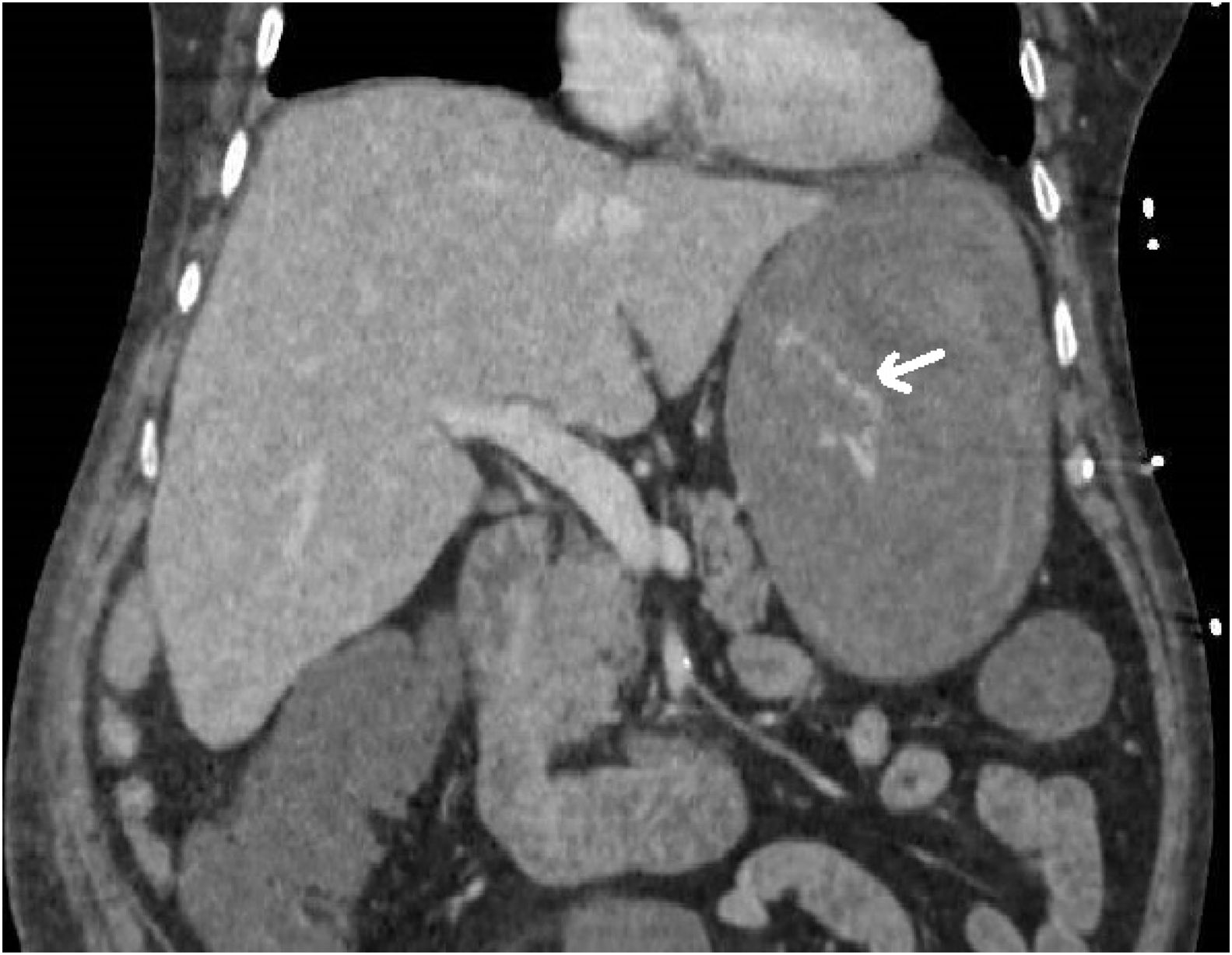
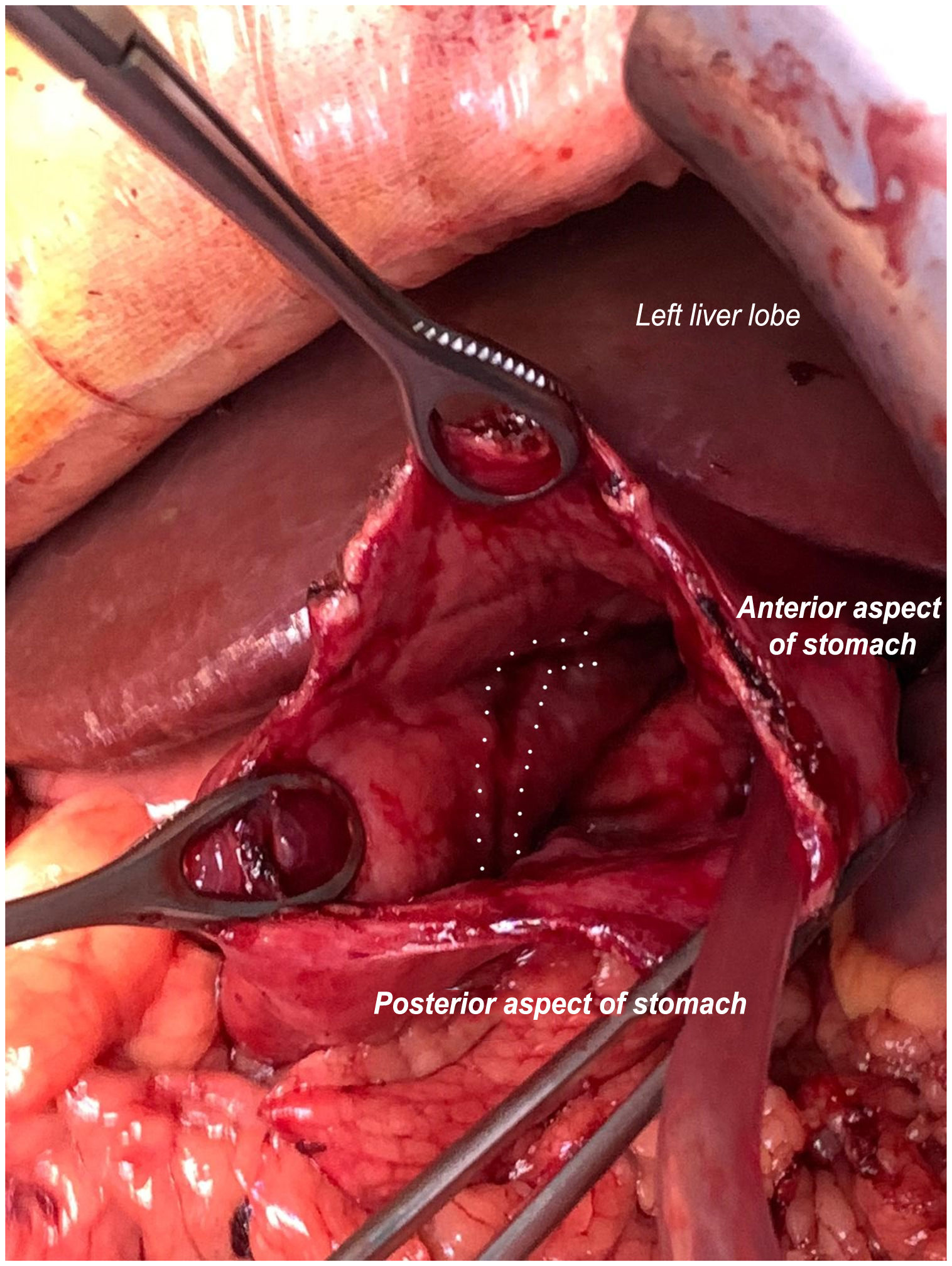
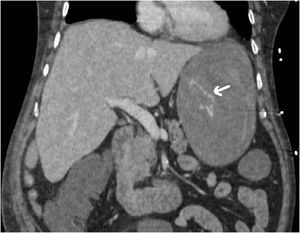
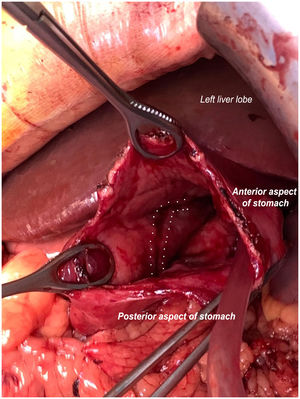
We report the case of a 65-year-old patient with ureteral stenosis admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) for septic shock of urological origin following double-J stent replacement; upon admission, he had a nasogastric tube placed. Initially, he followed a favourable course, but after six days, he presented upper gastrointestinal bleeding with anaemia and haemodynamic instability requiring blood products and vasoactive drugs. Computed tomography (CT) (Fig. 1) showed active gastric bleeding; therapeutic endoscopy was not feasible as extensive longitudinal tearing of the mucosa on the anterior aspect of the stomach was visualised. Emergency exploratory laparotomy was performed with gastrostomy and evacuation of multiple clots until blood was seen oozing from a filiform mucosal ulceration with a length of 10 cm in the lesser curvature, corresponding to pressure from the nasogastric tube (Fig. 2). Following interrupted suturing of the tearing, suitable haemostasis was achieved, and the patient subsequently followed a favourable course with no further bleeding.
Upper gastrointestinal bleeding due to lesions secondary to a nasogastric tube is rare and can be caused by trauma during placement or by prolonged use with ongoing irritation and necrosis due to pressure.1,2 As this is a life-threatening situation,3 early identification and treatment are crucial2: endoscopy is the initial procedure for diagnosis and treatment of choice, and surgery is pursued only when other treatments fail.
FundingThis study received no specific funding from public, private or non-profit organisations.
Conflicts of interestNone.
Please cite this article as: Pitarch Martínez M, Robles Quesada MT, Blanco Elena JA, Alberca Páramo A. Hemorragia gástrica masiva tras úlcera por decúbito de sonda nasogástrica en paciente crítico: una complicación inusual. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;45:291–292.