Although neck auscultation is a subjective diagnostic method that can identify the sounds and mechanical disruptions of swallowing, the acoustic analysis provides greater objectivity as it makes these sounds visible and the physiology of swallowing can clearly be seen.
ObjectiveTo determine the time and the sounds of swallowing in people 20–50 years of age in the city of Bucaramanga, Colombia.
Materials and methodsA quantitative descriptive study that included the swallowing process of 306 participants. These were recorded by acoustic analysis using a computer application and neck auscultation to determine the sounds and time whilst food passed from the mouth to the esophagus.
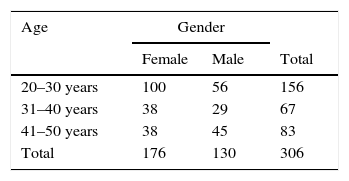
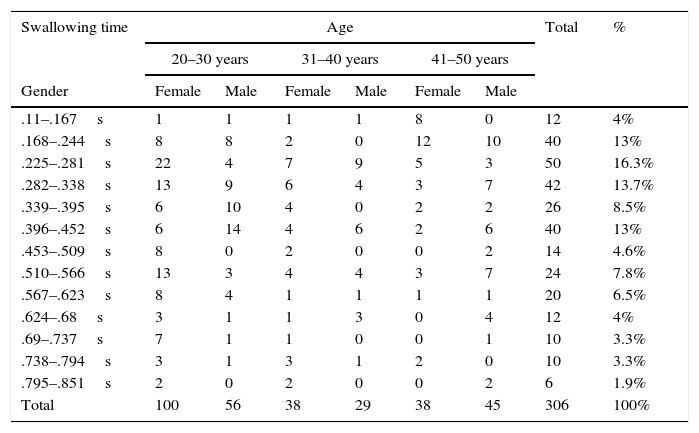
ResultsOf the 306 participants, 50.9% were between 20 and 31 years, and 57.5% were women between 20 and 50 years. The mean swallowing time in this study was .387s (compared to a mean of .5s in studies in other countries), with 16.3% taking between 0225 and 0281s.
ConclusionsIdentifying the sounds of swallowing using acoustic analysis improves the therapeutic processes performed by audiologists in patients with dysphagia.
La auscultación cervical es un método subjetivo para el diagnóstico que permite identificar los sonidos y las rupturas de la mecánica deglutoria, pero el análisis acústico brinda mayor objetividad, dado que hace visibles estos sonidos y permite apreciar con mayor claridad la fisiología de la deglución.
ObjetivoDeterminar el tiempo y los sonidos propios de la deglución en personas de 20 a 50años de edad de la ciudad de Bucaramanga.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un estudio descriptivo cuantitativo en donde se grabó el proceso deglutorio de 306 participantes a través de un software de análisis acústico y la auscultación cervical para determinar los sonidos y el tiempo que tarda el alimento en pasar de la boca al esófago.
ResultadosDe los 306 participantes, el 57.5% son mujeres de entre 20 y 50años, el 50.9% están entre los 20 y 31años y el 16.3% tarda entre 0.225-0.281segundos en deglutir, siendo el promedio deglutorio de 0.387 segundos según esta investigación. Investigaciones realizadas en otros países habrían determinado el promedio en 0.5 segundos.
ConclusionesLa identificación de los sonidos propios de la deglución a través del análisis acústico permite mejorar los procesos terapéuticos realizados por los fonoaudiólogos en pacientes con disfagia.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora