Entre las condiciones crónicas a nivel mundial, la hipertensión arterial se presenta en uno de cada 3 adultos>40 años, mientras que uno de cada 10 adultos padece de diabetes de tipo 2. Para ambas enfermedades la adherencia al tratamiento farmacológico es>30% y la autogestión, que considera además la dieta y la actividad física, es desconocida porque ningún instrumento permite medirla. El objetivo del siguiente trabajo fue adaptar y validar el instrumento SMP-T2D en español, en pacientes con hipertensión arterial y diabetes de tipo 2.
MétodosSe hizo un proceso de adaptación del cuestionario SMP-T2D mediante la traducción al español, para ser utilizado en pacientes con hipertensión arterial más diabetes de tipo 2. Se realizó la validación convergente y discriminante. Se incluyó a pacientes mayores de 50 años con hipertensión arterial y a pacientes con hipertensión arterial más diabetes de tipo 2. Se eliminó a aquellas personas con cuestionario incompleto o sin consentimiento informado.
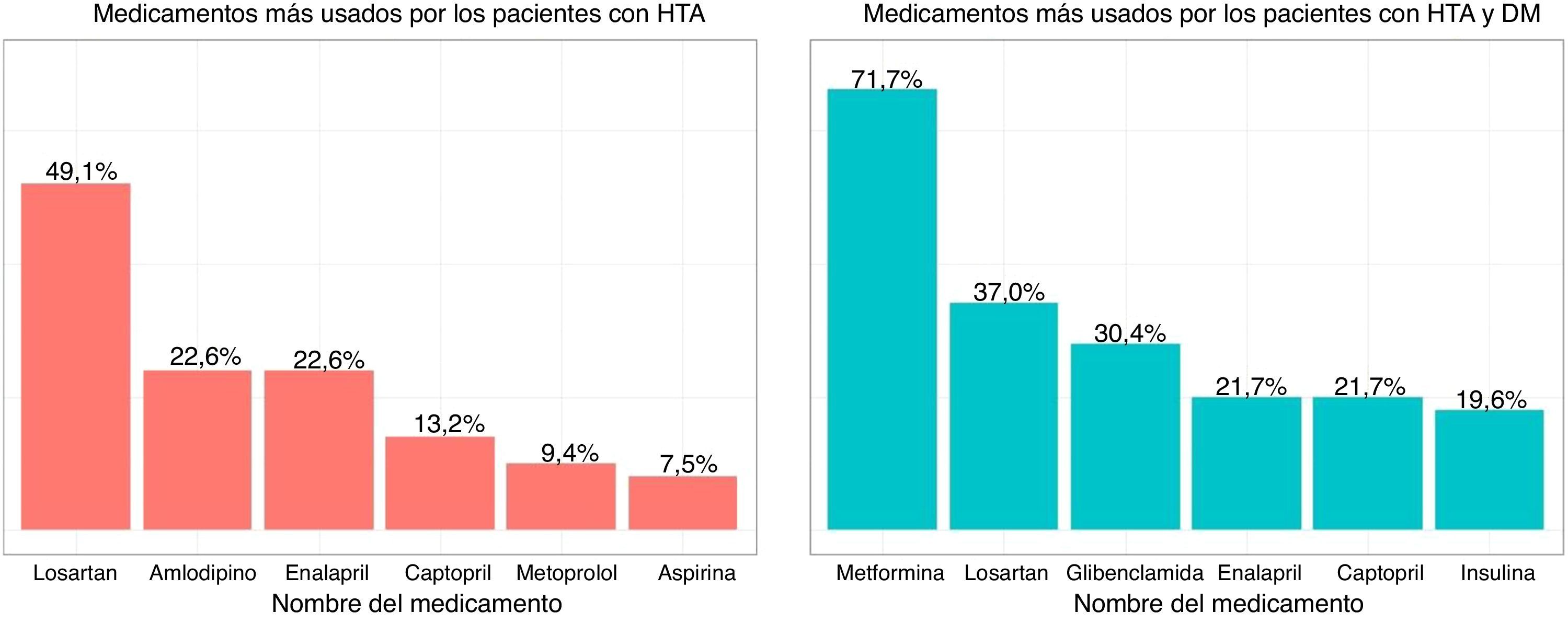
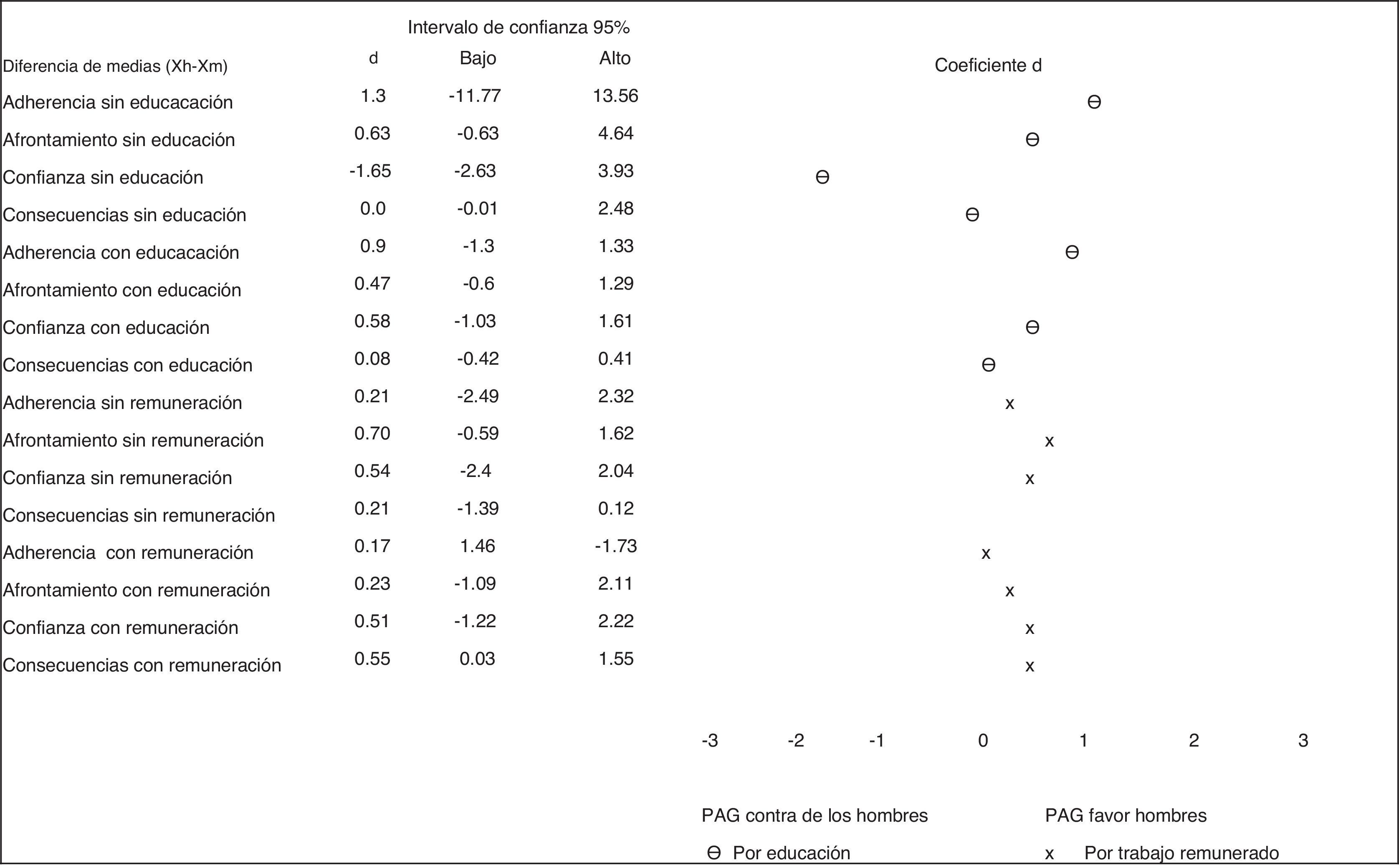
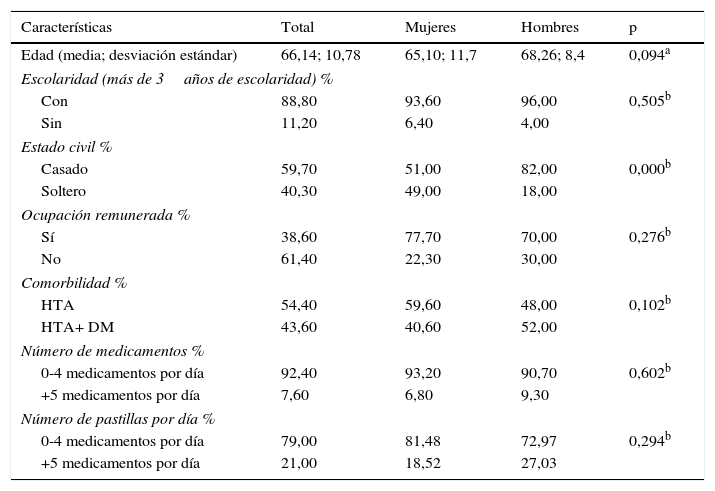
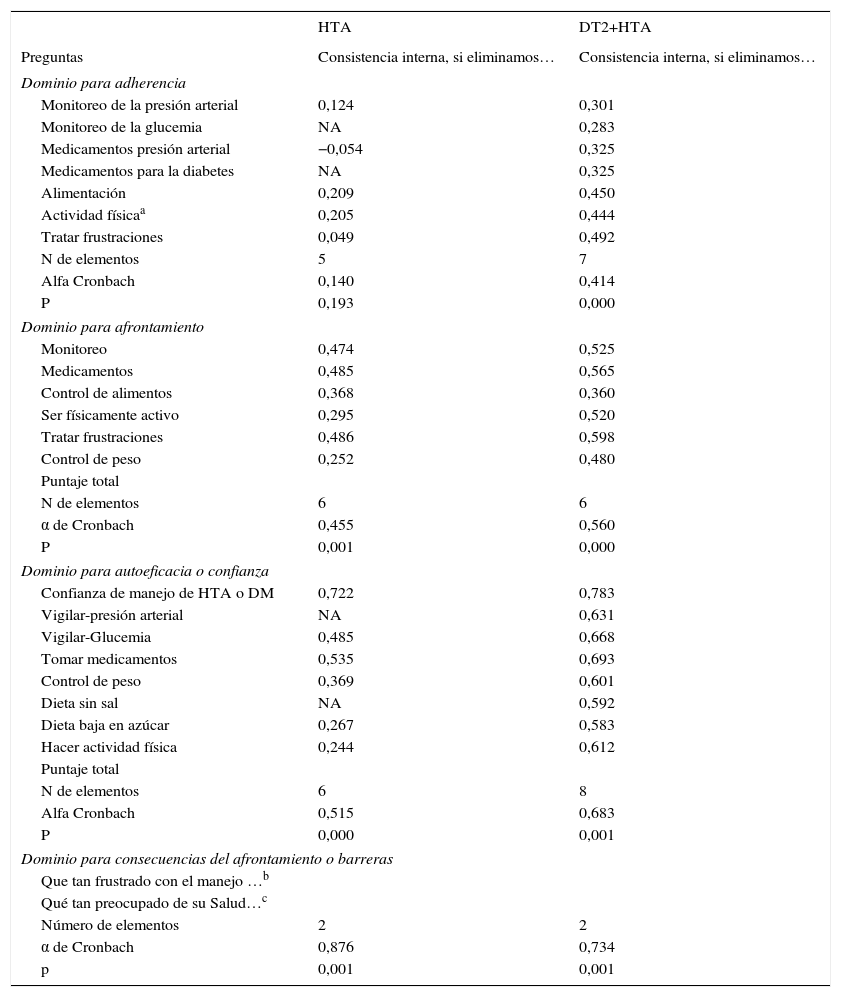
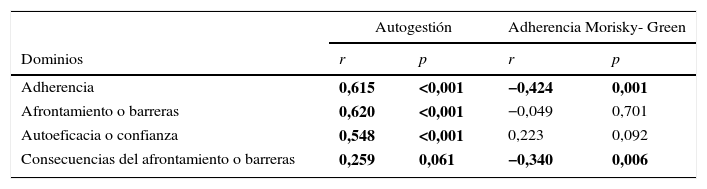
ResultadosEl PAG-DT2+HTA fue aplicado a 145 pacientes; de ellos, el 54,4% tenían solo hipertensión y el 43,6% hipertensión arterial más diabetes de tipo 2. La edad promedio fue de 66,14 años (DE=10,78), con una proporción de mujeres del 34,7% y de hombres del 65,3%. La consistencia interna por α de Cronbach del cuestionario fue 0,561 (p=0,000). La correlación del PAG-DT2+HTA y Morisky-Green fue significativa (p<0,05). Interesantemente, las personas con mayor educación y mayor remuneración económica alcanzaron una mejor gestión (validez de discriminación).
ConclusiónEl SMP-T2D que mide la autogestión en pacientes con diabetes de tipo 2, modificado y adaptado al español (PAG-DT2+HTA), también puede medirla en personas con diabetes de tipo 2+hipertensión arterial.
High blood pressure is one of the most common chronic conditions worldwide. It affects one in every 3 adults over 40, while one in 10 suffers from diabetes. For both diseases, adherence to pharmacological treatment is over 30%, and self-management, which takes into account diet and physical activity, is still unknown, as there is no tool available to measure self-management. Therefore, the object of this study was to adapt and validate the Spanish version of the self-management profile for type 2 diabetes (SMP-T2D) questionnaire in patients with type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure among users of first level care in the social security institution of Mexico.
MethodsThe SMP-T2D was adapted to Spanish by translation into Spanish, and being used only in patients with high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes-hypertension. A convergent and discriminatory validation was performed. Patients over 50 years old with high blood pressure were include. Those that did not complete the questionnaire or give informed consent were rejected.
ResultsThe Spanish version of the SMP-T2D was called PAG-DT2+HTA, and was applied to 145 people with hypertension: 54.4% with hypertension only, and 43.6% with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Mean age was 66.14 years (SD=10.78), with 34.7% women and 65.3% men. Internal consistency by α-Cronbach for the questionnaire was 0.561 (P=.000). The correlation between the PAG-DT2+HTA and Morisky-Green was significant. The ability to discriminate between people with and without education and with and without economic means was obtained.
ConclusionThe Spanish version of SMP-T2D (PAG-DT2+HTA) that measures self-management in type 2 diabetes, can be used to measure self-management in people with type 2 diabetes-hypertension.