Evaluar si la aparición de glucosa en el fluido obtenido espontáneamente del catéter epidural tras su inserción, durante la anestesia combinada intradural-epidural realizada con bupivacaína hiperbara, es un suceso habitual.
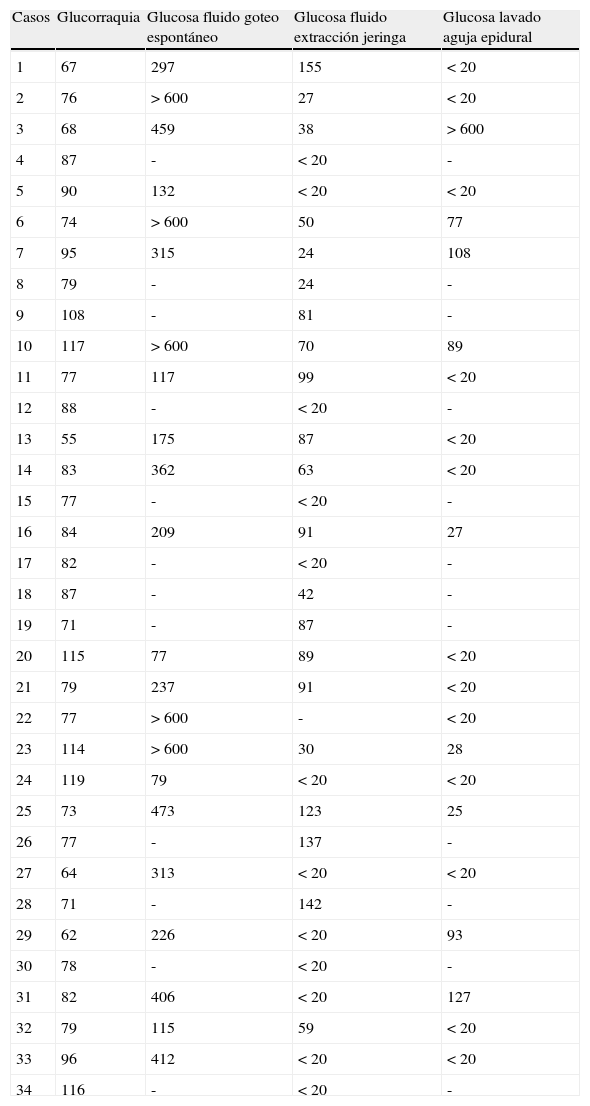
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional prospectivo en 34 pacientes con anestesia combinada intradural-epidural a los que después de localizar el espacio epidural con solución salina, insertar la aguja espinal e inyectar bupivacaína hiperbara, se les introdujo un catéter epidural. Tras observar si goteaba espontáneamente algún fluido por él, se determinó si este contenía glucosa. Retirada la aguja epidural y lavada su luz con solución salina, se comprobó si en el lavado existía glucosa. Las muestras se analizaron con un glucómetro. Cuando desapareció el bloqueo motor se administró una dosis de anestésico local por el catéter epidural. Se valoró la asociación de los parámetros demográficos con el goteo espontáneo por el catéter epidural.
ResultadosEn 22 pacientes se produjo goteo espontáneo por el catéter epidural tras su inserción. Todas las muestras obtenidas contenían glucosa. En 9 de 34 muestras del lavado de aguja epidural existía glucosa. Ningún paciente sufrió bloqueo sensitivomotor excesivo. Se encontró asociación estadísticamente significativa (p<0,05) de la edad con el goteo espontáneo por el catéter (a más edad, más goteo).
ConclusiónEl hallazgo de glucosa en el fluido obtenido por el catéter epidural es un suceso frecuente y sin significación clínica. Proponemos que pudo deberse a fuga de líquido cefalorraquídeo por el agujero de punción dural durante o después de la administración de la bupivacaína hiperbara y al derrame de esta en el espacio epidural.
To determine whether the appearance of glucose in the fluid spontaneously obtained by the epidural catheter after its insertion during combined intradural-epidural anaesthesia with hyperbaric bupivacaine is a usual occurrence.
Patients and methodsA prospective, observational study was conducted on 34 patients with combined intradural-epidural anaesthesia in whom an epidural catheter was introduced, after locating the epidural space with a saline solution, inserting a spinal needle and injecting hyperbaric bupivacaine. After observing whether any fluid was spontaneously dripping from it, it was determined if this contained glucose. Withdrawal of the needle and washing its lumen with saline solution, it was checked whether there was glucose in washout. The samples were analysed using a glucose meter. When the motor block disappeared a dose of local anaesthetic was administered through the epidural catheter. The relationship of the demographic parameters with the spontaneous dripping of the epidural catheter was evaluated.
ResultsSpontaneous dripping by the epidural catheter after its insertion was observed in 22 patients. All the samples obtained contained glucose. There was glucose in 9 out of 34 epidural needle wash samples. None of the patients suffered from excessive motor-sensory block. There was a statistically significant relationship between patient age (P<.05) and spontaneous dripping by the catheter (the higher the age, more dripping).
ConclusionThe finding of glucose in the fluid obtained by the epidural catheter is a frequent occurrence and is of no clinical significance. We propose that it could be due to a leak of cerebrospinal fluid by the dural puncture needle during or after the administering of the hyperbaric bupivacaine and the spillage of this into the epidural space.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora