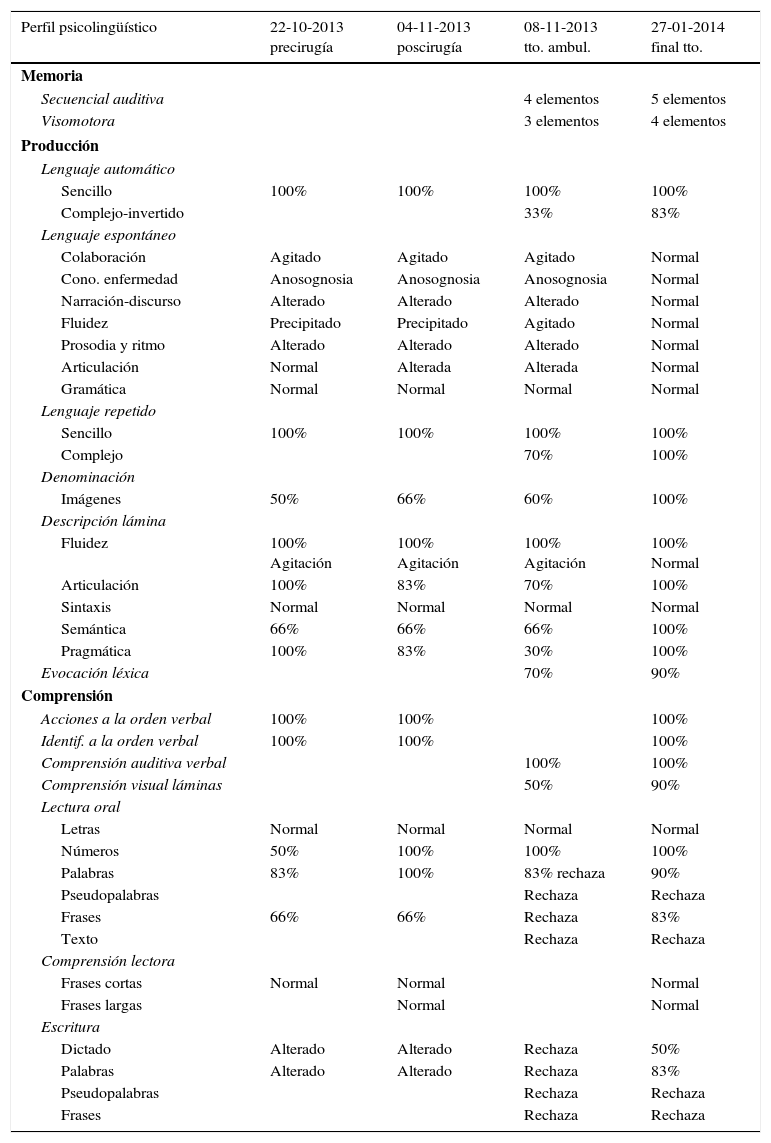
El mapeo cortical intraoperatorio es una técnica segura y de alta fiabilidad para la resección de tumores en el área elocuente sensitivo-motriz sin producir más déficit. Cada día se está implantando en más hospitales. Se necesita de un equipo multidisciplinar con profesionales altamente cualificados. La incorporación del médico foniatra y del logopeda a este equipo puede ser clave en cualquiera de sus fases. Durante la cirugía el paciente se mantiene despierto y colabora de forma activa cuando se trata de resecciones en áreas del lenguaje. Antes de extirpar se realiza el mapeo aplicando estimulación eléctrica cortical mientras se va explorando continuamente el lenguaje con el fin de minimizar secuelas. Finalizada la exéresis se vuelve a explorar lingüísticamente al paciente antes de dormirle para el cierre. El postoperatorio suele transcurrir sin complicaciones y el control con resonancia magnética postoperatoria confirma si la extirpación ha sido completa o no. Posteriormente se evalúa al paciente en planta y en consultas externas y se plantea un tratamiento precoz que identifique, recupere y/o compense los posibles déficits lingüísticos diagnosticados. El tratamiento de logopedia es de menor duración y con mejor pronóstico. La labor del servicio de foniatría-logopedia se torna relevante para colaborar antes, durante y después de la cirugía. Es importante conocer en profundidad esta técnica para abordar al paciente con mejores resultados. En el presente artículo se ilustra la técnica de mapeo cerebral intraoperatorio y la posterior rehabilitación a partir de un caso clínico.
The intraoperative cortical mapping is a safe and highly reliable technique for tumor resection in the eloquent sensorimotor cortex. This technique is currently being implemented in hospitals worldwide. For its implementation, a multidisciplinary team of highly qualified professionals is required and the incorporation of a phoniatrician and a speech therapist into this team may be crucial in any of its stages. During the surgical procedure, the patient remains awake and actively collaborates when it comes to language areas resections. While the mapping is applied, the patient performs a language test in order to minimize sequelae. Once the excision is complete, the patient is re-evaluated linguistically before putting to sleep in order to perform the closure of the craniotomy. Postoperative complications are rare and MRI controls can confirm whether the removal was complete or not. Eventually, the patient must be checked for any superimposed neurological deficits during admission or outpatient visits. Early treatment must be applied to identify, recover and/or compensates the possible linguistic deficits previously diagnosed. The speech and language therapy is shorter and with a better prognosis. The role of the phoniatry and speech therapy are significant before, during and after the surgical procedure. It is important to profoundly know this technique in order to treat the patient with better results. This article illustrates the intraoperative brain mapping technique and the subsequent rehabilitation process with phoniatry and speech therapy based on a clinical case.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora