Hemangioblastoma (HB) is a benign tumor of the central nervous system, associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL), or sporadic. The aim of this study was to compare and examine the clinical–pathological profile of patients with spinal hemangioblastoma and YAP expression.
MethodsA retrospective, descriptive, comparative study. All patients who underwent surgery for spinal HB between 2016 and 2023 were included. Clinical and radiological data were collected and analyzed. An immunohistochemistry panel including NeuN, neurofilaments (NF), and YAP-1, was performed.
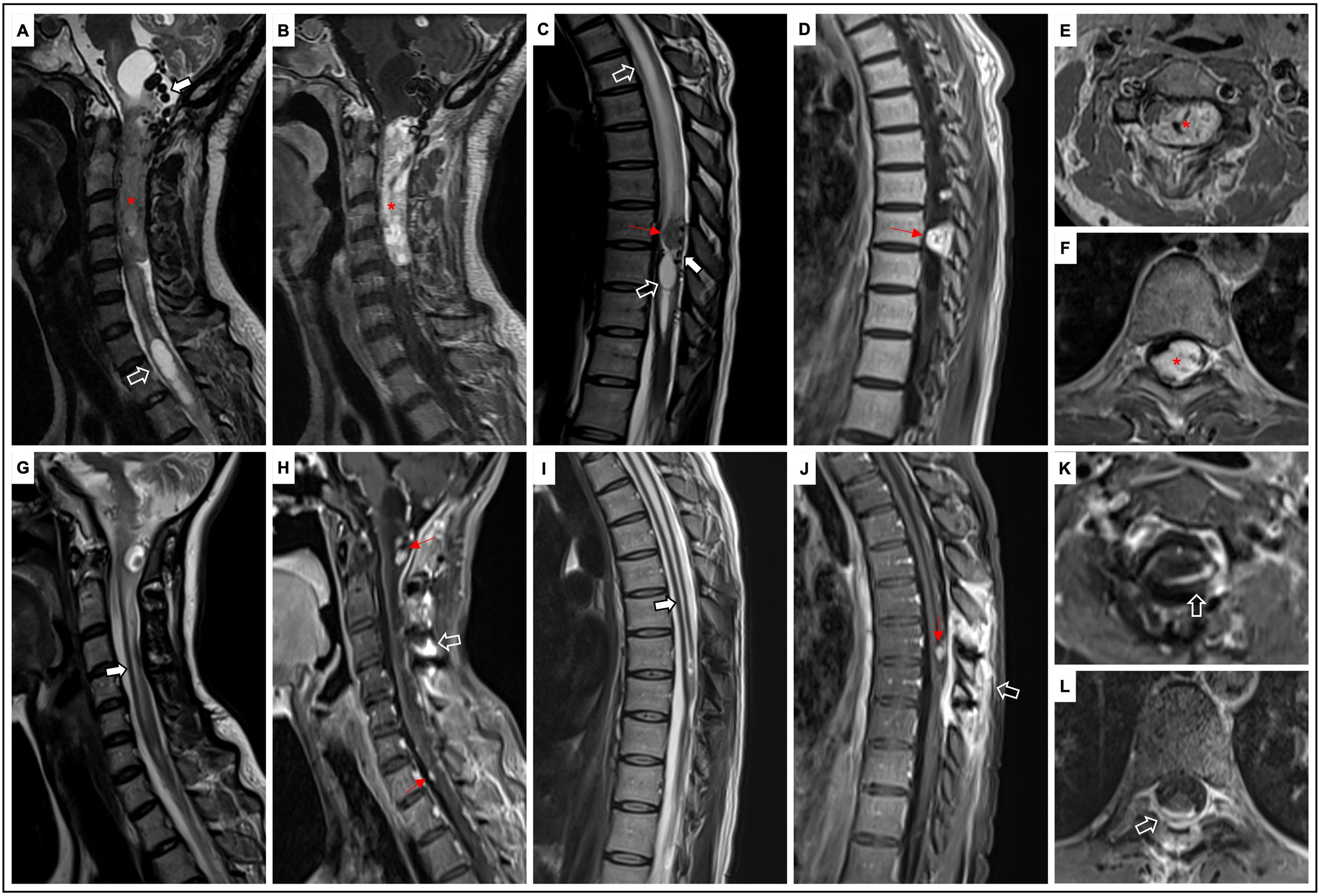
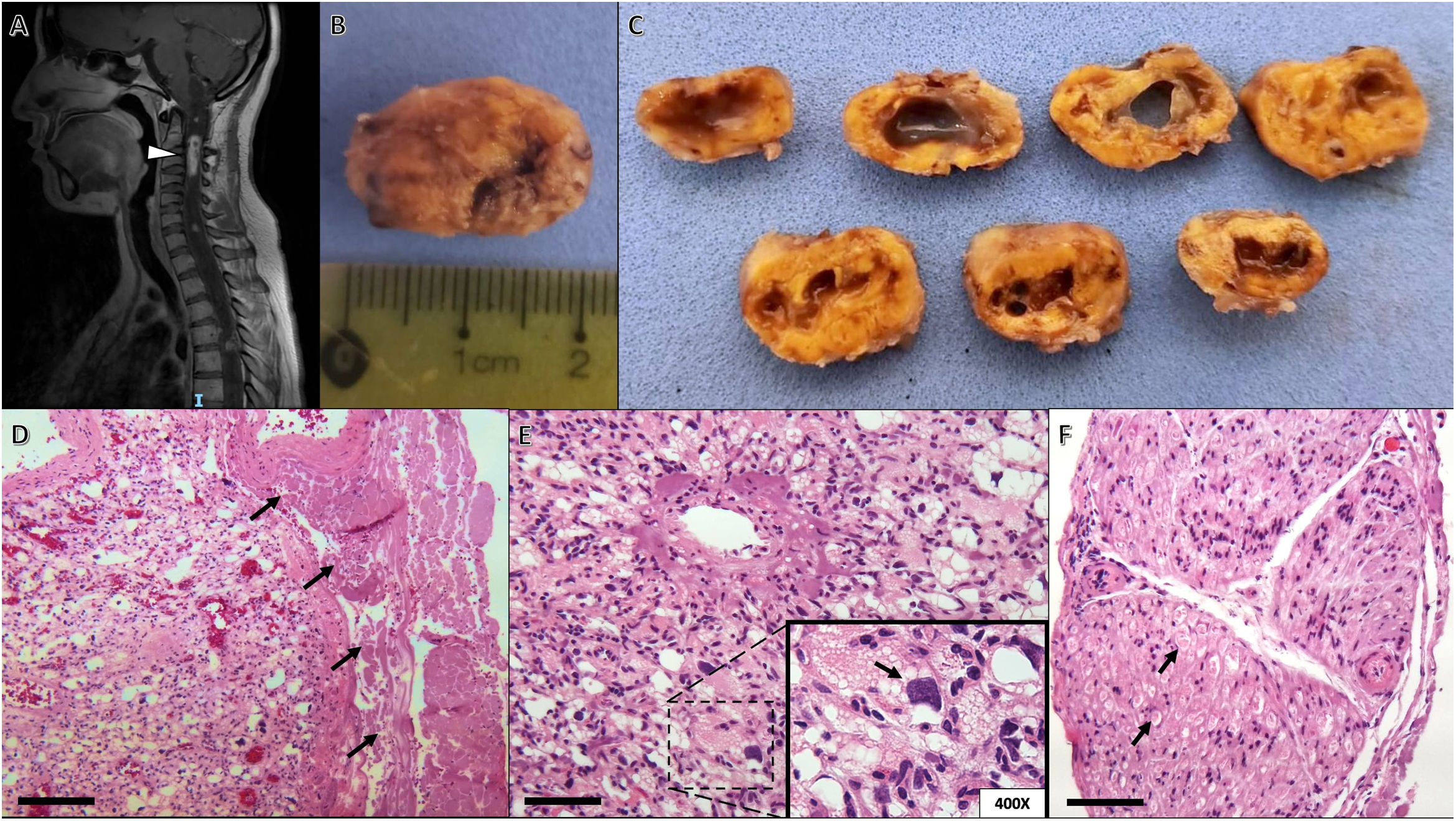
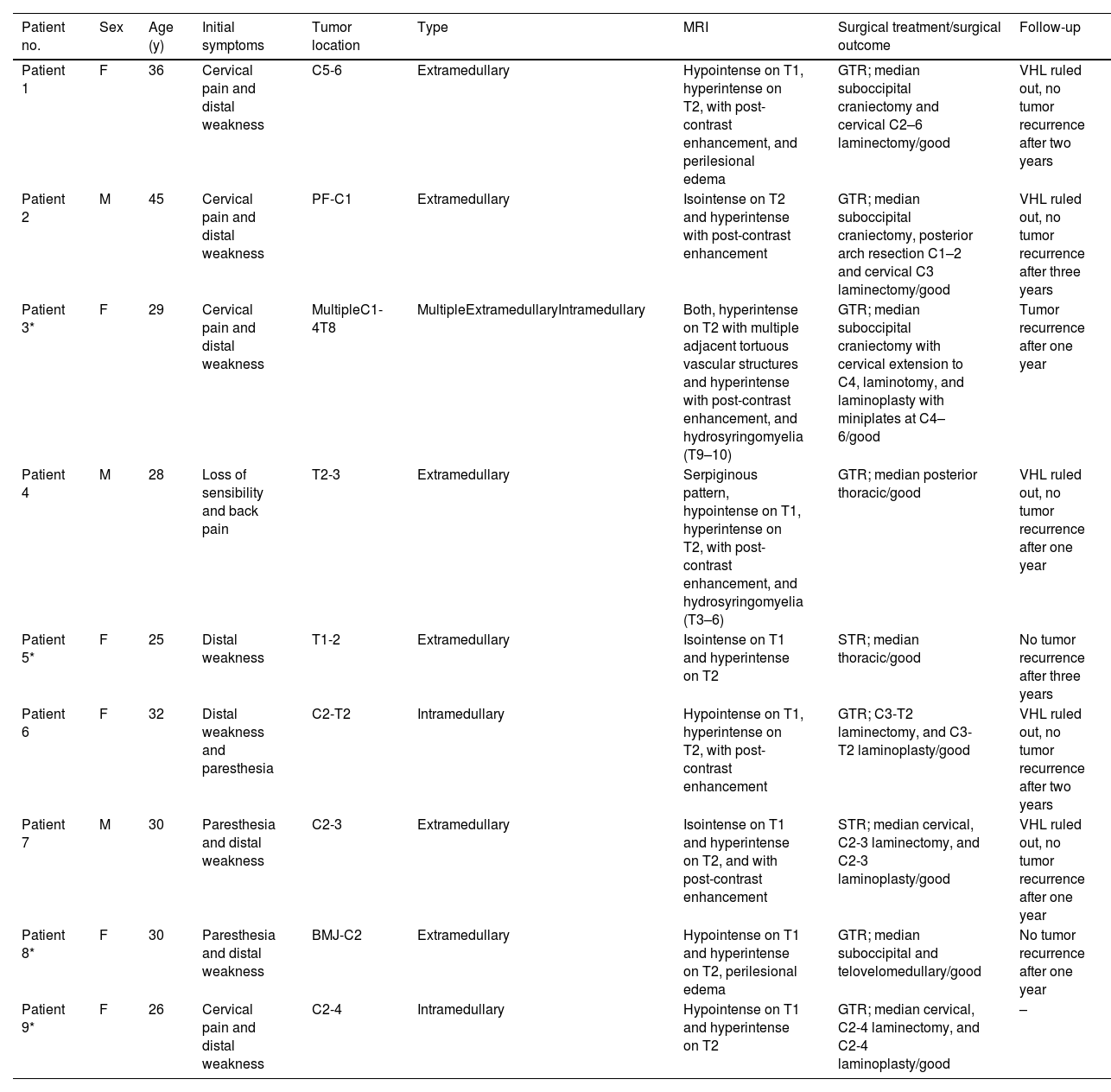
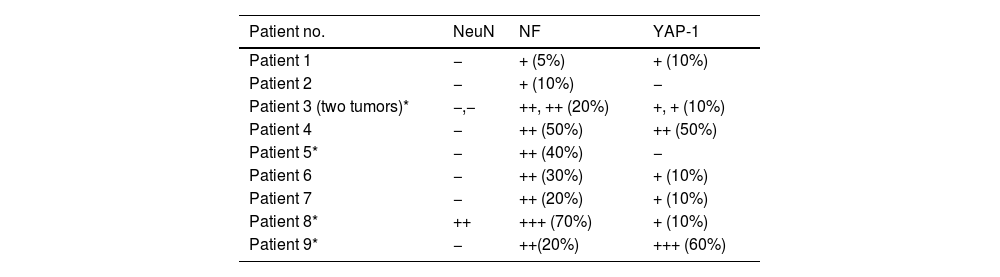
