Investigar en voluntarios sanos la debilidad muscular producida por dosis bajas de rocuronio y su tolerancia, con la idea general de producir una breve relajación muscular esquelética potencialmente aplicable en situaciones clínicas.
Pacientes y métodosTras autorización del Comité de Ética e Investigación Clínica de nuestro hospital, nos propusimos estudiar en voluntarios sanos los efectos de tres dosis de rocuronio (0,1, 0,05 ó 0,075mgKg−1), administradas en diferentes días, sobre la fuerza muscular a nivel subjetivo y objetivo (medida con un dinamómetro de puño), y la aparición de efectos adversos previstos (diplopia, disartria, disfagia).
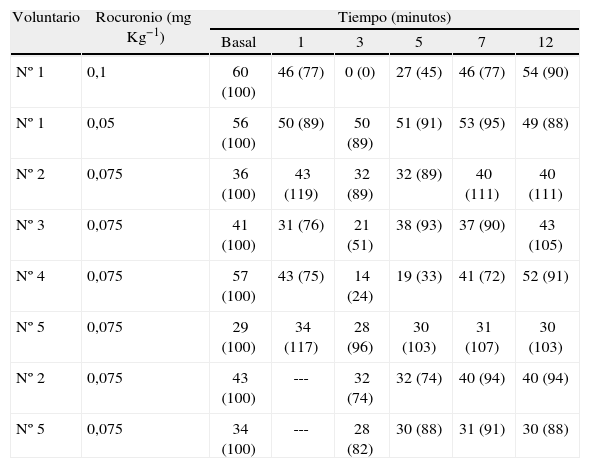
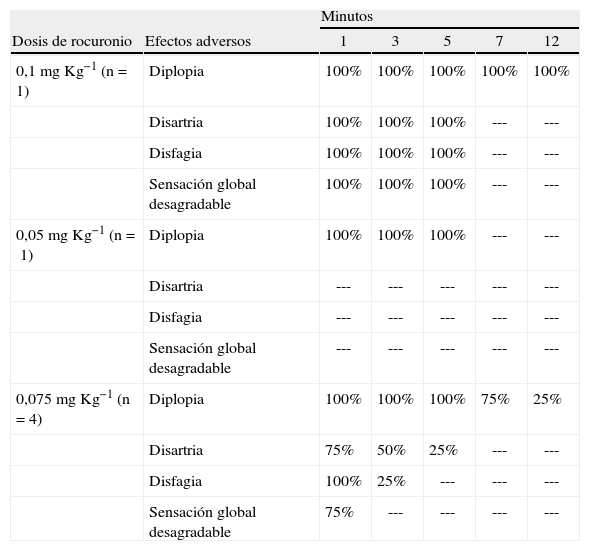
ResultadosSe incluyeron cinco voluntarios. En el primer sujeto la dosis de 0,1mgKg−1 de rocuronio resultó inadecuada por exceso de efecto (debilidad extrema de la musculatura esquelética; experiencia desagradable por diplopia, disartria y disfagia) y la dosis de 0,05mgKg−1 fue bien tolerada, pero sin sensación de debilidad ni efectos apreciables sobre la dinamometría. Estas dos dosis no se administraron al resto de sujetos. En los otros cuatro voluntarios, la dosis de 0,075mgKg−1 produjo una breve sensación de debilidad muscular considerada aceptable (aunque los resultados estuvieron interferidos por dos dinamometrías basales deficientes técnicamente), con leve y breve sensación desagradable (por disfagia principalmente).
ConclusionesDosis de rocuronio de 0,075mgKg−1 en sujetos sanos conscientes y respiración espontánea son aceptablemente toleradas y producen un breve estado de debilidad muscular que podría ser de utilidad en situaciones que precisen momentos puntuales de relajación muscular esquelética.
To study muscle weakness caused by low doses of rocuronium and rocuronium intolerance in healthy volunteers, with the general aim of producing brief skeletal-muscle relaxation that would have potential applications in clinical situations.
Patients and methodsAfter receiving authorization from the clinical research ethics committee of our hospital, we set out to study the effects on subjective and objective muscle strength of injecting 3 doses of rocuronium (0.1mg.kg−1, 0.05mg.kg−1, and 0.075mg.kg−1) in healthy volunteers, each dose on a different day. Objective muscle strength was measured using a hand dynamometer. We also recorded the development of expected adverse effects (diplopia, dysarthria, and dysphagia).
ResultsFive volunteers (all authors) were studied. In the first subject, the dose of 0.1mg.kg−1 of rocuronium was unsatisfactory because it was too strong, causing extreme skeletal-muscle weakness and discomfort due to diplopia, dysarthria, and dysphagia. The dose of 0.05mg.kg−1 was well tolerated but caused no subjective feeling of weakness or any effect measurable on dynamometry. These doses were not administered to the other subjects. In the 4 remaining volunteers, the dose of 0.075mg.kg−1 caused a brief feeling of muscle weakness that was considered to be acceptable, though the findings were compromised by 2 technically defective baseline dynamometry readings. The volunteers also reported brief, mild discomfort, principally due to dysphagia.
ConclusionsDoses of 0.075mg.kg−1 of rocuronium in healthy awake subjects breathing spontaneously are acceptably tolerated and cause brief muscle weakness that may be of use in situations that require skeletal muscle relaxation at specific moments.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora