To determine the effect of coaching and mentoring on nurses caring behavior and to identify the relationship between the nurses caring behavior and patient satisfaction.
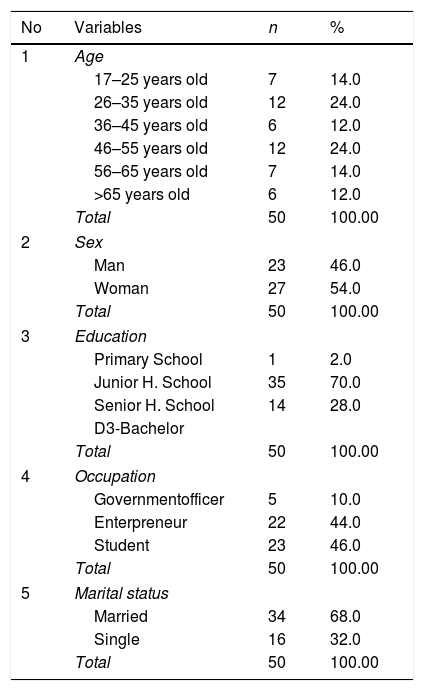
MethodPre-experiment with one group pre-posttest design. The populations were 89 nurses and 150 patients. The sampling technique used was purposive sampling. The number of nurse respondents was 56 people who get coaching and mentoring and there are 100 different patients who rate nurses caring behavior and the level of patient satisfaction; 50 patients gave an assessment before the intervention, and 50 patients post-intervention. The research instrument was questionnaires. Data analysis used the Paired t-test and Pearson Correlation Test.
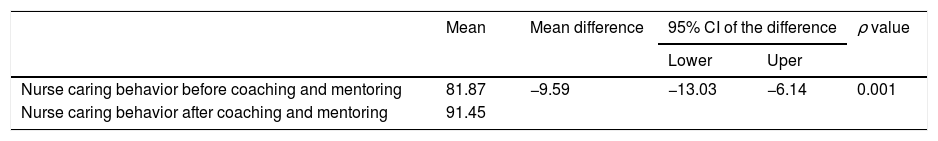
ResultsNurse caring behavior increased 9.98 points post-intervention and there was a significant relationship between nurses caring behavior with patient satisfaction (p=0.002).
Conclusionscoaching and mentoring increase the nurses caring behavior, and there is a significant positive relationship between nurses caring behavior and patient satisfaction.