ResultsNine patients were studied, six women and three men. Four patients had previously diagnosed VHL. The tumor location included: four cervical (44.44%), two thoracic (22.22%), two pontine with cervical extension (22.22%) and one patient with two lesions, one cervical and one thoracic (11.11%). Non-significant clinical differences were identified between VHL and sporadic patients. Imaging evidenced seven extramedullary and three intramedullary tumors.
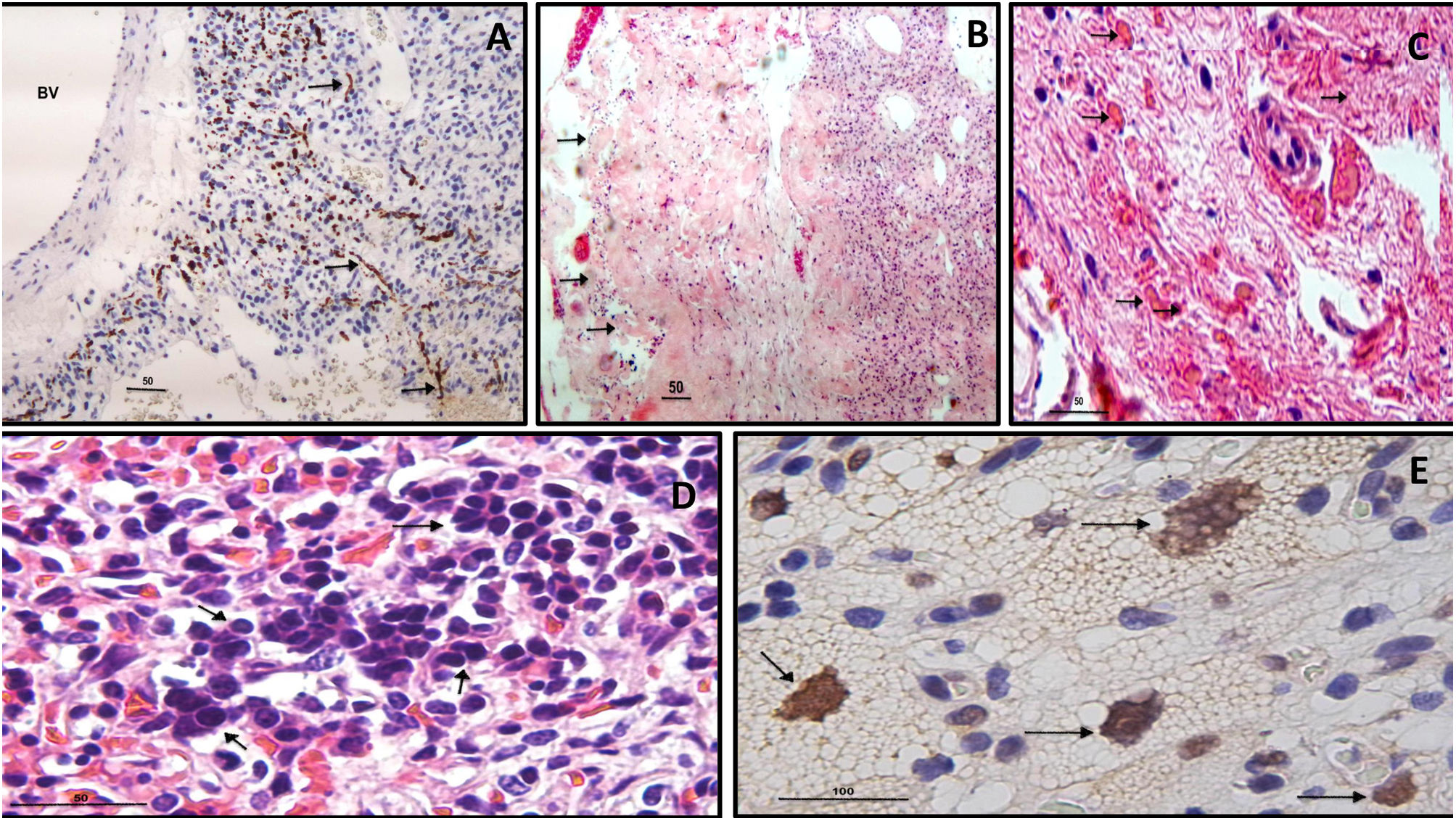
Histologically, intra-tumoral and perivascular axonal tracts were observed in all cases. One third of the tumors (two with VHL and one sporadic) presented extramedullary hematopoiesis. Seven cases (77.8%) expressed nuclear YAP (three with VHL and four sporadic HBs). The surgical outcome was good and only one patient with VHL undergoing subtotal resection had recurrence.
ConclusionsSpinal HBs can be associated with VHL or be sporadic. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to describe YAP expression in HB. It is important to investigate the involvement of the Hippo pathway in HBs as a possible therapeutic target.
El hemangioblastoma (HB) es un tumor benigno del sistema nervioso central, asociado con la enfermedad de von Hippel-Lindau (VHL), o esporádico. El objetivo de este estudio fue comparar y examinar el perfil clínico-patológico de los pacientes con hemangioblastomas espinales y la expresión de YAP.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo, descriptivo y comparativo. Se estudiaron los pacientes intervenidos quirúrgicamente por HB espinales entre los años 2016-2023. Se recolectó y analizó toda la información clínica y radiológica. Se aplicó un panel de inmunohistoquímica incluyendo NeuN, neurofilamentos y YAP-1.
ResultadosSe estudiaron 9 pacientes, 6 mujeres y 3 varones. Cuatro pacientes tenían VHL diagnosticado previamente. La localización tumoral incluyó: 4 cervicales (44,44%), 2 torácicos (22,22%), 2 pontinos con extensión cervical (22,22%) y una paciente con 2 lesiones, una cervical y una torácica (11,11%).
No se identificaron diferencias clínicas significativas entre los pacientes con VHL y esporádicos. Por imagen, fueron 7 tumores extramedulares y 3 intramedulares. Histológicamente, se observaron en todos los casos trayectos axonales intra-tumorales y perivasculares. Un tercio de los tumores (2 con VHL y uno esporádico) presentaron hematopoyesis extramedular. Siete casos (77,8%) expresaron YAP nuclear (3 con VHL y 4 HB esporádicos). El resultado quirúrgico fue bueno y solo un paciente con VHL sometido a resección subtotal tuvo recurrencia.
ConclusionesLos HB espinales pueden estar asociados con la enfermedad de VHL o ser esporádicos. Hasta donde sabemos, este es el primer estudio que describe la expresión de YAP en el HB. Es importante investigar la participación de la vía de señalización Hippo en los HB como posible objetivo terapéutico.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora