Some members of the Pseudallescheria (anamorph Scedosporium) have emerged as an important cause of life-threatening infections in humans. These fungi may reach the lungs and bronchial tree causing a wide range of manifestations, from colonization of airways to deep pulmonary infections. Frequently, they may also disseminate to other organs, with a predilection for the brain. In otherwise healthy patients, the infection is characterized by non-invasive type involvement, while invasive and/or disseminated infections were mostly seen in immunocompromised patients.
AimsWe reviewed all the available reports on Pseudallescheria/Scedosporium pulmonary infections, focusing on the geographical distribution, immune status of infected individuals, type of infections, clinical manifestations, treatment and outcome.
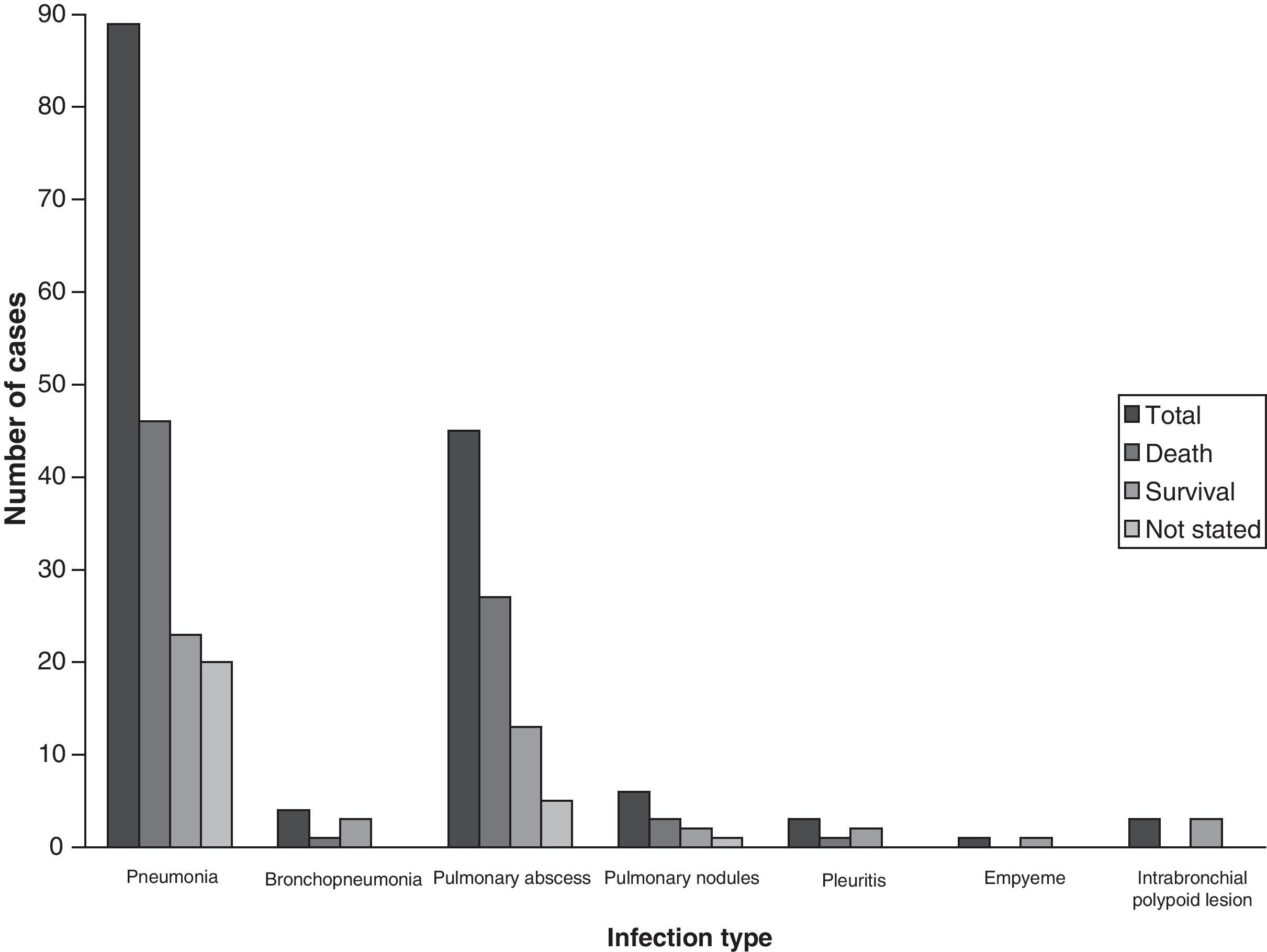
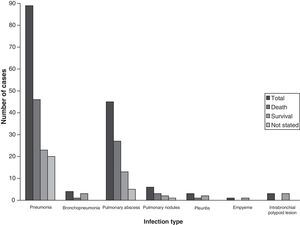
Results and conclusionsThe main clinical manifestations of the 189 cases of pulmonary pseudallescheriasis reviewed were pneumonia (89), followed by fungus ball (26), and chest abscess (18). Some patients had more than one type of invasive pulmonary manifestations. Among patients with pneumonia, several cases of pneumonia associated with near-drowning (10/89, 11.2%) have also been reported in immunocompetent hosts. Major underlying conditions for non-invasive pulmonary infection were preexisting lung cavities and medical immunosuppression for invasive pulmonary infection. Saprobic airway colonization was mostly seen in patients with mucosal dysfunction, i.e. patients with cystic fibrosis. The mortality rate was closely related to the infection type, being 26.8% in non-invasive type (fungus balls) and 57.2% in invasive type.
Algunos miembros del género Pseudallescheria (anamorfo Scedosporium) están emergiendo como causantes de infecciones humanas graves. Estos hongos pueden alcanzar los pulmones y el árbol bronquial causando una amplia variedad de manifestaciones clínicas, desde colonizaciones de las vías aéreas hasta infecciones pulmonares profundas. Frecuentemente estos hongos pueden diseminarse a otros órganos, mostrando una marcada predilección por el cerebro. En pacientes por otra parte sanos la infección no suele ser invasora, mientras que en el paciente inmunocomprometido se caracteriza por su carácter invasor.
ObjetivosSe ha llevado a cabo una revisón de los artículos disponibles sobre infecciones pulmonares por Pseudallescheria/Scedosporium, destacando la distribución geográfica de las mismas, el estado inmunitario de los pacientes, el tipo de infección, las manifestaciones clínicas, el tratamiento y curso clínico de la enfermedad.
Resultados y conclusionesLa principal manifestación clínica de los 189 casos de pseudalescheriasis pulmonar revisados fue neumonía (89), seguido por la presencia de bola fúngica (46), y absceso pulmonar (18). En algunos casos de sujetos inmunocompetentes la neumonía fue debida a aspiración con agua contaminada (10/89, 11,2%). Los principales factores de riesgo para las infecciones pulmonares no invasoras fueron la preexistencia de cavidades pulmonares y el tratamiento inmunosupresor para infecciones pulmonares invasoras. La colonización saprofítica de vías aéras se observó principalmente en pacientes con alteraciones de la mucosa, como aquellos con fibrosis quística. La tasa de mortalidad estuvo estrechamente relacionada con el tipo de infección, siendo del 26,8% en las infecciones no invasoras (bola fúngica) y del 57,2% en las invasoras.
Currently, Pseudallescheria/Scedosporium infections are some of the most prevalent mould infections in humans, being the respiratory tract the most commonly infected site.52 Recent molecular studies have demonstrated that Pseudallescheria/Scedosporium complex (PSC) includes several phylogenetic species,46 but since the degree of involvement of each individual species in human infections has not been determined, the present review will maintain the name PSC in all disease entities. The species of that complex and relatives recovered so far from clinical samples are: Scedosporium apiospermum (teleomorph Pseudallescheria apiosperma), Scedosporium aurantiacum, Scedosporium boydii (Pseudallescheria boydii), Pseudallescheria angusta and Pseudallescheria minutispora.46,47 Several types of respiratory system involvements of PSC have been described in both immunocompromised and immunocompetent individuals. Three general reviews, on a range of PSC infections29,52 and central nervous system (CNS) infections,68 have recently been published. In addition, a few more, shorter, reviews each covering a small number of previous cases6,9,14,82,109,113,115 have also been published. The clinical spectrum of the disease associated with PSC was examined by Rippon, in 1980.112 In the present study, the available case reports of PSC pulmonary infections have been reviewed chronologically to clarify many aspects associated particularly with these illnesses, including the risk factors and underlying conditions, clinical manifestations, diagnostic factors, treatment and outcome.
MethodsLiterature searchA computerized search of the MEDLINE database (National Library of Medicine, Bethesda, Maryland, USA) was made for cases reported in the literature between 1955 and mid-2009, with (by cross-referencing) the terms: “P. boydii” and “S. apiospermum”, “pulmonary”, “pneumonitis”, “lung abscess”, “pulmonary nodules”, “mycetomas”, “fungomas”, “respiratory system infection”, “disseminated” and “near-drowning”, “respiratory system colonization”, “Pseudallescherial colonization”, “fungal colonization” “cystic fibrosis”, “allergic bronchopulmonary pseudallescheriasis”, “scedosporiosis” and “pseudallescheriasis”. Additional search terms included were “Allescheria boydii”, “Monosporium apiospermum”, and “Petriellidium boydii” as referring to prior or other nomenclature for this fungus. These key words were used alone and/or in combination with an “and” statement. Additional cases were found by scanning the references cited in the original articles. Original full texts of all the relevant articles were found via MEDLINE, TUBITAK-ULAKBIM (Turkish Academic Network and Information Center), and/or other international libraries and were used for the analysis or personal communication of the authors.
DefinitionsA case was considered an invasive pulmonary infection when the presence of lesion and clinical syndrome consistent with pulmonary infection (involvement of lung parenchyma) was documented and any species of the PSC was recovered from the lesion, usually from lung tissue, mucosal biopsy, aspirate from an abscess or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL). Cases were included in the study as non-invasive involvement when the fungus grew in pre-existing lung cavities from a previous disease, i.e. tuberculosis or sarcoidosis, without invading the cavity wall. The mass may move within the cavity but does not invade the cavity wall.
Infection types that refer to a saprobic involvement, such as fungus ball or mycetoma were evaluated and categorized as reported by the authors. Duplicate publications were excluded and follow up reports were regarded as associated with a single case together with the previous report. The following data were recorded for each patient, if stated: age and sex, geographical location, predisposing factors (including underlying diseases and associated medical conditions), clinical symptoms, mode and time to diagnosis, other pathogens isolated or observed in specimens if any, antimicrobial agents administered, regimens and duration of antifungal therapy, invasive or surgical procedures, duration of hospitalization, and patient outcome.
ResultsThere were 231 case reports and records of isolation of PSC from pulmonary specimens identified from 1955 to end-2010. PSC was first reported as a cause of pulmonary disease in 1955 by Creitz and Harris,30 although the organism was probably a secondary invader, being inhaled from the soil. Four cases were described twice,22,67,74,84,85,109,134,145 due to the progression or reactivation of the disease. No details of the patients’ histories were available in two case reports.36,38 One case was summarized in a general report on brain abscesses following bone marrow transplantation,36 and the presence of the fungus in sputum was mentioned in an environmental study.31 In another case with bronchiectasis, in spite of PSC being repeatedly isolated from the patient's sputum it was not obtained in culture from the intercavitary mass, in which many Aspergillus fumigatus conidiophores were histologically observed.109 Of these 231 published cases, 56 involved patients with cystic fibrosis (CF).23,26,27,32,53,59,63,83,86,94,105,119,127,129,135,144,148 Twelve of these CF patients were reported to have invasive and two non-invasive pulmonary infection.53,83,86,94,127,135,144 A total of 189 cases were invasive or non-invasive infections with isolation of PSC from lower respiratory tract specimens.
Overall demographic and geographic featuresThe majority of those 189 pulmonary pseudallescheriasis were reported from the USA (78 cases), followed by Australia (40 cases), Japan (14 cases), France (14 cases) and Germany (7 cases). Occasionally, there were cases reported from Argentina, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, China, Congo, Croatia, Finland, India, Spain, Mexico, The Netherlands, Poland, Spain, Taiwan and the UK [total=80 female patients and 101 male, age range=2–90 years].
Portals of entry and route of disseminationPulmonary involvement, which mainly affected farmers, probably resulted from inhalation of the conidia.33,53,64,67,72,83,86,94,120,123,127,135,152 A case was reported in an immunocompetent patient who was working in a thermal bath, being in charge of scrubbing off the sedimented filth at the bottom of the pools after draining the water. S. apiospermum was isolated from several samples of the thermal water and the sediment filled the patient's working place.138 In one case, the patient suffered a lymphatic and haematogenous dissemination of the fungus via a skin injury while gardening and developed a lymphocutaneous syndrome, similar to sporotrichosis, along with a lung mass.74 Pulmonary involvement may have been secondary from septic emboli originated from lymphangitis or phlebitis in the left arm. Aspiration of polluted water was reported in 17 patients who developed a CNS infection. It is likely that after an invasive pneumonitis, the fungus can reach the CNS by haematogenous spread facilitated by the immunosuppression.52 The fungus could also be directly inoculated through a perforated chest wound, or inhaled,134,145 or transferred from an infected donor to an organ recipient.143 Patterson et al.,101 reported a case of nosocomial pseudallescheriasis in a liver transplant patient who was probably not colonized or infected as he was immunocompetent on admission but developed cavitary lung and brain lesions on day 25 post-transplant.
Colonization of bronchial lumen or intracavitary colonizationPSC can grow within poorly draining bronchi, causing an endobronchial saprobic colonization without tissue invasion. The fungus may colonize the respiratory tract of people exposed to a high environmental inoculum in the absence of anatomical or physiological abnormalities of the respiratory tract. This colonization would most likely be transient once the patient is removed from the environmental source. Transient colonization without apparent invasion has been recorded secondary to other diseases or conditions.67,109,111,126 Rippon and Carmichael111 reported a case of transient colonization of bronchial lumen in which the patient was on prednisone for 15 years for rheumatoid arthritis, and had coughing, wheezing, and pulmonary congestion. Direct examination of several sputum specimens revealed intertwined hyphal masses and PSC was cultured from all samples. Reddy et al.109 and Jung et al.67 described another transient colonization in a farmer's wife with chronic bronchiectasis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Castiglioni et al.22 reported the case of three solid-organ transplant patients who had airway colonization and received itraconazole (ITZ) prophylaxis, without evidence of disease. Similarly, in an allogenic bone marrow transplant patient with acute lymphocytic leukemia, treated with chemotherapy, cyclosporin and corticosteroids for graft-versus-disease complication, A. fumigatus was isolated from sputum culture 5 months following the transplantation. The patient was treated with ITZ and a follow up sputum culture revealed a heavy growth of PSC. Liposomal amphotericin B was added to the treatment and repeated sputum cultures and a bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were negative for PSC.12 Endobronchial chronic colonization by PSC has been reported in CF patients, often without pathological effects for the host.
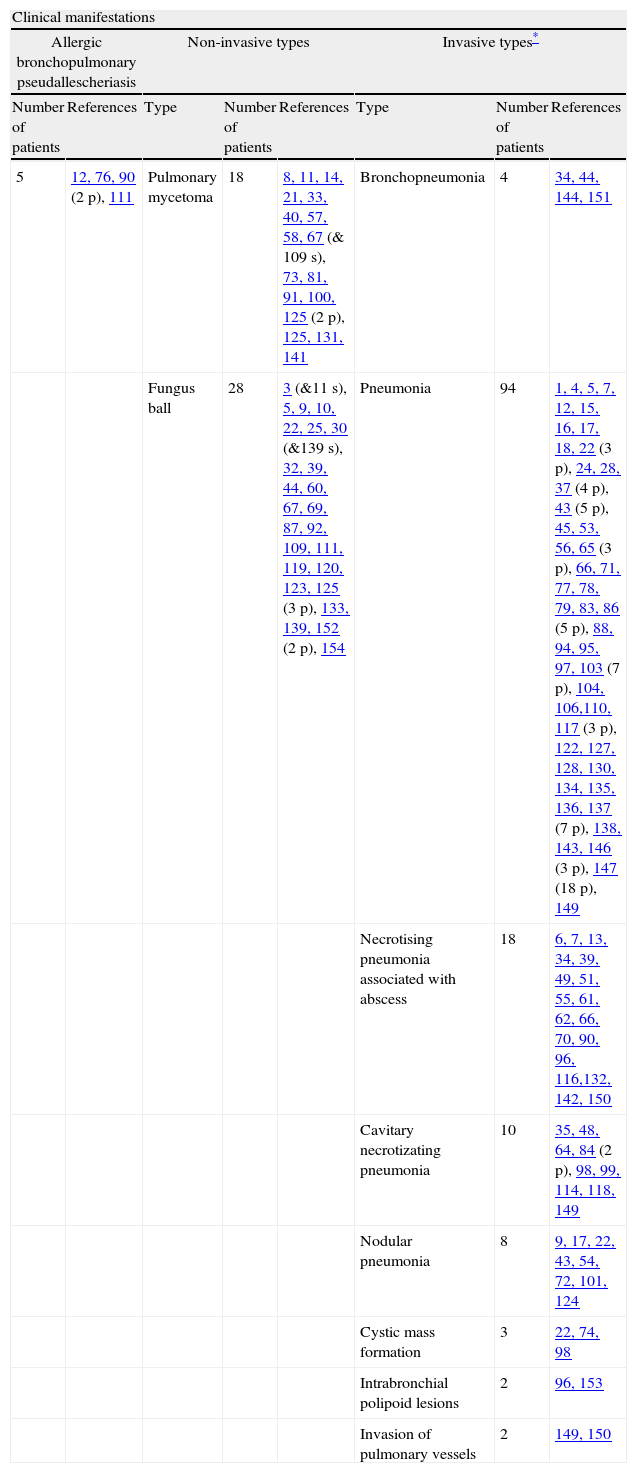
Clinical presentationsThe role of PSC in producing pulmonary lesions and some of their relevant conditions has already been discussed in earlier reports. However, pseudallescherial lung infections have continued to be reported and consequently their clinical spectrum has been considerably enlarged. The most relevant clinical manifestations of infection are outlined in Table 1. Of those, pneumonitis was the most common clinical manifestation (94/189, 49.7%). Although the chest X-rays were not specific, they were usually helpful in establishing the diagnosis. A dense infiltrate first appears, followed later by cavitation and in some cases by the development of a fungus ball, mostly in the upper lobes. Fulminant spread with invasion through the lung parenchyma and the pleura and development of pleural effusion has commonly been described. Case reports that have based the diagnosis of pulmonary disease on the isolation of PSC from sputum are contradictory.75 Most patients with this fungus in the sputum do not appear to have invasive infection.72 Cases of pulmonary pseudallescheriasis appear similar to pulmonary aspergillosis, clinically, radiologically, histologically, and in terms of severity. Macroscopically, pulmonary pseudallescherial infections produce inflammatory cystic or cavitary lesions. Regarding the data obtained from the above-mentioned cases, pulmonary pseudallescheriasis can be subdivided into three categories:
Overall clinical manifestations of 189 respiratory involvement by Pseudallescheria/Scedosporium complex.
| Clinical manifestations | |||||||
| Allergic bronchopulmonary pseudallescheriasis | Non-invasive types | Invasive types* | |||||
| Number of patients | References | Type | Number of patients | References | Type | Number of patients | References |
| 5 | 12, 76, 90 (2 p), 111 | Pulmonary mycetoma | 18 | 8, 11, 14, 21, 33, 40, 57, 58, 67 (& 109 s), 73, 81, 91, 100, 125 (2 p), 125, 131, 141 | Bronchopneumonia | 4 | 34, 44, 144, 151 |
| Fungus ball | 28 | 3 (&11 s), 5, 9, 10, 22, 25, 30 (&139 s), 32, 39, 44, 60, 67, 69, 87, 92, 109, 111, 119, 120, 123, 125 (3 p), 133, 139, 152 (2 p), 154 | Pneumonia | 94 | 1, 4, 5, 7, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, 22 (3 p), 24, 28, 37 (4 p), 43 (5 p), 45, 53, 56, 65 (3 p), 66, 71, 77, 78, 79, 83, 86 (5 p), 88, 94, 95, 97, 103 (7 p), 104, 106,110, 117 (3 p), 122, 127, 128, 130, 134, 135, 136, 137 (7 p), 138, 143, 146 (3 p), 147 (18 p), 149 | ||
| Necrotising pneumonia associated with abscess | 18 | 6, 7, 13, 34, 39, 49, 51, 55, 61, 62, 66, 70, 90, 96, 116,132, 142, 150 | |||||
| Cavitary necrotizating pneumonia | 10 | 35, 48, 64, 84 (2 p), 98, 99, 114, 118, 149 | |||||
| Nodular pneumonia | 8 | 9, 17, 22, 43, 54, 72, 101, 124 | |||||
| Cystic mass formation | 3 | 22, 74, 98 | |||||
| Intrabronchial polipoid lesions | 2 | 96, 153 | |||||
| Invasion of pulmonary vessels | 2 | 149, 150 | |||||
Abbrevations: p: patients; s: the same patient.
Forty-six case reports of non-invasive involvement of intrathoracic cavities, which can be divided into two groups as pulmonary mycetoma (18/46, 39.1%) and pseudallescherioma (28/46, 60.9%), were identified. The terminology used here is based on the specific descriptions made in the different case reports. Pulmonary mycetomas were reported to contain many small, greyish-yellow and white granules, measuring 1–2mm in diameter, within thick, brownish, semi-fluid, odourless exudate. The granules of pulmonary mycetoma consist of closely intertwined hyphal masses and occasional swollen cyst-like chlamydospores. In rare instances, white or yellow lobulated granules of up to 4mm in diameter have been observed.5,8,11,14,21,30,38,53,57,58,81,91,109,141 There has been no evidence of any cementing substance between the hyphae or production of conidia on the periphery of the granules.10,53,111
Intercavitary colonization may typically lead to the formation of a mass consisting of loose hyphal strands or conglomeration of intertwined fungal hyphae admixed with mucus and cellular debris within a preexisting pulmonary cavity or ectatic bronchus. A patient with this type of infection may have a chronic pulmonary infiltrate from a previously existing disease, such as sarcoidosis or tuberculosis.86,111,112 People who have pre-existing lung problems, especially with cavities typically affected by tuberculosis,92 sarcoidosis etc. are at risk of developing non-invasive amorphous fungal masses, called fungomas, fungus balls or in this case pseudallescheriomas. The fungus settles in a cavity and is able to grow free from interference because the immune system is unable to penetrate the cavity. As the fungus multiplies, it forms a ball which incorporates dead tissue from the surrounding lung, mucus, and other debris.
Pseudallescherioma of the lung is the extreme consequence of intercavitary colonization, where the mass of fungus reaches sufficient size to be visible radiologically.3,9,14,22,44,69,87,109,111,119,121,123,125,152,154 Radiographs of the pseudallescheriomas show the presence of a solid, round or oval mass with soft tissue opacity within a lung cavity.
Pseudallescherioma may be different in its morphological features; concentric rings of hyphae radiating from a central area were mainly noted.121 In addition, conidia occur on the surface where the mass is in contact with an air space, generally on the periphery of the pseudallescherioma.69,72,75,121 Similarly to that which occurs in aspergillosis, pseudallescherioma are found in the upper lobe of patients with pre-existing lung disease and are often associated with a thickening of the cavity wall and adjacent pleura.140
In non-invasive type cases, these fungi did not invade the tissues, their presence as a mass within cavities stimulated chronic active inflammation and a markedly vascular granulation tissue response. Based on two case reports,107,140 Przyjemski108 hypothesized that fungus balls may begin as “tissue balls” infiltrated by fungus. In the first case,107 the radiological progression from normal lung through poorly defined infiltrate to fungus ball occurred within two weeks and coincided with recovery from granulocytopenia and derived from infected lung sequestra with inflammatory infiltrate. Since surgically removed fungus balls usually fail to grow on laboratory media,3,5,69,110,115,140,141 the author concluded that the pseudallescherioma formation might be associated with improving host resistance.
Demographic and geographic featuresMost cases have been reported from the USA, with occasional cases from the UK, Germany, France, Poland, India, Japan, Canada, Brazil and Australia (female, n=24, male, n=20, gender was not indicated in the other reports, age range=11–81).
Predisposing factors and underlying conditions. Twenty seven of these 44 patients had associated diseases, which could have contributed to the occurrence and progression of the disease, i.e. tuberculosis and/or tuberculosis cavity (16), sarcoidosis (4), cavitary bronchiectasis (1), chronic bronchitis (1), secular bronch (1), anaplastic cavity in lung (1), lung transplantation (1), systemic lupus erythematosus (1) and alcoholism (1). Four of these 46 patients were otherwise healthy. Pulmonary involvement probably resulted from inhalation of the conidia or ascospores. Seven patients were long time rural residents, or worked closely with soil.
Signs and symptomsClinical symptoms varied from none to haemoptysis and general debilitation. Other symptoms included cough, purulent expectoration, malaise, weight loss, respiratory insufficiency, fatigue, and dyspnea. Haemoptysis was the most common, being noted in 16 cases. One patient was asymptomatic.81 Tuberculin skin test was positive in 5 patients. Precipitating antibodies to PSC were found in 15/56 patients with CF. Complement-fixing antibodies to A. fumigatus were present in one case.3,115
RadiologyRadiological examination may show a moon-shaped radiolucent sign which caps the fungus ball like the one seen in aspergilloma.5 In some cases, the mass is separated from the wall of the cavity by an airspace of variable size and shape, resulting in the “air-crescent” sign which is believed to indicate invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.5,25 Radiographs of one of the cases presented as a solitary round lesion proved to be related to cancer on pathological examination.33 In three cases, the pseudallescherioma was bilateral, in 13 it was localized in the right upper lobe, and in 3 in the left upper lobe.
Laboratory diagnosisIn most cases, the fungus was isolated from sputum cultures. In 17 cases, it was isolated from surgical specimens. In the case reported by Rosen et al.,115 PSC was repeatedly isolated from the sputum and intracavitary exudate of a man with cavitary bronchiectasis, A. fumigatus also being found in the lungs at autopsy. In a case reported by McCarthy et al.,87 the diagnosis was made by precipitin test, which gave a strong reaction to the extract of PSC and a weak reaction to Aspergillus versicolor. Neither fungus was cultured from the sputum, possibly because of a lack of free communication of the mycetoma with the bronchi. PSC and A. versicolor were isolated from cavity contents obtained by thoracotomy. Although repeated sputum cultures and serum immunoprecipitin tests may be helpful,14,53 surgical excision was often needed to make the diagnosis.
Treatment and outcomeOf the 46 patients, 20 were managed surgically. Lobectomy was performed in three cases and pneumonectomy in two. Twelve patients were managed medically. Twelve cases were fatal (26.8%), and 22 patients (47.5%) who had undergone surgery (15) or had been treated with miconazole (MCZ),119 ITZ,23,32 voriconazole (VRZ)44,154 or had no therapy,67,131 survived. In one case, sputum cultures continued to be positive. Following a course of amphotericin B (AMB), the patient remained clinically well without any symptoms.11 Outcome was not reported in the other cases. Regarding these data, in suitable patients surgery appears a successful treatment choice for a cavitary lesion containing a fungus ball.
(ii) Allergic bronchopulmonary pseudallescheriasis (ABPP)Although most allergic bronchopulmonary mycoses have been attributed to Aspergillus species, this syndrome has been reported in PSC as well.23,76,90,144 Allergic bronchopulmonary fungal disease is characterized by asthma, peripheral blood eosinophilia, infiltrates on the chest radiograph, raised IgE levels, precipitating antibodies and immediate cutaneous reactivity to the casual fungus.50
Lake et al.76 first suggested allergic bronchopulmonary manifestations induced by PSC. The authors described a case of a 24-year-old woman with asthma and clinical symptoms similar to allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) who, on chest roentgenogram, was found to have infiltrates, an elevated serum total IgE, skin prick test reactivity and precipitins against this fungus. Hyphae were seen on direct examination of sputum.
Five ABPP cases were reported from Canada, and Australia.23,76,131,144 Three of the subjects were female, while gender was not mentioned in the remaining reports; the age of the patients ranged from 18 to 48 years. Five of them had associated diseases such as asthma and CF and two had previously received prednisone therapy for rheumatoid arthritis or previous ABPA.
Little is known about the immunological and allergic features of pulmonary pseudallescheriasis. Precipitating antibodies are frequently present in Aspergillus mycetoma, but skin tests are usually negative, in contrast to ABPA, in which typically an intermediate (type I) cutaneous reaction occurs, and a delayed (Arthus type III) reaction frequently follows, giving a dual response.19,20,50,80,102 Likewise, precipitating antibodies to PSC were reported in several cases in which the fungus proliferated in the airway lumen21,27,57,69,87,91,111 and failed to continue after surgery in those who underwent resection69,81 or after antifungal treatment.91 In most of them, no reaction was detected with extracts of other fungi, including A. fumigatus. Eosinophilia was noted in only one patient.57 Of the three patients reported by Reddy et al.,109 one was skin tested with an extract of PSC, but had no response. Rippon and Carmichael111 reported a case of a patient with transient endobronchial colonization with several sputum specimens positive for PSC. Chest radiograph examination showed diffuse interstitial infiltrates; and precipitins against PSC were positive. Although the disease was somewhat similar to ABPP, there was no eosinophilia recorded and skin test sensitivity was not established.
Cimon et al.,27 reported two cases of ABPP in a prospective study in 128 CF patients, both chronically colonized by PSC and one with previous ABPA treated with a combination of corticosteroids and ITZ, leading to a remission of symptoms. In most cases in this study, colonization with PSC was not associated with allergic disease.
Mixed allergic bronchopulmonary disease due to PSC and Aspergillus was also described by Lake et al.76 in an asthmatic woman without CF, and in two additional cases by Miller et al.,90 but mixed infections seem uncommon. In the second report, two patients with probable diagnosis of ABPA also presented the fungus in sputum and strongly positive pseudallescheriasis serology, which suggests a contributory role of this fungus in the allergic bronchopulmonary disease.90
ABPP was seen in patients with long-standing asthma76,90 or with CF.27 On pathological analysis, this form of pulmonary pseudallescheriasis was characterized by the presence of obvious plugs in sputum containing PSC cells and eosinophilia.
(iii) Invasive pulmonary pseudallescheriasis (IPP)Before the 1980s, PSC was rarely reported as a cause of systemic disease. We have retrospectively examined 138 cases of invasive pulmonary pseudallescheriasis (IPP) including pneumonia, pulmonary abscess, pleuritis and other manifestations. As outlined in Table 1, IPP can vary from nodular pneumonia to necrotizing pneumonias, lung abscess,6,51,66,89,141 empyema,16,137 and pleurisy.16,22,34,35,45,72,74,82,103,136,138,150 Asymptomatic coin lesion,151 cystic mass98 and polypoid lesions96,153 were also occasionally reported. Of these, nodular pneumonia and pleural effusion15,16,22,34,35,45,54,72,82,103,136 were the most common. One case was also reported of simultaneous pulmonary infection with Aspergillus terreus and PSC64 and a pulmonary infection by Mycobacterium avium concomittant with a polypoid bronchial lesion by PSC.149 Similarly, Morales et al. reported A. fumigatus and PSC isolation from sputum of a patient with CF and Mycobacterium abscessus infection after lung transplantation.43
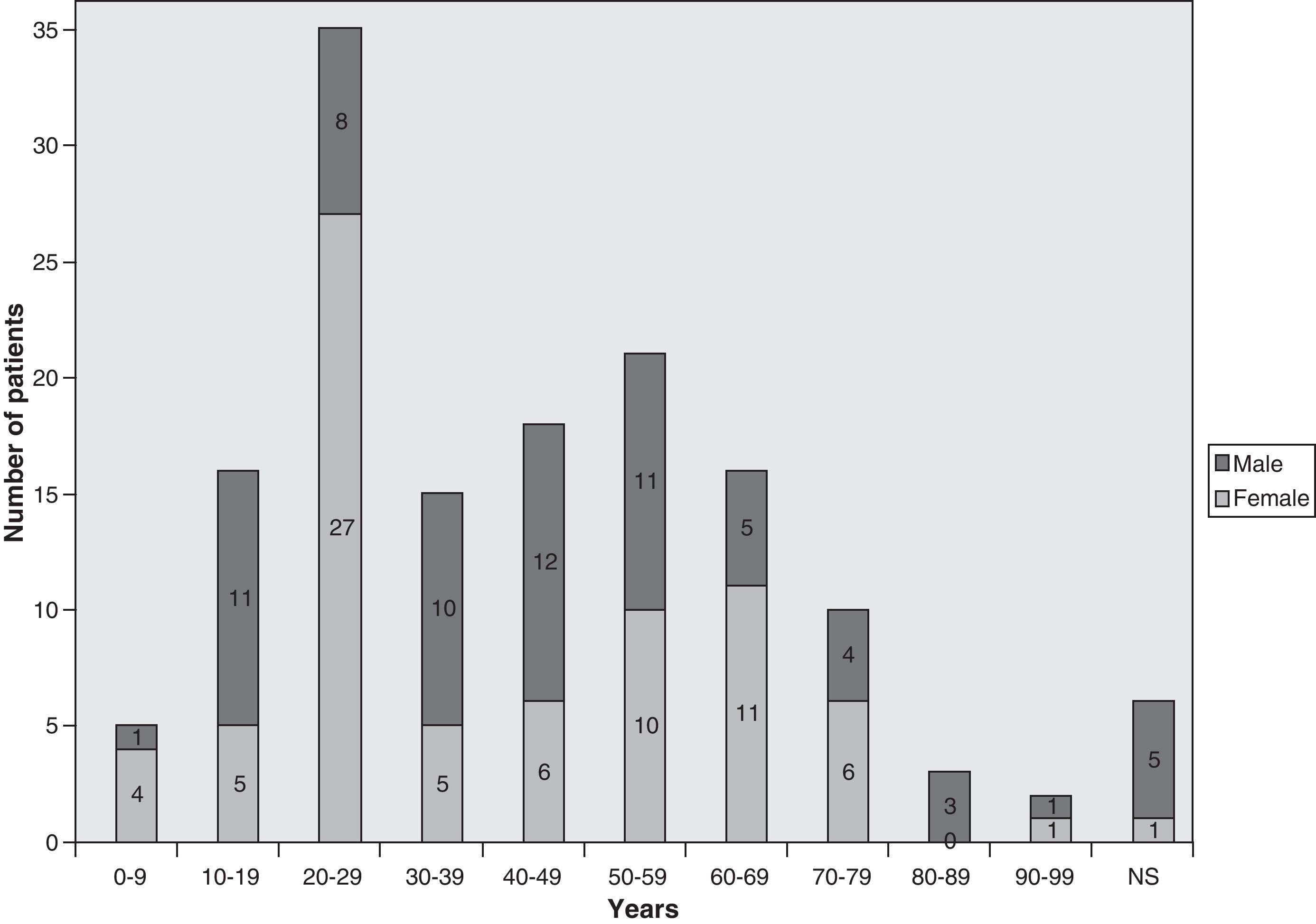
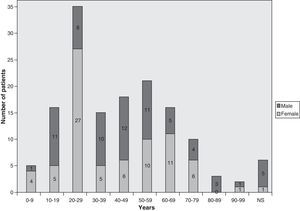
Demographic and geographical featuresThe majority of the 138 invasive pulmonary infections by PSC were reported from the USA, with occasional cases from UK, France, Finland, Germany, Spain, Netherlands, Brazil, Congo, Australia, Japan and Taiwan. Of those, 78 were female and 52 male. The age of the patients ranged from 2 to 90 years, although age was not reported in 8 cases (Fig. 1).
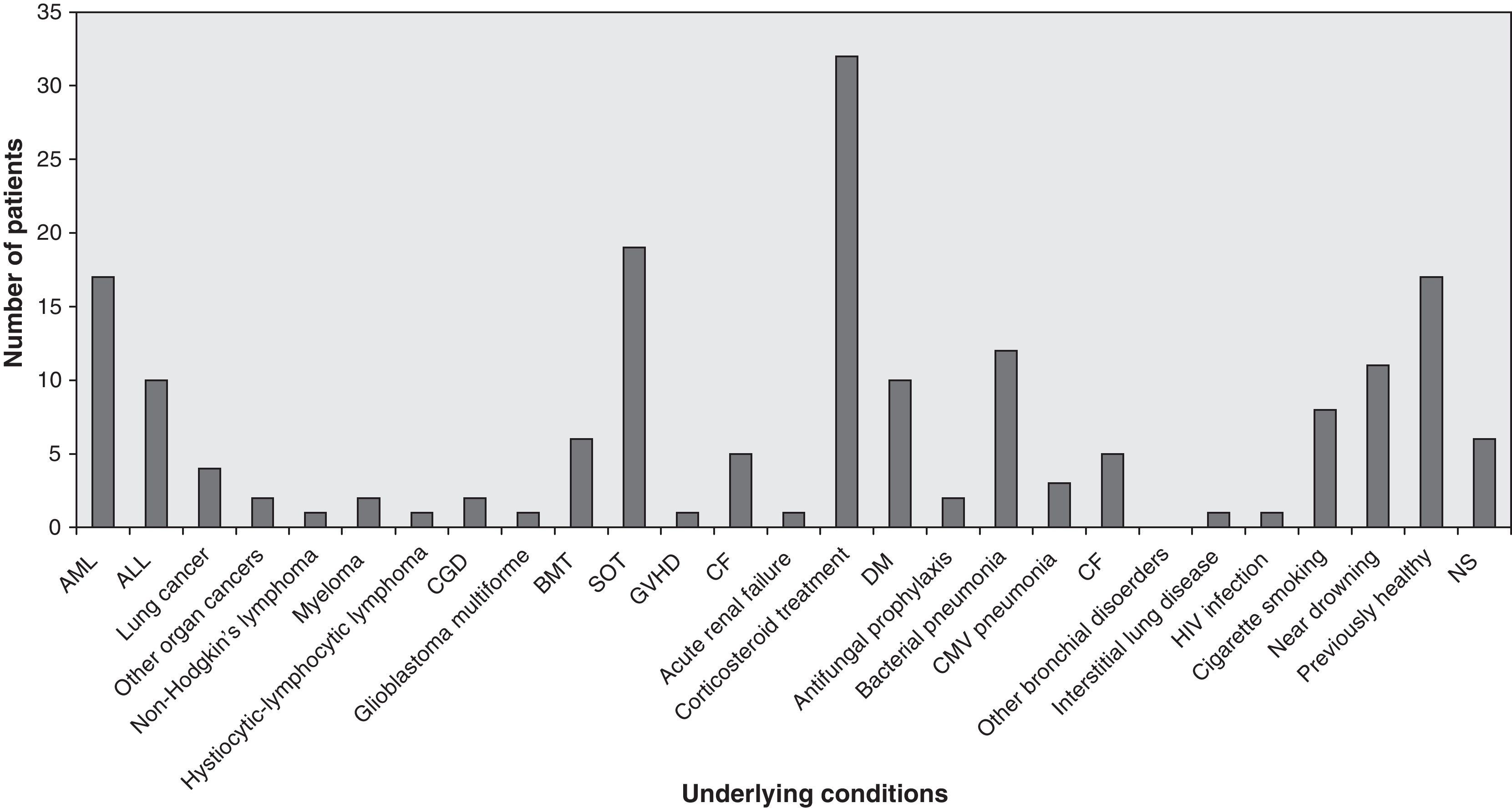
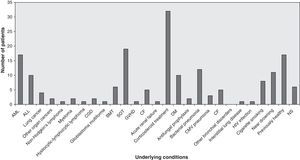
Predisposing factors, underlying conditionsThe most frequent underlying conditions reported were corticosteroid treatments, solid organ transplantations (lung 194, heart 5, liver 1, kidney 3) and haematological malignancies. Most patients showed a history of underlying chronic lung disease, cigarette smoking or occupational exposure. Ten patients who suffered near-drowning but who had previously been healthy and two further patients were occupationally exposed to fungal conidia; one patient was immunocompetent with a perforated chest wound; one case occurred in a liver transplant patient following a skull fracture in an accident; and no predisposing conditions or underlying disease were stated in six patients. Fig. 2 shows the frequency of any underlying conditions reported in the reviewed cases, such as cellular immunity and, in particular, neutrophils that might have an important role in the pathogenesis of IPP. Tables 4 and 5 list the underlying conditions and predisposing factors, respectively, found in 44 patients who survived and 75 who died. In the other cases, patient outcome was not reported.
Frequency of underlying conditions reported in 138 cases of IPP. ALL: acute lymphocytic leukemia; AML: acute myeloid leukemia; BMT: bone marrow transplantation; CGD: chronic granulomatous disease; CMV: cytomegalovirus;DM: diabetes mellitus; GVHD: graft versus host disease; NS: non-stated; SOT: solid organ transplantation.
Clinical symptoms are often insidious and nonspecific, such as chronic cough, sputum production, fever, night sweats, chest pain and shortness of breath. Patients often complained of weakness and malaise. Other local and systemic symptoms include pleuritic pain, chills, fever, easy tiredness, anorexia, and weight loss. One patient with a polypoid bronchial lesion had no complaint,96 and two others were asymptomatic.142,151
RadiologyRadiologically, IPP might have manifested itself as consolidation (in 7 patients), nodules (in 13 patients), necrotizing pneumonia (in 9 patients), pulmonary abscess (in 15 patients), and pleural effusions (in 10 patients). Radiological examination might have been less specific, with diffuse infiltration and pneumonia.5 PSC pneumonia, i.e. lobar pneumonia56,62,77,84,99,114,136 and bilateral consolidation22,138 were seen in several cases; two of them43 occurred in patients with no predisposing conditions. Chest radiographs and CT scan images may show ill-defined nodular opacities.22,84 The opacity with a peripheral rim of ground glass, known as the “halo sign”, was reported in one case.149 Nodules surrounded by a halo of ground-glass is often considered to be evidence of haemorrhagic infarcts and believed to represent the peripheral rim of haemorrhagic infarction, described in the angioinvasive fungal diseases, aspergillosis, zygomycosis and described as well in PSC infections.41 Angioinvasive pseudallescheriasis was characterized histologically by the invasion and occlusion of small to medium-sized pulmonary arteries by fungal hyphae.39,79
The “air crescent sign”5,45 can be seen in a pulmonary cavitary process, which is caused by air surrounded by radiopaque material along both its inner and outer margins. The air crescent may transform into a cavity space, filled with necrotic debris, including neutrophils, and fungal elements. However, a similar appearance has been described in a number of infections, including mucorales, Candida, herpes simplex or cytomegalovirus, or other conditions such as Wegener granulomatosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and haemorrhagic metastasis. The “air crescent sign” is considered characteristic of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) when seen in the appropriate clinical setting.2 Therefore, it is important not to confuse IPP with IPA.
Clinical manifestationsIn several cases, the existence of necrotizing pneumonia was detected histologically, characterized by the presence of tissue necrosis and granulomatous inflammation.22,34,116,138 IPP is characterized by haemorrhagic infarction of lung tissue, secondary to vascular invasion by fungal organisms, causing thrombosis of small arterioles and, sometimes, larger pulmonary vessels, as seen in IPA and invasive fusariosis. Saadah and Dixon116 described a truly invasive PSC, necrotizing pneumonia in an apparently normal host. The disease was relatively destructive, traversing multiple pulmonary segments, the surrounding pleura, and the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Smears of intrabronchial pus obtained from the surgical specimen had an abundance of septate branching hyphae, while in the tissue sections hyphae were very rare. Based on this finding and a literature review, the authors suggested that actual tissue invasion by PSC is rare and most of the tissue damage in the lung is secondary to the severe inflammatory reaction of the host incited. This hypothesis has been put forward previously to explain the severe tissue reaction present in chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis with the relative absence of the organism in the inflamed tissue. There have been several other cases reported of an absence of fungal elements in lung tissue sections but with positive cultures for PSC.33,62 Another typical presentation, described in several cases, is pulmonary abscess.4,17,30,49,66,82,136,140,141
A coin lesion is a less frequent presentation of the IPP, defined as a single, discrete pulmonary opacity smaller than 3cm in diameter surrounded by normal lung tissue, and not associated with adenopathy or athelectasis.93 Although the fungal solitary pulmonary nodules are usually caused by pathogenic dimorphic fungi and usually the result of a self-limiting Woodard151reported a case of a solitary pulmonary nodule due to PSC. Histopathological examination of the patient's lesion revealed a fibrosis encapsulated granulomatous nodule with central necrosis and grey granules.151
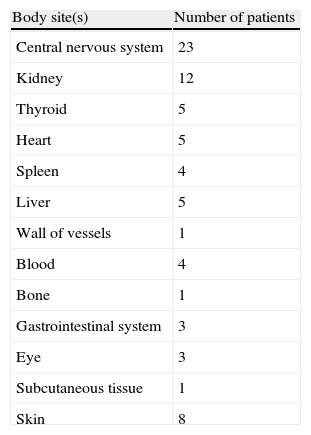
Cystic mass98 and polypoid lesions96,153 due to PSC observed in fiberoptic bronchoscopy have been reported in two cases. Yano et al.153 described a bronchus completely obscured by a dark grey necrotizing lesion after the whitish polypoid lesion by a biopsy forceps. Murayama et al.96 reported a case in combination with M. avium pulmonary disease. Loosely formed grains have also been reported within sinus tracts in lungs in a pediatric patient with disseminated disease.88 Pleurisy was commonly found in several IPP cases.16,22,34,45,54,82,86,103,136 Disseminated infection was reported in 29 patients. Table 2 outlines other sites of involvement.
Laboratory diagnosisDiagnosis was made through histological examination and culture (in 17 cases), or only culture (in 28 cases) of the excised lesion or other respiratory tract samples (sputum, bronchial secretions, endobronchial brushings). Fungi from tissue samples grew in 11 cases, but failed to grow in six. Respiratory tract samples gave negative results. In one patient a thoracic needle aspiration was performed and the diagnosis was made by examining a stained smear specimen and culture124; diagnosis was made postmortem in nine cases. A histopathological study of nodules was made on some patients, and revealed a round pulmonary ischemic infarction due to arterial invasion by the fungus,42 granuloma with central necrosis,151 fibrosis mixed with granuloma and microabscess or an abscess.6,22,39,49,62,64,82,116,136,142 Regarding the questionable significance of isolating PSC, Jung et al.,67 established criteria for diagnosis as follows: (i) repeated isolation of the fungus, at least four positive cultures per patient being considered to be significant; (ii) growth of the fungus from the excised surgical material; (iii) positive cultures from samples obtained from bronchial washings or selective brushing from the pulmonary lesions through the fiberoptic bronchoscope; and (iv) evidence of tissue invasion in tissue sections.
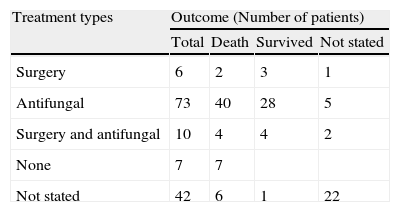
Treatment and outcomeTable 3 shows the treatment and outcome of those patients analyzed with IPP. Of 138 patients, 5 were managed surgically, and 73 were managed medically with systemic antifungal agents, such as AMB, liposomal AMB, MCZ, ketoconazole (KTZ), ITZ, fluconazole (FLZ), VRZ and terbinafine (TRB). A young immunocompetent patient with previous trauma and having been treated with ITZ suffered a relapse after 20 months of therapy despite adequate serum concentrations.134 The patient was treated with oral TRB (500mg/d) and after 4 months bronchoscopy showed no evidence of fungal infection.145 Seventy nine of the 138 patients with IPP died (57.2%) and 43 (31.1%) survived, while the outcome was not reported in the remaining cases. Tables 4 and 5 summarize the data on survivors and no survivors.
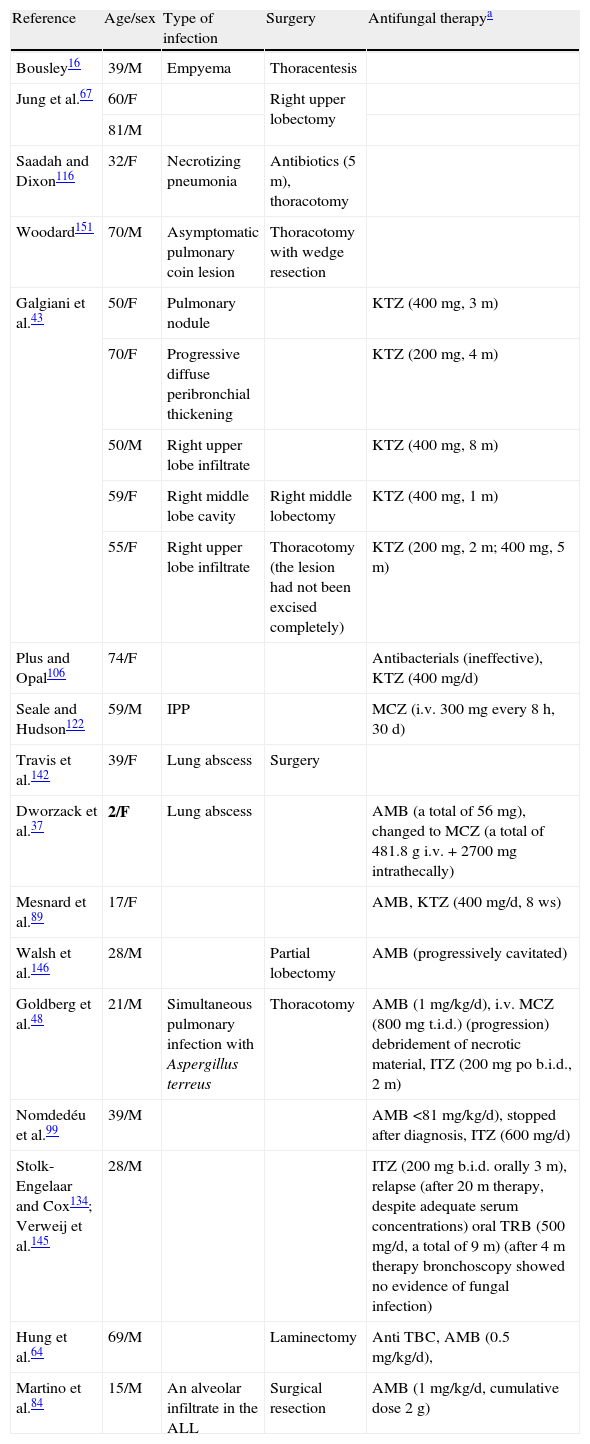
Demographic characteristics, other sites of infection, and therapy given to survivors of IPP (N=44).
| Reference | Age/sex | Type of infection | Surgery | Antifungal therapya |
| Bousley16 | 39/M | Empyema | Thoracentesis | |
| Jung et al.67 | 60/F | Right upper lobectomy | ||
| 81/M | ||||
| Saadah and Dixon116 | 32/F | Necrotizing pneumonia | Antibiotics (5m), thoracotomy | |
| Woodard151 | 70/M | Asymptomatic pulmonary coin lesion | Thoracotomy with wedge resection | |
| Galgiani et al.43 | 50/F | Pulmonary nodule | KTZ (400mg, 3m) | |
| 70/F | Progressive diffuse peribronchial thickening | KTZ (200mg, 4m) | ||
| 50/M | Right upper lobe infiltrate | KTZ (400mg, 8m) | ||
| 59/F | Right middle lobe cavity | Right middle lobectomy | KTZ (400mg, 1m) | |
| 55/F | Right upper lobe infiltrate | Thoracotomy (the lesion had not been excised completely) | KTZ (200mg, 2m; 400mg, 5m) | |
| Plus and Opal106 | 74/F | Antibacterials (ineffective), KTZ (400mg/d) | ||
| Seale and Hudson122 | 59/M | IPP | MCZ (i.v. 300mg every 8h, 30d) | |
| Travis et al.142 | 39/F | Lung abscess | Surgery | |
| Dworzack et al.37 | 2/F | Lung abscess | AMB (a total of 56mg), changed to MCZ (a total of 481.8g i.v.+2700mg intrathecally) | |
| Mesnard et al.89 | 17/F | AMB, KTZ (400mg/d, 8ws) | ||
| Walsh et al.146 | 28/M | Partial lobectomy | AMB (progressively cavitated) | |
| Goldberg et al.48 | 21/M | Simultaneous pulmonary infection with Aspergillus terreus | Thoracotomy | AMB (1mg/kg/d), i.v. MCZ (800mg t.i.d.) (progression) debridement of necrotic material, ITZ (200mg po b.i.d., 2m) |
| Nomdedéu et al.99 | 39/M | AMB <81mg/kg/d), stopped after diagnosis, ITZ (600mg/d) | ||
| Stolk-Engelaar and Cox134; Verweij et al.145 | 28/M | ITZ (200mg b.i.d. orally 3m), relapse (after 20m therapy, despite adequate serum concentrations) oral TRB (500mg/d, a total of 9m) (after 4m therapy bronchoscopy showed no evidence of fungal infection) | ||
| Hung et al.64 | 69/M | Laminectomy | Anti TBC, AMB (0.5mg/kg/d), | |
| Martino et al.84 | 15/M | An alveolar infiltrate in the ALL | Surgical resection | AMB (1mg/kg/d, cumulative dose 2g) |
Abbrevations: ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; AMB: amphotericin; b.i.d.: bis in die (twice in day); d: day; F: female; IPP: invasive pulmonary pseudallescheriasis; i.v.: intravenous injection; ITZ: itraconazole; KTZ: ketoconazole; LAMB: lyposomal amphotericin B; M: male; m: month; MCZ: miconazole; t.i.d.: tree times a day; TBC: tuberculosis; TRB: terbinafine.
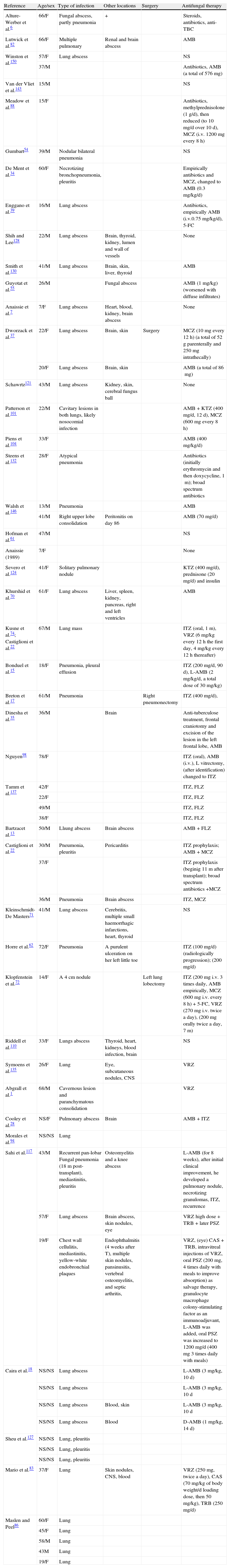
Demographic characteristics, other sites of infection, and therapy given to non survivors of IPP (N=79).
| Reference | Age/sex | Type of infection | Other locations | Surgery | Antifungal therapy |
| Alture-Werber et al.6 | 66/F | Fungal abscess, partly pneumonia | + | Steroids, antibiotics, anti-TBC | |
| Lutwick et al.82 | 66/F | Multiple pulmonary | Renal and brain abscess | AMB | |
| Winston et al.150 | 57/F | Lung abscess | NS | ||
| 37/M | Antibiotics, AMB (a total of 576mg) | ||||
| Van der Vliet et al.143 | 15/M | NS | |||
| Meadow et al.88 | 15/F | Antibiotics, methylprednisolone (1g/d), then reduced (to 10mg/d over 10d), MCZ (i.v. 1200mg every 8h) | |||
| Gumbart54 | 39/M | Nodular bilateral pneumonia | NS | ||
| De Ment et al.34 | 60/F | Necrotizing bronchopneumonia, pleuritis | Empirically antibiotics and MCZ, changed to AMB (0.3mg/kg/d) | ||
| Enggano et al.39 | 16/M | Lung abscess | Antibiotics, empirically AMB (i.v.0.75mg/kg/d), 5-FC | ||
| Shih and Lee128 | 22/M | Lung abscess | Brain, thyroid, kidney, lumen and wall of vessels | None | |
| Smith et al.130 | 41/M | Lung abscess | Brain, skin, liver, thyroid | AMB | |
| Guyotat et al.55 | 26/M | Fungal abscess | AMB (1mg/kg) (worsened with diffuse infiltrates) | ||
| Anaissie et al.7 | 7/F | Lung abscess | Heart, blood, kidney, brain abscess | None | |
| Dworzack et al.37 | 22/F | Lung abscess | Brain, skin | Surgery | MCZ (10mg every 12h) (a total of 52g parenterally and 250mg intrathecally) |
| 20/F | Lung abscess | Brain, skin | AMB (a total of 86mg) | ||
| Schawrtz121 | 43/M | Lung abscess | Kidney, skin, cerebral fungus ball | None | |
| Patterson et al.101 | 22/M | Cavitary lesions in both lungs, likely nosocomial infection | AMB+KTZ (400mg/d, 12d), MCZ (600mg every 8h) | ||
| Piens et al.104 | 33/F | AMB (400mg/kg/d) | |||
| Steens et al.132 | 28/F | Atypical pneumonia | Antibiotics (initially erythromycin and then doxycycline, 1m); broad spectrum antibiotics | ||
| Walsh et al.146 | 13/M | Pneumonia | AMB | ||
| 41/M | Right upper lobe consolidation | Peritonitis on day 86 | AMB (70mg/d) | ||
| Hofman et al.61 | 47/M | NS | |||
| Anaissie (1989) | 7/F | None | |||
| Severo et al.124 | 41/F | Solitary pulmonary nodule | KTZ (400mg/d), prednisone (20mg/d) and insulin | ||
| Khurshid et al.70 | 61/F | Lung abscess | Liver, spleen, kidney, pancreas, right and left ventricles | AMB | |
| Kusne et al.74; Castiglioni et al.22 | 67/M | Lung mass | ITZ (oral, 1m), VRZ (6mg/kg every 12h the first day, 4mg/kg every 12h thereafter) | ||
| Bonduel et al.15 | 18/F | Pneumonia, pleural effusion | ITZ (200mg/d, 90d), L-AMB (2mg/kg/d, a total dose of 30mg/kg) | ||
| Breton et al.17 | 61/M | Pneumonia | Right pneumonectomy | ITZ (400mg/d), | |
| Dinesha et al.35 | 36/M | Brain | Anti-tuberculose treatment, frontal craniotomy and excision of the lesion in the left frontal lobe, AMB | ||
| Nguyen98 | 78/F | ITZ (oral), AMB (i.v.), L vitrectomy, (after identification) changed to ITZ | |||
| Tamm et al.137 | 42/F | ITZ, FLZ | |||
| 22/F | ITZ, FLZ | ||||
| 49/M | ITZ, FLZ | ||||
| 38/F | ITZ, FLZ | ||||
| Bartzacet al.13 | 50/M | Llıung abscess | Brain abscess | AMB+FLZ | |
| Castiglioni et al.22 | 30/M | Pneumonia, pleuritis | Pericarditis | ITZ prophylaxis; AMB+MCZ | |
| 37/F | ITZ prophylaxis (beginig 11 m after transplant); broad spectrum antibiotics +MCZ | ||||
| 36/M | Pneumonia | Brain abscess | ITZ, MCZ | ||
| Kleinschmidt-De Masters71 | 41/M | Lung abscess | Cerebritis, multiple small haemorrhagic infarctions, heart, thyroid | NS | |
| Horre et al.62 | 72/F | Pneumonia | A purulent ulceration on her left little toe | ITZ (100mg/d) (radiologically progression); (200mg/d) | |
| Klopfenstein et al.72 | 14/F | A 4cm nodule | Left lung lobectomy | ITZ (200mg i.v. 3 times daily, AMB empirically, MCZ (600mg i.v. every 8h)+5-FC, VRZ (270mg i.v. twice a day), (200mg orally twice a day, 7m) | |
| Riddell et al.110 | 33/F | Lungs abscess | Thyroid, heart, kidneys, blood infection, brain | NS | |
| Symoens et al.135 | 26/F | Lung | Eye, subcutaneous nodules, CNS | VRZ | |
| Abgrall et al.1 | 68/M | Cavernous lesion and paranchymatous consolidation | VRZ | ||
| Cooley et al.28 | NS/F | Pulmonary abscess | Brain | AMB+ITZ | |
| Morales et al.94 | NS/NS | Lung | |||
| Sahi et al.117 | 43/M | Recurrent pan-lobar Fungal pneumonia (18m post-transplant), mediastinitis, pleuritis | Osteomyelitis and a knee abscess | L-AMB (for 8 weeks), after initial clinical improvement, he developed a pulmonary nodule, necrotizing granulomas, ITZ, recurrence | |
| 57/F | Lung abscess | Brain abscess, skin nodules, eye | VRZ high dose+TRB+later PSZ | ||
| 19/F | Chest wall cellulitis, mediastinitis, yellow-white endobronchial plaques | Endophthalmitis (4 weeks after T), multiple skin nodules, pansinusitis, vertebral osteomyelitis, and septic arthritis, | VRZ, (eye) CAS+TRB, intravitreal injections of VRZ, oral PSZ (200mg, 4 times daily with meals to improve absorption) as salvage therapy, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor as an immunoadjuvant, L-AMB was added, oral PSZ was increased to 1200mg/d (400mg 3 times daily with meals) | ||
| Caira et al.18 | NS/NS | Lung abscess | L-AMB (3mg/kg, 10d) | ||
| NS/NS | Lung abscess | L-AMB (3mg/kg, 10d | |||
| NS/NS | Lung abscess | Blood, skin | L-AMB (3mg/kg, 10d | ||
| NS/NS | Lung abscess | Blood | D-AMB (1mg/kg, 14d) | ||
| Sheu et al.127 | NS/NS | Lung, pleuritis | |||
| NS/NS | Lung, pleuritis | ||||
| NS/NS | Lung, pleuritis | ||||
| Mario et al.83 | 37/F | Lung | Skin nodules, CNS, blood | VRZ (250mg, twice a day), CAS (70mg/kg of body weight/d loading dose, then 50mg/kg), TRB (250mg/d) | |
| Maslen and Peel86 | 60/F | Lung | |||
| 45/F | Lung | ||||
| 58/M | Lung | ||||
| 43M | Lung | ||||
| 19/F | Lung |
Abbrevations: AMB: amphotericin B; L-AMB: liposomal amphotericin B; 5-FC: flucytosine; ITZ: itraconazole; FLZ: fluconazole; KTZ: ketoconazole; MCZ: miconazole; VRZ: voriconazole; PSZ: posaconazole; TRB: terbinafine; CAS: caspofungin; NS: not stated, i.v.: intravenous injection; h: hours; d: day; m: month; TBC: tuberculosis; CNS: central nervous system.
Thirty-two patients had a history of corticosteroid treatment. Murayama et al.96 diagnosed a bronchial polypoid lesion in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. In this case, surgical treatment was not undertaken because of extensive M. avium pulmonary disease, but methylprednisolone was discontinued soon after establishing the definitive diagnosis and there was no evidence of worsening during a two-year follow up. Similarly, in a report by Rippon and Carmichael,111 the patient's bronchial lesions disappeared when steroid therapy was discontinued. Horre et al.62 reported a fatal pneumonia in a patient who had a long history of corticosteroid therapy. Lionakis and Kontoyiannis79 suggested that the use of steroids, although necessary, could have facilitated opportunistic mould infections in cancer patients. The use of steroids may render the patient susceptible to opportunistic mycoses. Despite having a normal neutrophil count, affected patients have functional neutropenia because the function of the neutrophils is inhibited by the use of high-dose steroids. Based on that data, discontinuation of steroids and immunomodulation of neutrophyl functions, if needed, may be an optional treatment approach.
Tamm et al.137 analysed risk factors, and the clinical course and outcome of seven lung transplant recipients who had developed IPP infection diagnosed through BAL specimens. The fungus was detected 9–58 months after transplantation. Five patients had been treated for several months with ITZ because of previous detection of Aspergillus in BAL. S. prolificans was first cultured in three cases and a few months later S. apiospermum was found. All seven patients showed airway problems. Combined treatment with ITZ and FLZ was not able to eradicate PSC. Four of the seven patients died 3–35 months after the diagnosis of IPP. The authors concluded that IPP was seen in lung transplant recipients with structurally abnormal airways and under long term therapy with ITZ. Eradication of the fungus proved difficult, but under combined treatment with ITZ and FLZ this infection did not disseminate. Although the role of both drugs in the control of the infections is difficult to understand, ITZ has demonstrated in general poor efficacy against these fungi and FLZ is not usually used for treatment of mycoses caused by filamentous fungi. Differences in mortality rates are outlined in Fig. 3.
ConclusionIn most instances non-invasive forms of pulmonary pseudallescheriasis have been superimposed on some structural abnormalities such as bronchectasis, tuberculosis or sarcoidosis. Invasive pulmonary infection may result in patients whose immune responses are impaired by underlying disease, chemotherapy, or both. Pulmonary infection with PSC has no pathogenomic manifestations. Chest radiographs may show cavitation and a fungus ball or may resemble tuberculosis. Because other opportunistic agents, particularly Aspergillus species, can display similar images, CT findings should be interpreted with caution both in non-invasive and in invasive forms of IPP. Serum precipitating antibodies against PSC have been demonstrated in all forms of pulmonary presence of PSC and is a significant criteron for ABPP. Distinction between pseudallescheriasis and aspergillosis can only be made by culturing the organism. Management of pseudallescheriasis is limited; when it is localized, surgical resection of residual nodules or cavities should be performed. For IPP, conventional antifungal agents and therapy strategies have some effect on the moderately immunocompromised and immunocompetent hosts; the prognosis is very poor for severely immunocompromised hosts. Whenever possible, surgical drainage and debridement of necrotic tissues is essential to the success of therapy, even in immunocompromised hosts.
Conflict on interestThe authors have no conflict of interest to declare