Air pollutants have a significant impact on public health.
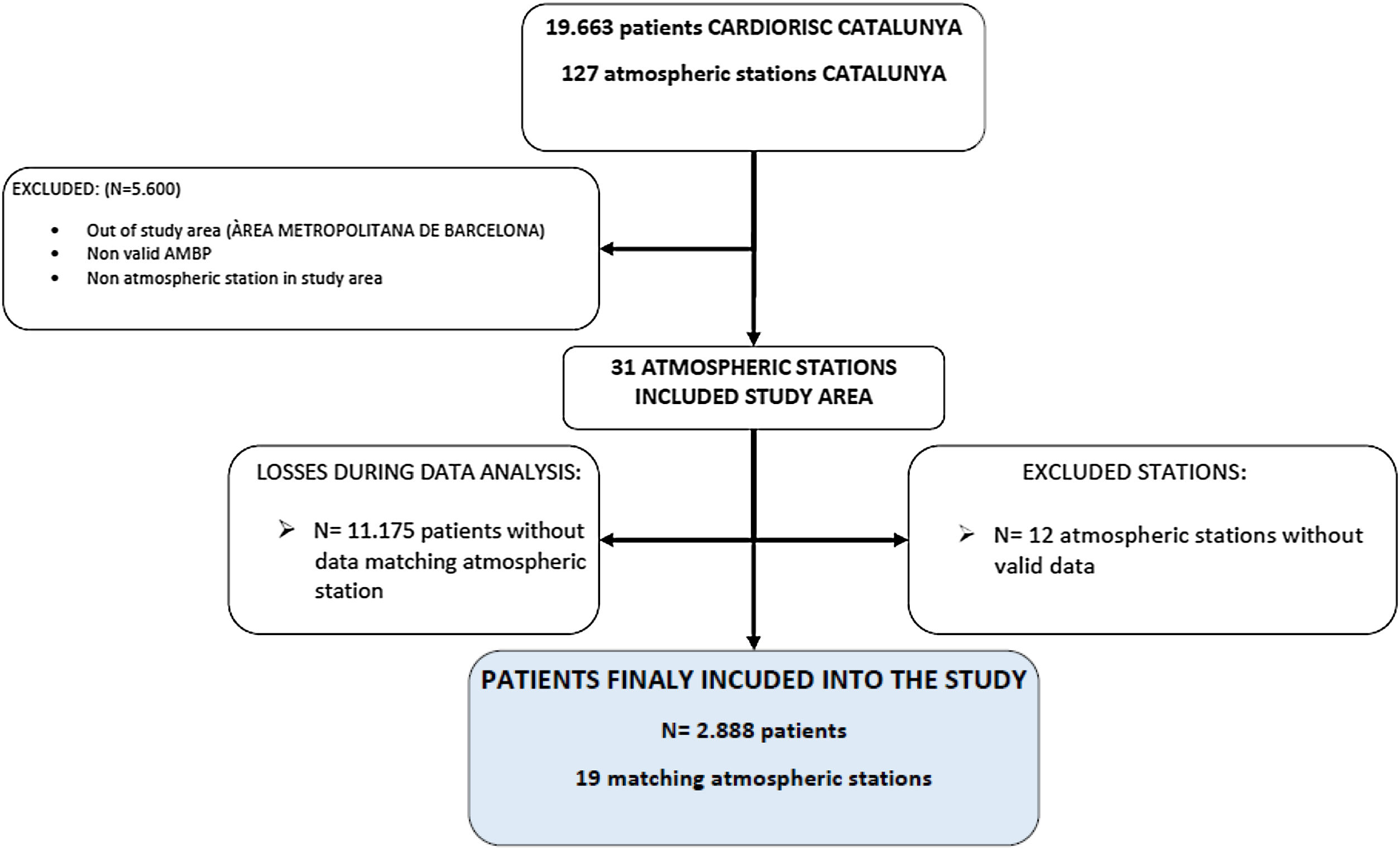
The aim of the study was to find out the relationship between ambulatory blood pressure measured by 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) and the atmospheric pollutants that are measured regularly (PM10, PM2.5, NO2 and SO2). An observational study of temporal and geographic measurements of individual patients (case-time series design) was carried out in Primary Care Centres and Hypertension Units in the Barcelona metropolitan area. We included 2888 hypertensive patients≥18 years old, untreated, with a first valid ABPM performed between 2005 and 2014 and with at least one air pollution station within a radius of <3km.
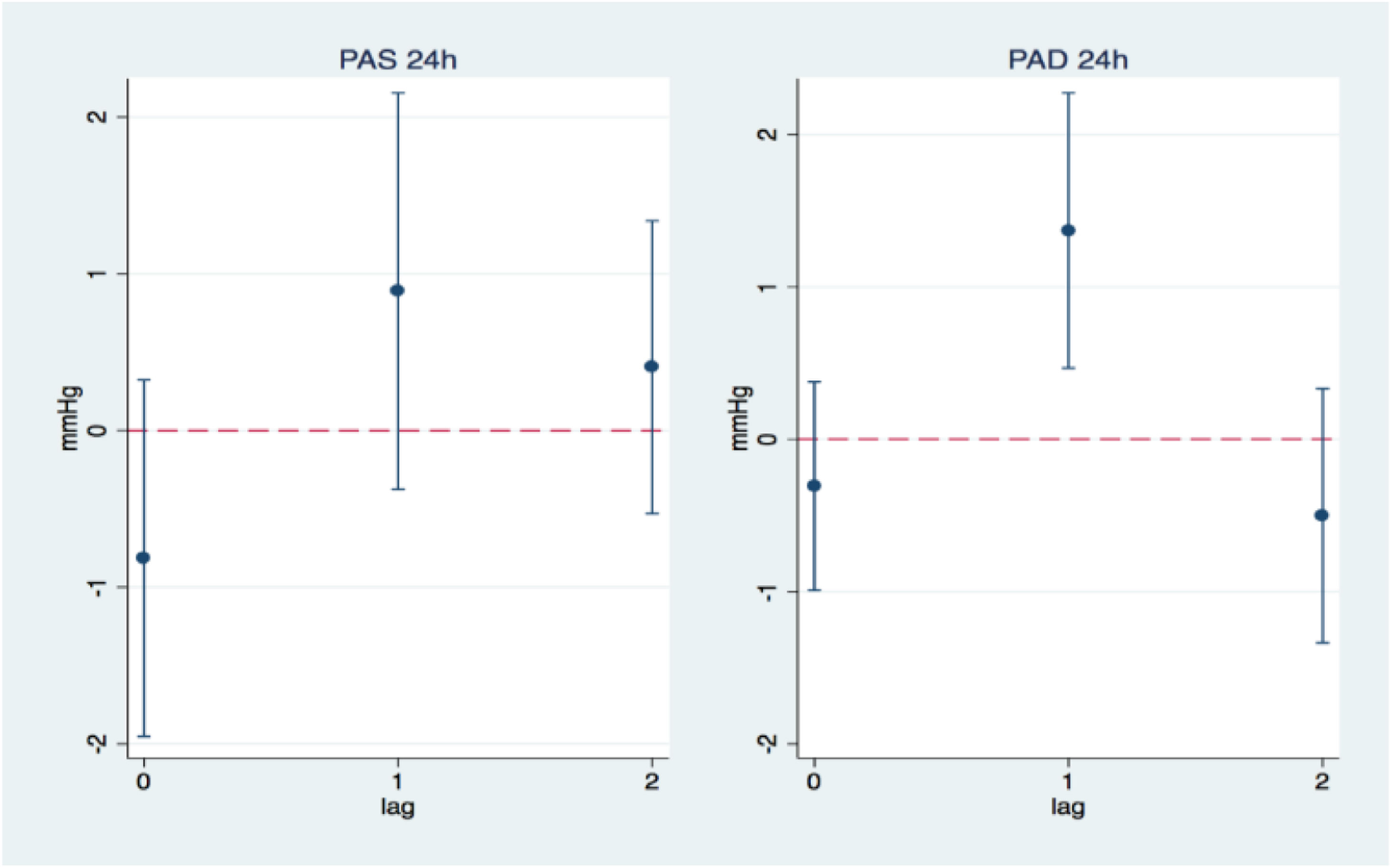
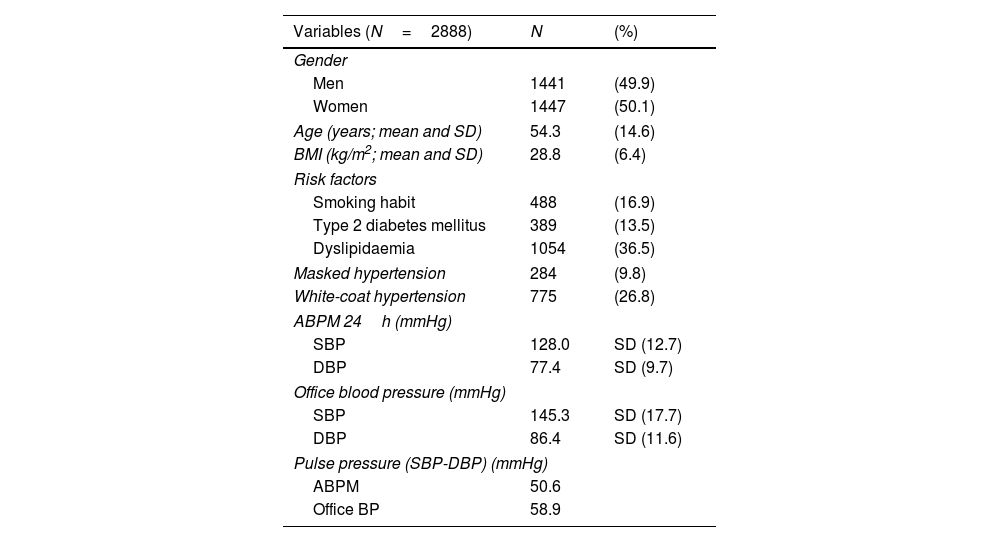
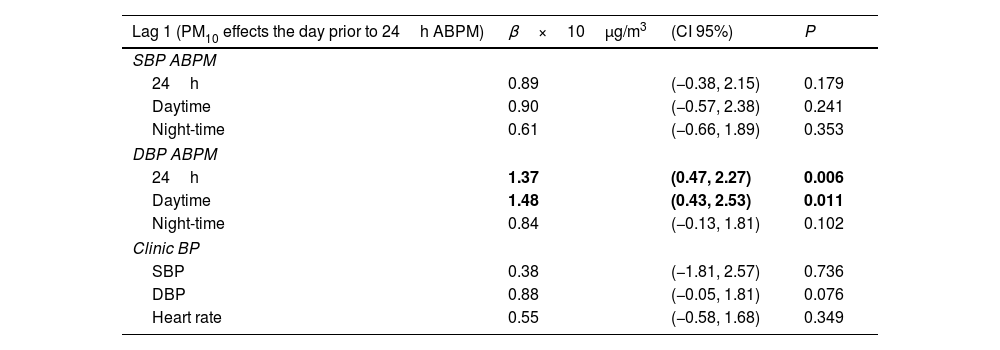
Results and conclusionsThe mean age was 54.3 (SD 14.6) years. 50.1% were women and 16.9% of the sample were smokers. Mean 24-h blood pressure (BP) was 128.0 (12.7)/77.4 (9.7) mmHg. After adjusting for mean ambient temperature and different risk factors, a significant association was found between ambulatory diastolic BP (DBP) and PM10 concentrations the day before ABPM. For each increase of 10μg/m3 of PM10, an increase of 1.37mmHg 24-h DBP and 1.48mmHg daytime DBP was observed. No relationship was found between PM2.5, NO2 and SO2 and ambulatory BP, nor between any pollutant and clinical BP.
The concentration of PM10 the day before the ABPM is significantly associated with an increase in 24-h DBP and daytime DBP.
Los contaminantes aéreos tienen un impacto importante en la salud pública.
El objetivo del estudio era conocer la relación entre la presión arterial ambulatoria medida mediante monitorización ambulatoria de la presión arterial (MAPA) de 24h y los contaminantes atmosféricos que se miden regularmente (PM10, PM2,5, NO2 y SO2). Se realizó un estudio observacional de medidas temporales y geográficas de pacientes individuales (case-time series design) en centros de atención primaria y unidades de hipertensión del área metropolitana de Barcelona. Se incluyeron 2.888 pacientes hipertensos≥18 años, no tratados, con una primera MAPA válida realizada entre 2005-2014 y al menos con una estación de contaminación atmosférica en un radio<3km.
Resultados y conclusionesLa media de edad fue de 54,3 (DE 14,6) años. El 50,1% eran mujeres y el 16,9% de la muestra eran fumadores. La presión arterial (PA) de 24h fue de 128,0 (12,7)/77,4 (9,7)mmHg. Tras ajustarse por la temperatura ambiental media y por los diferentes factores de riesgo se halló una asociación significativa entre PA diastólica (PAD) ambulatoria y las concentraciones de PM10 del día anterior a la MAPA. Por cada incremento de 10μg/m3 de PM10 se observaba un aumento de 1,37mmHg PAD 24h y de 1,48mmHg PAD diurna. No se halló relación entre PM2,5, NO2 y SO2 y PA ambulatoria, ni entre ningún contaminante y PA clínica.
La concentración de PM10 del día anterior a la realización de la MAPA se asocia significativamente con un aumento de PAD 24h y PAD diurna.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora