Evaluar la asociación entre biomarcadores del metabolismo del colágeno, índice de masa ventricular izquierda (IMVI) y función diastólica en pacientes con hipertensión arterial (HTA) refractaria.
Pacientes y métodoSe estudiaron 52 pacientes diagnosticados de HTA refractaria y se compararon con 24 individuos sanos. Se midió en suero el propéptido C-terminal de la molécula de procolágeno tipo I (PICP) y el factor de crecimiento transformante beta 1 (TGFβ1) por métodos de enzimoinmunoanálisis, y el telopéptido C-terminal del colágeno tipo I (ICTP) por inmunoensayo electroquimioluminiscente. A los pacientes se les practicó una ecocardiografía donde se calculó el IMVI por la fórmula de Devereux y se valoró la función diastólica a partir de la relación entre las ondas E y A (E/A) y la velocidad de propagación mitral. También se les practicó un registro de monitorización de la presión arterial (PA) de 24h.
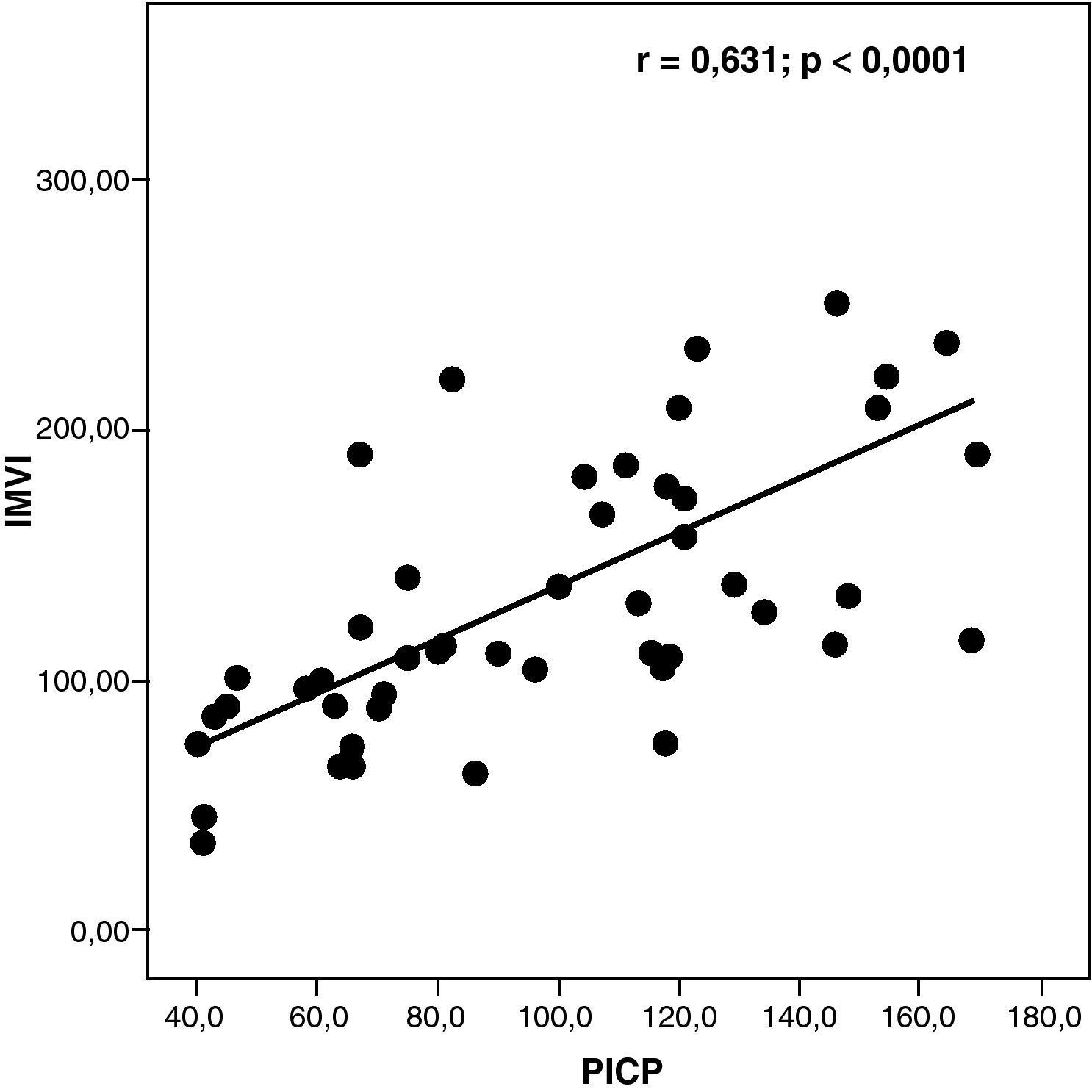
ResultadosLos hipertensos mostraron valores (media ±DE) superiores de PICP e inferiores de ICPT que los controles: 83,7 (24,7) frente a 55,0 (8,7), p<0,0001, y 175,0 (136,4) frente a 323,3 (121,3), p<0,0001. En los hipertensos existió una relación significativa entre el PICP y el IMVI (r=0,631, p<0,0001) y disfunción diastólica (r=–0,519, p<0,0001). Los grupos con y sin hipertrofia, y con o sin función diastólica, diferían en los citados péptidos pero no en las cifras de PA.
ConclusionesNuestros hallazgos sugieren que diferentes marcadores de la síntesis y de la degradación del colágeno pueden relacionarse con la presencia de hipertrofia miocárdica o disfunción diastólica con independencia de las cifras de PA.
To evaluate the association between circulating biomarkers of collagen metabolism in serum, left ventricular mass index (LVMI) and diastolic dysfunction in patients with resistant hypertension.
Patients and methodsFifty-two patients with resistant hypertension and 24 healthy individuals were included. The following biomarkers of collagen metabolism were analyzed by ELISA: carboxy-terminal propeptide of procollagen type I (PICP) and transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFβ1). The biomarker C-terminal telopeptide of collagen type-I (ICTP) was assayed by electrochemiluminescence immunoassay. In the patient's group a record of 24-h blood pressure monitoring was obtained and an echocardiography was performed. Left ventricular mass was measured according to the formula of Devereux and the diastolic function according to the relation of E and A waves and mitral propagation velocity.
ResultsHypertensive patients showed higher levels of PICP and lower levels of ICTP than controls: 83.7 (24.7) vs. 55.0 (8.7), P<.0001; and 175.0 (136.4) vs. 323.3 (121.3), P<.0001). Hypertensive patients showed a significant relationship between PICP and LVMI (r=0.631, P<.0001) and between PICP and diastolic dysfunction (r=–0.519, P<.0001). The groups with and without hypertrophy, and with or without diastolic dysfunction, differed in the mentioned peptides but not in BP values.
ConclusionsOur findings suggest that the analyzed markers of synthesis and degradation of collagen may be related to myocardial hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction independent of blood pressure values.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora