Los screening o cribados permiten detectar anomalías que se pueden tratar e identificar a los pacientes que requieren derivación al especialista. Nuestro objetivo es identificar las diferentes áreas de investigación y determinar las publicaciones más citadas sobre los cribados en atención primaria.
MétodosSe ha realizado un análisis de publicaciones y visualización de redes de citación mediante el programa informático Citation Network Explorer. La búsqueda bibliográfica se ha realizado con la base de datos Web of Science (WOS) empleando el término de búsqueda: «screening AND (vision OR eye OR ocular OR visual)».
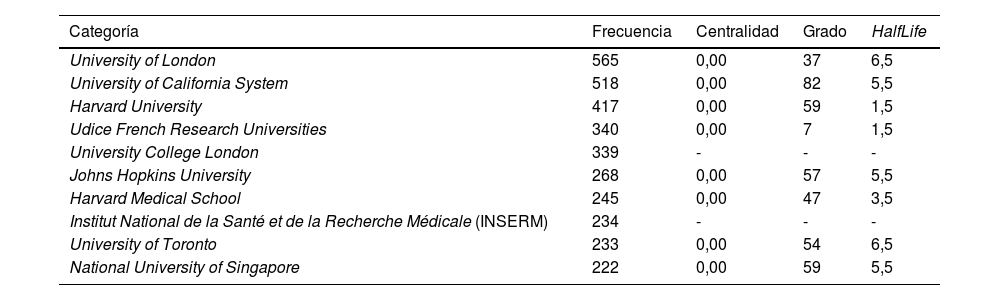
ResultadosAnalizamos 16.707 publicaciones en todos los campos, se han encontrado 23.919 redes de citación. El número de publicaciones ha aumentado, siendo el 2021 el año con mayor número. La mayoría son artículos científicos y el idioma predominante es el inglés.
El artículo más citado es un metaanálisis mundial sobre la prevalencia del glaucoma, el cual muestra la importancia de realizar cribados para la detección precoz del mismo, ya que es fundamental para evitar la ceguera.
Mediante la función clustering encontramos ocho grupos con número significativo de publicaciones donde tenemos bibliografía sobre determinadas enfermedades oculares: glaucoma, retinopatía diabética (RD), ambliopía pediátrica, queratocono y ojo seco.
ConclusionesLas principales áreas de estudio en relación con los cribados son la detección de enfermedades como el glaucoma, retinopatía del prematuro, queratocono y ojo seco. Así como la detección mediante análisis visual de la ambliopía infantil y la pérdida de visión del paciente anciano. También da importancia a la realización de pruebas de motilidad ocular en problemas de daño cerebral adquirido.
Screenings make it possible to detect anomalies that can be treated and identify patients who require referral to a specialist. The objective is to identify the different areas of research and determine the most cited publications on screening in primary care.
MethodsAn analysis of publications and visualization of citation networks has been carried out using the Citation Network Explorer software. The bibliographic search was carried out with the Web of Science (WOS) database using the search term: “screening AND (vision OR eye OR ocular OR visual)”.
ResultsWe analyzed 16707 publications in all fields, 23919 citation networks have been found. The number of publications has increased, with 2021 being the year with the highest number. The majority are scientific articles and the predominant language is English.
The most cited article is a global meta-analysis on the prevalence of glaucoma, showing the importance of screening for its early detection since it is essential to avoid blindness.
Using the clustering function we found 8 groups with a significant number of publications where we have bibliography on certain eye diseases: glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, pediatric amblyopia, keratoconus and dry eye.
ConclusionsThe main areas of study in relation to screening are the detection of diseases such as glaucoma, retinopathy of prematurity, keratoconus and dry eye. As well as the detection through visual analysis of childhood amblyopia and vision loss in elderly patients. It also gives importance to performing ocular motility tests in problems of acquired brain damage.
Artículo
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEMERGEN, (https://www.semergen.es/index.php?seccion=biblioteca&subSeccion=revistaSEMERGEN ) y autentifíquese.
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora