Guerrero, 2014; Yusr et al., 2017) or even that this relationship is a negative one (4). Those studies that indicate that no relationship exists, or that the relationship is a negative one, point out that this lack of relationship may be due to the bureaucracy that may be created by a quality management system (Aminbeidokhti, Jamshidi, & Hoseini, 2016), lack of employee creativity by closely following rules and procedures, a desire to obtain short-term results that may be a constraint on innovation (Bourke & Roper, 2017) or even to the need to include other mediating variables that may account for this relationship, such as, for instance, social capital (Donate, Ruiz-Monterrubio, Sánchez de Pablo, & Peña, 2019). Out of these thirteen studies that point out that there is no relationship or that it is a negative one, 7 are on TQM, 2 on ISO 9000, 2 on quality management and 2 on quality management practices. Besides, some studies in Table 2 include contextual variables, such as firm size or sector, to account for these relationships (Escrig-Tena et al., 2018; Mangiarotti & Riillo, 2014; Perdomo-Ortiz, González-Benito, & Galende, 2009a; Vujović et al., 2017).
On the basis of the review shown in Table 2, it may be said that, in general, quality management practices facilitate product innovation (Zeng et al., 2017) and process innovation (Abrunhosa & Sa, 2008; Perdomo-Ortiz et al., 2006), both incremental and radical (Kim et al., 2012). For instance, people management helps employees to be more proactive and detect small changes in production processes that may lead to incremental innovations in work processes (Kafetzopoulos, Gotzamani, & Gkana, 2015). Similarly, training employees may increase their capabilities, which allows them to better perform their tasks and general issues related to the firm itself, such as, the creation of new work processes, thus introducing radical innovations (Gowen, Mc Fadden, & Settaluri, 2012). Also, performing stable, detailed routines facilitates incremental product innovation. If, on the other hand, such routines are simple and flexible, what is facilitated is radical product innovation (Kim et al., 2012).
4.6Relationship between quality management and performanceThe review (Table 3) suggests that quality management practices have positive effects on operational and financial performance. Most of the papers in Table 3 show a positive relationship between quality management and financial performance (22) and between quality management and operational performance (13). Others show a relationship between quality and both types of performance: operational and financial (4). Two of the articles show that there is no relationship between quality and operational performance, or that it is a negative one. One of the articles analyses quality management practices and the other deals with the ISO 9000 standard. Results indicate that customer management does not affect performance in ISO 9000 contexts. The reason could be that customers only define product specifications, and it is the firm that then adjusts such specifications (Prajogo et al., 2012). This suggests that there might be differences between customer specifications and their fit within production processes, which might not generate effects or generate negative ones. Out of the papers on quality and financial performance, 22.72% (5 of 22) suggest that this relationship does not exist or is a negative one (Kusumah & Fabianto, 2018; Roca-Puig & Escrig-Tena, 2017). Two articles are observed analysing TQM, 2 studying the ISO 900 standard, and one that analyses this relationship from the point of view of quality management. This could be due to a low implementation of quality management and to the need for an integrated management of quality management in order to generate positive outcomes. It could also be due to the fact that those firms with a late access to quality management may obtain worse financial performance than pioneering firms, which is the case, for instance, of the ISO 9000 standard (Benner & Veloso, 2008). Besides, there are also studies in Table 3 which include firm size or sector as contextual variables to account for these relationships (Ataseven, Prajogo, & Nair, 2014; Chatzoglou et al., 2015; Kober, Subraamanniam, & Watson, 2012; Pham, 2020; Sharma, 2005; Sila, 2020; Wayhan, Kirche, & Khumawala, 2002).
In this way, on the basis of the review shown in Table 3, it may be said that quality has an influence on customer satisfaction (Chatzoglou et al., 2015), employee performance (Prajogo et al., 2012), on productivity (Anh & Matsui, 2011), on efficiency (Baird, Hu, & Reeve, 2011), on defect reduction (Prajogo et al., 2012) and on production costs (Khan et al., 2020). This is the case because quality practices make it possible to define objectives, document processes, promote employee participation, increase training, etc., which facilitates error reduction (Prajogo et al., 2012), improved product quality, employee satisfaction (Samson & Terziovski, 1999) and improved productivity (Nair & Choudhary, 2016). Similarly, in general it may be said that there is a positive relationship between quality management and financial performance. In this respect, firm managers must interconnect quality management practices because the interconnection between such practices (leadership, employee management, customer focus, supplier management, process management or information and analysis) may have an influence on financial performance. Table 3 shows that many studies indicate that those firms which have made great efforts to implement quality management practices obtain a greater positive, direct impact on financial performance (Abbas et al., 2020; Samson & Terziovski, 1999). It may be observed, amongst other examples, which quality management practices, such as process management, information and analysis (Augustyn, et al., 2021), people management, leadership (Nair & Choudhary, 2016), and customer focus (Albuhisi & Abdallah, 2018) have positive effects on financial performance. Other studies also point out that this relationship may be a positive, but an indirect one, through other practices. For instance, as has been said above, leadership facilitates other quality management practices leading to improved financial performance (Agus & Sagir, 2001). Similarly, quality management practices improve customer satisfaction, which in turn has an impact on financial performance (Chatzoglou et al., 2015). This indicates that certain quality management practices and operational performance may act as mediating variables (Agus, Krishnan, & Kadir, 2000).
4.7Innovation and performanceThe review on innovation and performance (Table 4) indicates that most studies positively relate innovation to financial performance (47) and a lower number, to operational performance (6). Also, there are other studies relating innovation to both types of performance (1). However, 11 articles (20.37%) find no relationship or show a negative relationship. The reasons may be the lack of short-term financial effects (Aguilera-Caracuel & Ortiz-de-Mandojana, 2013), that the investment needed to innovate is greater than the financial benefits (de Oliveira & da Silva, 2018) or that these innovations imply maintaining the firm's leadership in the market, which at times does not entail improved financial performance (Jaskyte, 2020). On the other hand, research is also found proposing firm size or sector as contextual variables in order to analyse these relationships (Aas & Pedersen, 2011; Gök & Peker, 2017; Hsueh & Tu, 2004; Liao, 2018; Przychodzen & Przychodzen, 2015; Przychodzen et al., 2020; Rezende, Bansi, & Rodrigues, 2019).
In this way, from the results in Table 4 it may be said that process and product innovation has a direct, positive effect on operational performance (Al-Sa'di, Abdallah, & Dahiyat, 2017) and financial performance (Muharam, Andria, & Tosida, 2020). Similarly, incremental and radical innovation also has direct positive effects on operational and financial performance (Duhaylongsod & De Giovanni, 2019). In this respect, those firms that invest in assets facilitate the creation of radical innovations. Such radical innovations, when considered in the long term, may increase sales, market share or profitability (Xin, Yeung, & Cheng, 2008). On the other hand, other studies suggest that the relationship between innovation and financial performance could be a positive, indirect one, through operational performance (Liao & Rice, 2010) because innovation makes it possible to improve products and processes through continuous improvement.
4.8Quality management, innovation and performanceSome of the studies in Tables 2, 3 and 4 show joint relationships between quality management, innovation and performance. For instance, Sadikoglu & Zehir (2010) point out that quality management has a positive influence on operational performance through innovation. Akgün et al. (2013) establish that innovation is a mediating element between quality management and financial performance. Along the same lines, Wilson & Slobodzian, 2019 show that customer focus influences financial performance through innovation. Mahmud et al. (2019) indicate that quality management does not have a relationship with innovation or with operational or financial performance in a direct way, although there is a relationship mediated by innovation. Kafetzopoulos et al. (2019) state that quality practices have an influence on operational and financial performance through product and process innovation. On the other hand, Agus et al. (2000) indicate that quality management practices may have an influence on financial performance through operational performance. Some of these studies show that firm size or sector might be variables with a potential influence on these relationships. Although some authors point out that size or sector has no influence on these relationships (Akgün et al., 2013), others point out that it would be interesting to study the effect of size or sector on these joint relationships in future studies (Sadikoglu & Zehir 2010). These ideas suggest that quality management has an influence on operational and financial performance through innovation and that, besides, quality management may have an influence on financial performance through operational performance.
5Discussion5.1Characteristics of the articlesThe results of the literature review show that the terms TQM, quality management and quality management practices are those most used to refer to quality management. In the case of the terms TQM or quality management, these variables include items referring to quality practices. Other terms used to a lesser extent are ISO 9000 or EFQM model. These different ways to apply quality may lead to different outcomes. In this respect, a lower development of quality (for instance, through its practices, the ISO 9001 standard or the EFQM model) may lead firms to obtain less results. As for innovation, although the term is used in most studies with no reference to its dimensions, when innovation is analysed as a multidimensional variable, the dimensions incremental and radical, product and process, may be introduced in order to analyse the relationship between quality-innovation. Also, the most frequent terms concerning performance are operational and financial performance. In this way, future studies analysing joint relationships between these variables could use, as constructs, quality management practices, incremental and radical product and process innovation, and operational and financial performance.
Most of the studies analysed are quantitative. The studies use structural equations as their main analysis tools; these are recommended in order to analyse joint relationships between quality, innovation and performance. However, it would also be appropriate to supplement the studies with other quantitative tools, such as, for instance, a cluster analysis to identify quality levels, innovation levels and result levels. Besides, although quantitative studies continue to be performed, more qualitative studies (for instance, based on the case method) would also be of interest to know the how and the why of these joint relationships. Such qualitative research might also help to complement the result of quantitative research.
The review shows that it is still interesting to continue carrying out further studies in the service sector, in order to be able to draw comparisons with manufacturing sectors and find out which practices have a greater influence on innovation and on performance in these sectors. It may also be said that there are few studies on these variables in some European countries like France or Germany, or in developing countries.
5.2Relationships between quality management, innovation and performanceThe search results indicate that quality management practices may improve product/service innovation and incremental and radical process innovation, which agrees with part of the literature (Donate et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2012). This is the case because quality management practices (leadership, people management, supplier management, etc.) help to improve processes (Kim et al., 2012) and products (Lee, Ooi, Tan, & Chong, 2010) because, amongst other reasons, they facilitate: (a) employee participation in continuous improvement activities, (b) introducing customers’ needs and expectations in products and processes, and (c) improved cooperation with suppliers in order to improve efficiency and efficacy in product and process development.
The results of the review also show a clear positive relationship between quality management and operational performance (for instance, customer and employee satisfaction, and product quality), supporting the group of studies which emphasize this relationship (Anh & Matsui, 2011; Khan et al., 2020; Prajogo et al., 2012; Youssef & Youssef, 2018). In this way, when firms implement quality practices, they may improve customer satisfaction (Albuhisi & Abdallah, 2018), employee satisfaction (Phan, Nguyen, Trieu, Nguyen, & Matsui, 2019) and product quality (Khan et al., 2020). This is the case because quality practices may increase efficiency in complaint resolution if firms place a greater emphasis on what products clients want and how they want them (Chatzoglou et al., 2015). Similarly, quality practices make it possible to document processes so that employees have a clearer idea of the specifications of the work to be performed, which may increase employee satisfaction (Nair & Choudhary, 2016).
On the other hand, the literature is not unanimous regarding the positive relationship between quality management and financial performance. Although there are studies that point out that no positive relationship exists (Kusumah & Fabianto, 2018; Roca-Puig & Escrig-Tena, 2017), in general, the results of the search show that quality management improves financial performance in a direct and indirect way. Concerning direct improvement, quality management practices may increase market share (Chatzoglou et al., 2015; Sila, 2020) because they facilitate the adaptation of processes and products to the needs of customers and other stakeholders. As for indirect influence, the review suggests that quality improves financial performance through operational or innovation performance (Agus & Sagir, 2001; Akgün et al., 2013). This is the case because improved customer satisfaction or product quality may lead to increased sales, and an improvement in processes or in products may lead to financial improvements. In this way, these financial benefits arise from the introduction of a quality culture in the firm (Augustyn, et al., 2021), which facilitates a more advanced development of quality management practices (Abbas et al., 2020), and a greater usage of available resources, which may lead to increased sales and increased market share or profitability (Chapman, Murray, & Mellor, 1997).
In this way, process and product innovation may improve operational performance (Al-Sa'di et al., 2017; Chen & Chiu, 2018) and financial performance (Muharam et al., 2020; Saeidi et al., 2018). The relationship with financial performance may be a direct one (Xie et al., 2019) or an indirect one (Lee, Choong, & Wong, 2015b). The indirect relationship suggests that those firms innovating in their products and processes in an incremental and/or radical manner may improve customer and employee satisfaction, reduce their costs and improve the quality of their products/services, which in turn may lead to improved financial performance.
Similarly, the review also indicates that size or sector may be variables to be considered when analysing these relationships (Sila, 2020). Some authors point out that quality, for instance, through the ISO 9000 standard, may generate greater innovation in small firms (Mangiarotti & Riillo, 2014) or that larger firms may obtain better operational (Ataseven et al., 2014) and financial performance (Rezende et al., 2019). Regarding sectors, some authors indicate that quality is more widely applied in industrial sectors (Mangiarotti & Riillo, 2014) or that in certain sectors there may be less innovation (Escrig-Tena et al., 2018). Although studies are found showing that size and sector do not have an influence on these relationships, others indicate that this relationship does exist. This suggests that the effects of organization size and sector may be considered in the relationships between quality management, innovation and performance.
All these ideas indicate that quality management practices may directly improve innovation, operational performance and financial performance. They may also improve operational performance through innovation, and financial performance through innovation and/or operational performance. In this way, quality management creates a suitable environment facilitating incremental and radical product and process innovation (Kim et al., 2012). These innovations deriving from quality practices improve customer satisfaction and the firm's competitiveness, which suggests improvements in operational performance (Sadikoglu & Zehir, 2010) and financial performance (Wilson & Slobodzian, 2019). Besides, these relationships may be influenced by the sector and size contextual variables, which suggests that these variables might have a moderating effect. All these ideas make it possible to establish a relationship model amongst all these variables, as shown in Fig. 2: (a) relationships between quality management, innovation and performance, and (b) moderating effects of size and sector. This model may help future researchers to analyse these joint relationships, and managers to understand these potential relationships.
5.3Practical implicationThis study may provide guidelines to managers on the importance of innovations deriving from quality, in order to improve operational and financial performance. Managers may observe that quality management may be carried out by adopting quality management practices or adopting the ISO 9000 standard or other quality models, and that it is possible to obtain satisfactory results regardless of the strategy followed. Whichever the approach, it is always important to create a quality culture reflecting a commitment to quality management practices. Also, managers may understand that they may develop a variety of innovations, such as, for instance, product and process innovations, and that it is not necessary to perform only radical innovations in order to obtain better performance, but by making incremental improvements it is also possible to obtain positive outcomes. Managers must understand that quality practices may improve product and process innovation in an incremental and radical manner. These innovations may help to improve operational and financial performance.
5.4Theoretical implicationsThis study shows future researchers the terms used to measure quality management and its relationship with innovation and performance, the research methods applied, and the sectors and countries analysed. Besides, it also indicates that, when analysing the relationships between quality management, innovation and performance, it is interesting to consider incremental and radical product and process innovation, and operational and financial performance. Authors might consider in future research the mediating relationships of innovation and operational performance in the relationship between quality management and financial performance. Such future research might supplement the few studies that jointly analyse the relationships between quality management, innovation, and performance (Sadikoglu & Zehir, 2010; Wilson & Slobodzian, 2019) by including the four dimensions of innovation and both types of results. Besides, this work supplements the work by previous authors on the relationship between quality and incremental and radical product and process innovation (Kim et al., 2012; Moreno-Luzón et al., 2013) by including operational and financial performance.
6ConclusionsQuality management practices have positive, direct effects on incremental and radical product/service and process innovation. Besides, they may also improve operational performance (customer and employee satisfaction and product quality) and financial performance (for instance, market share).
Quality management may also have a positive indirect influence on operational and financial performance through incremental and radical product and process innovation. In the same way, quality management practices may have a positive, indirect impact on financial performance through operational performance, that is, product errors and quality costs must be reduced first, so that as a consequence sales and market share may be increased. These relationships indicate that those firms that innovate in their products and processes in an incremental and/or radical way on the basis of quality management may improve their customers’ and employees’ satisfaction, reduce costs and increase the quality of their products/services, which in turn, may lead them to improve their financial performance.
This works contributes to expanding and supplementing previous literature by proposing the following relationships: (a) positive, direct relationship between quality management and process and product innovation (incremental and radical); (b) positive, direct relationship between quality management and operational and financial performance; (c) positive, indirect relationship between quality and financial performance through innovation and/or operational performance, and (d) moderating relationship of firm size and del sector.
6.1Limitations and future lines of researchAlthough the databases used are widely accepted by academics, such as Web of Science or Scopus, in the future the search might be expanded by using other databases. This work has considered four innovation dimensions which are relevant for the relationships between quality and innovation. Future research might include other types of innovation, such as administrative innovation, considered by previous authors (Kim et al., 2012). Similarly, other mediating variables could be included, such as, for instance, competitive strategies or social responsibility, or even other moderating variables (for instance, the ISO 9000 standards). Finally, as there are few studies that perform a joint empirical analysis of these relationships, it might be interesting in the future to empirically analyse, within one single study, the direct and indirect relationships between all these variables.